Methods and kits for the detection of powdery mildew
A diagnostic kit and powdery mildew technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/testing, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem that grapevine powdery mildew cannot be cultured in vitro, transformation scheme has not been established, and low temperature is difficult Preservation and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
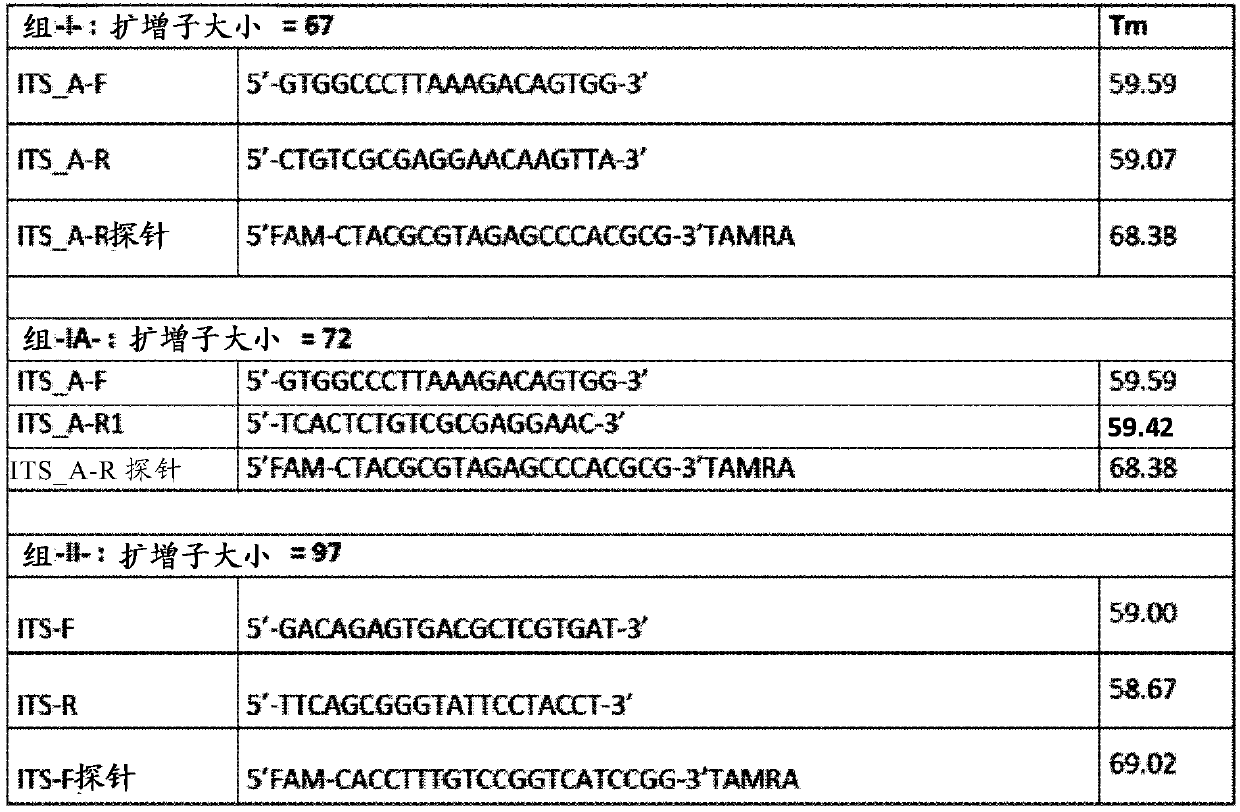
[0073] Example 1 : Design of specific primers for powdery mildew of grape
[0074] Several powdery mildew isolates were used to perform the qPCR method. These isolates were purified and maintained on isolated grape (Vitis Vinifera cv. Cinsaut) leaves. Bioassay inoculation was performed by blowing spores from sporulated 12-14 day old leaves onto the upper surface of sterilized leaves by an air pump in a Plexiglas settling tower. Infected leaves were cultured at 22°C in a growth chamber (12 / 12h light / dark photoperiod) and transferred to fresh agar medium every 3 to 4 days. Fungal material growing on leaf surfaces was scraped into Eppendorf tubes and contaminated leaf disks were frozen at -20°C.
[0075] According to the manufacturer's instructions, according to plantII kit (Macherey-Nagel), DNA extraction from Erysiophora vine fungus isolates. DNA extracts were stored at -20°C.
[0076]Using ITS1 and ITS4 primers, PCR amplification and sequencing of the ITS region of thre...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2 : In Vivo Quantification of Erysiophora viticola DNA on Grapevine Leaves
[0090] To validate the sensitivity and accuracy of the method on biological samples, qPCR analysis was applied in laboratory bioassays to total DNA extracted from leaf disks contaminated with serial dilutions of Erysipha spp. spores. Total DNA was extracted from 4 leaf discs and 100 ng of DNA per spore concentration tested at different culture periods was analyzed using qPCR analysis.
[0091] Quantities of E. viticilis target genes were determined from a plasmid DNA standard curve. The lowest concentration of 2 spores / cm was detected at cycle Ct=27,13 2 (tested immediately after spraying (d+0)), equivalent to 9.4×10 2 copies of a gene. Notably, qPCR quantification of spore concentrations from other tests showed that gene copy number increased proportionally with the number of E. viticilidis spores on the leaf surface. The highest spore concentration tested was detected at Ct = 21...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Example 3 : Evaluation of Erysiophora viticola DNA by qPCR Analysis in Field Contamination
[0094] To validate the qPCR method under field conditions, grapevine parcels were artificially contaminated on different days using laboratory prepared inoculums of different densities.
[0095] From April to August 2013, measurements were carried out at the French vineyard St Martin d’Armagnac (Gros Manseng). Planted vineyard plots with 10 plants were tested together with adjacent uninoculated 5 plant plots. By spraying different concentrations of grape powdery mildew spore solution (C1 (0.1 spores / cm 2 ), C2 (1 spore / cm 2 ) and C3 (10 spores / cm 2 )) to contaminate the leaves. Artificial inoculation with powdery mildew spores was performed on three different dates: 18 April, 7 May and 23 May. For each condition, 5 leaves were collected on d+0, d+7, d+14 and d+30 days after contamination for qPCR analysis.
[0096] For each test condition, 5 leaves were sampled and mixed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com