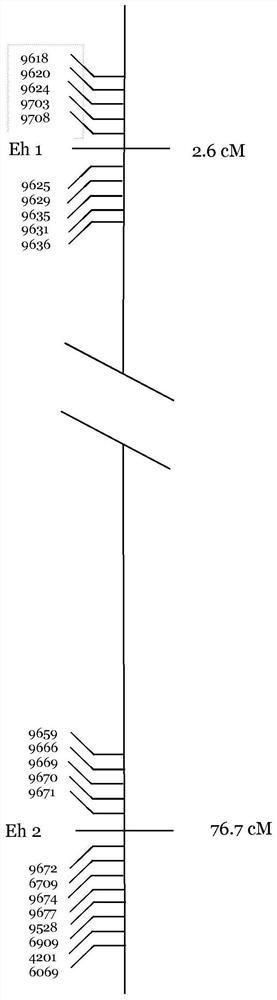
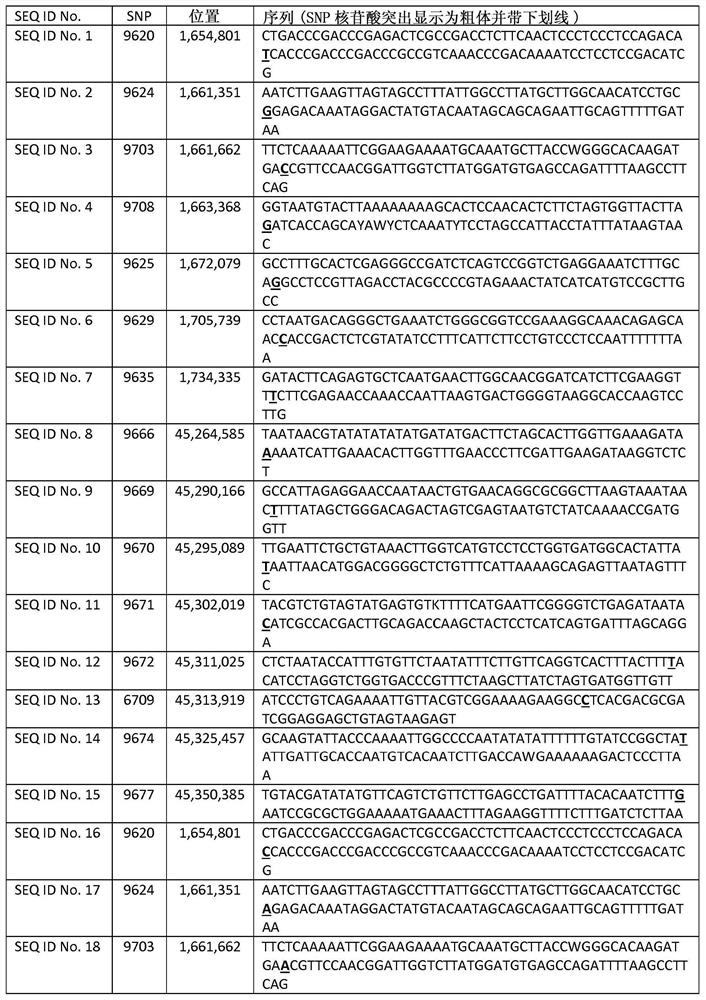
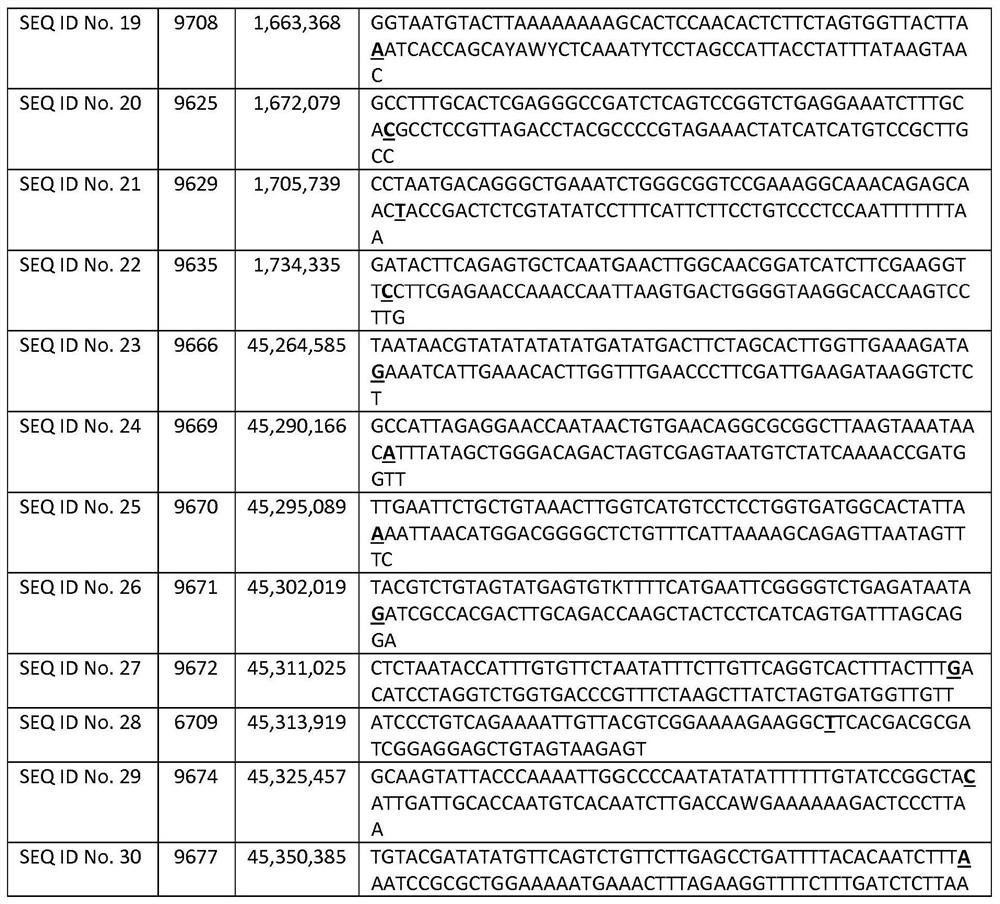
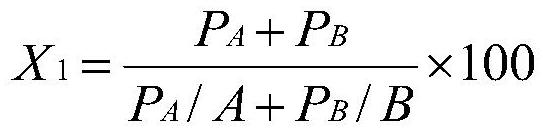Patents
Literature
34 results about "Erysiphe necator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
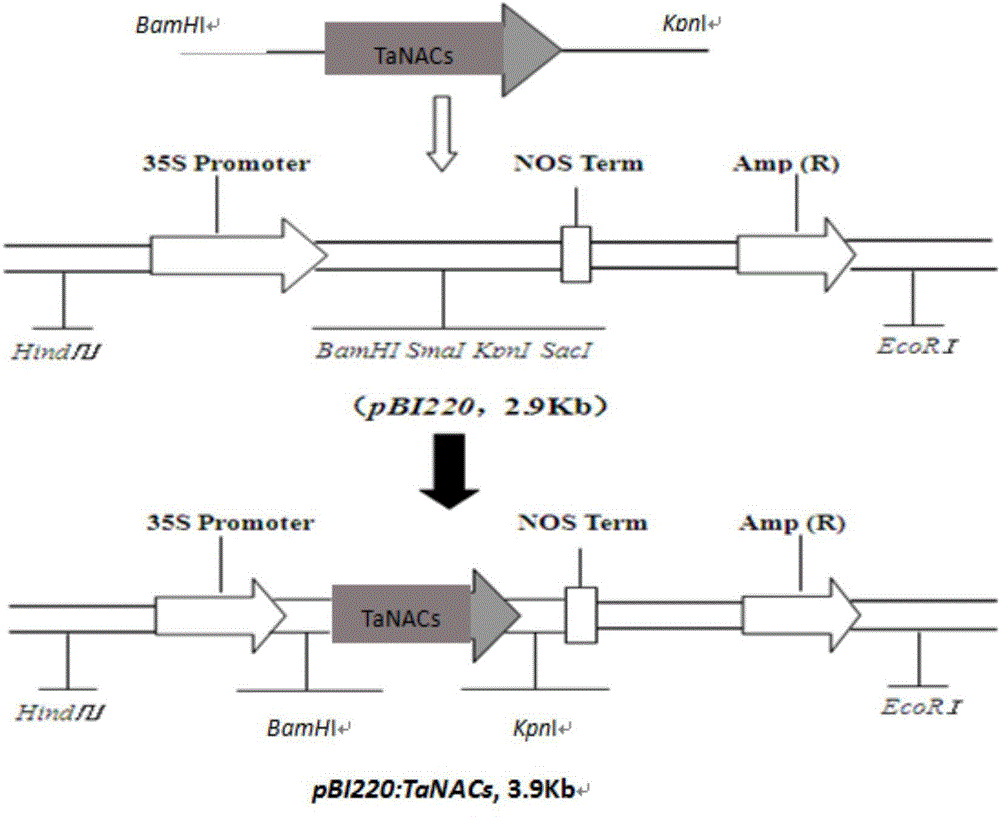
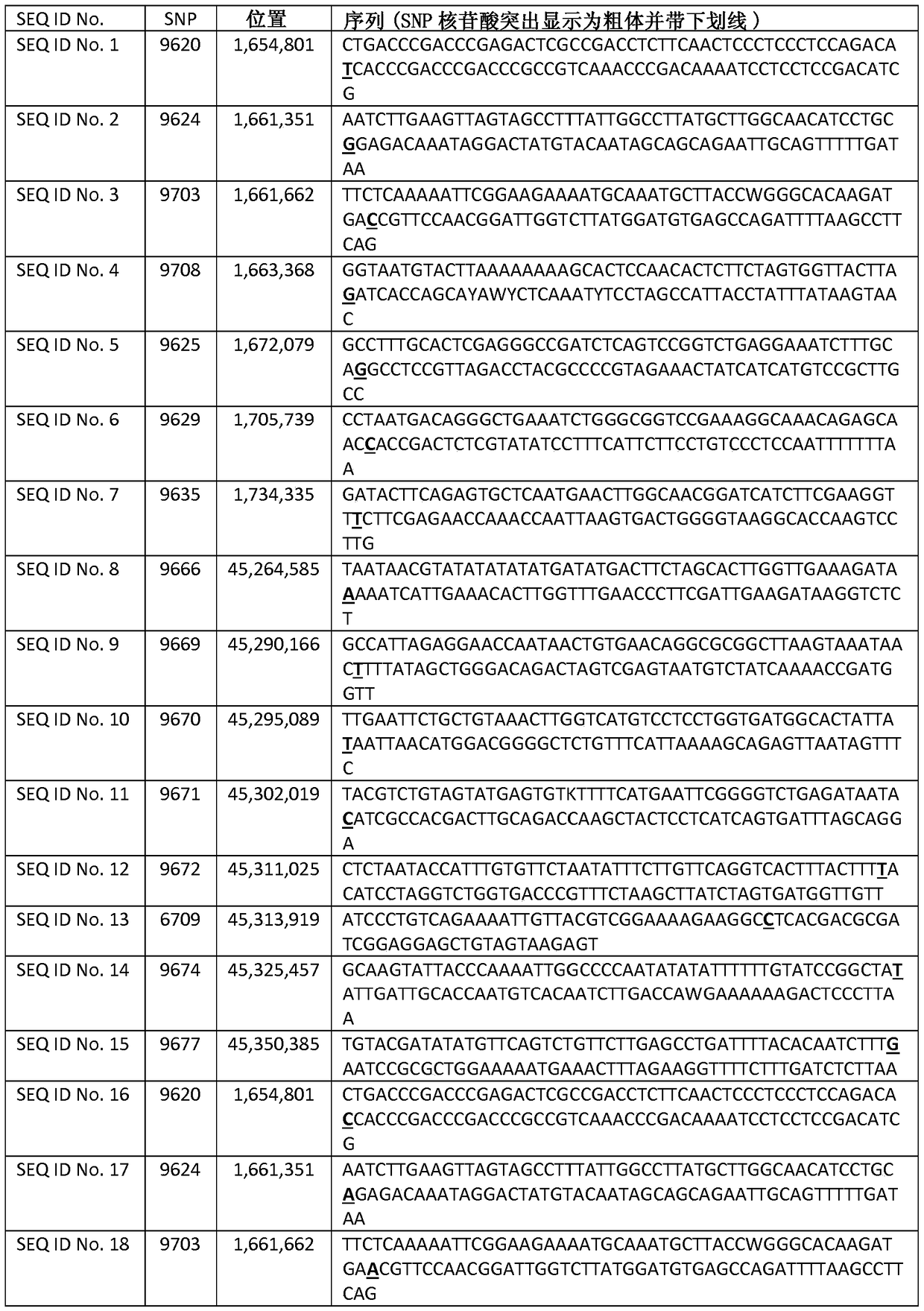
NAC transcription factor gene TaNACs in wheat as well as expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN104630235AIncrease resistancePowdery mildew resistantPlant peptidesFermentationGene conversionCommon wheat
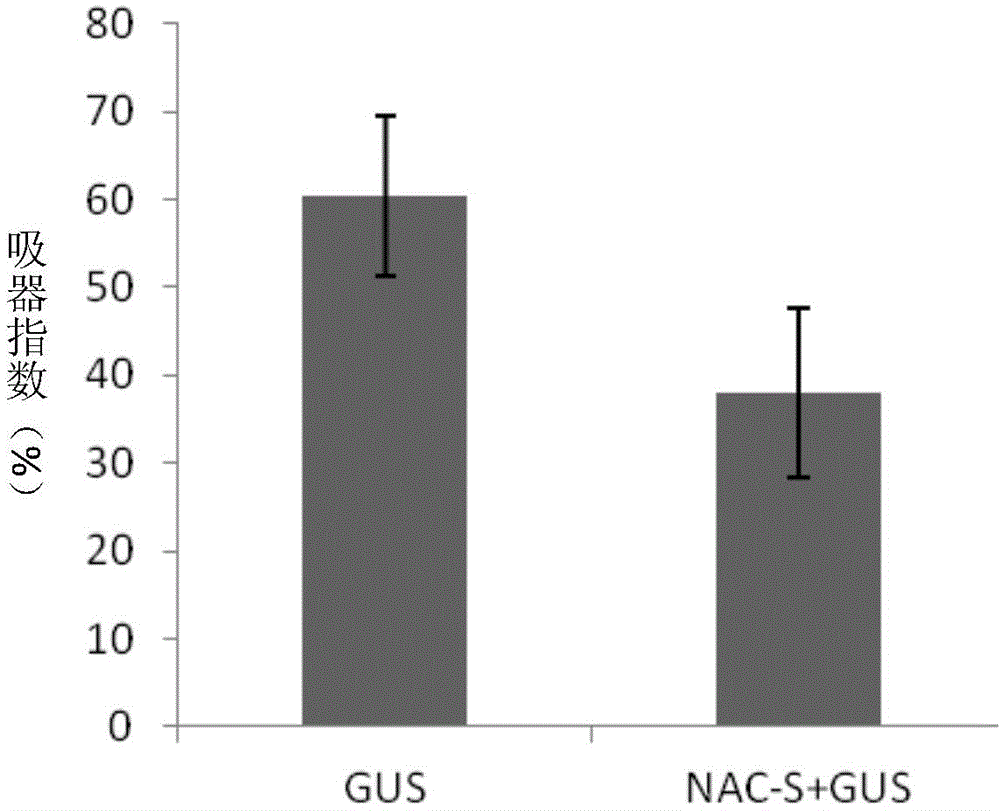
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and discloses a NAC transcription factor gene TaNACs in wheat as well as an expression vector and application thereof. A cDNA sequence with NAC transcription factor gene TaNACs is SEQ ID No.1, and the coded amino acid sequence is SEQ ID No.2. The gene comes from common wheat (Triticum asetivum L.) Nannong 9918. The expression of TaNACs is enhanced under the induction of powdery mildew in the powdery mildew-resistant wheat variety Nannong 9918, and the expression level is much higher than the expression level in a susceptible wheat variety Yangmai 158. The susceptible wheat variety Yangmai 158 is transformed with the gene through transient expression, and the result indicates that overexpression of TaNACs can reduce the haustorium index of Yangmai 158. Therefore, TaNACs is expected to be applied to gene engineering breeding; and the powdery mildew resistance of wheat is expected to be improved by introducing TaNACs into a wheat variety susceptible to powdery mildew.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sequence of dasypyrum villosum 6VS DNA permeating into powdery mildew resistant near-isogenic line of wheat and application
InactiveCN104278028ALess matchingInhibit exchangeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiotechnologyHigh resistance
The invention discloses a preparation method of a powdery mildew resistant near-isogenic line Jing 411 / 6VS.6AL / Jing 411<7> and a DNA fragment sequence of a 6VS permeating into the near-isogenic line. The near-isogenic line is obtained by the following steps: by using a powdery mildew resistant translocation line T6VS.6AL as an anti-disease gene donor parent and cultured wheat Jing 411 which is excellent in agronomic character but is not powdery mildew resistant as a recurrent parent, after hybridization of T6VS.6AL and Jing 411, carrying out continuous back cross by using the obtained F1 and Jing 411 for 7 generations; selfing for 1 generation and breeding to obtain the near-isogenic line 411 / 6VS.6AL / Jing 411<7>; and selecting an anti-disease single plant under stress of powdery mildew for hybridization and backcross every time. The experimental result provided by the invention shows that EACG / M14-301 is a specific molecular marker on 6VS and can be used for screening of germplasm resources of powdery mildew resistance of wheat, mechanism study of characteristics of high resistance and broad-spectrum resistance of Pm21 and researches of wheat origin and evolution, parent selection of distant hybridization and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
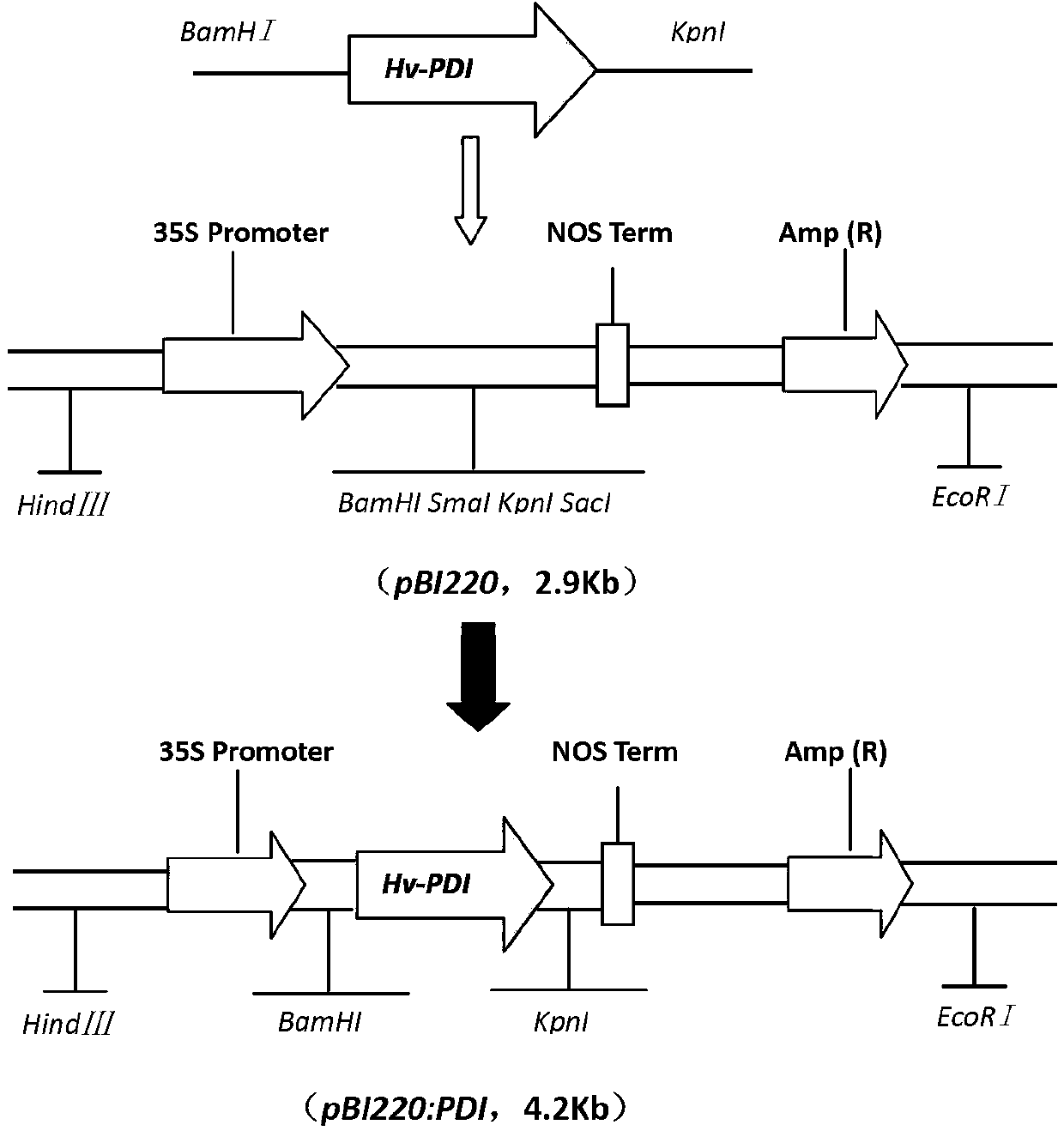
Haynaldia villosa disulfide isomerase gene and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering and discloses a haynaldia villosa disulfide isomerase gene and an application thereof. The cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of Hv-PDI (Hantaan Virus-Protein Disulfide Isomerase) is SEQ ID NO. 1, and the encoded amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO. 2. The gene derives from diploid haynaldia villosa (haynaldia villosa VV, 2n=14), is induced by powdery mildew in powdery mildew-resistant diploid haynaldia villosa, and is greatly expressed. Through transient expression, the gene is transformed to an infected wheat variety Yangmai 158, a result shows that excessive expression of Hv-PDI is capable of reducing the haustorium index of Yangmai 158. Therefore, the Hv-PDI is expectedly used for genetic engineering breeding, and the resistance of wheat to powdery mildew is hopefully improved when the Hv-PDI is introduced to wheat varieties susceptible to powdery mildew.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
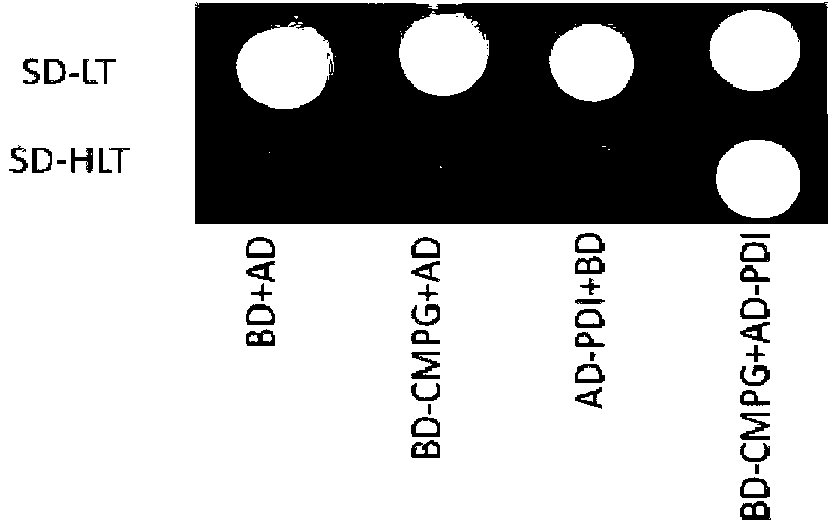
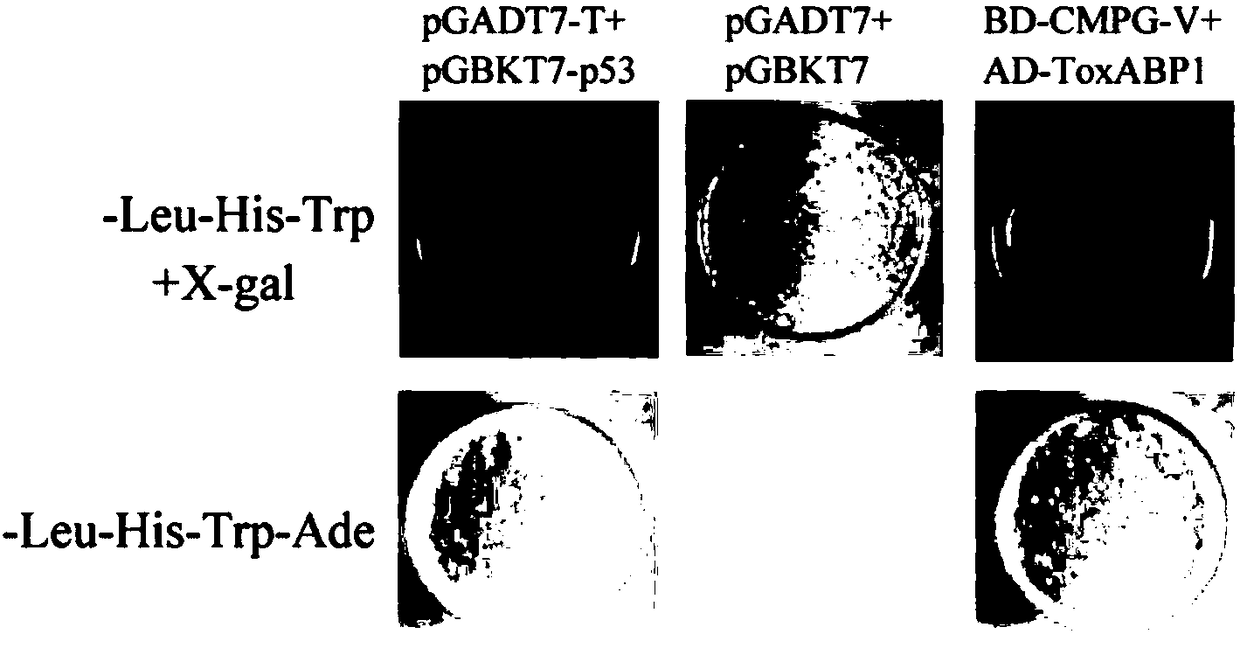
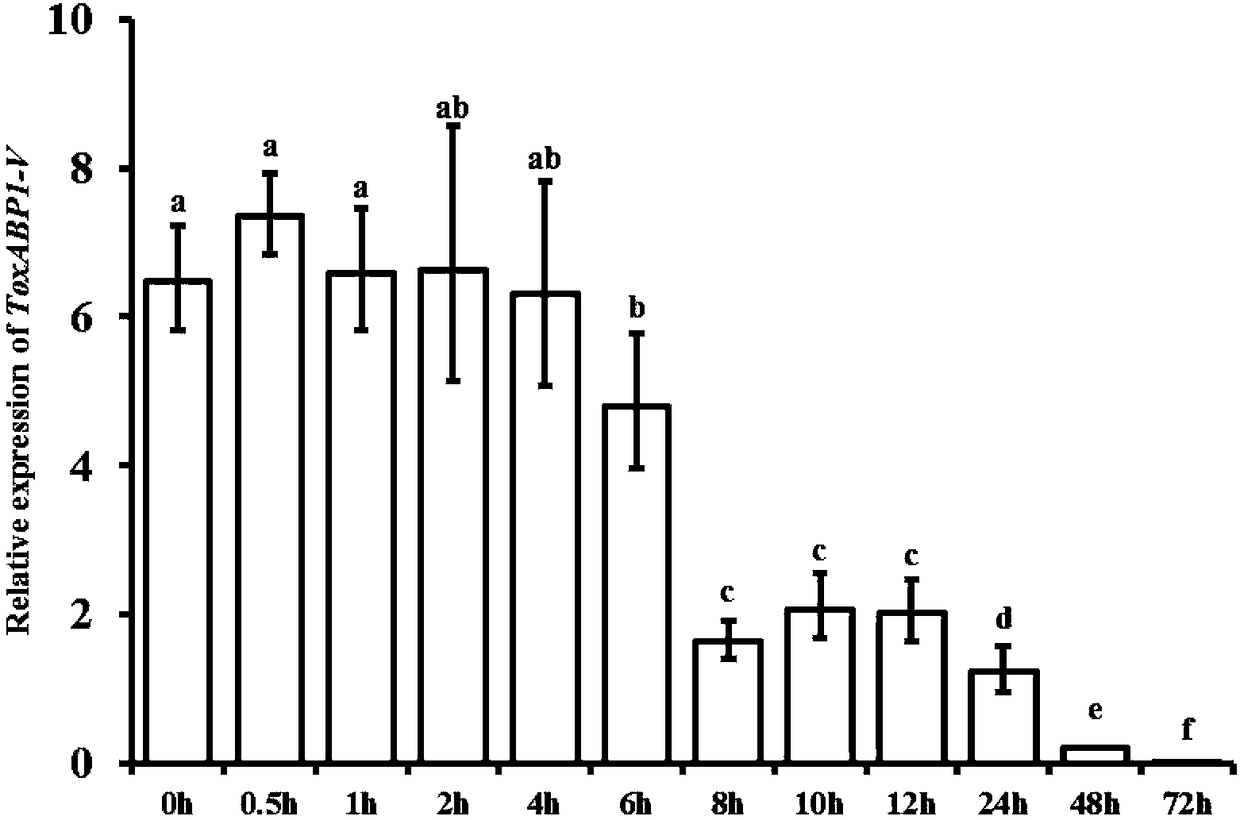
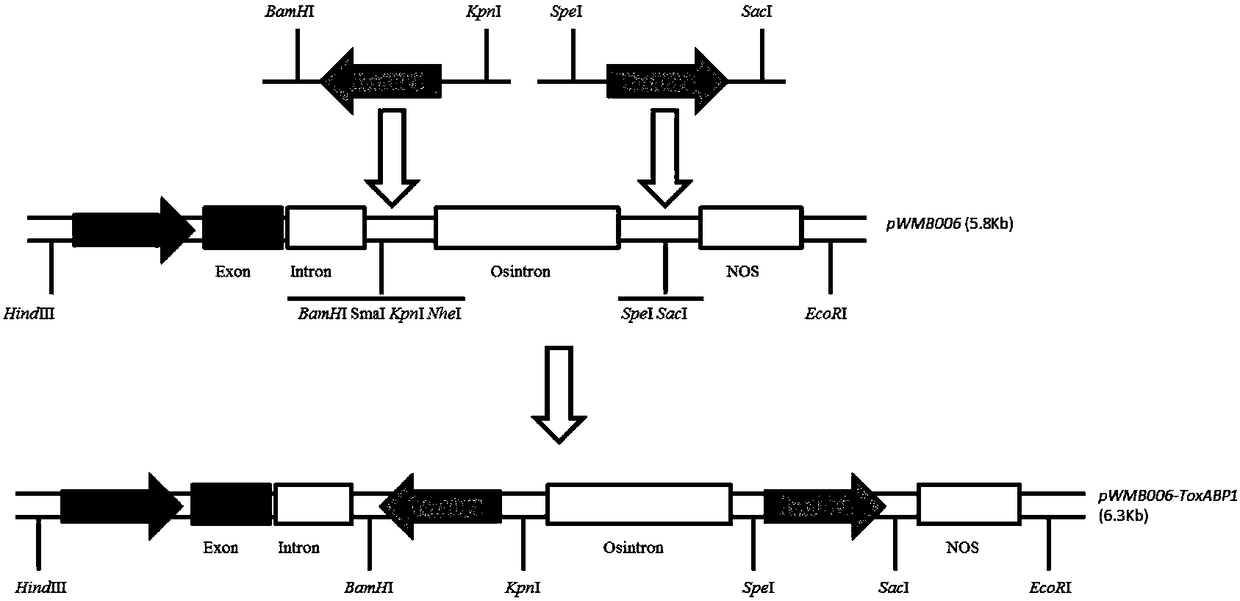
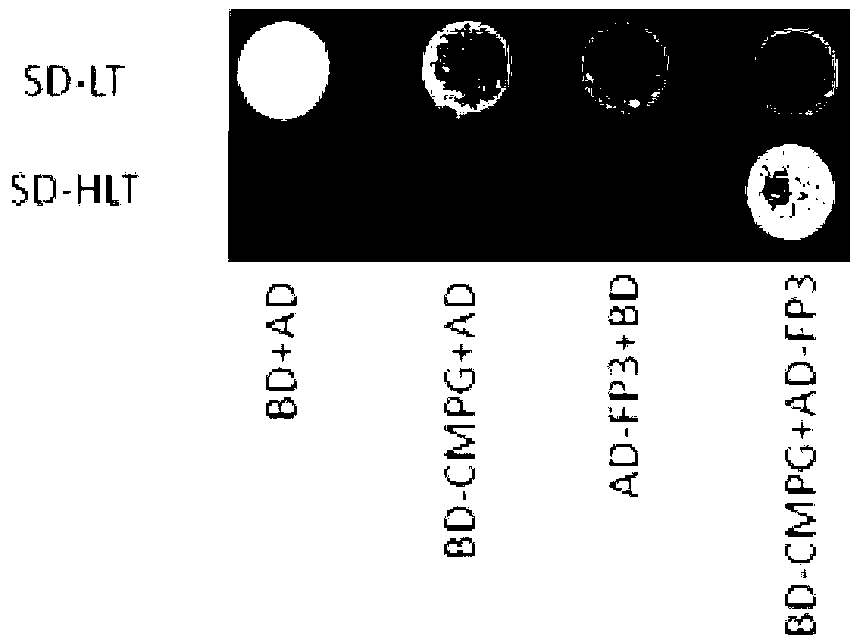
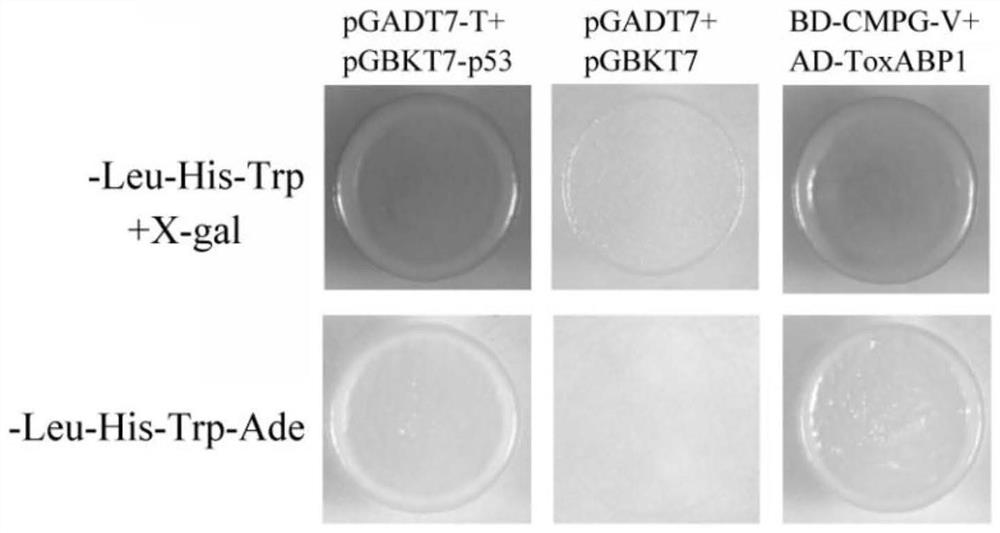
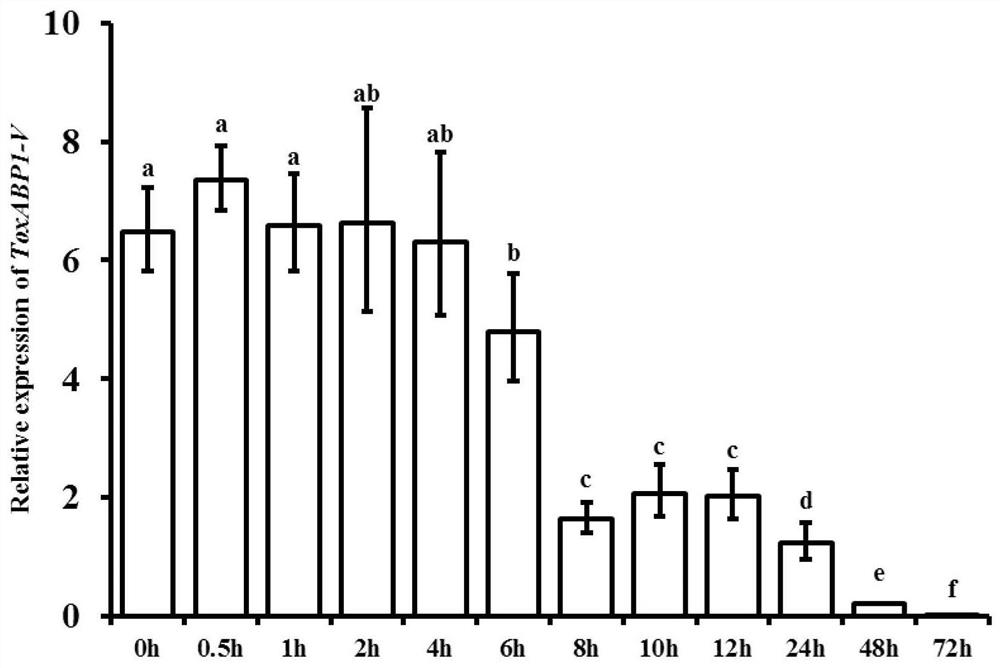
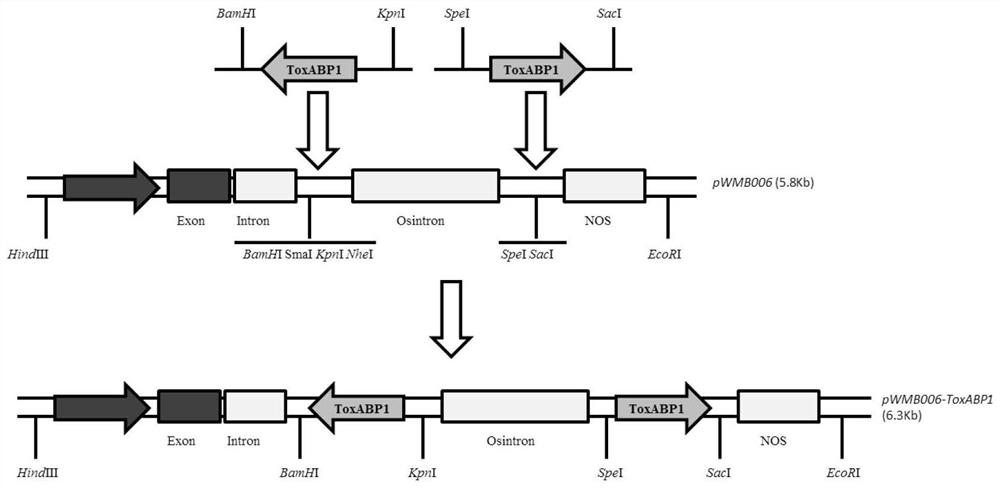
Chloroplast locating gene ToxABP1-V and its application
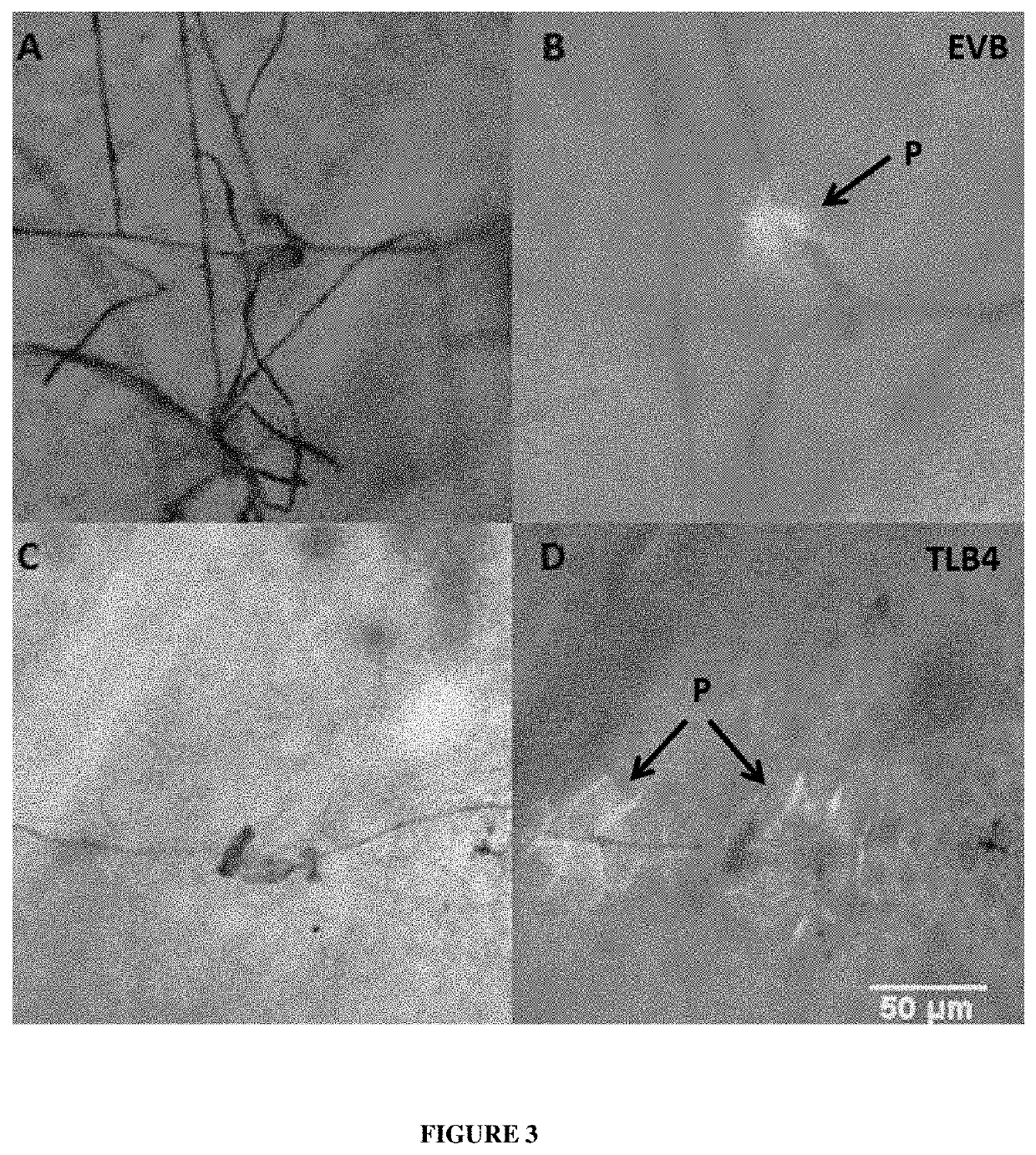
The invention discloses a chloroplast locating gene ToxABP1-V and its application. The cDNA sequence of ToxABP1-V is SEQ ID No. 1, and an amino acid sequence coded by ToxABP1-V is SEQ ID No. 3. The gene is derived from diploid Haynaldia villosa, can interact with the powdery mildew resistance-related gene CMPG1-V, and undergoes down-regulated expression in the powdery-mildew-resistant diploid Haynaldia villosa under the induction of powdery mildew. The RNAi silencing vector pWMB006-ToxABP1 of the gene is used for transforming the susceptible wheat variety Yangmai 158 by using single-cell transient silencing techniques, and results show that transient silencing of ToxABP1 can reduce the haustorium index of Yangmai 158. Three positive RNAi transgenic plants are obtained by using transgenic technology, and the plants show moderate and high resistance to powdery mildew of wheat. Therefore, ToxABP1-V is expected to be used for genetic engineering breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
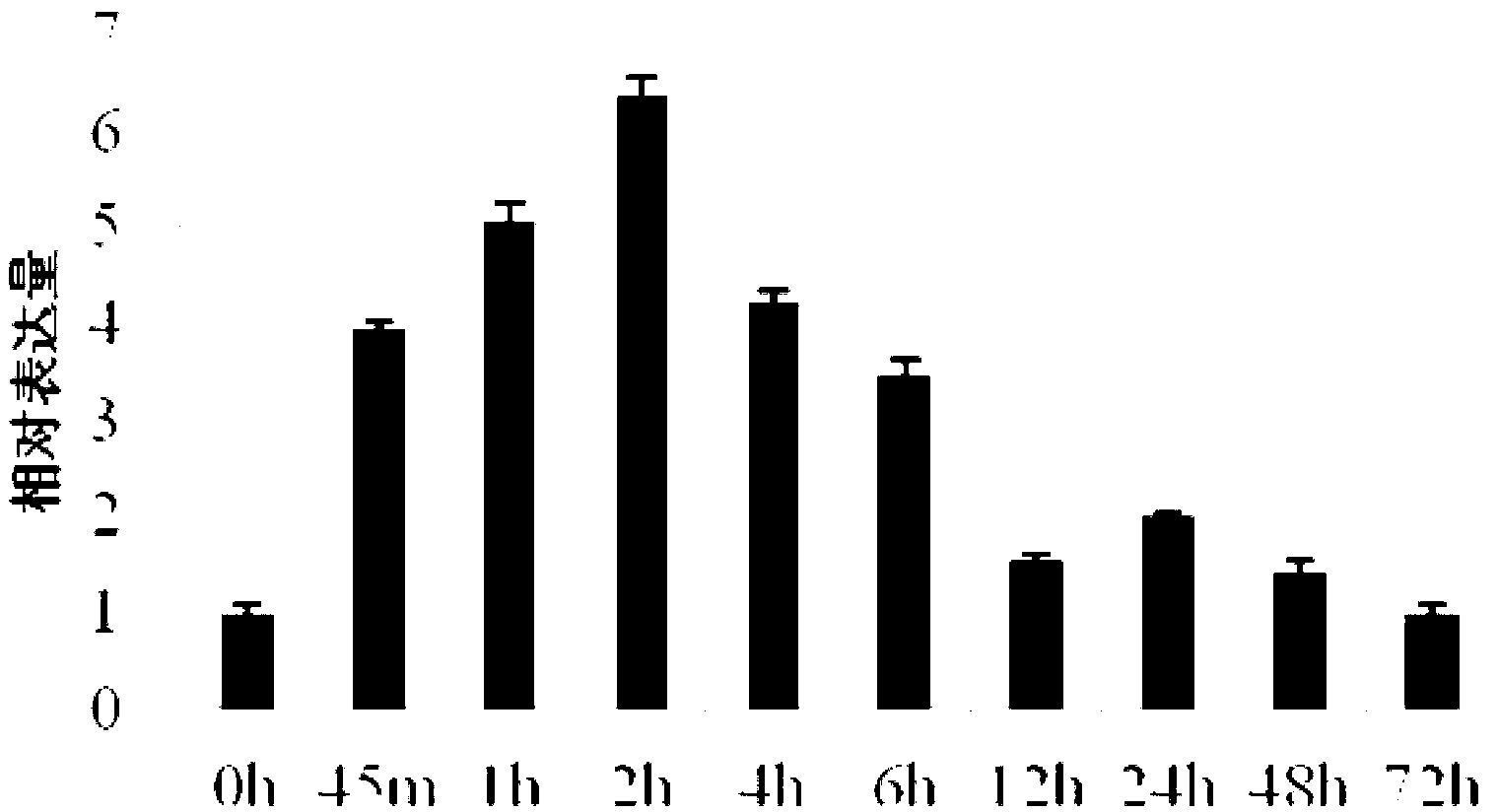
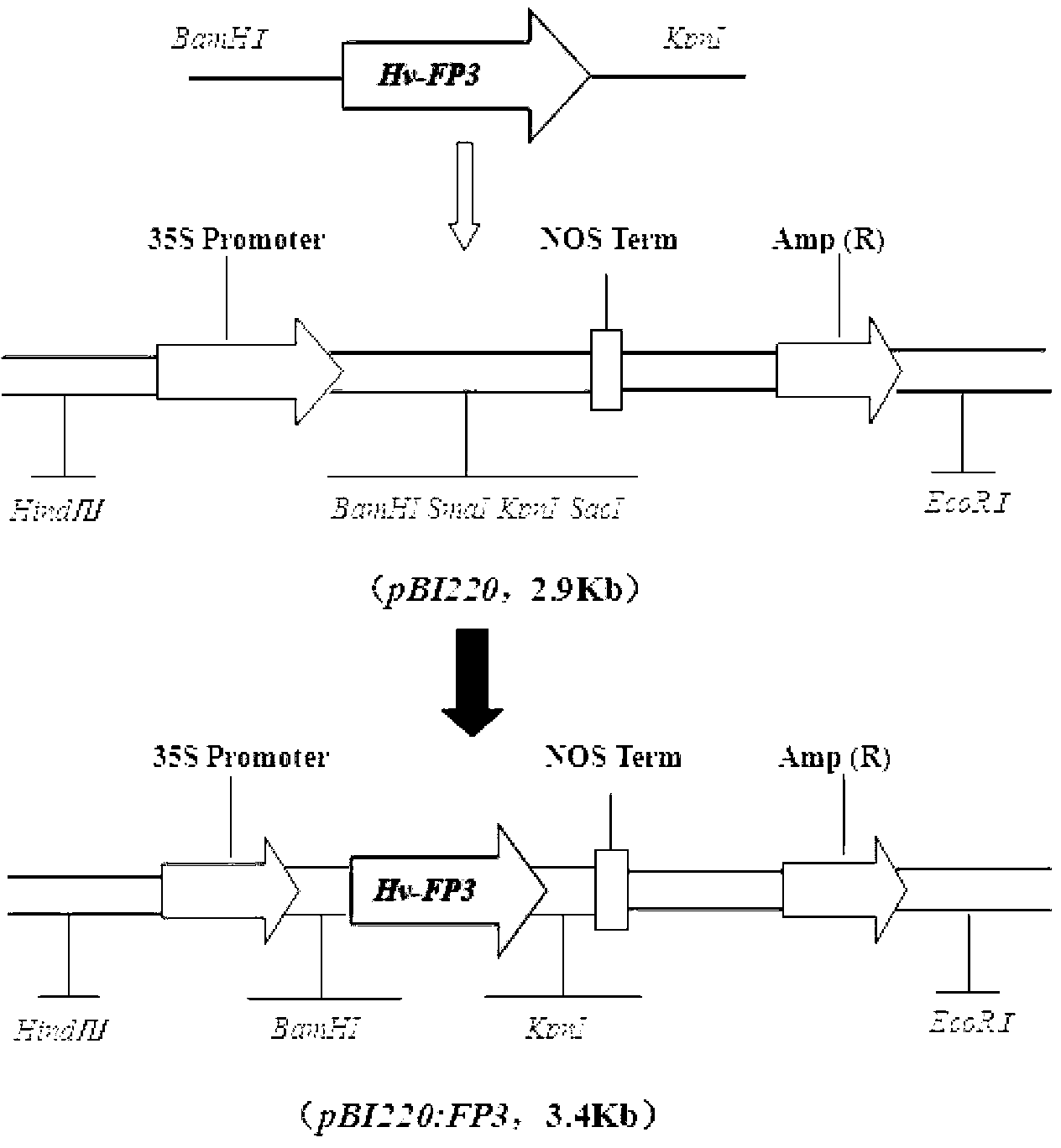
Haynaldia villosa metal transport protein gene, protein coded by haynaldia villosa metal transport protein gene and application of haynaldia villosa metal transport protein gene
The invention discloses a haynaldia villosa metal transport protein gene, protein coded by the haynaldia villosa metal transport protein gene and an application of the haynaldia villosa metal transport protein gene, and belongs to the field of gene engineerings. A cDNA (complementary DNA) sequence of Hv-FP3 is SEQ ID NO. 1 and an amino acid sequence coded by the Hv-FP3 is SEQ ID NO. 2. The gene comes from diploid haynaldia villosa (Haynaldia villosa, VV, 2n-14), and expression of the gene is enhanced because the gene is induced by powdery mildew in powdery mildew resistance diploid haynaldia villosa. The Hv-FP3 gene is transformed to be a susceptible powdery mildew wheat variety Yangmai 158, a transgenic T0 generation plant is subjected to powdery mildew resistance identification, and the result shows that over-expression of the Hv-FP3 gene can improve resistance of the Yangmai 158 to the powdery mildew. The Hv-FP3 is possibly applied to gene engineering breeding; and the Hv-FP3 is induced into the susceptible powdery mildew wheat variety, and the powdery mildew resistance of the wheat is possibly improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and kits for the detection of powdery mildew
PendingCN107849566AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpecific detectionBiology
The present invention relates to means, methods and kits for the specific detection of the causing agent of powdery mildew on grapes, the fungus Erysiphe necator. More specifically, the methods according to the invention are quantitative methods based on quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Owner:拜耳简易股份有限公司
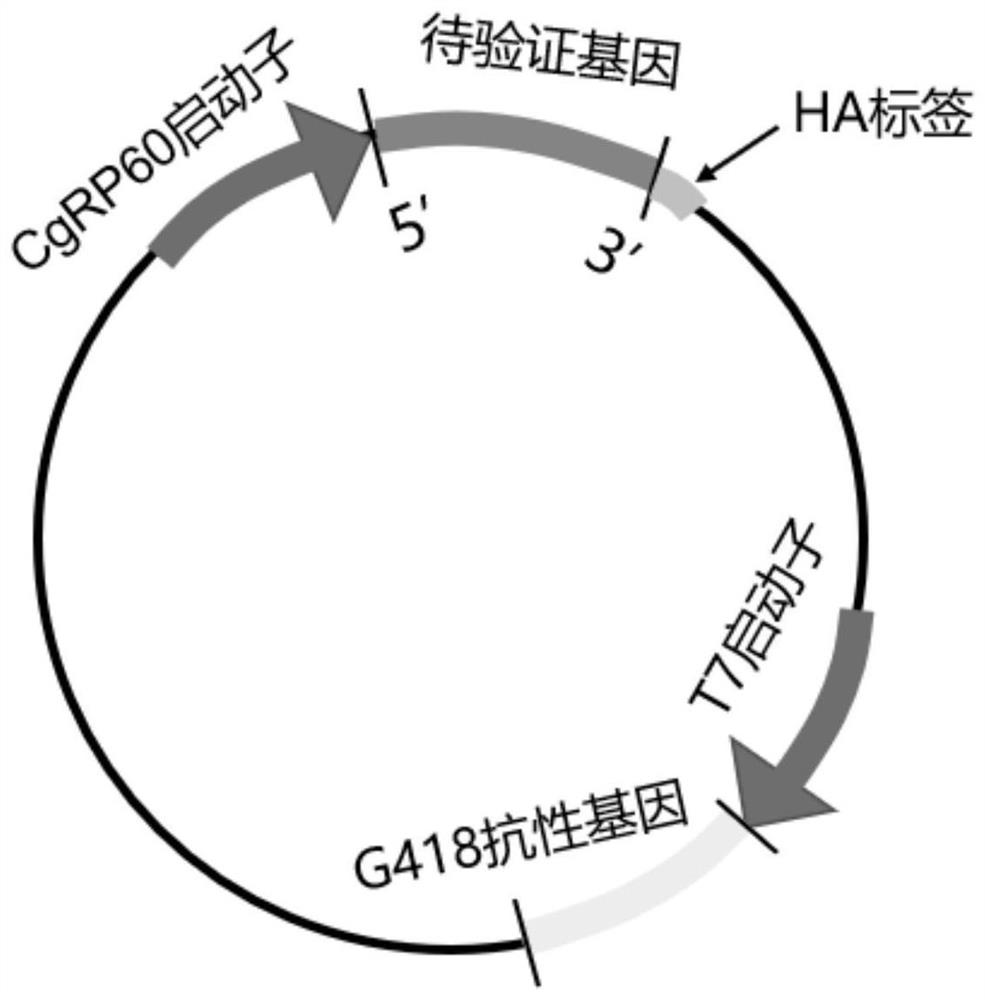
Fluorescent vector for marking powdery mildew of rubber tree as well as expression method and application of fluorescent vector
PendingCN114317586AConvenient researchHigh expressionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCloning Site
The invention discloses a fluorescent vector for marking powdery mildew of a rubber tree, the fluorescent vector is a plasmid pJNARG-RP60-GFP modified based on a pJNARG plasmid, a carbendazim resistance gene is inserted into the plasmid at an XcmI restriction enzyme cutting site, and a multiple cloning site of the plasmid pJNARG-RP60-GFP is between a promoter RP60 and a green fluorescent protein coding gene of the GFP. The invention provides a powerful tool for evaluating the conversion efficiency of the powdery mildew, i.e., plasmids containing fluorescent genes are converted by an electric shock conversion method, so that the plasmids express the fluorescent genes in powdery mildew cells, and the conversion efficiency of the powdery mildew is calculated by fluorescently labeling the converted powdery mildew cells. Therefore, the research on the effect of other exogenous or self genes simultaneously introduced into powdery mildew cells is facilitated.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Fungus capable of capturing conidium of mulberry powdery mildew
InactiveCN103642699AThe generation ofIncreased number of lesionsFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPathogenicity
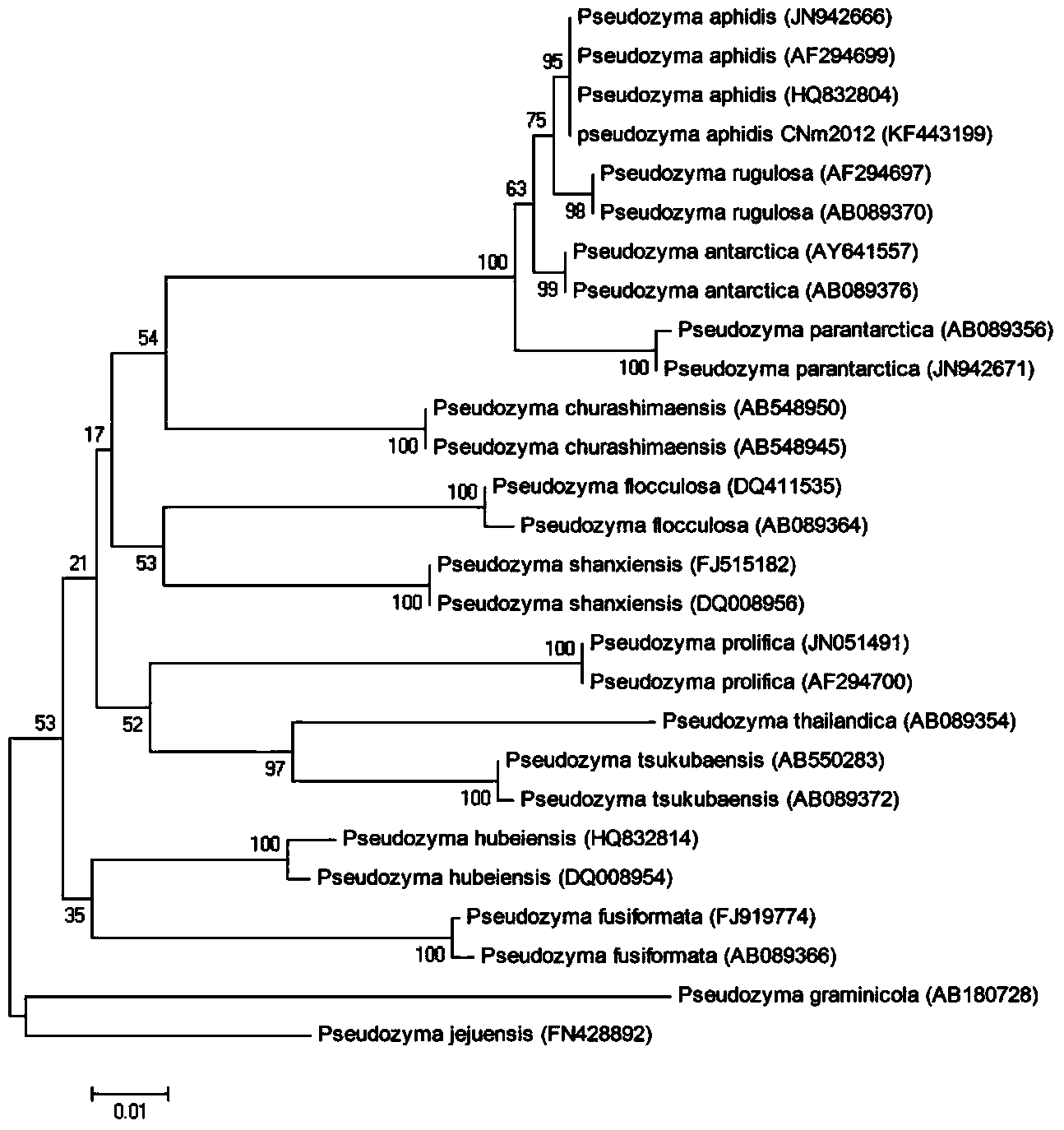
The invention discloses a fungus (pesudozyma aphidis CNm2012) capable of capturing conidium of mulberry powdery mildew, and the preservation number of the fungus is CCTCC No. M2013563. The bacterium strain is separated from mulberry leaf surface, is a yeast-like fungus, the color of the fungus colony is pink in a potato plate culture medium, smooth yeast-like colonies exist in the middle part, and hyphae grow on the edge; the bacterium strain is cultured in a Sabourand liquid culture medium for 7 days, the bacterial shape is like a shuttle in different sizes, many oil-drop-like substances exist in the bacterial cells, hyphae grow as the bacterium strains grow; the proper temperature for the growth of bacterium stain is 20 to 30 DEG C, the proper pH value is 6.5 to 7.5; the 18Sr strain's DNA sequence is 1416bp, and the NCBI serial number is KF443200; the 28Sr strain's DNA sequence is 627bp, and the serial number is KF443201; the ITSr strain's DNA sequence is 784bp, and the serial number is 443199. The fungus can capture and eat conidium of mulberry powdery mildew so as to carry out biological prevention on mulberry powdery mildew, and does not have any pathogenicity on mulberries or silkworms.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
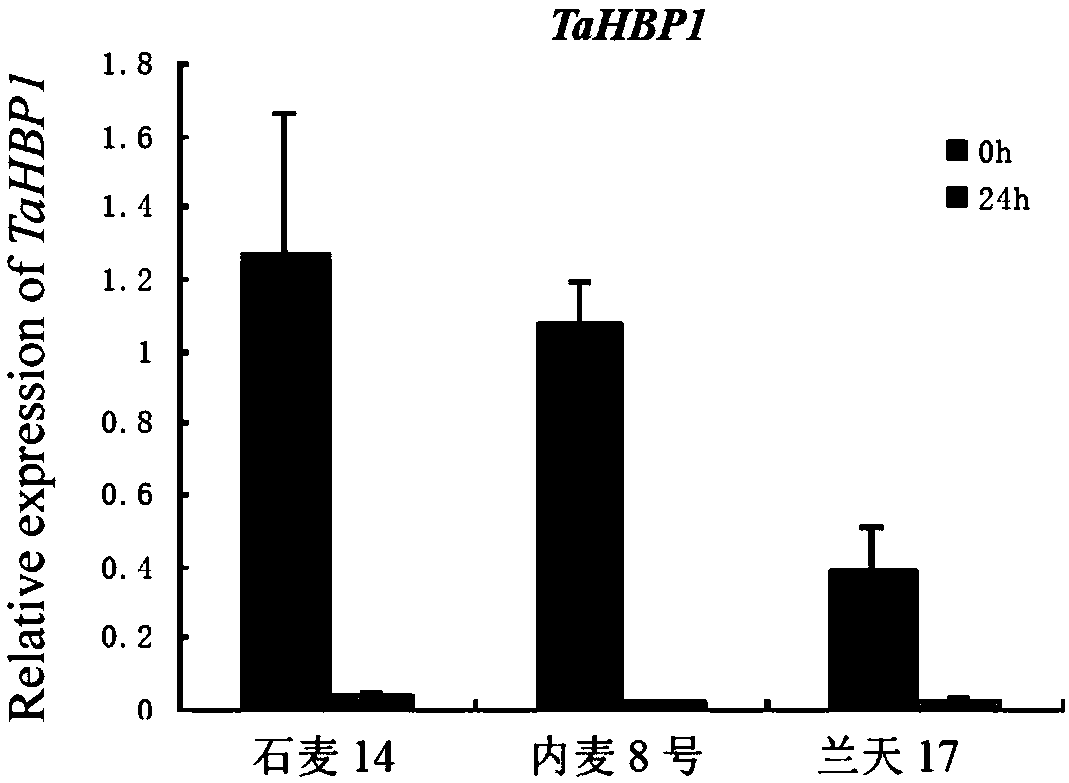
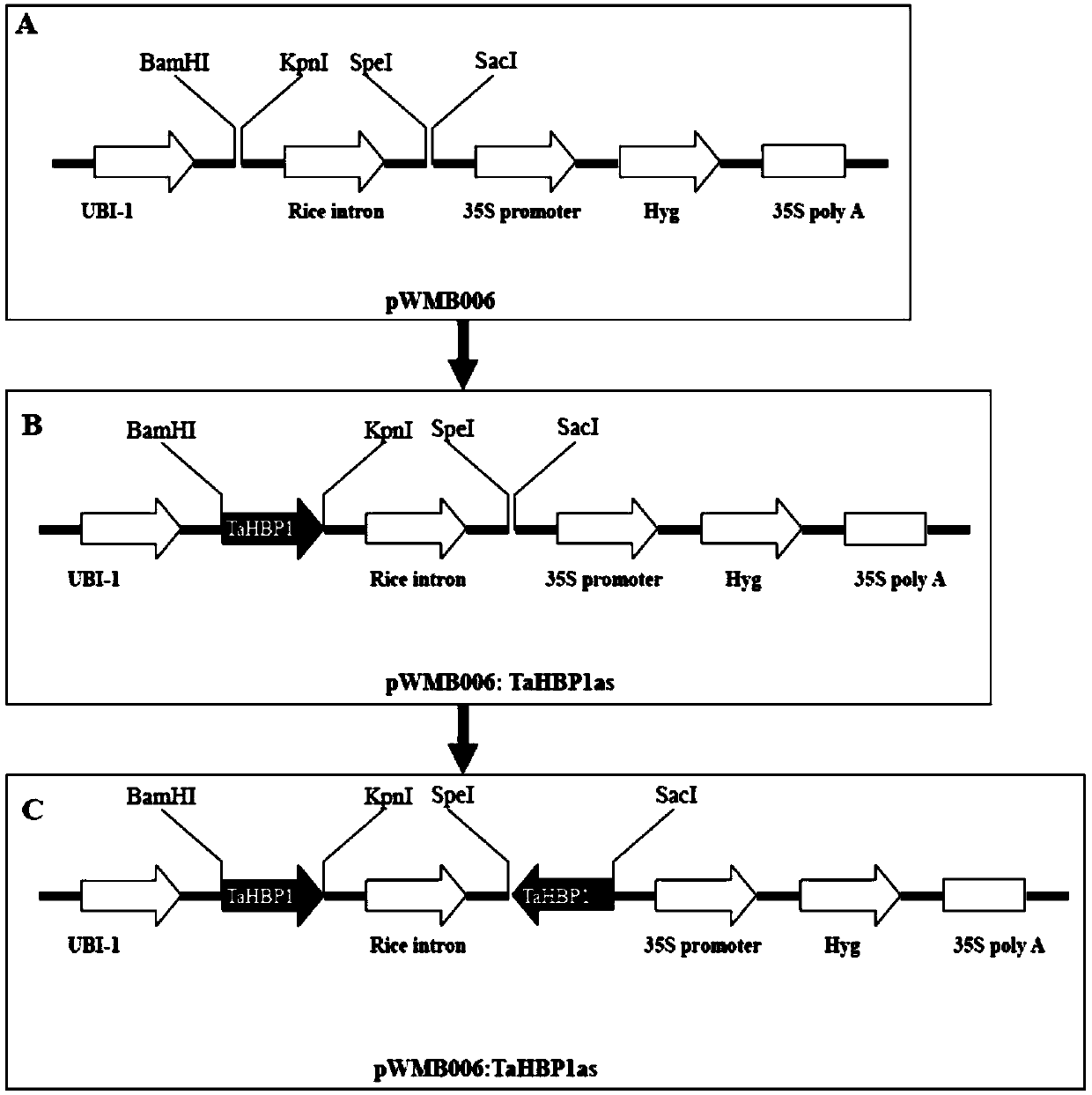
Heme-binding protein gene TaHBP1, and recombinant interference vector and application thereof
ActiveCN109535236AImprove powdery mildew resistanceIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationTriticeaeDigestion
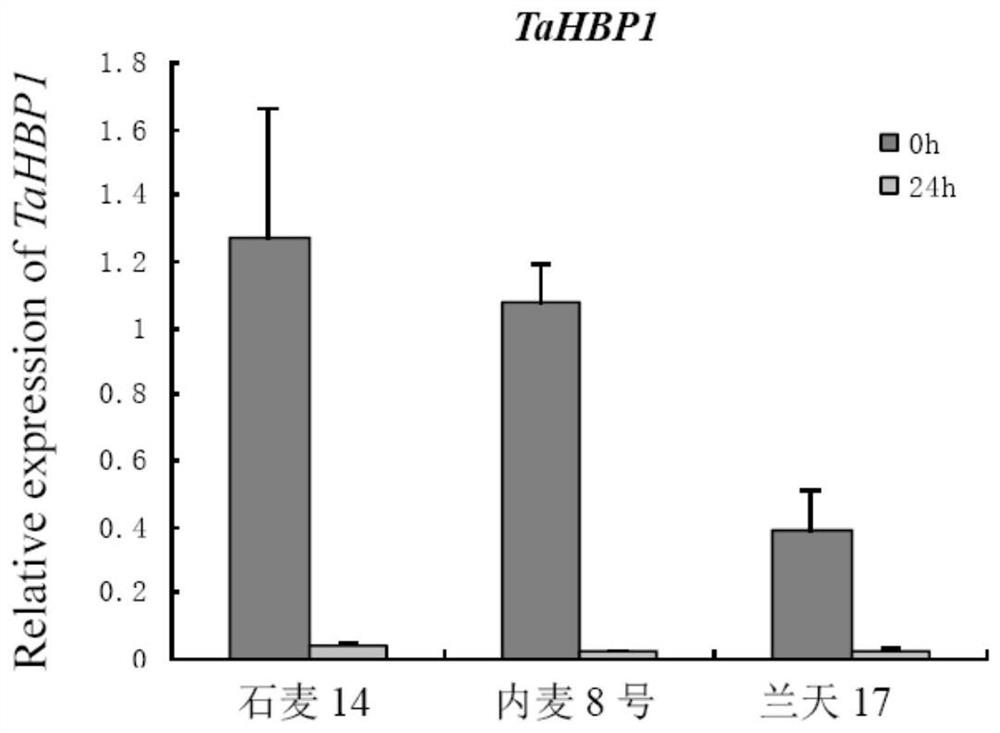
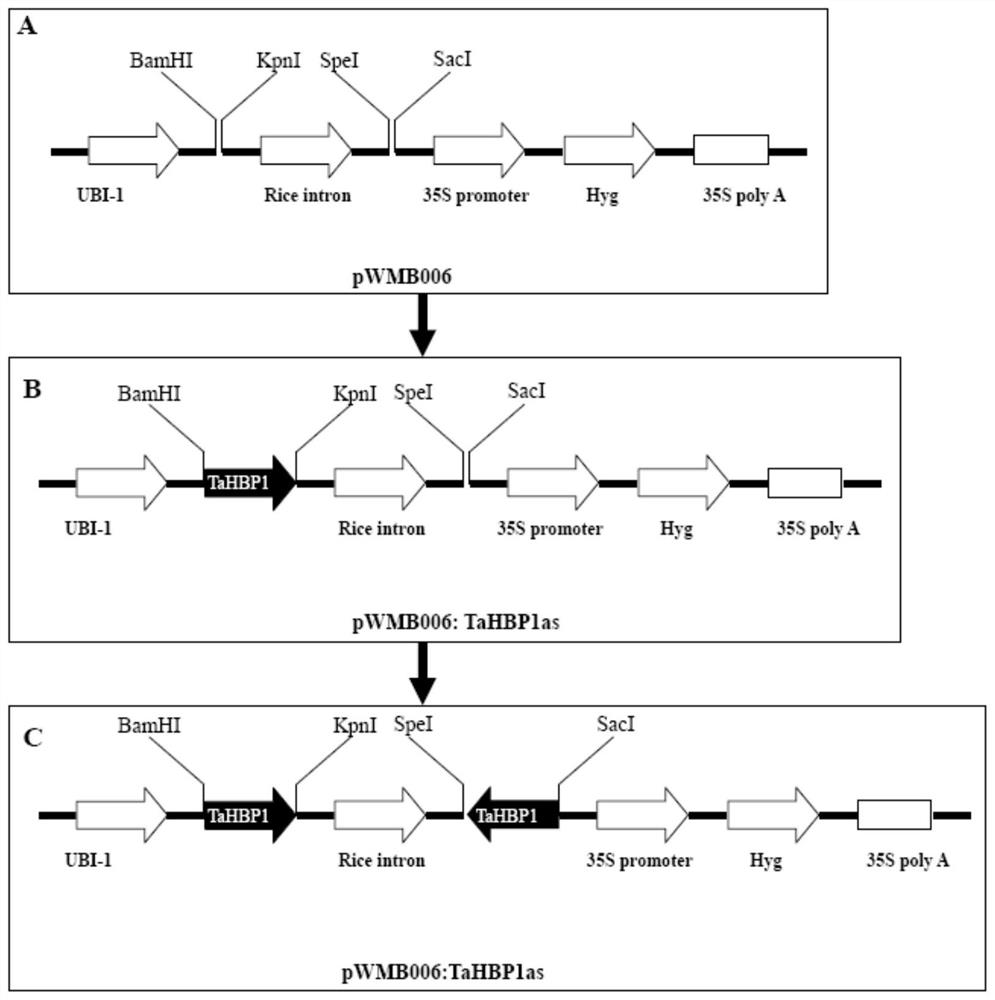
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a gene TaHBP1 with a heme-binding domain, and a recombinant interference vector and an application thereof. The gene TaHBP1 with the heme-binding domain has the cDNA sequence of SEQ ID NO.1 and a coding amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.2. The gene comes from ordinary triticum asetivum l. Yangmai 158. The expression of the TaHBP1 in powdery mildew-susceptible triticum asetivum l. variety Yangmai 158 is induced to enhance by erysiphe cucurbitacearum, and the expression level is much higher than the expression level in disease-resistant triticum asetivum l. variety Nannong 9918. A positive sequence of the TaHBP1 is inserted between BamHI and KpnI digestion sites of pWMB006, and at the same time, a reverse sequence is inserted between SpeI and ScI of pWMB006 to obtain interference expression vectors. The powdery mildew-susceptible triticum asetivum l. variety Yangmai 158 is transformed. The identification result of powdery mildew resistance of positive transformed plants shows that the resistance of powdery mildew-susceptible triticum asetivum l. varieties on powdery mildew is improved with decreasing expression of the TaHBP1.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
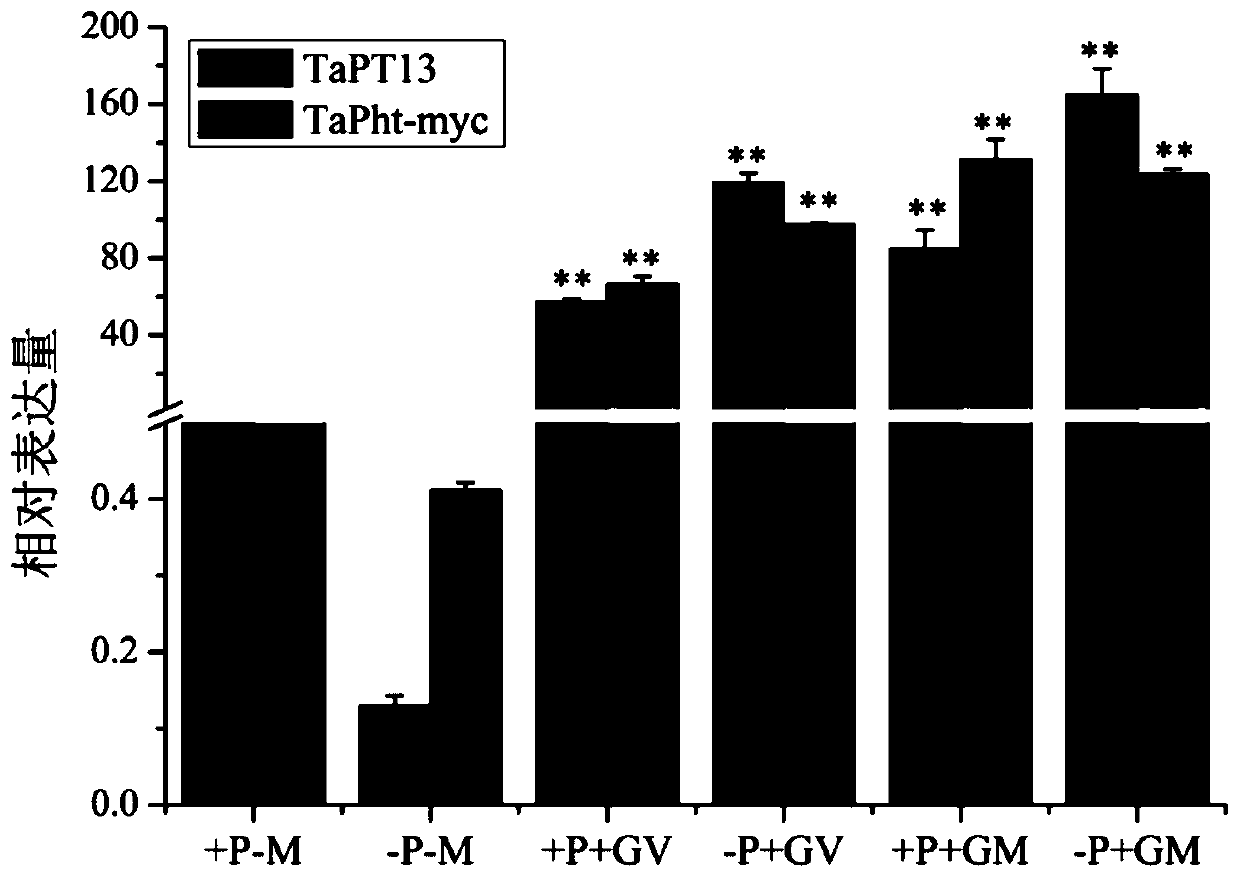
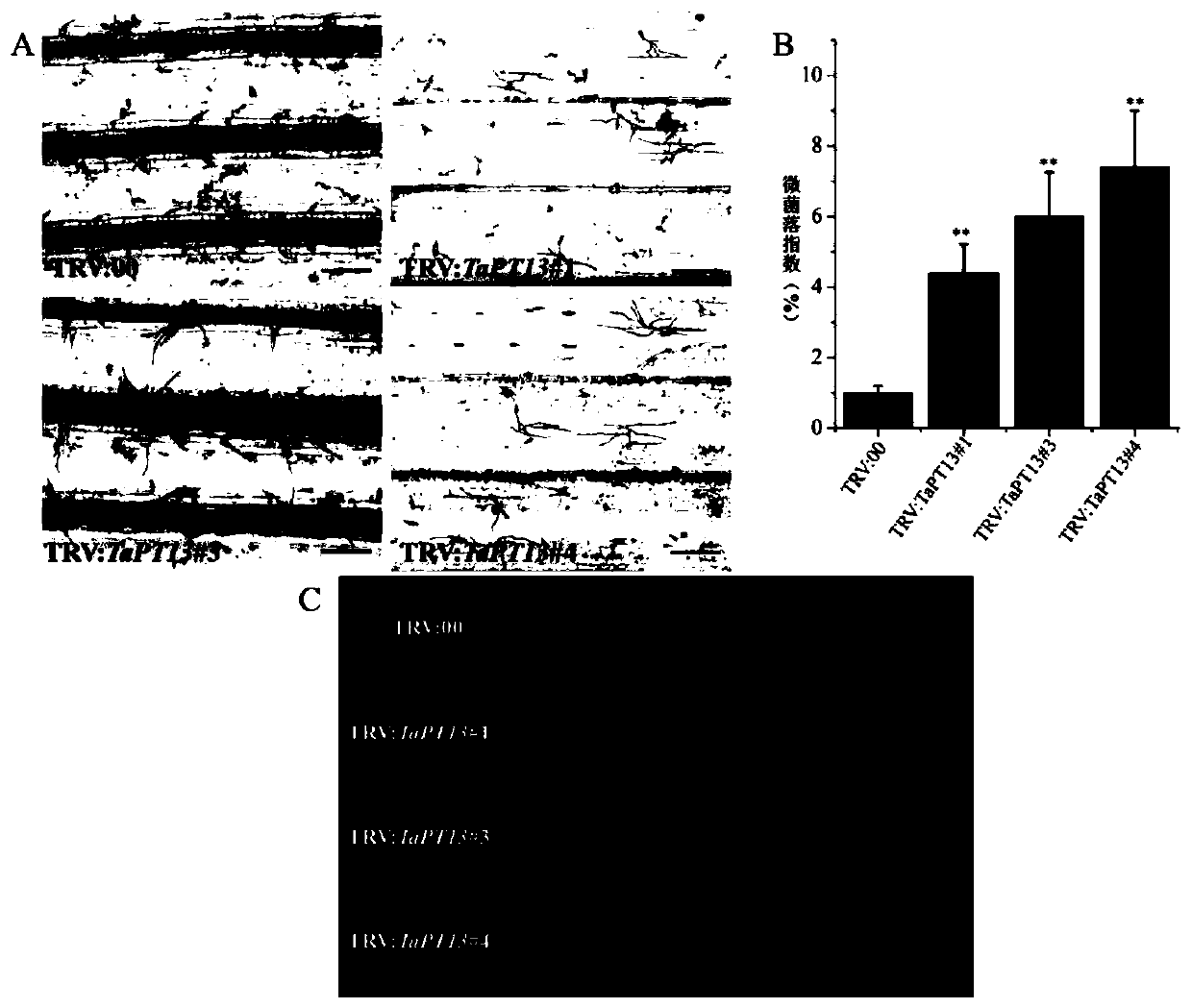
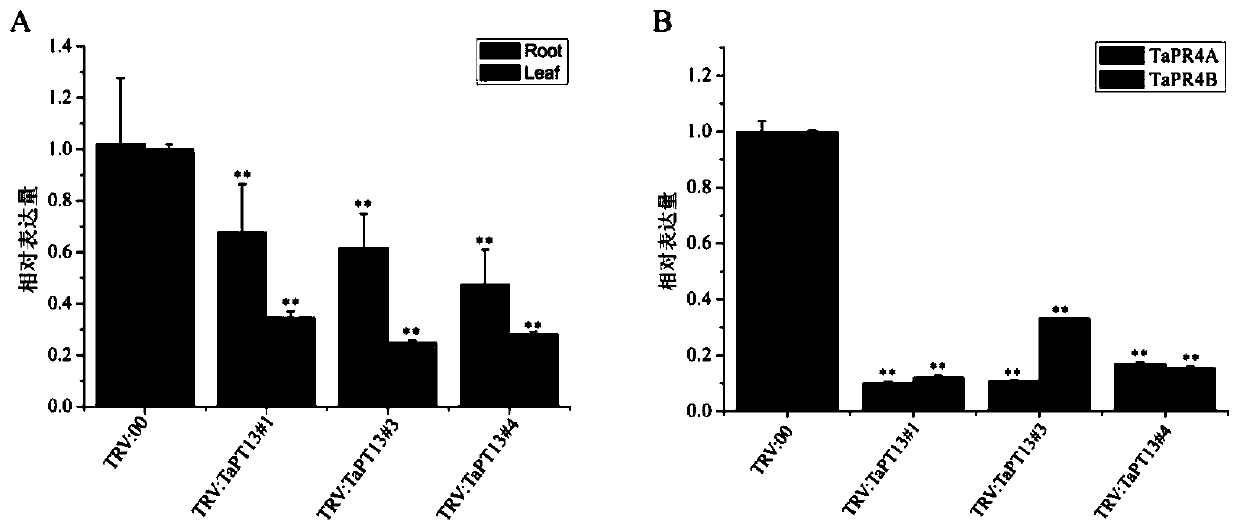
Application of gene TaPT13 in improving resistance of plants to powdery mildew
ActiveCN111424049AEffective absorptionImprove disease resistanceClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural biology, and particularly relates to an application of a gene TaPT13 in improving resistance of plants to powdery mildew. The specific phosphorus transporter gene TaPT13 of arbuscular mycorrhiza can be used for improving disease resistance of plants, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene TaPT13 is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. According to the invention, the TaPT13 gene is determined to be a specific phosphate transporter gene of arbuscular mycorrhiza. After plants are inoculated with powdery mildew, the expression amount of the TaPT13 gene is obviously improved; and after the TaPT13 gene is silenced in the plants, susceptibility of the plants is increased, and the expression amount of a disease-resistant marker gene is reduced. Therefore, the TaPT13 gene can be used for improving resistance of wheat to powdery mildew, and has wide application space in plant breeding and cultivation.
Owner:HENAN INST OF SCI & TECH
Biological methods for controlling phytopathogenic fungi
The present invention relates to methods for controlling phytopathogenic fungi using biological control agents. More specifically, the invention relates to methods for controlling phytopathogenic fungi having a long incubation period. In particular, the methods according to the invention are particularly suited for controlling the causal agent of powdery mildew on grapes, the fungus Erysiphe necator.
Owner:拜耳简易股份有限公司
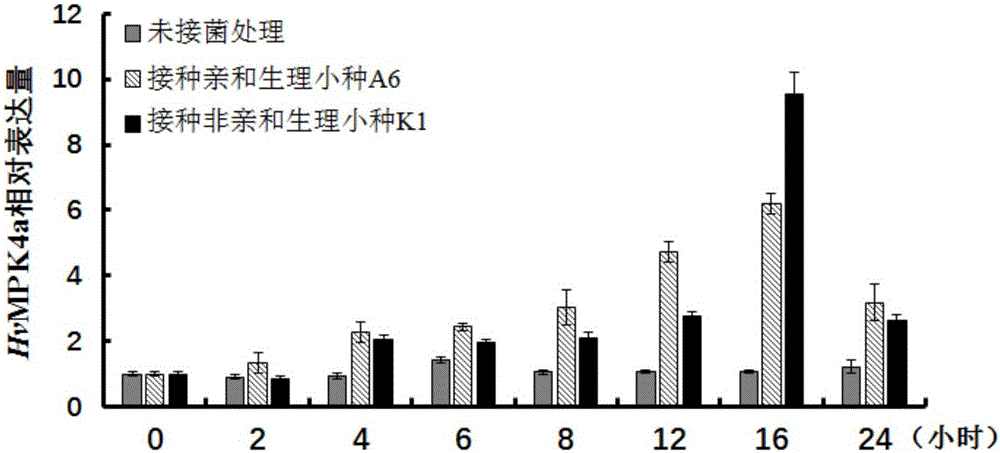
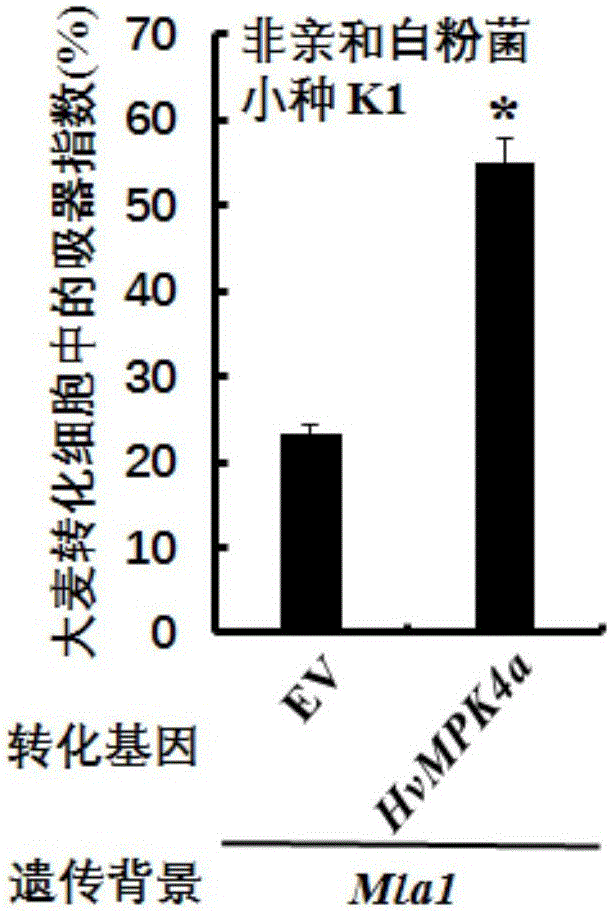
Protein kinase HvMPK4a related to barley powdery mildew resistance and encoding gene and application of protein kinase HvMPK4a
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and molecular breeding, and in particular relates to protein kinase HvMPK4a related to barley powdery mildew resistance and an encoding gene and an application of the protein kinase HvMPK4a. The protein kinase HvMPK4a related to barley powdery mildew resistance is protein formed by an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1. Through analysis on expression profiles of the HvMPK4a, the expression quantity of the HvMPK4a in the infection process of powdery mildew on barley significantly ascends, which indicates that the HvMPK4a participates into the process that the barley prevents infection of the powdery mildew and plays the biological function. Through transient overexpression on the HvMPK4a and inoculation of non-affinity powdery mildew through barley epidermal cells, the resistance of the barley on the powdery mildew is significantly reduced; the HvMPK4a is silenced in the barley and affinitive powdery mildew is inoculated through virus-induced gene silencing, so that the resistance of the barley on the powdery mildew is enhanced; and the resistance of the barley on the powdery mildew is negatively regulated and controlled by the HvMPK4a.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rubber tree erysiphaceae avirulence gene screening method, effect protein and application
PendingCN113999859ATransformed expression is effectiveEfficient screeningFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyErysiphe sp.
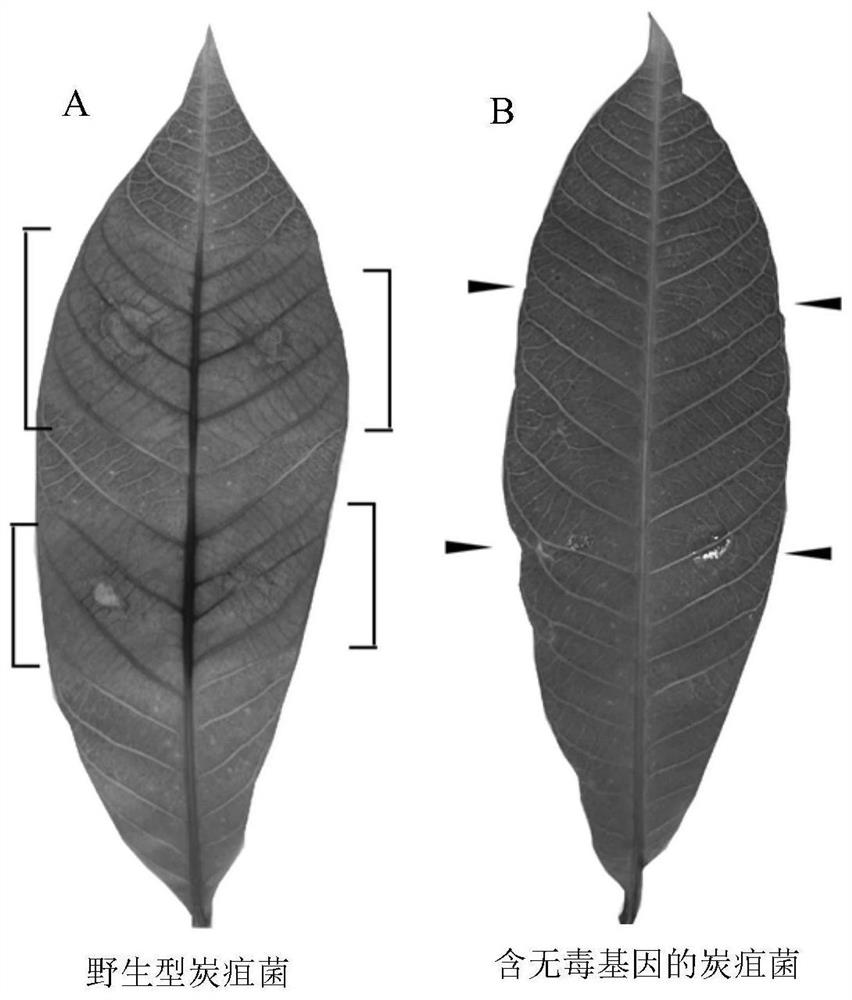
The invention provides a rubber tree erysiphaceae avirulence gene screening method, effect protein and application. The screening method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a coding gene A of potential effect protein from rubber tree erysiphaceae genes; (2) constructing a rubber tree erysiphaceae effect protein expression vector, and expressing and transforming a potential effect protein gene A of erysiphaceae in colletotrichum gloeosporioides to obtain a colletotrichum transformant; and (3) culturing the colletotrichum transformant with high expression degree of the effect protein, inoculating the colletotrichum transformant to an in-vitro rubber leaf, determining the pathogenic ability of the colletotrichum transformant, and if the pathogenicity of the colletotrichum gloeosporioides transformant is reduced compared with that of wild colletotrichum gloeosporioides, indicating that the effect protein coding gene A is an avirulence gene. According to the screening method disclosed by the invention, the erysiphaceae avirulence gene can be directly screened through pathogenicity of protein gene transformants with different effects, so that the avirulence gene of the erysiphaceae of the rubber tree can be more quickly screened and identified, and prevention and control of rubber erysiphaceae and breeding of disease-resistant varieties can be enhanced.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Vitis vinifera with reduced MLO expression and increased resistance to powdery mildew
Provided herein are Vitis vinifera exhibiting Erysiphe necator resistance. In particular, provided herein are Vitis vinifera having in their genome mildew resistance locus O (MLO) genes, in particular an MLO7 gene and an MLO6 gene, where the MLO7 gene and MLO6 gene have reduced expression and / or function.
Owner:FOND EDMUND MACH
A method for rapid identification of disease resistance by using powdery mildew of grapes to inoculate detached leaves of grapes
InactiveCN104313117BHigh sporulationStrong pathogenicityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseHighly pathogenic
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying disease resistance by inoculating grape powdery mildew to detached grape leaves. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: separating grape powdery mildew strain microspecies, purifying and infecting; performing rDNA sequence amplification and evolution analysis so as to obtain a grape powdery midew NAFU1 with high pathogenicity; analyzing the preservation and the expanding propagation of the strain; inoculating the strain with the detached grape leaves, dyeing by using trypan blue, inoculating to sick leaves in different periods, and observing indexes such as the time of spore germination, growth velocity, hypha length and necrocytosis, thereby rapidly and accurately detecting the disease resistance of grape. The grape powdery mildew preserved and amplified by using the method is high in sporulation quantity, the spore is fresh and high in pathogenicity, the defects that the conventional field identification period is long, the repeatability is poor and the weather influence can be caused are overcome, not only is the efficiency in detecting the disease resistance of a grape germplasm resource in large scale improved, but also direct reference values in rapidly identifying the disease resistance of the grape germplasm resource as well as hybrid progeny and transgenosis plants of the grape germplasm resource in large scale are achieved.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Powdery mildew resistance genes in carrot
The present invention relates to powdery mildew, and especially powdery mildew caused by the plant pathogen Erysiphe heraclei, resistant carrot plants or Daucus carota plants, wherein the powdery mildew resistance is provided by one or two dominant powdery mildew resistance genes. The present invention further relates to molecular markers genetically linked to the present powdery mildew, and especially powdery mildew caused by the plant pathogen Erysiphe heraclei, resistance providing genes and the use thereof for identifying carrots plants, or Daucus carota plants, being resistant to powderymildew, and especially powdery mildew caused by the plant pathogen Erysiphe heraclei. The present invention also relates to seeds, plant parts, pollen, egg cells, callus, suspension culture, somatic embryos and edible plant parts of the present plants.
Owner:贝霍种子有限公司
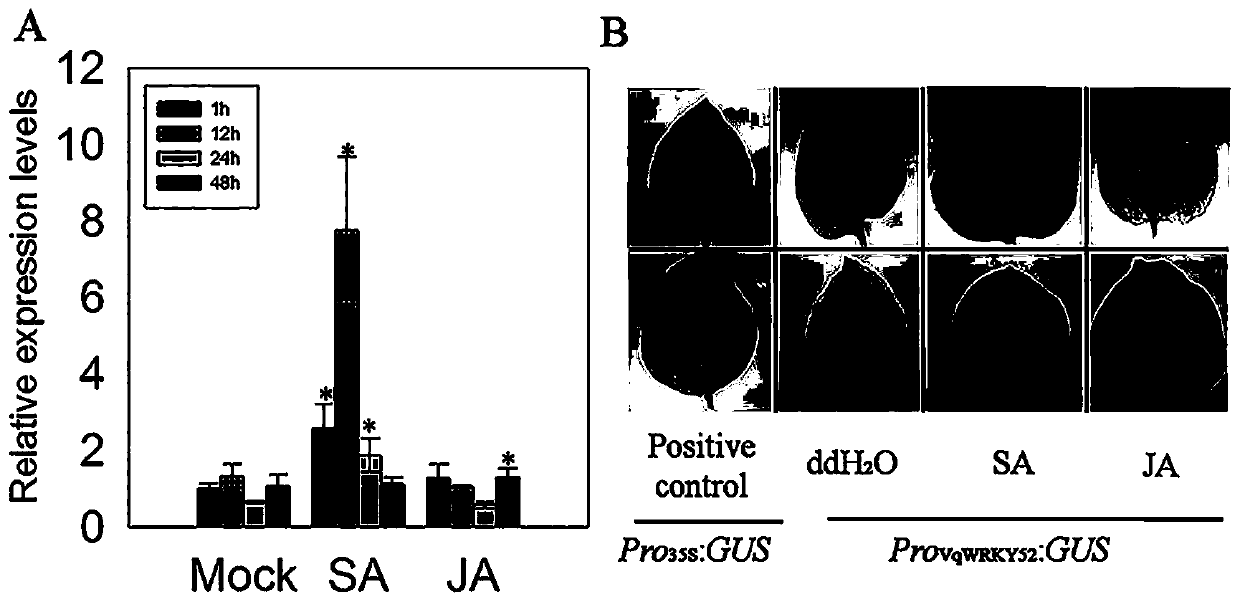
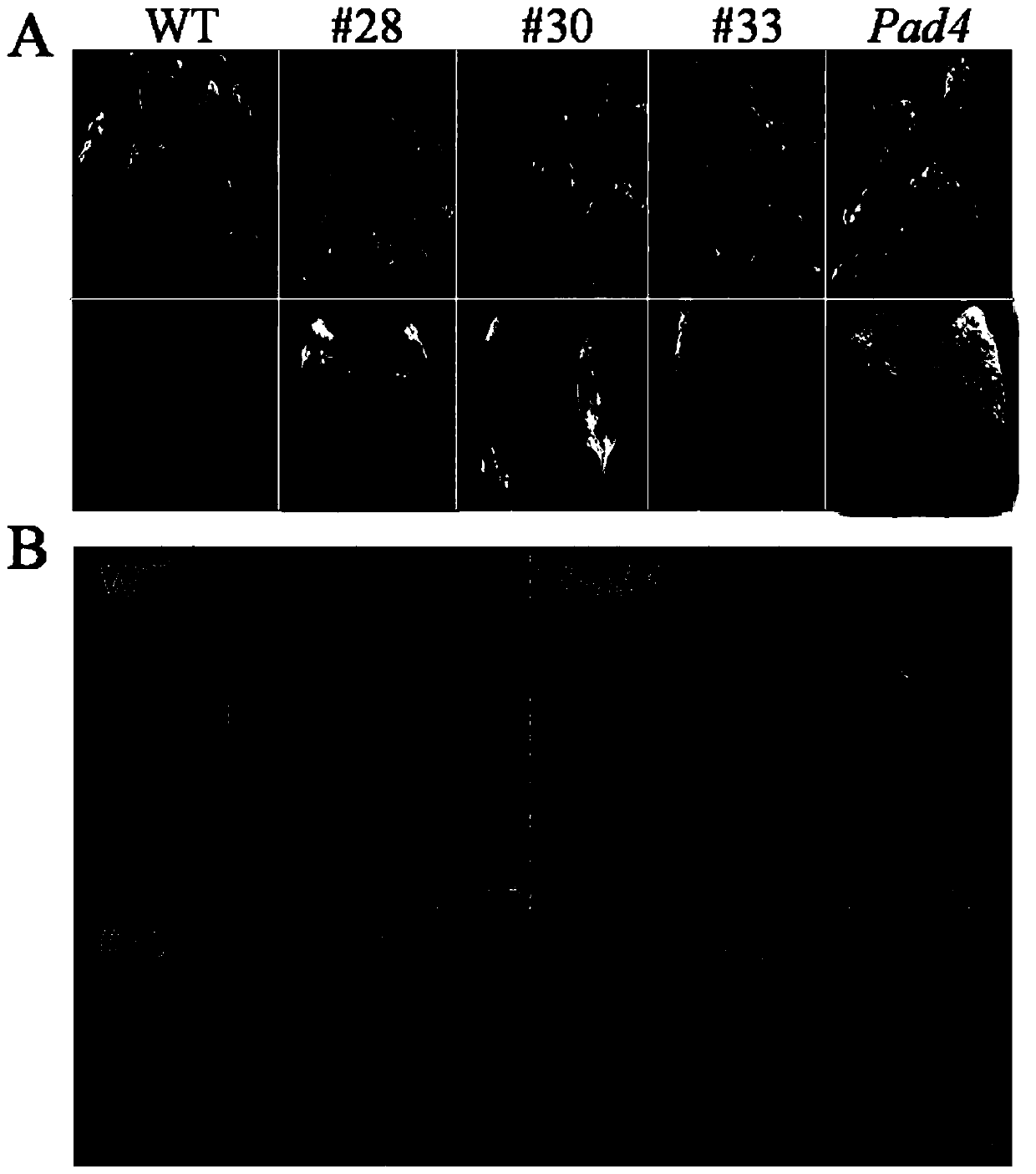
Disease resistance gene of wild grapevine and its application
ActiveCN106591323BRestrict growthSevere allergic reactionPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyOpen reading frame
The invention discloses a wild vitis. quinquangularis anti-disease gene and application thereof. The full length of a complete open reading frame sequence is 1095bp, and 364 amino acids are encoded. Moreover, a pCAMBIA2300-35S-VqWRKY52 over-expression vector is constructed, a model plant, namely, arabidopsis thaliana is imported by an inflorescence infection method, and over-expression is performed in the arabidopsis thaliana, so that the resistance of the arabidopsis thaliana to powdery mildew and pseudomonas syringae parasitic in living organisms is improved remarkably, and the resistance to saprophytic botrytis cinerea is lowered. A wild vitis. quinquangularis-24 anti-disease gene VqWRKY52 participates in an SA-mediated anti-disease signal path, can enhance the anaphylactic reaction, can be used for enhancing the resistance of plants to the fungus powdery mildew and the pseudomonas syringae parasitic in the living organisms, and plays a role in regulating and controlling the anaphylactic reactions of the plants through regulation and control of the expression of the VqWRKY52 gene, so that the reactions of the plants to different pathogenic bacteria are regulated and controlled.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Saccharomyces 17wy1, its microbial preparation and its application in the control of wheat powdery mildew
The invention discloses a Sporospora 17wyl, its microbial preparation and its application in preventing and treating wheat powdery mildew, aiming to solve the technical problem of chemical control hazards. The preservation number of the bacteria is CGMCC No: 14148, and its microbial preparation contains Sporospora sp. 17wy1 or / and its metabolites; the preparation method of said microbial preparation includes (1) preparation of seed culture; (2) preparation of fermentation broth; (3) Preparations. When the microbial preparation containing Sporospora saccharomyces 17wy1 or / and its metabolites is used in inhibiting the germination of wheat powdery mildew conidia and its growth and reproduction, it has an antagonistic effect on the germination and growth of wheat powdery mildew conidia, and has an antagonistic effect on the germination and growth of wheat powdery mildew conidia. Powdery mildew on both in vitro and in vivo wheat leaves had good control effects. The raw material used in the present invention has low cost, is safe to the environment, and avoids hidden dangers of agricultural safety.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Vitis Vinifera with Reduced MLO Expression and Increased Resistance to Powdery Mildew
ActiveUS20200291421A1Plant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyErysiphe sp.
Owner:FOND EDMUND MACH
Application and method of tobacco mlo2, mlo6 and mlo12 genes in preparing tobacco varieties resistant to powdery mildew
ActiveCN109722439BStrong resistanceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
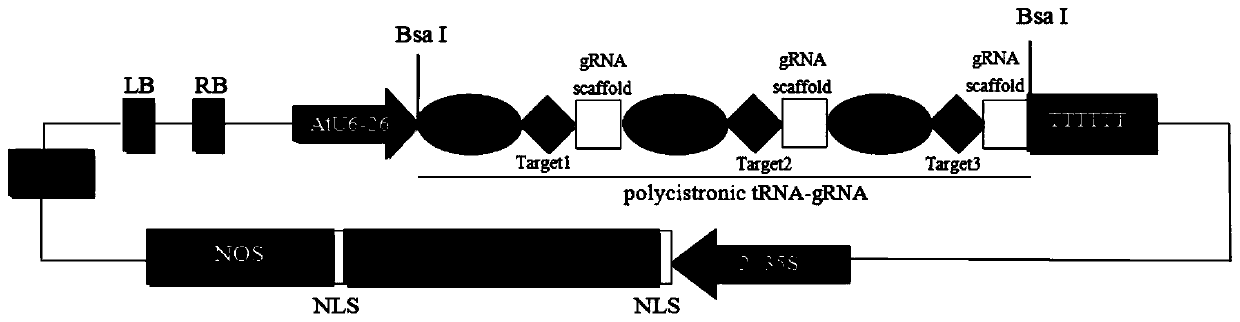
The invention discloses applications of tobacco Mildew resistance locus O (MLO) genes MLO2, MLO6 and MLO12 in the preparation of tobacco varieties resistant to powdery mildew, and a method for preparing the tobacco varieties resistant to powdery mildew. Through the construction of an editing inactive carrier containing polycistron tRNA-gRNA editing MLO2, MLO6 and MLO12 genes, tobacco can show obvious resistance on powdery mildew after the MLO2, MLO6 and MLO12 genes are inactivated by editing; and research results have important application values on researching the anti-disease immune mechanisms of plant on fungi and cultivating the tobacco varieties resistant to the powdery mildew.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
A cutting seedling identification method for resistance to powdery mildew of melon
ActiveCN109197423BPromote rootingImprove survival rateHorticulture methodsVegetative propogationSporelingHigh survival rate
The invention discloses a cutting seedling identifying method for muskmelon powdery mildew resistance. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, cutting seedlings with relatively large rooting amount and high survival rate are obtained by adopting muskmelon lateral branch cutting, then a powdery mildew spore suspension liquid spraying method is adopted for carrying out inoculation on thecutting seedlings, and the cutting seedlings are cultured in a high-humidity environment and are subjected to the resistance identification, and the identification result is consistent with an outdoorfield disease-resistant and inoculation experiment result. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the powdery mildew resistance of the muskmelons can be identified under the condition that the environment conditions are controllable, the method is advantageous in that the operation is simple and feasible, and the form is visual and reliable, the period is short, the muskmelon plantsare not damaged, and the method has important significance for resistance heredity on powdery mildew resistance of the muskmelons and breeding research.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A hemopexin gene tahbp1 and its recombinant interference vector and application
ActiveCN109535236BImprove powdery mildew resistanceIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyRestriction site
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a gene TaHBP1 with a heme-binding (Heme-binding) domain, its recombination interference carrier and its application. The cDNA sequence of the gene TaHBP1 with Heme-binding domain is SEQ ID NO.1 and the encoded amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.2. The gene is from common wheat (Triticum asetivum L.) Yangmai 158. The expression of TaHBP1 in powdery mildew-susceptible wheat variety Yangmai 158 was induced by powdery mildew, and the expression level was much higher than that in disease-resistant wheat variety Nannong 9918. The forward sequence of TaHBP1 was inserted between the BamHI and KpnI restriction sites of pWMB006, and the reverse sequence was inserted between SpeI and SacI of pWMB006 to obtain an interference expression vector, and the wheat variety Yangmai 158 susceptible to powdery mildew was transformed, and the positively transformed plants The powdery mildew resistance identification results showed that the reduced expression of TaHBP1 could improve the resistance of powdery mildew susceptible wheat cultivars to powdery mildew.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
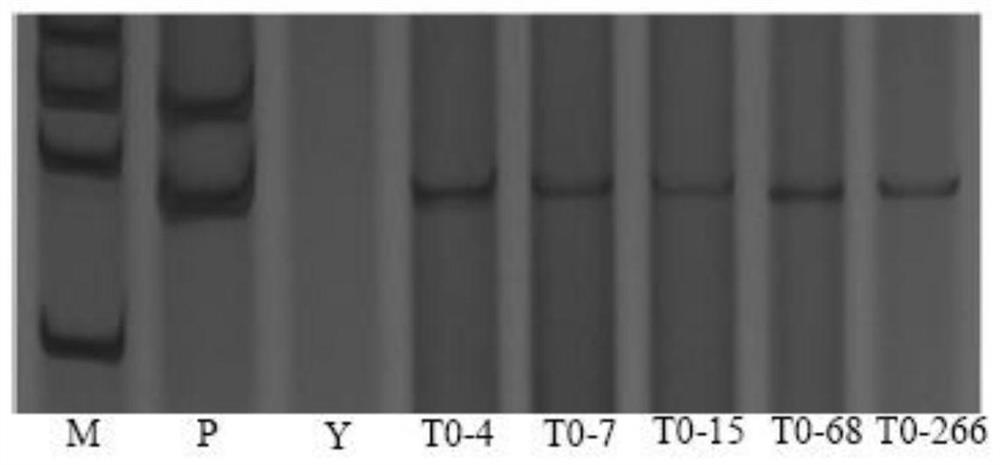
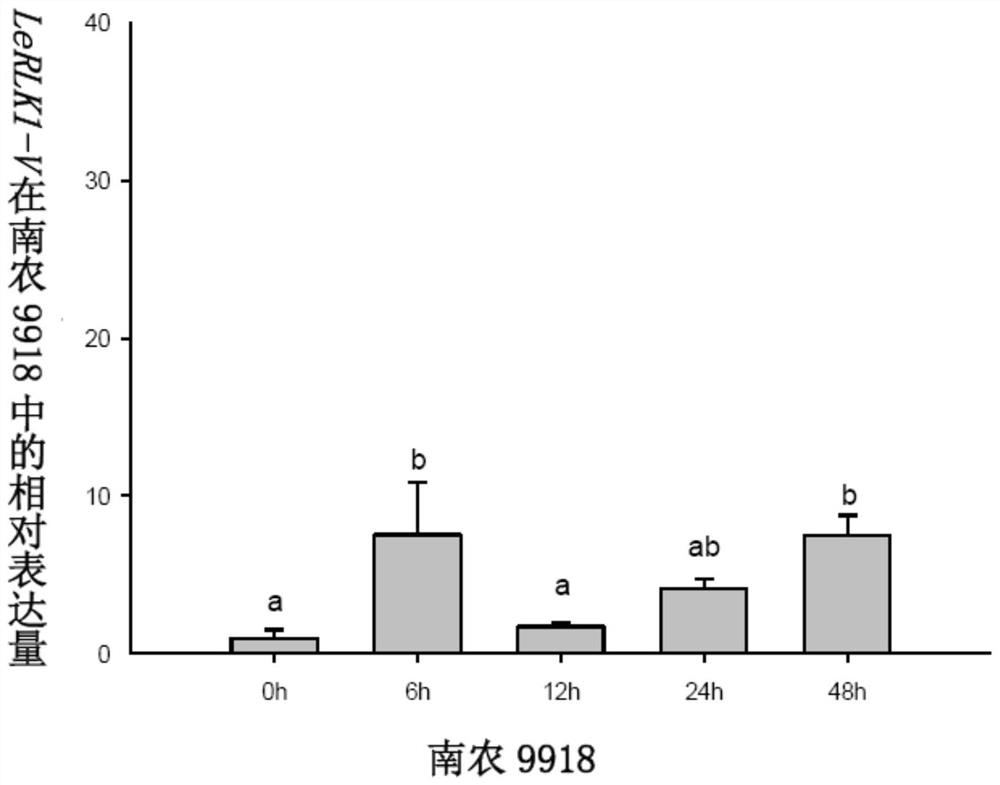
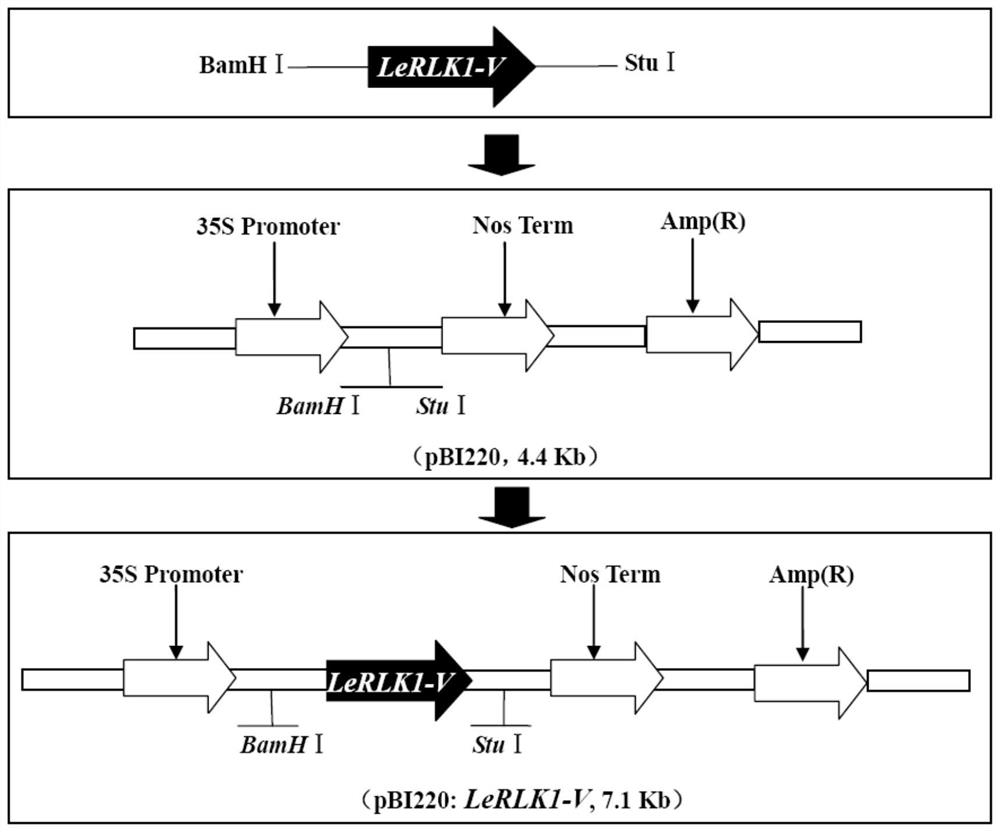
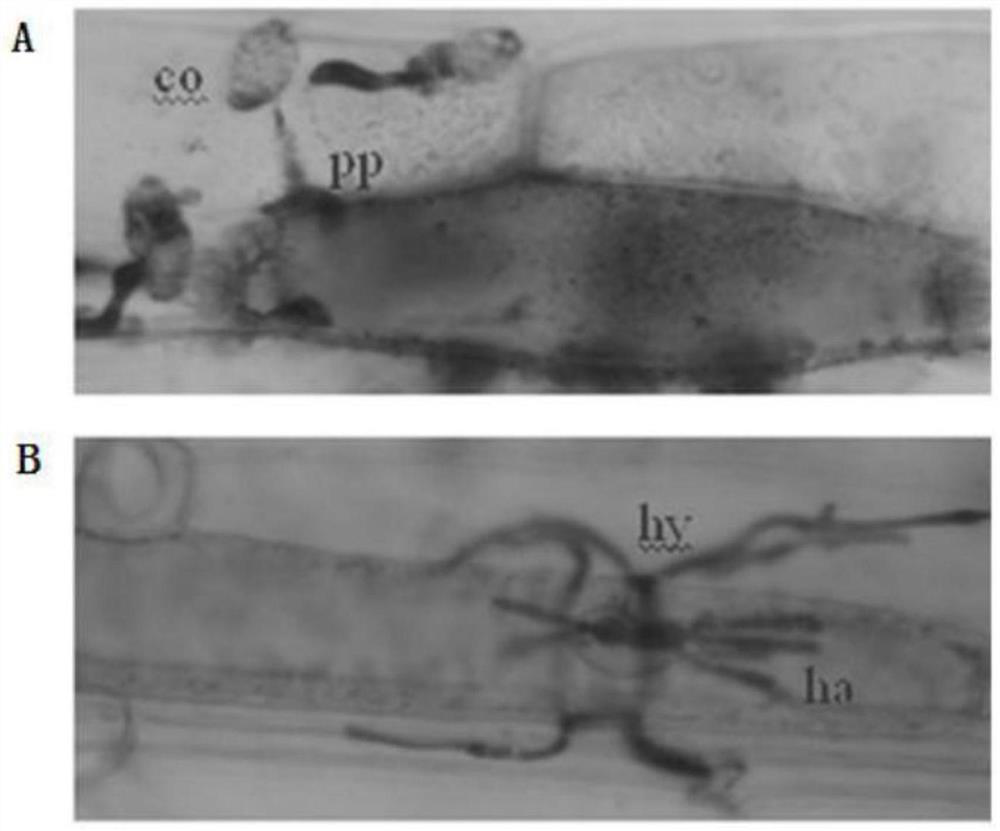
A kinase gene lerlk1-v and its expression vector and application
ActiveCN108342401BPowdery mildew resistantTransferasesFermentationGenetic engineeringHaynaldia villosa
The invention discloses a kinase gene LeRLK1-V, and an expression vector and application thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. The cDNA sequence of LeRLK1-V is SEQ ID No. 1, and an amino acid sequence coded by LeRLK1-V is SEQ ID No. 2. The gene LeRLK1-V is derived from the 6VS chromosome arm of the Triticum aestivum-Haynaldia villosa translocation line 6VS / 6AL Nannong 9918. LeRLK1-V is enhanced in expression under the induction of powdery mildew in the powdery-mildew-resistant wheat variety Nannong 9918. The gene is used for transforming the susceptible wheat variety Yangmai158 by transient expression, and results show that the overexpression of LeRLK1-V can reduce the haustorium index of Yangmai 158. Therefore, LeRLK1-V is expected to be applied to genetic engineering breeding; and as LeRLK1-V is introduced into wheat varieties susceptible to powdery mildew, the powdery mildew resistance of the wheat varieties is expected to be improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A chloroplast positioning gene toxabp1-v and its application
The invention discloses a chloroplast positioning gene ToxABP1‑V and its application. The cDNA sequence of ToxABP1‑V is SEQ ID NO.1 and the encoded amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.3. The gene comes from diploid Trichopyrhiza, can interact with powdery mildew resistance-related gene CMPG1‑V, and its expression is down-regulated by powdery mildew-resistant diploid Trichopyrhiza. The gene RNAi silencing vector pWMB006‑ToxABP1 was transformed into the susceptible wheat variety Yangmai 158 by single-cell transient silencing technology, and the results showed that transient silencing of ToxABP1 could reduce the haustoria index of Yangmai 158. Three positive RNAi transgenic plants were obtained by transgenic technology, which showed medium to high resistance to wheat powdery mildew. Therefore, ToxABP1‑V is expected to be used in genetic engineering breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of wheat powdery mildew spray inoculation method
InactiveCN107460231BAccurate quantification of inoculum concentrationUniform inoculationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiotechnologySporeling
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION & SOIL FERTILIZER HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
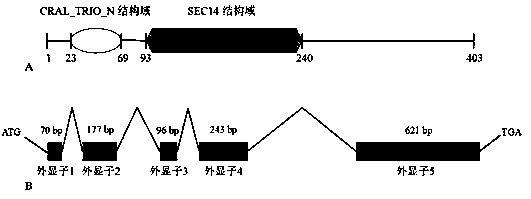
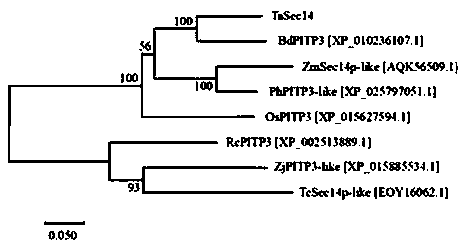
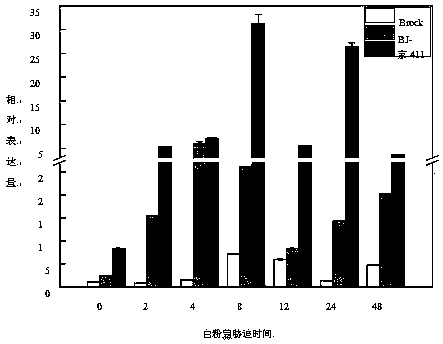
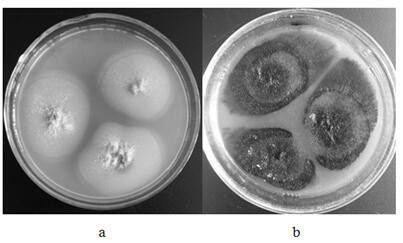
Triticum aestivum PITP TaSec14 gene and application thereof
InactiveCN111138520AIncrease resistanceBreeding for improved resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a cDNA sequence and an amino acid sequence of a PITP (Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Protein) gene TaSec14 cloned in powdery mildew infected triticum aestivum variety of Jing 411. The cDNA full length of the gene is 1546 bp; the DNA full length is 2186 bp; an open reading frame is 1212 bp; 403 amino acids are coded; 80.45-percent homology is realized with PITP3(XP_010236107.1) in Bd (Brachypodium Distachyon); SEC14 conserved domains are contained; and the gene is named as TaSec14. After inoculation with the powdery mildew, the TaSec14 has the consistent expression trendin Jing 411 and a near-isogenic line BJ-1 thereof, and the expression amount is respectively higher than that of a disease-resistant triticum aestivum variety of Brock. A virus induced gene silencingtechnology is used for knocking down the Tasec14 gene in Jing 411; through the expression reduction of the TaSec14 gene, the resistance of the diseased triticum aestivum Jing 411 on the powdery mildewcan be improved to a certain degree; and the TaSec14 gene has the regulation and control effects in the interaction process of the triticum aestivum with the powdery mildew. The invention provides anovel genetic resource for the triticum aestivum powdery mildew resistance mechanisms and disease resistance breeding.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A Plant Endophytic Trichotheca fungus m7sb 41 and Its Application
ActiveCN110468057BPromote growthEnhanced inhibitory effectFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a fungus of the genus Diptera in plants ( Seimatosporium sp.) M7SB 41, the preservation number of which is CGMCC NO.18114 in the General Microorganism Center of the China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee; the strain can be applied to the prevention and treatment of tobacco powdery mildew. Erysiphe cichoracearum Tobacco powdery mildew caused by DC) has good antagonism, can significantly promote the growth of infected tobacco, and improve its disease prevention and resistance ability; the present invention has broad application prospects in the field of biological control of powdery mildew, and is a biological control agent for powdery mildew The development and application of the strain provide strain resources and theoretical basis.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
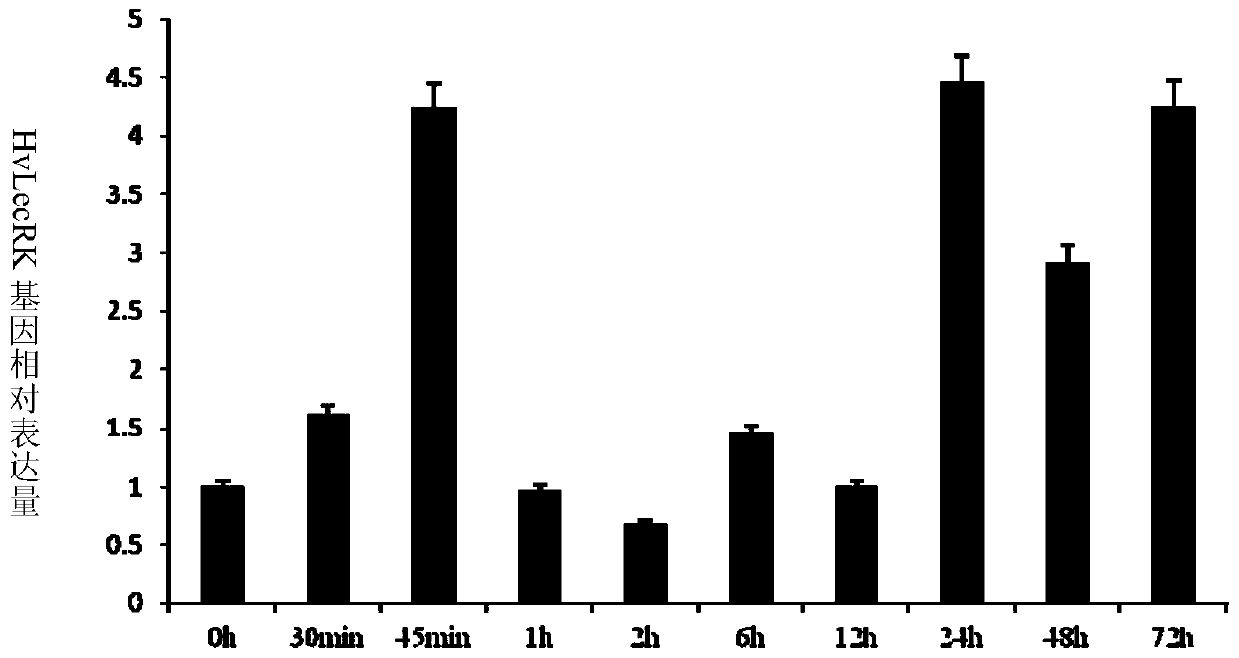
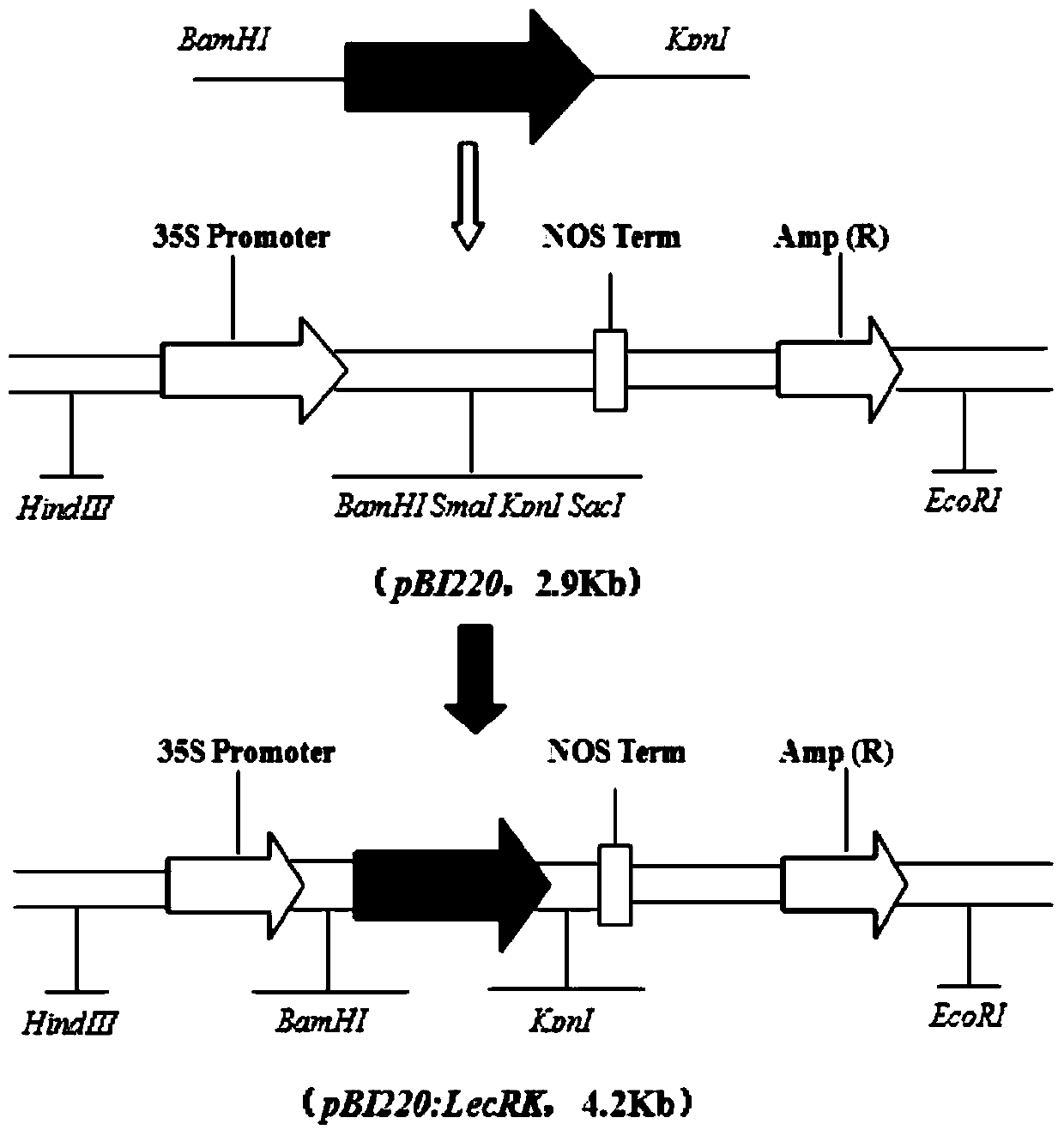
A tufted wheat lectin receptor kinase gene and its expression vector and application
ActiveCN105821055BIncrease resistanceImprove powdery mildew resistanceTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyReceptor
The invention discloses a haynaldia villosa agglutinin receptor-like kinase gene, its expression vector and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. According to the invention, cDNA sequence of Hv-LecRK is SEQ ID NO.1 and amino acid sequence coded by Hv-LecRK is SEQ ID NO.2. The gene is derived from Haynaldia villosa L.(2n=2x=14, genome VV), and can interact with powdery mildew resistance-related gene Hv-CMPG. Expression of the gene is enhanced when the gene is induced by powdery mildew in the powdery mildew resistant diploid haynaldia villosa. Through transient expression, the gene is transformed to a susceptible wheat variety Yangmai 158. It shows through results that overexpression of the Hv-LecRK gene can reduce haustorium index of Yangmai 158. Thus, the Hv-LecRK is expected to be used in genetic engineering breeding. By introducing the Hv-LecRK into a wheat variety susceptible to powdery mildew, powdery mildew resistance of wheat is expected to be raised.
Owner:王秀娥 +2
Powdery mildew resistance gene in carrot
The present invention relates to powdery mildew and in particular to powdery mildew, resistant carrot plants or wild carrot (Daucus carota) plants caused by the phytopathogen Erysiphe heraclei, wherein the powdery mildew resistance is controlled by one or two dominant powdery mildews disease resistance genes. The present invention also relates to molecular markers genetically linked to the powdery mildew of the invention and in particular to powdery mildew caused by the phytopathogen Erysiphe miltiorrhiza, genes conferring resistance and their use for identifying tolerant powdery mildew and in particular by the phytopathogen Use of carrot plants or wild carrot plants with powdery mildew caused by Erysipha lovii. The invention also relates to seeds, plant parts, pollen, egg cells, callus, suspension cultures, somatic embryos and edible plant parts of the plants of the invention.
Owner:贝霍种子有限公司
Composition for preventing and treating mulberry powdery mildew
PendingCN114521565AImprove the effect of prevention and controlReduce doseBiocideFungicidesBerberinePesticide residue
The invention belongs to the technical field of mulberry disease control, and particularly relates to a composition for controlling mulberry powdery mildew. The composition for preventing and treating the powdery mildew of the mulberry trees is formed by compounding chlorohydrin and berberine, and the chlorohydrin is formed by compounding meconazole and flutriafol. When the flutriafol, the flutriafol and the berberine are compounded according to a certain mass ratio, a synergistic effect is achieved on mulberry powdery mildew, the prevention and treatment effect on mulberry powdery mildew can be improved, the application dosage of chemical agents can be reduced, pesticide residues are reduced, and the effect of preventing and treating mulberry powdery mildew is achieved. Therefore, normal growth of silkworms and quality and yield of silkworm cocoons are guaranteed.
Owner:来宾市农业科学院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com