Hydrophobic porous polymer conductive material and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of porous polymers and hydrophobic polymers, applied in electrical components, magnetic field/electric field shielding, coatings, etc., can solve problems such as the decline of electromagnetic shielding effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] First, flatten the loofah silk, cut it into 10cm×10cm×2cm blocks, put it on a graphite plate, put it in a furnace and charcoalize it to 500°C, and spread the porous carbon-based skeleton obtained after charcoalization on sandpaper; Then, 1 g of polyvinylidene fluoride was dissolved in 10 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide, and mechanically stirred at 80 ° C for 2 h until it was completely dissolved to obtain a uniform polymer solution; next, the polymer solution was coated on On the porous carbon-based framework, ensure that the porous carbon-based framework is close to the sandpaper and soaked by the polymer solution for 10 minutes, then place the porous carbon-based framework at room temperature for water vapor micro-phase separation, and finally put it in an oven at 80°C for drying 6h, a polymer conductive material with a thickness of 2 mm was obtained.
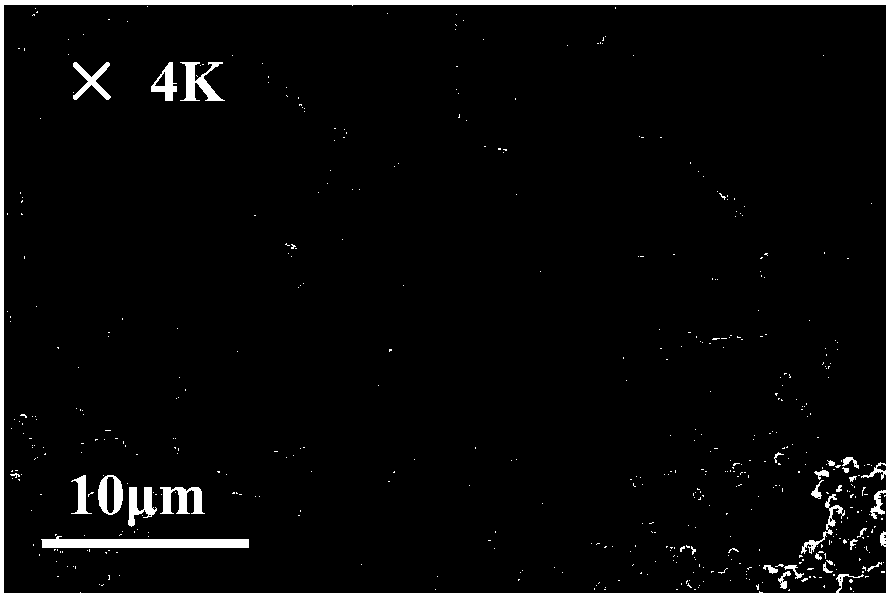
[0028] figure 1 Shown is the microscopic topography of the surface of the polymer conductive material prepared in this ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The preparation method of this example is basically the same as that of Example 1, except that the loofah charcoal is burned to 1000°C.
[0032] After testing, the static water contact angle of the polymer conductive material prepared in this example close to the sandpaper surface is 148.2±2°, and the static water contact angle of the evaporation surface is 134.1±2°. The material exhibits excellent superhydrophobicity. The electromagnetic shielding effect of the polymer conductive material on the U-band ranges from 34.6dB to 43.8dB.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The preparation method of this example is basically the same as that of Example 1, except that the luffa charcoal is burned to 1500°C.
[0035] After testing, the static water contact angle of the polymer conductive material prepared in this example close to the sandpaper surface is 148.7±2°, and the static water contact angle of the evaporation surface is 135.2±2°. The material exhibits excellent superhydrophobicity. The polymer conductive material has a U-band electromagnetic shielding effect ranging from 37.2dB to 46.7dB.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com