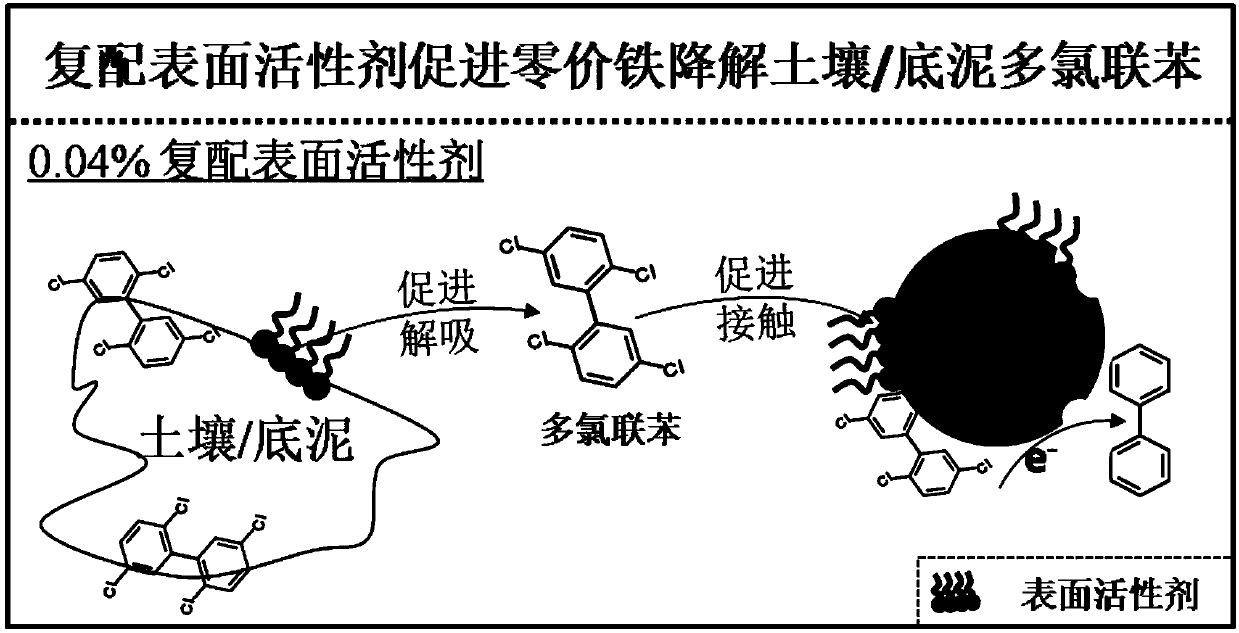
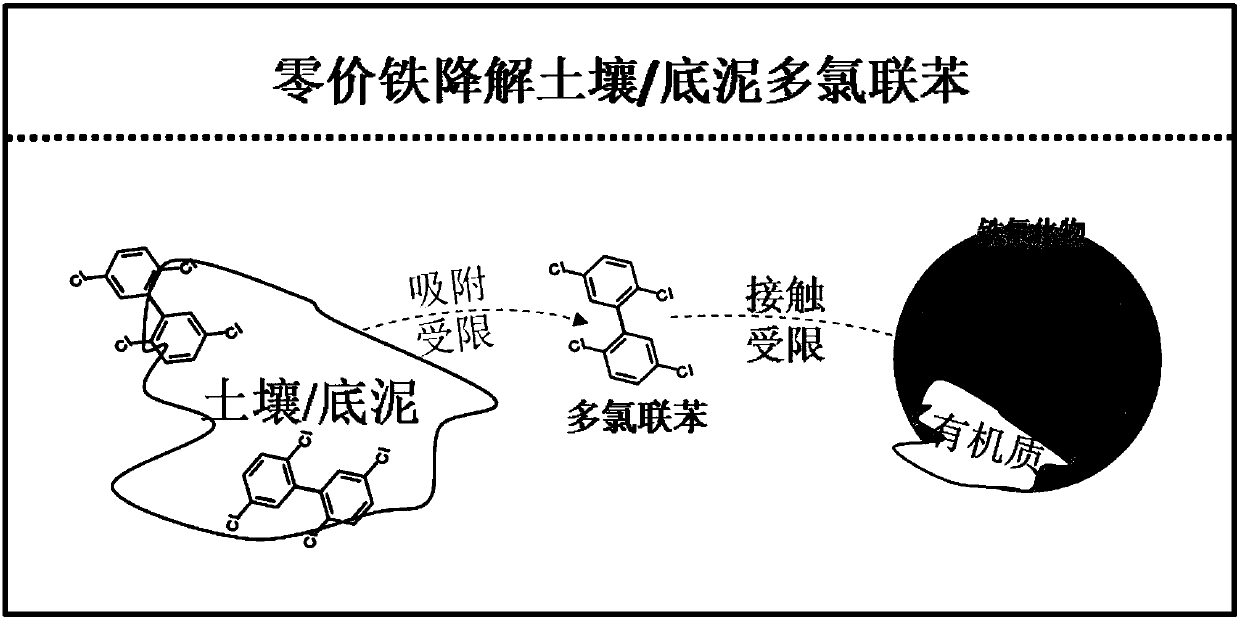
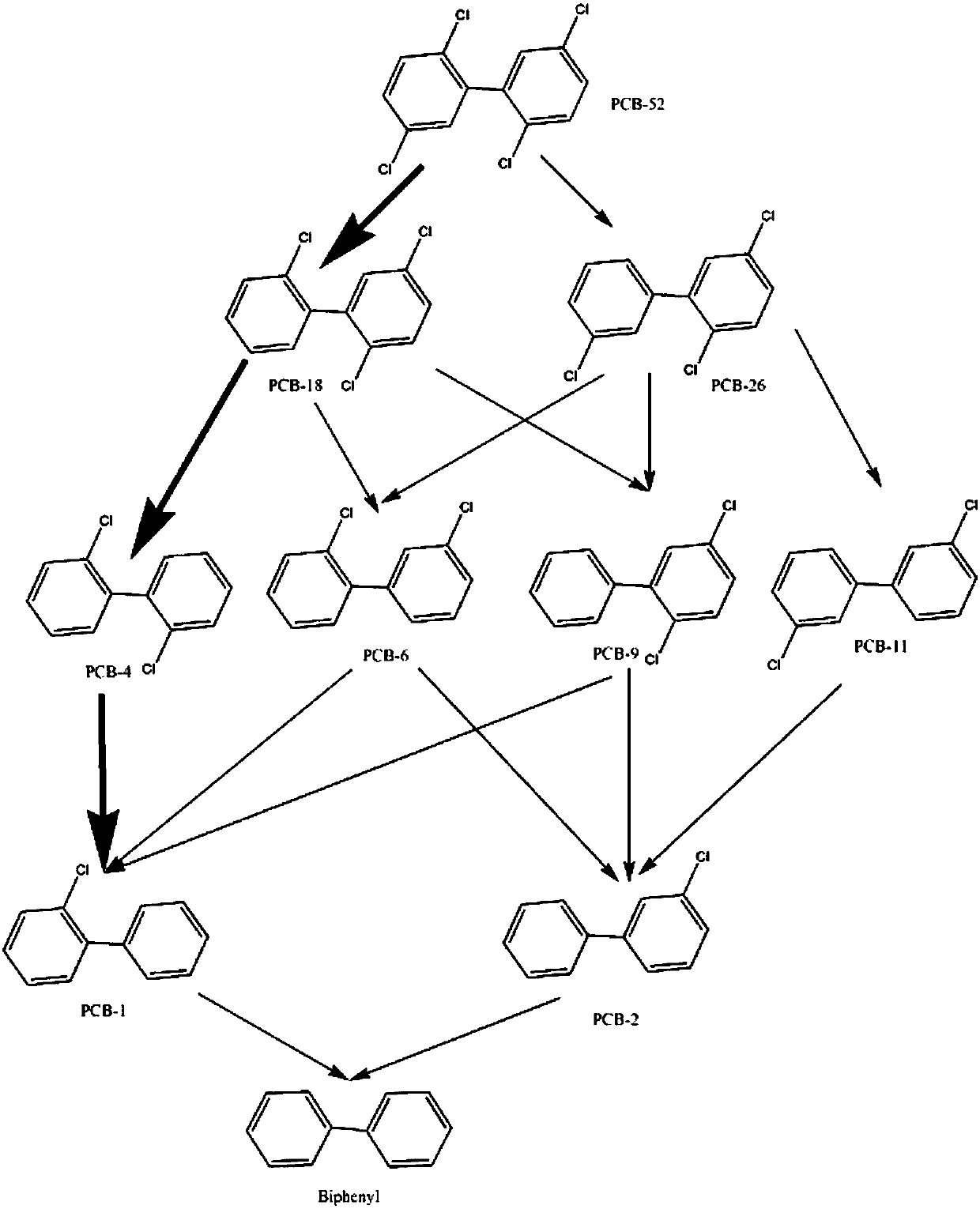
Method for promoting polychlorinated biphenyl degradation by zero-valent iron
A technology of polychlorinated biphenyls and zero-valent iron, applied in the field of soil or sediment restoration, can solve the problems of large application amount, limitation, unfavorable restoration cost, etc., and achieve the effect of improving degradation efficiency and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Step (1) prepare mixed surfactant solution: take by weighing 4.534g nonionic surfactant Tween-80 and 1.204g anionic surfactant sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS), dissolve it in deionized Prepare 0.04wt% mixed surfactant solution in water.
[0030] Step (2) Degradation of PCBs: In the anaerobic box, add 0.10g of zero-valent iron powder and 0.50g (dry weight) of PCB-contaminated bottom sludge to 10mL of the above-mentioned 0.04wt% mixed surfactant solution medium; do not adjust the pH of the solution, and tighten the polytetrafluoroethylene cock after mixing thoroughly; then place the sample at room temperature (25±2°C) and shake at 200rpm for 7 days; take out the suspension at the set time point, pass through 0.45 The μm glass fiber filter membrane separates the solid-liquid two-phase to terminate the leaching reaction, and determines the total amount of PCBs in the solution and solid phase.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Steps and process conditions refer to Example 1, the difference from Example 1 is that the concentration of the mixed surfactant solution is 0.02wt%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com