Diatom UPA (universal plastid amplicon) gene analyzing method and application thereof in legal medical expert detection
A genetic analysis, diatom technology, used in the field of forensics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
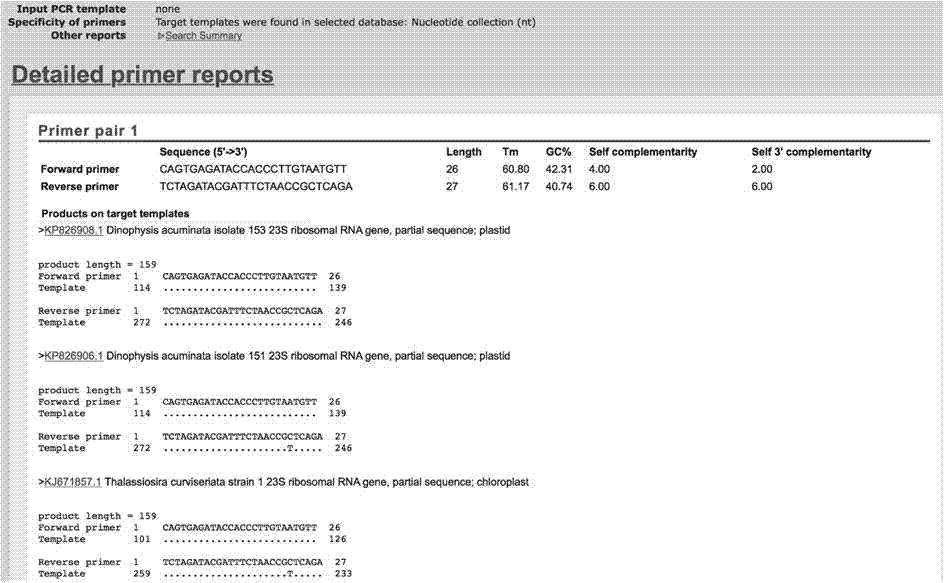
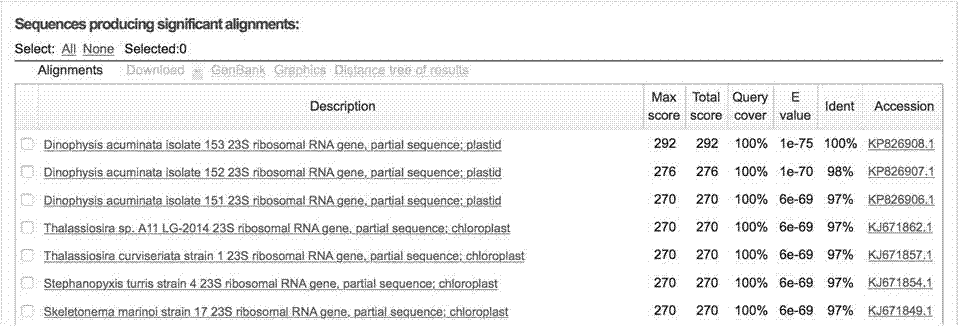
[0025] Example 1 Primer Design and Proof of Primer Specificity
[0026] A pair of upstream and downstream primers were designed according to the UPA gene of diatoms:
[0027] Upstream primer (as shown in SEQ ID NO.1):
[0028] 5'-CAGTGAGATACCACCCTTGTAATGTT-3'
[0029] Downstream primer (shown as SEQ ID NO.2):
[0030] 5'-TCTAGATACGATTTCTAACCGCTCAGA-3'
Embodiment 2
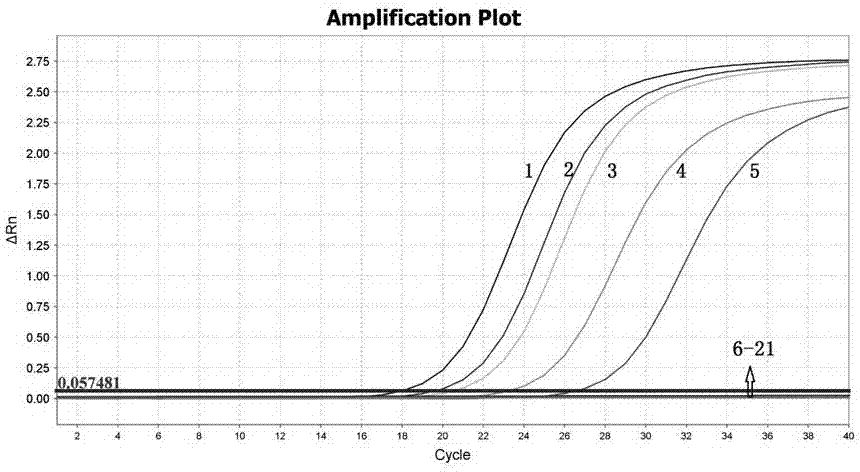
[0031] Example 2 Specific verification of primer pairs
[0032] Use the above primers and probes to perform real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection of DNA from different samples. The 5' end of the probe is labeled with a FAM fluorescent reporter group, and the 3' end is labeled with a NFQ-MGB fluorescent quencher group. Five common silicon Algae, two human commensal bacteria and a variety of non-diatom algae DNA for primer specificity verification.
[0033] 1: Cyclotella; 2: Nitzkita; 3: Navicula; 4: Acinebacteria; 5: Alternaria variabilis; 6: Escherichia coli; : Aeromonas victorii; 10: Aeromonas sobria; 11: Chlorella pyrenoidosa; 12: Chlorella vulgaris; 13: Scenedesmus obliquus; 16: Anabaena; 17: Monofidophyta; 18: A. tenatinosa; 19: Toxigenic Microcystis aeruginosa; 20: Non-toxic Microcystis aeruginosa; 21: Ultrapure water (negative control)
[0034] obtained after amplification figure 2 Amplification curves are shown. attached by figure 2 It can be seen that...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3 Animal group control experiment
[0037] Samples of lung, liver and kidney (organs of the systemic circulation) of the artificially drowned experimental pig group (n=15), the experimental pig mechanically sacrificed into the water group (n=15) and the blank control group (n=5) of non-drowning experimental pigs Under the same amplification system, the genomic DNA extracted from the sample was amplified by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR with the primer probe designed in Example 1. It was stipulated that an amplification curve appeared and the Ct value (Cyclethreshold) was less than 35, which meant positive amplification, and the result was judged as The detection and detection rate results are shown in Table 1.
[0038] Table 1 The number of cases and positive rate of diatom UPA gene detected in the organs of animal circulation in each group
[0039]
[0040]As can be seen from the above experimental results, using the method of the present invent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com