Method for restoring underground water and soil by means of in-situ construction of catalytic oxidation reaction zone
A catalytic oxidation and groundwater technology, applied in the field of environmental pollution control, can solve the problems of slow speed and poor degradation effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for in-situ construction of a catalytic oxidation reaction zone for repairing groundwater and soil, in which a mixed solution of permanganate and stabilizer is injected into the polluted formation in situ, and the heated permanganate and stabilizer The reaction creates a catalytic reaction zone where an oxidizing agent is injected upstream of the contaminated formation where the oxidizing free radicals degrade organic pollutants in the formation. The groundwater environment is in an anaerobic or anoxic environment, and the degradation rate of organic pollutants in this environment is very slow or even difficult to degrade. The degradation of organic pollutants by strong oxidizing free radicals can be achieved by injecting oxidants into the soil. The method is simple, fast and efficient; and it can avoid digging and building permeable reaction walls, which reduces economic costs and does not require additional supply o...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The method in Example 1 is used to form a catalytic reaction zone in situ, specifically: prepare 30 mL of KMnO with a concentration of 2 mmol 4 solution, add 36mmol ethylene glycol, stir and mix evenly; after moving the mixed solution to a hydrothermal reactor with a capacity of 50mL, tighten and seal the reactor cover; put the hydrothermal reactor into a blast oven, Heated for 4 hours to obtain the in-situ catalytic material of the catalytic reaction zone in Example 1 of the present invention, washed with ultrapure water, and vacuum-dried at 60° C. to obtain a purified in-situ catalyst.
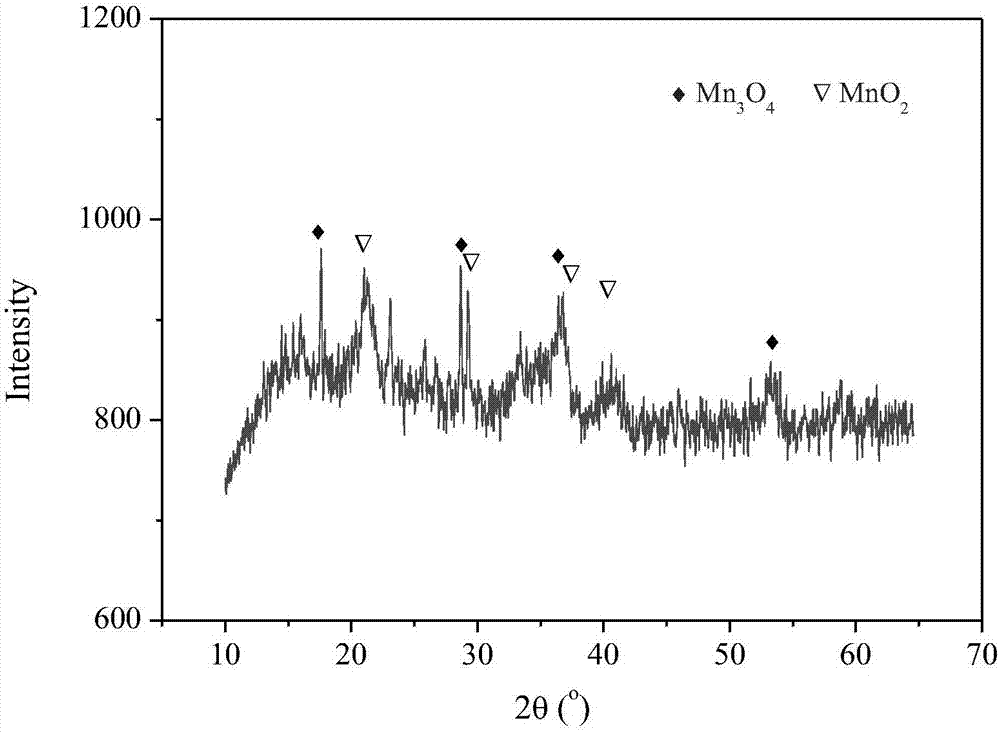
[0026] Refer to attached figure 2 , the in-situ catalyst is characterized by X-ray diffraction, and the main component of the in-situ catalyst is Mn 3 o 4 and MnO 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0028] The method of the embodiment of the present invention is adopted to simulate the groundwater area polluted by organic pollutants in the sealed soil column reactor, and inject 30 mL of the mixed solution of potassium permanganate and ethylene glycol into the soil layer in the middle of the soil column, wherein the dosage of potassium permanganate is The dosage of ethylene glycol is 2mmol, and the dosage of ethylene glycol is 36mmol. At the same time, potassium permanganate and ethylene glycol are fully reacted and converted into a solid manganese oxide catalytic reaction zone by steam heating for 1 hour.
[0029] After the soil column is saturated with water, use nitrogen to remove oxygen to simulate the anoxic environment of groundwater, open the peristaltic pump to use simulated groundwater to discharge the air in the conduit, connect the conduit to the soil column, and control the flow rate so that the water output rate is controlled at 0.1 mL / min, so that the soil col...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com