Disc and plate strip structure-based composite laser amplifier
A laser amplifier and slab structure technology, applied in the laser field, can solve the problems of low power, low laser energy, and poor beam quality, and achieve the effects of energy extraction, high flexibility, high amplification efficiency, and output light quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
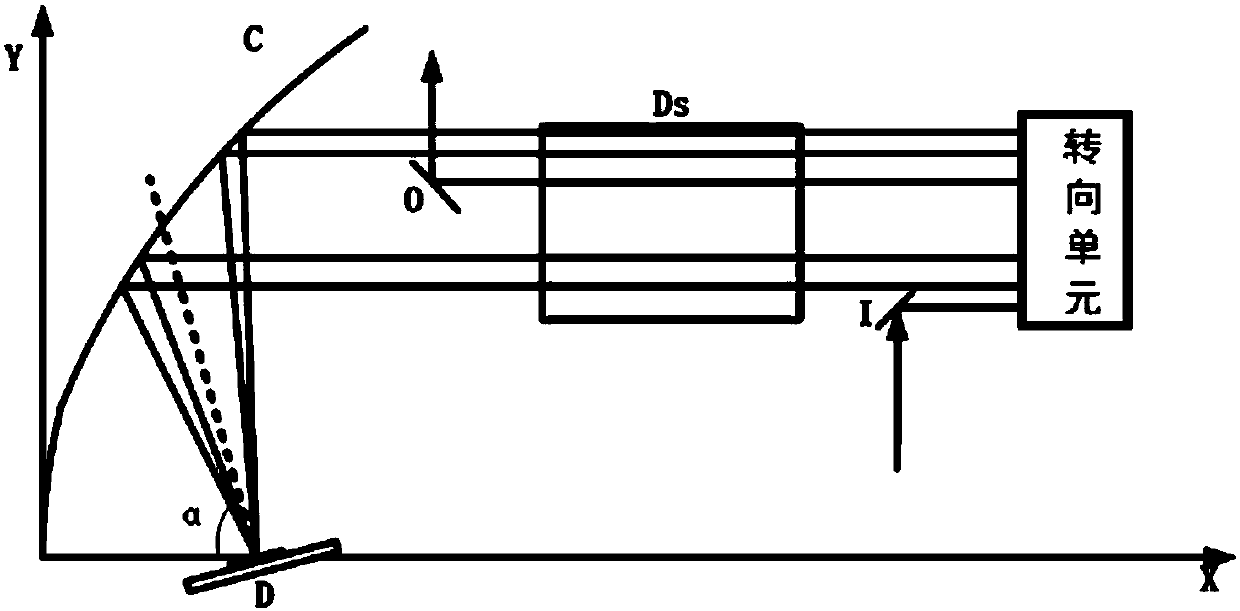
[0067] Figure 6 It is the schematic plan view of the structure of the disk laser amplifier of embodiment 1, comprising disk crystal D, slab crystal Ds, rectangular prism M, parabolic mirror surface C and incident and outgoing unit I, O; the focal point of parabolic mirror is positioned at the center of disk crystal place; the front of the disc crystal has an anti-reflection film, and the back has a total reflection film; its back is oppositely provided with a parabolic reflector for reflecting the output pump light to the back of the disc crystal. By selecting the pump module inside the disc crystal, the spot size of the pump light can be made to be the same as that of the seed light. When the active particles inside the disc crystal absorb the pump light, they transition from the ground state to the excited state, and then under the action of the seed light, stimulated radiation occurs between the energy levels of the active particles, so that the energy of the seed light is...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Figure 8 It is a schematic plan view of the disk laser amplifier of Example 2. Except that the right-angle prism is replaced by a parabolic mirror and a disc crystal, the rest of the device structure is the same as that of Embodiment 1. It is worth noting that although the parabolic mirror C1 and the disc crystal D1 are mirror-symmetrical to the parabolic mirror C2 and the disc crystal D2, there must be one difference in the angle of the disc crystal or the upper and lower positions of the parabolic mirror, otherwise the seed light will enter the laser amplifier. It can only repeat the trajectory of one route, and cannot fully utilize the lath-shaped crystals, nor can it achieve multiple amplifications of the seed light.
[0073] Figure 9 It is the structural space schematic diagram of the disk laser amplifier of embodiment 2, we can obtain the specific propagation route of seed light as:
[0074] I→C2→D2→C2→Ds→C1→D1→C1→Ds→C2→D2→C2
[0075] →Ds→C1→D1→C1→Ds→C2→D2→C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com