Composite electrode and preparation method thereof, and heterojunction solar cell and preparation method thereof
A technology of solar cells and composite electrodes, applied in circuits, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem that the photoelectric conversion efficiency needs to be further improved.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0076] A method for preparing a compound electrode structure of a heterojunction solar cell, comprising the steps of:
[0077] An interface buffer layer is formed on the doped amorphous silicon layer; when the doped amorphous silicon layer is P-type, the work function of the interface buffer layer is greater than or equal to 5V; when the doped amorphous silicon layer is N-type, the interface buffer layer The work function is less than or equal to 4.2eV;
[0078] forming a transparent conductive layer on the interface buffer layer;
[0079] Electrodes are formed on the transparent conductive layer.
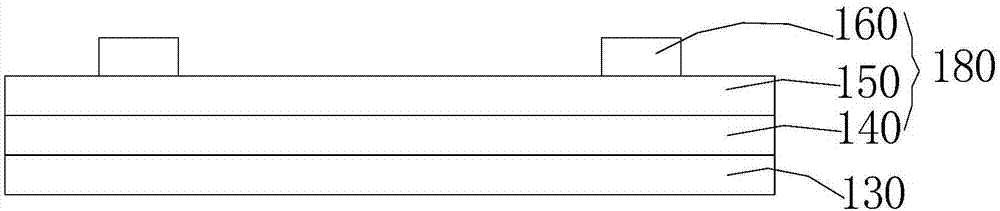
[0080] Preferably, when the doped amorphous silicon layer is P-type, the interface buffer layer is formed by physical vapor deposition. For example, vacuum evaporation or sputter evaporation formation.
[0081] Preferably, when the interface buffer layer is lithium fluoride or cesium fluoride, the interface buffer layer is deposited by vacuum evaporation. When the interface buf...
Embodiment 1
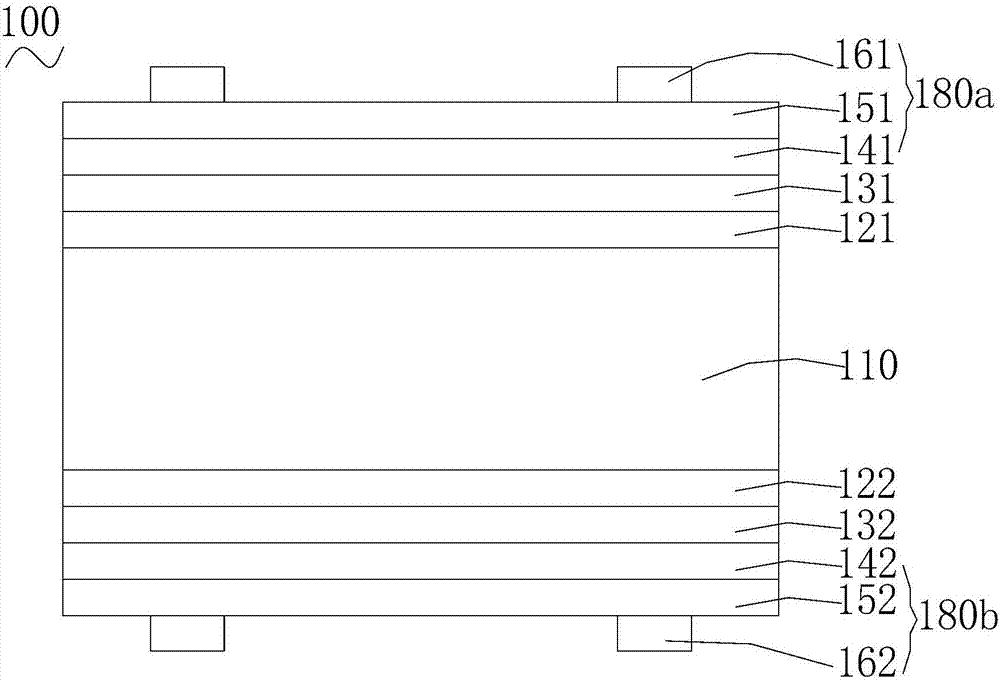
[0090] The N-type crystalline silicon wafer is passed through an alkaline solution to remove the damaged layer; the N-type crystalline silicon wafer is cleaned and textured, and the surface phosphosilicate glass is removed.
[0091] On one surface of the N-type crystalline silicon wafer, the intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (i-a-Si:H) and the N-type hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (n-a-Si:H) are deposited by PECVD to form the second intrinsic layer and a second doped amorphous silicon layer.
[0092] On the other surface of the N-type crystalline silicon wafer, the intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (i-a-Si:H) and the P-type hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (p-a-Si:H) were deposited by PECVD to form the first intrinsic layer and the first doped amorphous silicon layer.
[0093] Non-stoichiometric molybdenum oxide is grown on the first doped amorphous silicon layer by vacuum evaporation with a thickness of 6 nm.
[0094] Reactive plasma depositi...
Embodiment 2
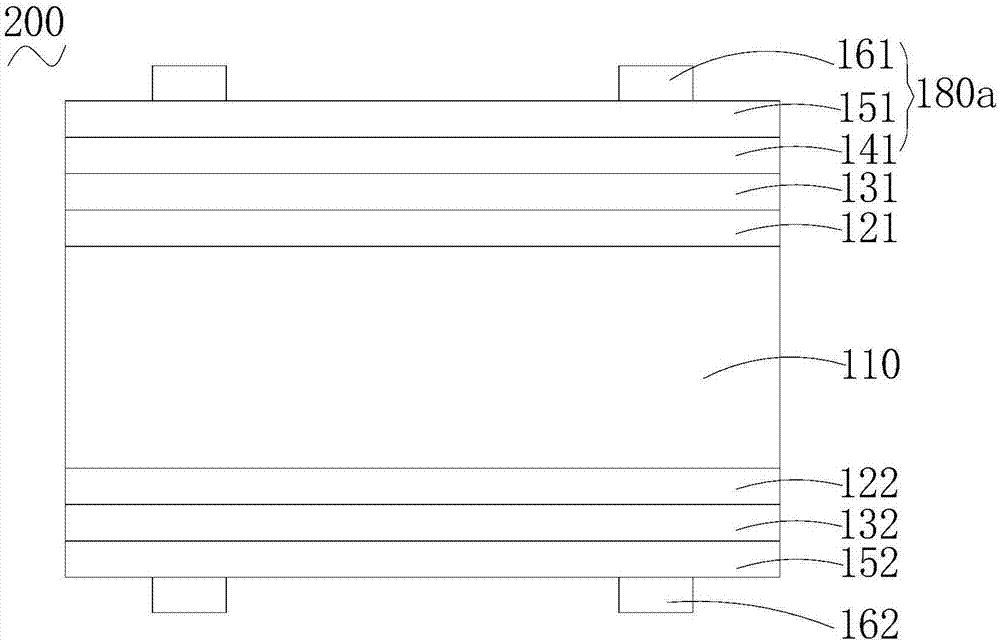
[0098] The N-type crystalline silicon wafer is passed through an alkaline solution to remove the damaged layer; the N-type crystalline silicon wafer is cleaned and textured, and the surface phosphosilicate glass is removed.
[0099] On one surface of the N-type crystalline silicon wafer, the intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (i-a-Si:H) and the N-type hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (n-a-Si:H) are deposited by PECVD to form the second intrinsic layer and a second doped amorphous silicon layer.
[0100] On the other surface of the N-type crystalline silicon wafer, the intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (i-a-Si:H) and the P-type hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (p-a-Si:H) were deposited by PECVD to form the first intrinsic layer and the first doped amorphous silicon layer.
[0101] Non-stoichiometric molybdenum oxide is grown on the first doped amorphous silicon layer by vacuum evaporation with a thickness of 6 nm.
[0102] Non-stoichiometric titan...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Work function | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Work function | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com