Miniaturized linear femtosecond laser pulse shape and width measurement device
A femtosecond laser, pulse shape technology, applied in the direction of instruments, can solve the problems of complex optical path adjustment, difficult real-time measurement, complex structure, etc., to achieve the effect of firm and simple structure, easy adjustment, and small measuring device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments, but the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited thereby.
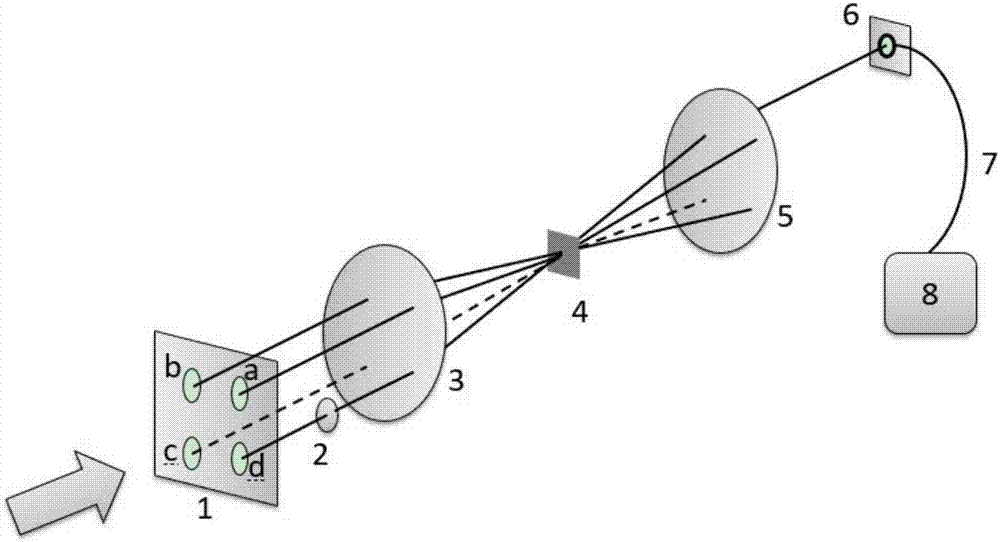
[0017] see first figure 1 , it can be seen from the figure that the miniaturized linear femtosecond laser pulse shape width measuring device of the present invention comprises: along the incident beam direction of the pulse to be measured, there are four small hole diaphragm plates 1, an attenuation delay plate 2, and a first convex lens 3 , a third-order nonlinear medium 4, a second convex lens 5, a fiber coupler 6, a single-mode fiber 7 and a spectrometer 8;
[0018] Described four-hole aperture plate 1, first convex lens 3 and second convex lens 5 are on the same optical axis, and four apertures of the same size are arranged on described four-hole aperture plate 1, and four apertures are in a On the four vertices of the square, the center of the square is loca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com