Forging process for forge piece
A technology of forgings and crafts, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, metal processing equipment, forging/pressing/hammer devices, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient structural strength, poor surface flatness, low finish, etc., achieve fast heating time, increase hardness, The effect of increasing production rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
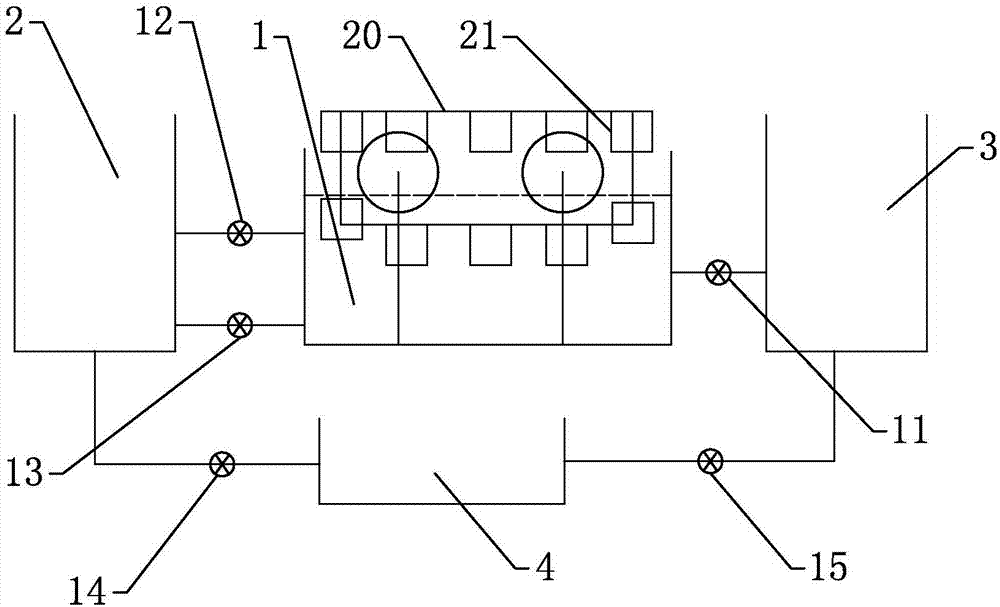
[0034] Step (1) blanking: the forging material is automatically cut into blanks of corresponding length by a fully automatic high-speed circular saw machine;
[0035] Step (2) Heating: put the raw material into the heating furnace, set the heating temperature to 1220±50°C, adopt continuous feeding, and the heating time is 15-30 seconds;
[0036] Step (3) Pre-forging: the blank is placed on the upsetting mold and upset by the punch;
[0037] Step (4) Forging mold forming: put the pre-forged blank in the center of the rough forging cavity of the mold, first hammer with a light hammer, then blow off the scale, and then continuously forge 2-3 hammers;
[0038] Step (5) Trimming: When the temperature of the blank is ≥ 750°C, put the blank into the trimming mold and trim the edge with a punch to form the required forging, and then heat-shape the forging after trimming;
[0039] Step (6) Heat treatment: the first step, normalizing: place the forging in the resistance furnace, make t...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The difference from Example 1 is that step (4) forging die forming: place the pre-forged blank in the center of the rough forging cavity, forge 5-6 times from light to heavy with an electro-hydraulic hammer, and then transfer Forging 2-3 times in the precision forging cavity to form a blank, and remove the scale during forging;
[0046] Punch holes before trimming in step (5);
[0047] Step (6) heat treatment: the first step, quenching, put the forging into the quenching tank 1 for high temperature quenching, the temperature of the quenching oil for high temperature quenching is controlled at 180-200°C, and the temperature of the forging is controlled at 220-240°C after high temperature quenching, after high temperature quenching Place the forging in the air for air cooling. After air cooling, the temperature of the forging is controlled at 160-180°C, and then the air-cooled forging is placed in the quenching tank 1 for low-temperature quenching. The temperature of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The difference from Example 1 is that step (3) pre-forging: the blank is first rolled and drawn out by a semicircular rolling machine for multiple times, and then bent by a press to form a rough blank;
[0055] Step (4) Put the pre-forged blank in the center of the rough forging cavity of the mold, first hammer lightly, then blow off the scale, and then continuously forge 3-5 hammers, and then place the rough forged material Put the embryo into the fine forging cavity and forge 2-3 times;
[0056] Punch holes before trimming in step (5);
[0057] Step (6) Heat treatment: the first step, quenching: the forging after trimming is directly dipped in oil to cool, so that its hardness reaches HRC50-52, the oil temperature in the quenching tank is controlled below 60°C, and the oil temperature is evenly stirred after stirring; the second Step 1, tempering: place the forging in the resistance furnace, make the temperature of the forging reach 675°C±20°C, set the resistance fur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com