Brake pad friction material
A friction material and brake pad technology, applied in friction linings, gear transmission mechanisms, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of low actual utilization rate of phosphogypsum, low economic and social benefits, etc., and achieve the effect of purifying the environment and reducing pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] 13% resin, 4% friction powder, 5% tire powder, 10% mineral fiber, 12% silica fume wool, 6% glass fiber, 8% graphite, 10% barium sulfate, 6.4% coke powder, 3% alumina, oxide Zinc 3%, iron ore powder 3%, bauxite 4%, vermiculite 2%, zinc stearate 0.6%, phosphogypsum 10%. Total 100%
[0017] The above materials were made into brake pads according to the conventional pressing method, and tested according to the GB5763-2008 standard on a constant-speed friction testing machine according to category 3. The results are shown in Table 1.
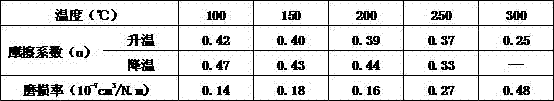
[0018] Table 1:
[0019]
[0020] It can be seen from the data in Table 1 that the brake pad obtained in Example 1 of the present invention has a friction coefficient of 0.25-0.42 in the heating stage and a friction coefficient of 0.33-0.47 in the cooling stage, and the wear rate is small, which fully meets the national standard.
Embodiment 2
[0022] 13% resin, 4% friction powder, 5% tire powder, 10% mineral fiber, 12% silica fume cotton, 6% glass fiber, 8% graphite, 6.4% coke powder, 3% aluminum oxide, 3% zinc oxide, iron Mineral powder 3%, bauxite 4%, vermiculite 2%, zinc stearate 0.6%, phosphogypsum 20%. Total 100%
[0023] The above materials were made into brake pads according to the conventional pressing method, and were tested according to category 3 on a constant-speed friction testing machine according to the GB5763-2008 standard. The results are shown in Table 2.
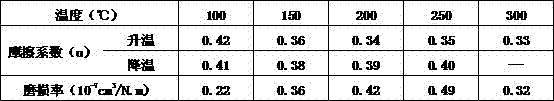
[0024] Table 2:
[0025]
[0026] It can be seen from the data in Table 2 that the brake pad obtained in Example 2 of the present invention has a friction coefficient of 0.33-0.42 in the heating stage and a friction coefficient of 0.38-0.41 in the cooling stage, and the wear rate is small, which fully meets the national standard.
Embodiment 3
[0028] 13% resin, 4% friction powder, 5% tire powder, 10% mineral fiber, 12% silica fume wool, 6% glass fiber, 8% graphite, 5% barium sulfate, 6.4% coke powder, 3% alumina, oxide Zinc 3%, iron ore powder 3%, bauxite 4%, vermiculite 2%, zinc stearate 0.6%, phosphogypsum 15%. Total 100%
[0029] The above materials were made into brake pads according to the conventional pressing method, and were tested according to category 3 on a constant-speed friction testing machine according to the GB5763-2008 standard. The results are shown in Table 3.
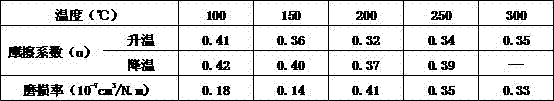
[0030] table 3:
[0031]
[0032] It can be seen from the data in Table 3 that the brake pad obtained in Example 3 of the present invention has a friction coefficient of 0.32-0.41 in the heating stage and a friction coefficient of 0.37-0.42 in the cooling stage, and the wear rate is small, which fully meets the national standard.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com