Identification method of robot motor system based on Kalman filtering through calibration of quasi model
A technology of Kalman filtering and robot movement, applied in general control systems, control/adjustment systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient fitting and linearization, achieve convenient parameter adjustment, wide range of Q value selection, and identification good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
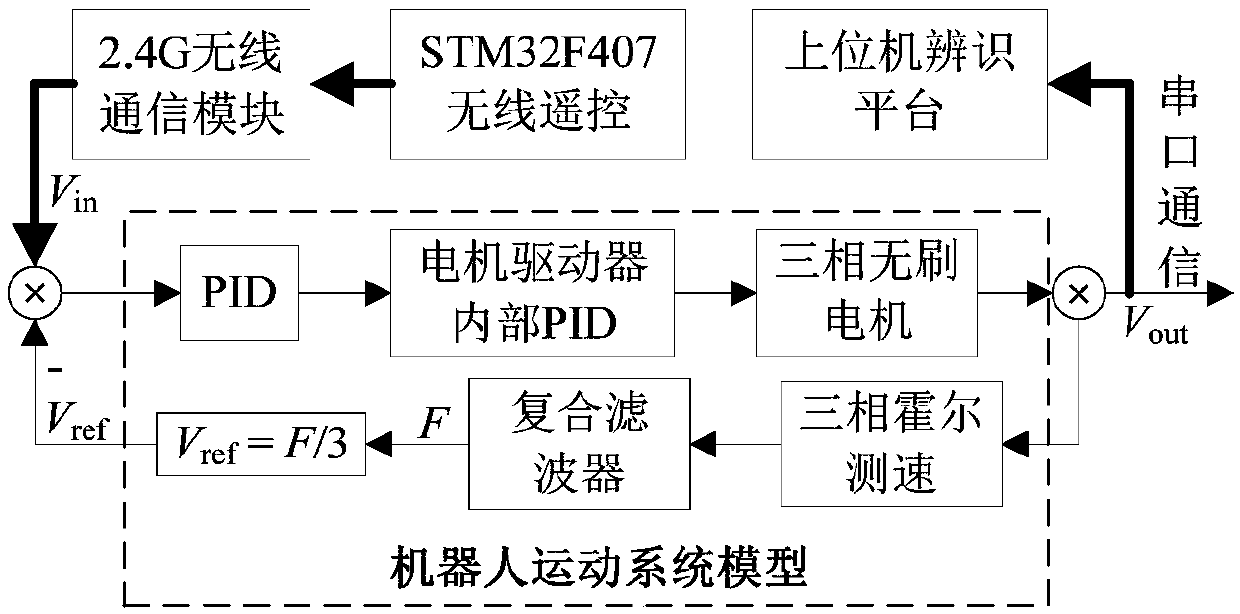
[0047] figure 1 Shown here is a schematic diagram of the identification platform structure of the inspection robot motion system of this embodiment. The inspection robot control platform consists of a remote controller with STM32F407ARM as the main control chip, a PID main controller with STM32F103ARM as the core, a 2.4G wireless communication module, and a motor driver Module, Hall speed sensor, composite filter, etc.
[0048] During normal operation, the robot is in automatic inspection mode without manual intervention. The handheld remote controller is used to manually remotely control the robot to perform corresponding actions when an abnormal situation occurs. The main controller is used to receive instructions from the remote control, and obtain speed information by decoding the instructions from the remote control. And the given speed information is calculated by PID algorithm to obtain the PWM wave signal of the corresponding duty cycle, and the PWM wave signal is outpu...
Embodiment 2
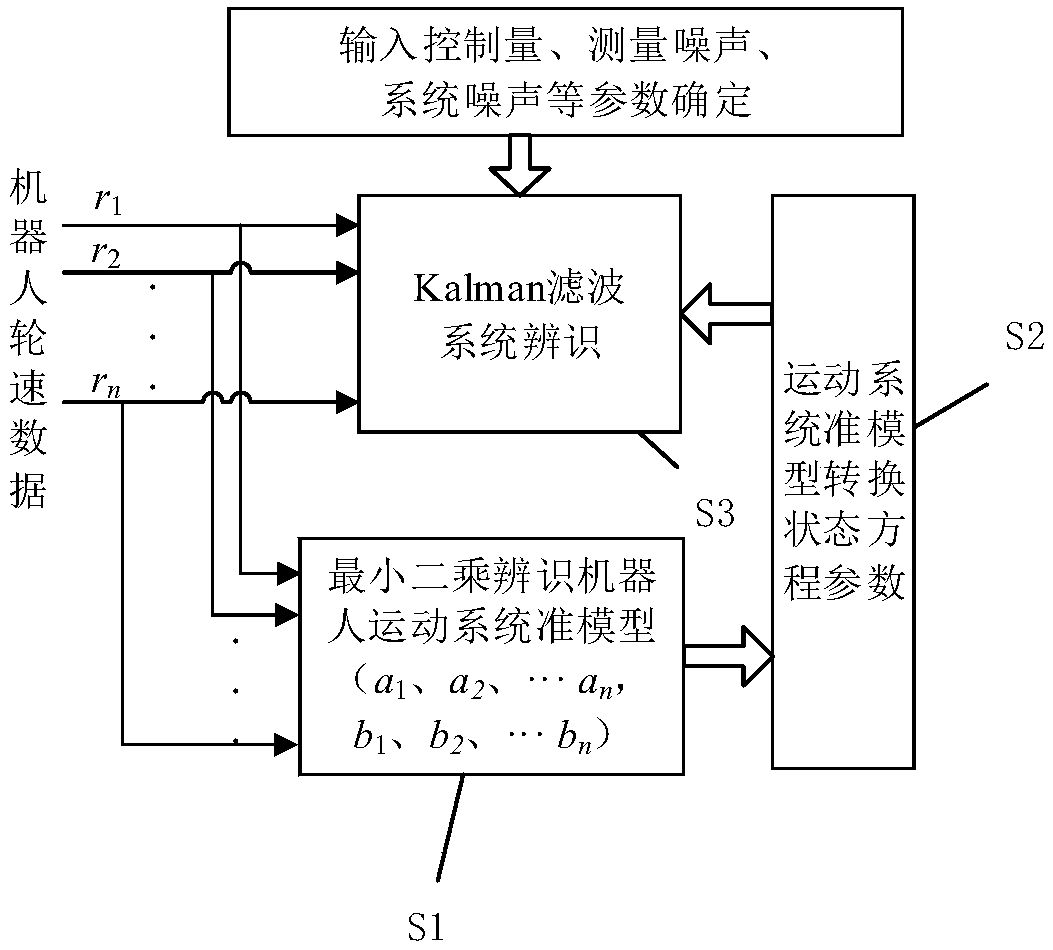
[0092] This embodiment compares the identification effects of Kalman filtering with quasi-model calibration and non-quasi-model calibration at the same set wheel speed.
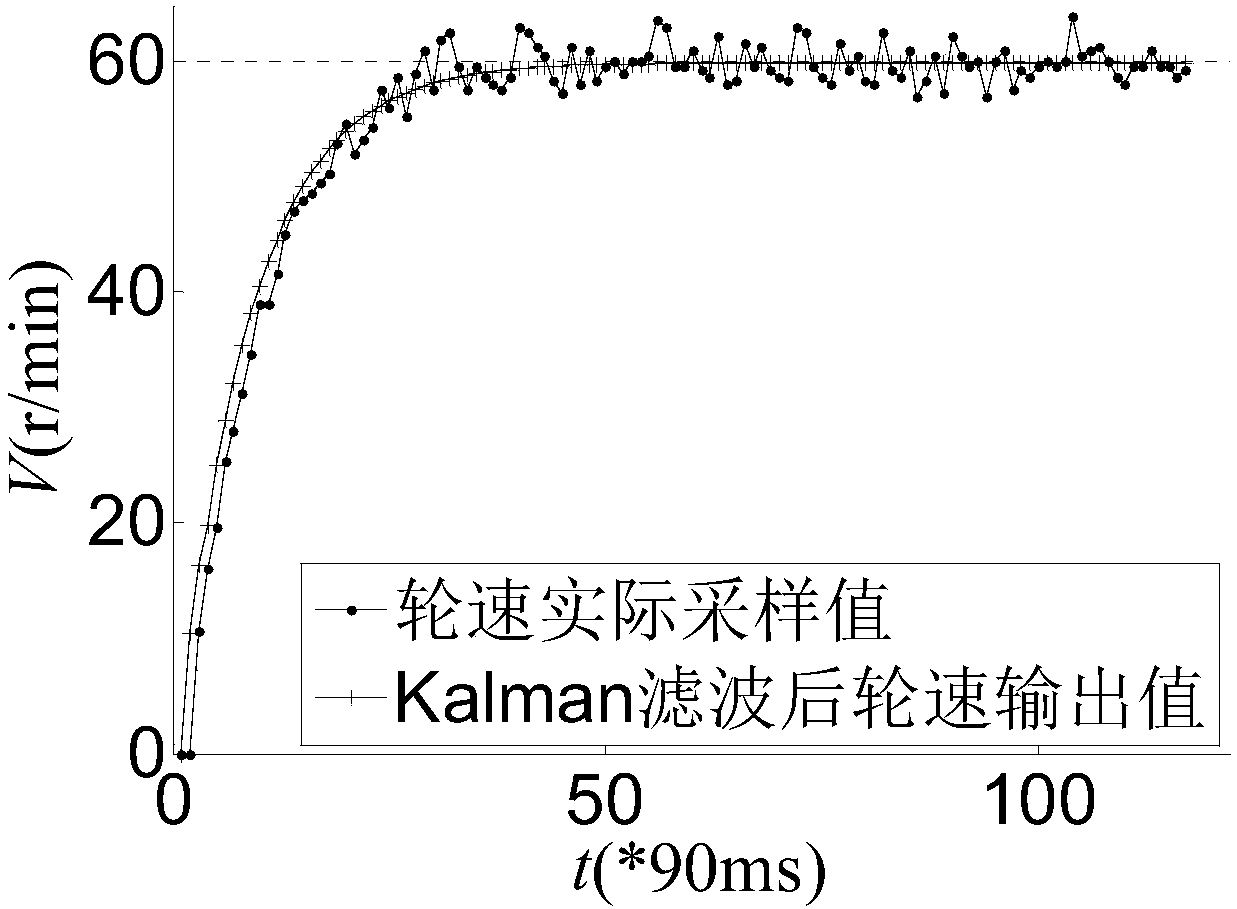
[0093] Using the same set of robot wheel speed sampling data, the kalman filter with quasi-model calibration and the Kalman filter with inaccurate model are used to identify the motion system. The identification effect is compared and verified by the identification curve graph and identification related parameters, and finally the comparison effect in the two cases is obtained. Since the quasi-model is integrated in the Kalman filter algorithm, the Q value of the system noise parameter can be appropriately reduced, and the value of Q is 0.015 in this embodiment. When the robot wheel speed is set to 60r / min, a set of wheel speed adjustment data is collected, and the quasi-model of the least square fitting is substituted into the Kalman filter to draw a fitting curve, such as image 3 As shown, "*90ms" in parenthe...
Embodiment 3
[0103] This embodiment compares the robustness of Kalman filter identification with quasi-model calibration and non-quasi-model calibration, uses different Q values for identification, and creates an identification curve and a key parameter quantitative analysis table.
[0104] Take a sample of the robot wheel speed with a rotation speed of 60r / min, Figure 7-9 Shown are the identification curves of using the quasi-model calibration Kalman filter to identify the set of samples when Q takes different values. Table 2 shows the corresponding identification key quantities. Such as Figure 10-12 As shown, when Q takes different values, the non-standard model calibration Kalman filter identifies the identification curve of the set of samples. Table 3 is a list of the corresponding identification key quantities.
[0105] Since there is no accurate model of Kalman filtering, a large number of sample points are needed for calibration. In order to improve the calibration efficiency, a large...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com