Method for Biologically Storing and Restoring Data
A data and data division technology, which is applied in the fields of synthetic biology, computer and bioinformatics, can solve the problems of reduced conversion efficiency, increased cost of DNA synthesis and sequencing, and large distances in information storage density, so as to prevent generation, The effect of preventing single-base consecutive repeats
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0203] Embodiment 1 Conversion and restoration of text data
[0204] The following takes text type data as an example to illustrate the data conversion process and restoration process of the present invention.
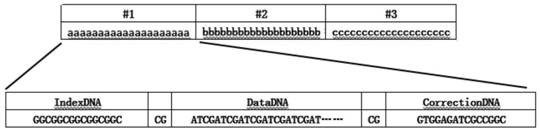
[0205] The different types of data have been preprocessed and the data format converted into a text file "written" by characters in the ASCII table. Therefore, the converter will be faced with a string literal, which can also be understood as a very long sequence of strings. Convert a data text to a data DNA sequence in units of string units of the data text. Such as figure 2 As shown, every 20 characters form a string, which is a conversion unit, and is encoded into a data DNA sequence single strand. Starting from the first conversion unit (#1) of the data text, each conversion unit (#2, #3, etc.) is encoded sequentially to generate multiple data DNA sequence single strands.
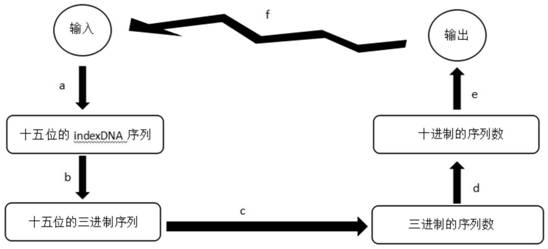
[0206] Generation and reduction of indexDNA sequences
[0207] (1) Algorithm for gener...
Embodiment 2
[0294] Embodiment 2 algorithm test and result
[0295] Based on the above algorithm and design as the core, a simple biological converter was written, and the performance of the converter was tested.
[0296] (1) Storage of small-scale text data
[0297] The first generation of converters did not have index and correction modules, so they could only convert some very short texts. When dealing with some short texts, since there is no indexDNA sequence and correctionDNA sequence part, the length of the data DNA sequence is shortened, the efficiency is improved, and the cost is reduced at the application level. On the other hand, in the short term, what is currently applied to short-text biological storage will be more common. Take "Dai Lab, Tsinghua University, Synthetic Yeast, Synthetic Biology" as the test text, and convert it to the dataDNA sequence shown in Table 6:
[0298] Table 6 Storage test results of small-scale text data
[0299]
[0300]The above dataDNA seque...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com