SNP marker combination and its application for traceability identification of beef cattle individual and meat products
An individual, beef technology, applied in recombinant DNA technology, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve problems such as easy loss, difficulty in achieving traceability of meat products, and easy tampering of traceability information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
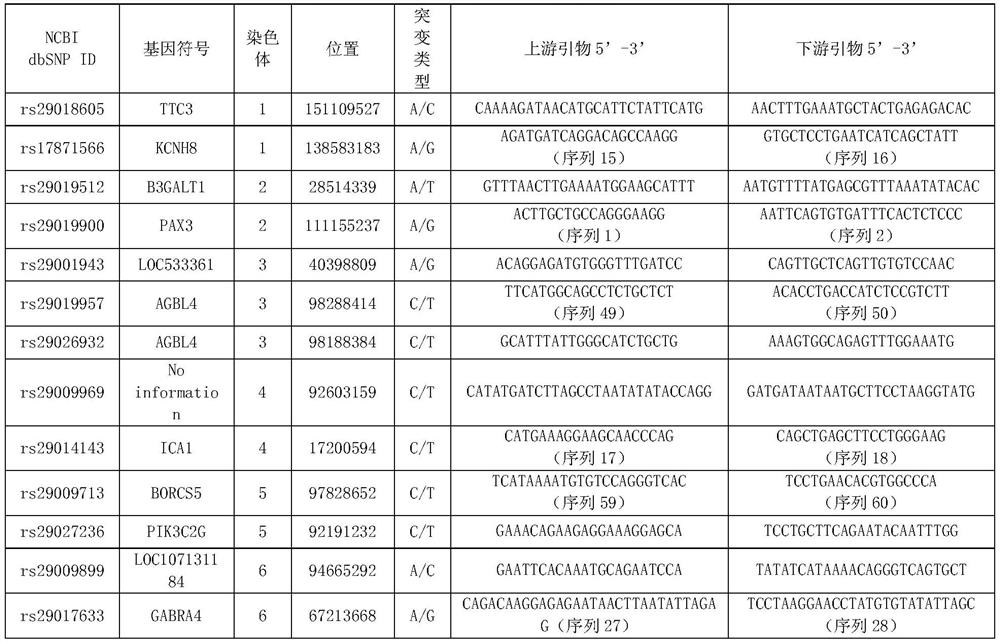
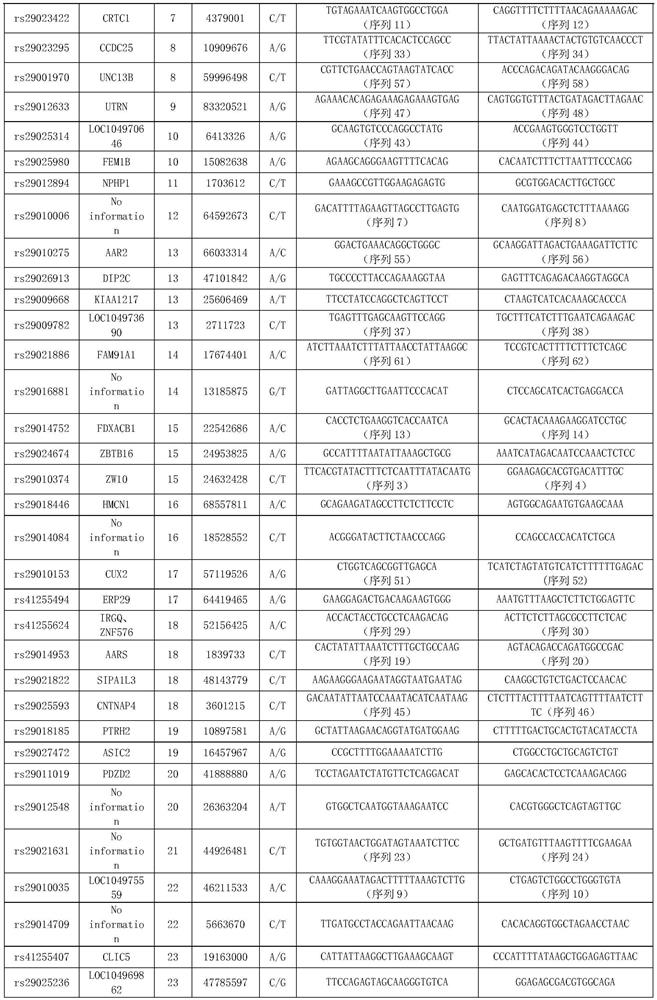
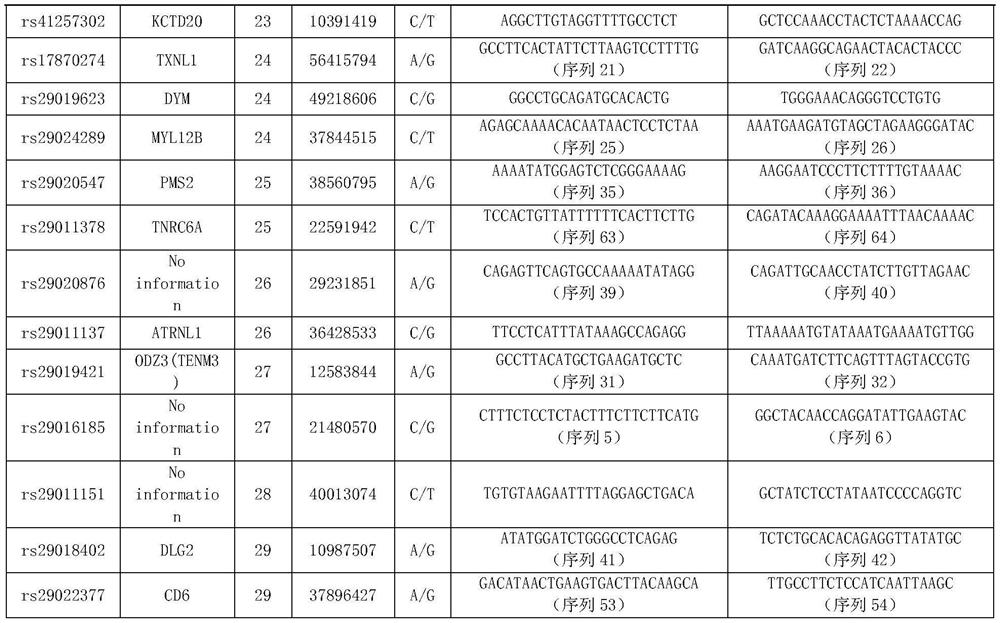
[0083] Example 1. SNP marker combination for traceability identification of individual beef cattle and meat products
[0084]1. Sample collection and genomic DNA extraction
[0085] 1. Collection of samples
[0086] The samples of the present invention come from 192 individuals of 8 varieties in the Chinese market, namely Simmental cattle (n=43), Luxi cattle (n=34), Xinjiang black cattle (n=24), Limu Zan cattle (n=30), yaks (n=16), Nanyang yellow cattle (n=15), black Wagyu cattle (n=15), and Jiaxian red cattle (n=15). A large group consisting of 192 individuals of 8 breeds was a mixed group.
[0087] 2. Genomic DNA extraction
[0088] Blood samples were collected in EDTA anticoagulated blood collection tubes (5 mL), and blood DNA was extracted using GeneJET Genomic DNA purification Kit (Thermo Scientific, #k0721). Nanodrop2000c was used to measure DNA purity and concentration, and 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis was used to measure the integrity of DNA fragments, and the ...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Example 2, the application of SNP site combination in the traceability identification of beef cattle products
[0115] 1. Sample collection and genomic DNA extraction
[0116] In a beef cattle breeding base (M), blood samples were randomly collected from 15 cattle including Simmental cattle, Luxi yellow cattle and Xinjiang black cattle by tail vein blood collection. The blood sample numbers were MB1-MB15, and recorded Ear tag number for each cow. When the above-mentioned cattle are slaughtered and marketed, the corresponding meat samples are taken, and the meat sample numbers are MM1-MM15. In addition, the meat samples of the other 5 cattle are randomly collected in the market, and the meat sample numbers are NM1-NM5. DNA extraction and quality control are the same as in Example 1.
[0117] 2. Genotype determination of samples and traceability identification of meat products
[0118] (1) Combination of 9 SNP sites
[0119] Using the following 9 SNP sites with the hi...
Embodiment 3
[0128] Example 3, the application of SNP locus combination in the identification of yak meat and other varieties of beef
[0129] 1. Sample collection and genomic DNA extraction
[0130] A total of 36 yak meat samples were collected from Qinghai, Gansu, Tibet, and Yunnan. A total of 50 samples of beef from other breeds including Simmental, Luxi cattle, Xinjiang black cattle, and Limousin cattle were collected for DNA analysis. Extraction and quality control, concrete operation is the same as embodiment 1.
[0131] 2. Genotype determination of samples and identification of yak meat from other varieties of beef
[0132] Select the sites in Table 3 that do not have polymorphisms in the yak population and have higher polymorphisms in other populations (other 30 SNP sites except rs29014752 and rs29020876 sites), and select among the 30 SNP sites The following 8 SNP loci are used to identify yak meat from other breeds of beef: rs2901990, rs29010374, rs29016185, rs29010006, rs29010...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com