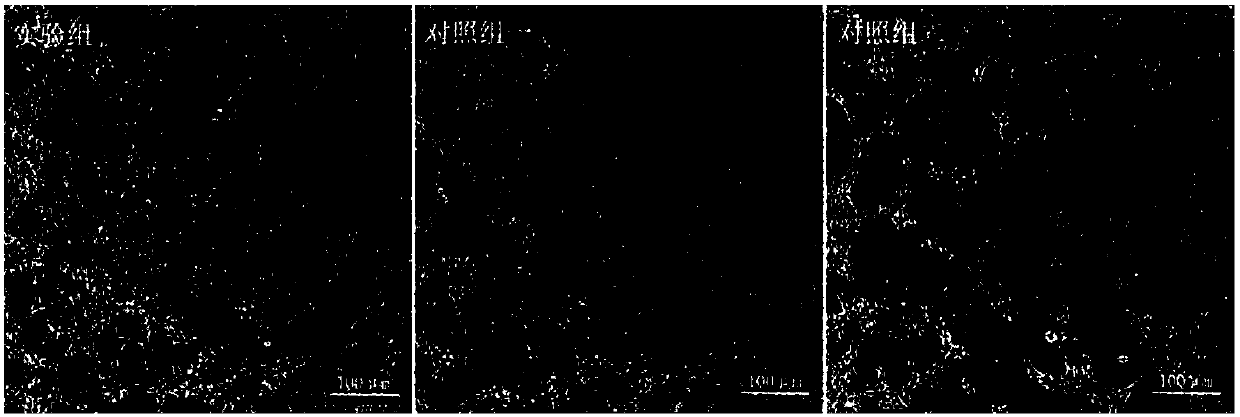
Method for inducing human spinal cord motor nerve precursor cells to differentiate into spinal cord motor neurons
A motor neuron and motor nerve technology, applied in nervous system cells, vertebrate cells, animal cells, etc., can solve the problems of long differentiation time, introduction of pathogenic microorganisms, low differentiation efficiency, etc., to achieve clear chemical composition and eliminate batches. Effects of quality differences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
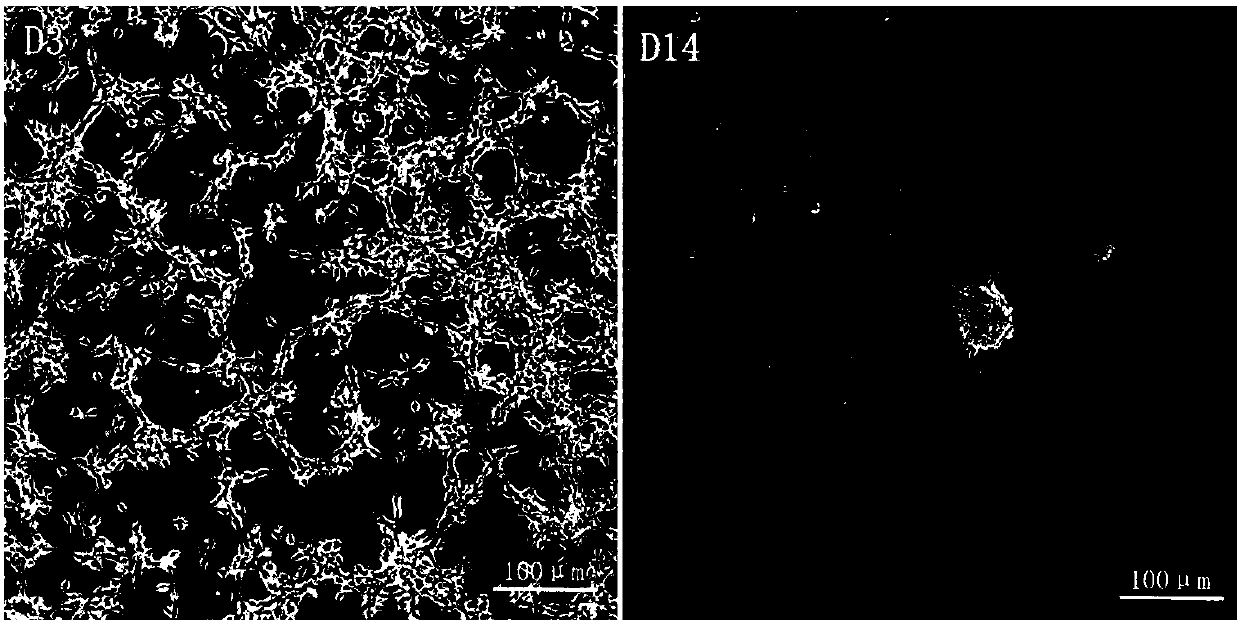
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1 Method for Differentiation of Human Spinal Motor Nerve Precursor Cells into Spinal Motor Neurons
[0042] 1. Preparation of culture medium
[0043] 1.1. Coating of PLO-Laminin culture dish:
[0044] Dilute poly-L-ornithine (PLO) with PBS to 15 μg / mL, add to the culture dish until the bottom of the culture dish is submerged, incubate at 37°C for 2 hours or overnight at 4°C, do not let the Dry the bottom of the culture dish; discard PLO, rinse twice with PBS, and once with DMEM / F12; See Table 1 for the amount added, and incubate at 37°C for 2 hours or overnight at 4°C.
[0045] Table 1 The amount of PLO and Laminin required to coat the culture dish
[0046] Petri dish specification
Growth area (cm 2 )
Amount added (mL)
6-well plate
10cm 2 / well
1mL / well
12-well plate
4cm 2 / well
0.4mL / well
24-well plate
2cm 2 / well
0.2mL / well
35mm culture dish
10cm 2
1mL
60mm culture...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2 Method for Differentiation of Human Spinal Motor Nerve Precursor Cells into Spinal Motor Neurons
[0070] 1. Preparation of culture medium
[0071] 1.1 The coating of petri dish is the same as embodiment 1
[0072] 1.2 Spinal cord motor nerve precursor cell culture medium
[0073] Basal medium (volume ratio): 50% DMEM / F12 medium and 50% Neurobasal medium;
[0074] Nutritional additives: the components and final use concentrations of the nutritional additives are: human insulin 10mg / L, vitamin C 50mg / L, glutathione 50mg / L, linolenic acid 1mg / L, carnitine 20mg / L, N-acetylcysteine 5μM, ethanolamine 5mg / L, linoleic acid 1mg / L.
[0075] 1.3 Basic complete medium
[0076] Basal medium (volume ratio): 50% DMEM / F12 medium and 50% Neurobasal medium;
[0077] Nutritional additives: the components and final use concentrations of the nutritional additives are: human insulin 10mg / L, vitamin C 50mg / L, glutathione 50mg / L, linolenic acid 1mg / L, carnitine 20mg / L, N-ace...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Example 3 Method for Differentiation of Human Spinal Motor Nerve Precursor Cells into Spinal Motor Neurons
[0091] 1. Preparation of culture medium
[0092] 1.1 The coating of petri dish is the same as embodiment 1
[0093] 1.2 Spinal cord motor nerve precursor cell culture medium
[0094] Basal medium (volume ratio): 50% DMEM / F12 medium and 50% Neurobasal medium;
[0095] Nutritional additives: the components and final use concentrations of the nutritional additives are: human insulin 20mg / L, vitamin C 200mg / L, glutathione 100mg / L, linolenic acid 5mg / L, carnitine 20mg / L, N-acetylcysteine 500μM, ethanolamine 10mg / L, linoleic acid 5mg / L.
[0096] 1.3 Basic complete medium
[0097] Basal medium (volume ratio): 50% DMEM / F12 medium and 50% Neurobasal medium
[0098] Nutritional additives: the components and final use concentrations of the nutritional additives are: human insulin 20mg / L, vitamin C 200mg / L, glutathione 100mg / L, linolenic acid 5mg / L, carnitine 20mg / L, N...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com