Method for reducing and removing nitride in lithium metal or lithium alloy
A lithium alloy and metal lithium technology, applied in the field of lithium metal, can solve the problems of inability to remove metal lithium, and achieve the effects of low cost, low residual amount and wide application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1 Nitrogen removal by metal lithium with excessive nitrogen content
[0044] Put 1.51 kg of battery-grade lithium metal with nitrogen content exceeding the standard in a sealed reactor, evacuate the reactor to stabilize it to <0.1Pa, and heat the material at a heating rate of 200°C / h. When the lithium metal is completely melted Stop heating and start stirring to ensure that the nitrogen content in each part of the lithium solution is evenly distributed, and then take a sample to analyze the nitrogen content in the product according to the national standard analysis method, and the measured nitrogen content is 950ppm. Add accurately weighed metal aluminum foil to the molten lithium liquid in a molar ratio of Al:N=1:1. Reheat the reactor, control the heating rate at 200°C / h, and control the reaction temperature at 220°C, and the stirring rate is 300rpm, first stir forward at 300rpm for 5-15min, then reversely stir at 300rpm for 5 minutes ~15min, cycle like this u...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Processing Lithium Metal under the Changed Situation of Nitrogen Removal Source
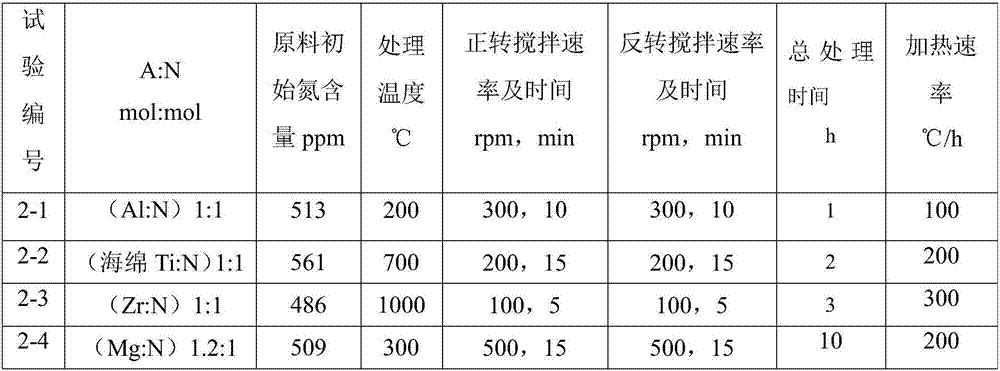
[0049] The experimental method is as described in Example 1. The nitrogen removal source in the experiment is changed to obtain the treatment results under different conditions. These factors are the use of metal aluminum, metal titanium, metal zirconium or metal magnesium (the shape is all metal foil). The test arrangement is shown in Table 2, and the residual amount of nitrogen and nitrogen removal source in the lithium metal after nitrogen removal and the recovery rate of metal lithium are shown in Table 3.
[0050] Table 2
[0051]
[0052] table 3
[0053] Test No. A content (ppm) N content (ppm) Recovery rate of Li (%) 2-1 (Al)3 47 98 2-2 (Ti)4 45 98 2-3 (Zr)3 48 99 2-4 (Mg)5 50 98
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Nitrogen removal by lithium aluminum alloy with excessive nitrogen content
[0055] Put 1.78kg of lithium aluminum alloy (standard aluminum content is 3000±300ppm) whose nitrogen content exceeds the standard due to damaged packaging in a sealed reactor, feed nitrogen into the reactor, and heat the material under the protection of nitrogen. The heating rate is 200°C / h. When the alloy is completely melted, stop heating and start stirring to ensure that the nitrogen content in each part of the lithium liquid is evenly distributed. After sampling and analyzing the nitrogen content and aluminum content in the product according to the industry standard analysis method, the nitrogen content is measured. It is 467ppm, and the aluminum content is 2915ppm. Add 1.603 g of accurately weighed metal aluminum foil to the molten lithium liquid at a molar ratio of Al:N=1:1. Reheat the reactor, the heating rate is controlled at 200°C / h, and the reaction temperature is controll...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com