Primer and probe combination for detecting candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus and detection method
A technology of citrus huanglong and primer probes, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/testing, etc., can solve problems such as long incubation period and uncontrollable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050]Example 1, Design and synthesis of RPA primers and probes for identification of Huanglongbing citrus
[0051] According to the sequence of the 16S ITS region of H. citriensis Asiatica, multiple sets of theoretically feasible RPA primers (including three upstream primers and three downstream primers) were designed using primer design software, as shown in Table 1.
[0052] Table 1 RPA candidate primers and probe sequences (5'-3')
[0053]
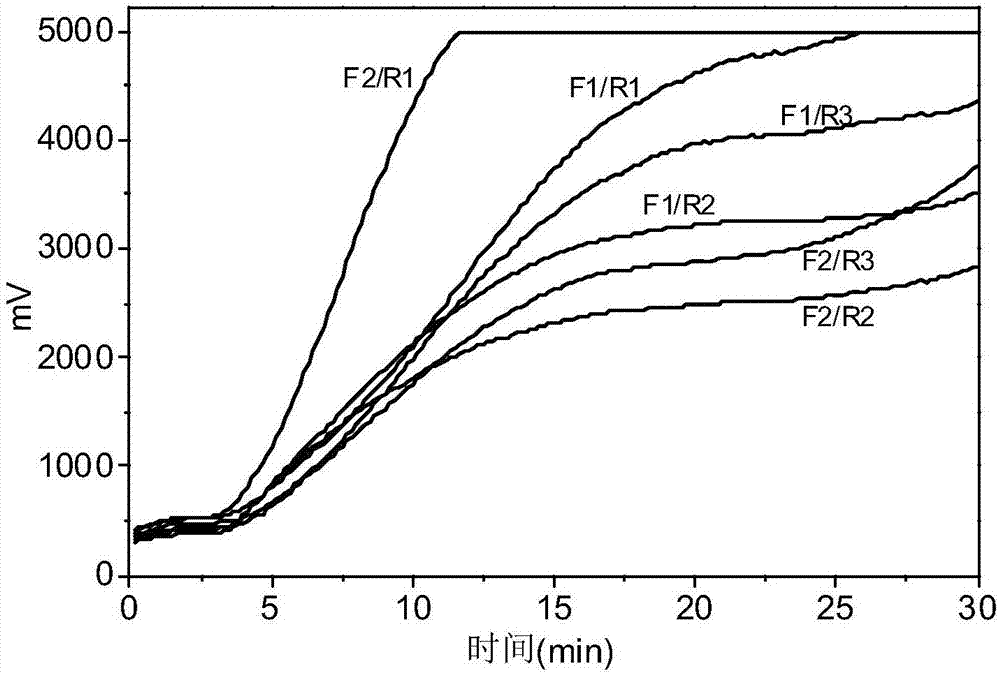
[0054] Different combinations of upstream primers and primers (F1 / R1, F1 / R2, F1 / R3, F2 / R1, F2 / R2, F2R3) in Table 1 were used for effect verification, sensitivity analysis, and specificity analysis (see the implementation for specific operation methods) Example 2-4), the result is as follows figure 1 As shown, F2 / R1 has the best sensitivity and amplification efficiency. Using F2 / R1 to detect citrus chlorophyll DNA, phytoplasma phytoplasma and phytoplasma papaya microphylla did not produce positive results, which met the specificity...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Embodiment 2, establishment of RPA detection method
[0063] 1. Use the magnetic bead method plant genomic DNA extraction kit (Tiangen Biochemical Technology DP342) to extract the total DNA of the citrus plant leaf veins to be tested. The specific operations are as follows:
[0064] Take about 100 mg of the leaf vein or root bark tissue of the citrus plant to be tested, add liquid nitrogen and grind it thoroughly. Quickly transfer the ground powder to a centrifuge tube pre-filled with 400 microliters of buffer GPM and 5 microliters of RNase A (10mg / ml), quickly invert and mix well, then place the centrifuge tube in a 70°C water bath for 10 minutes, Invert the centrifuge tube several times during the water bath to mix the sample. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm (~13,400×g) for 4 minutes, and transfer 300 microliters of the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube. Add 300 μl buffer GHB, 300 μl isopropanol and 15 μl magnetic bead suspension G, shake and mix for 5 minutes. Place t...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3, the specificity of RPA detection method
[0071] Samples for testing: citrus plants infected with citrus H. asiatica; citrus plants not infected with citrus H. chinensis; bamboo plants infected with Phytoplasma chinensis; Papaya plants infected with Phytoplasma papaya .
[0072] The detection method established in Example 2 was used to detect the RPA of each sample.
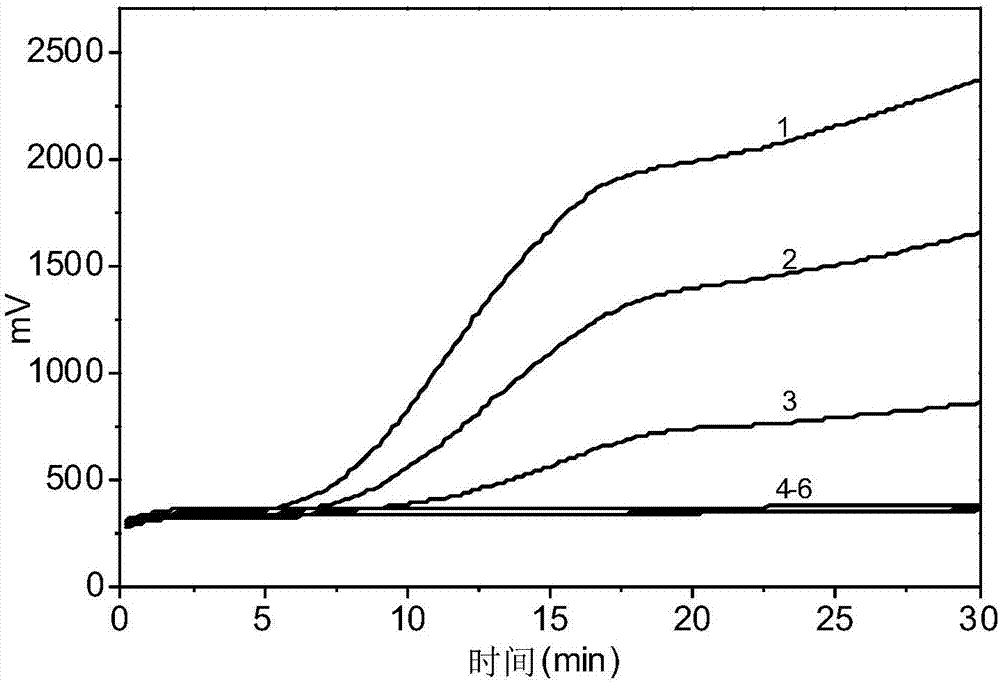
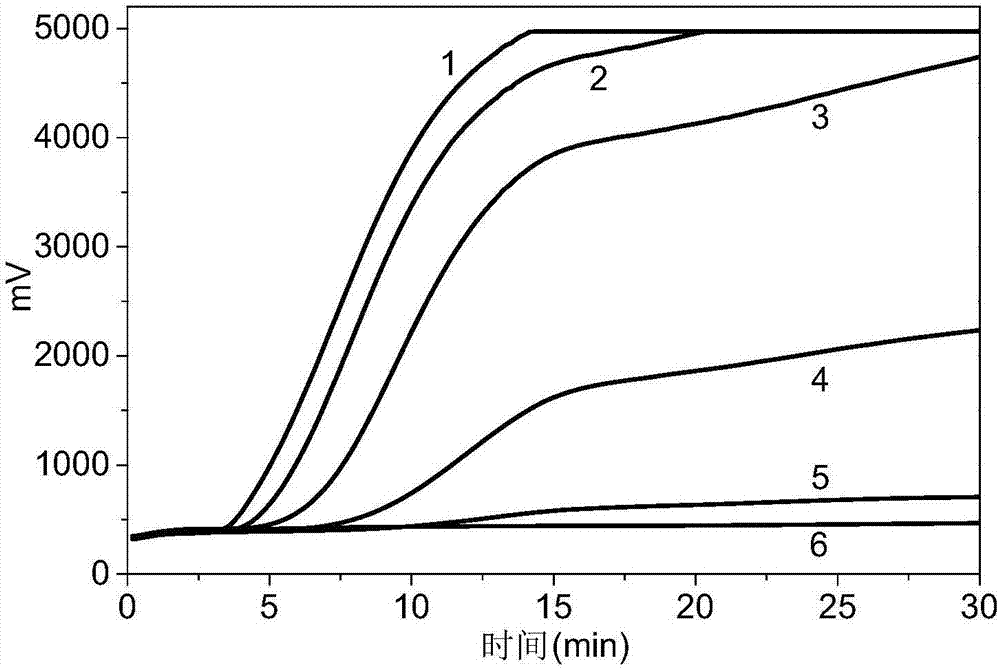
[0073] The result is as figure 2 shown. figure 2 Among them, curves 1-3 are RPA real-time fluorescence curves obtained by template amplification of leaf vein DNA extracted from three citrus Huanglongbing bacteria-infected citrus plants, respectively. Curve 4 is the DNA of uninfected citrus leaves, curve 5 is the DNA of leaves infected with Phytoplasma papaya, and curve 6 is the DNA of leaves infected with Phytoplasma papaya.
[0074] The results showed that only the vein DNA samples (curves 1, 2, 3) of plants that had been infected with citrus huanglongbing had fluorescent signals to ri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com