Polymer electrolyte membrane and preparation method thereof
An electrolyte membrane and polymer technology, applied in the manufacture of electrolyte batteries, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, electrolyte immobilization/gelation, etc., can solve the problem of unavailable, increased process/raw material costs, reduced ion exchange capacity and proton conductivity to achieve high proton conductivity, comprehensive performance improvement, and excellent mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
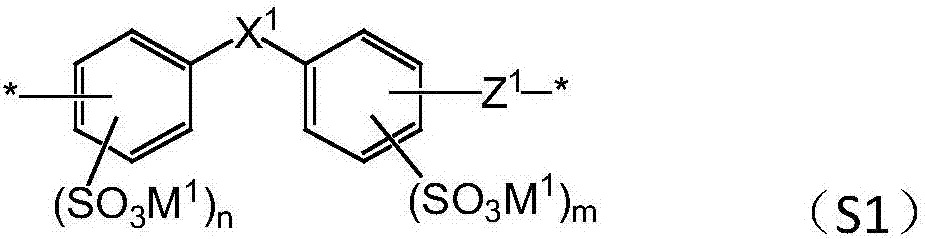
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0111] (1) Raw materials
[0112] Polyether ether ketone film1
[0113] (2) Performance characterization
[0114] The polyetheretherketone film 1 has a thickness of 30 micrometers and an IEC of 0.5 mmol / g.
[0115] The polyether ether ketone film 1 had a dimensional change rate of 2.9% in the MD direction and a 2.9% dimensional change rate in the TD direction, and was excellent in water resistance. The mechanical strength was measured using a universal tensile machine, and the Young's modulus was 1.1 GPa, and the elongation at break was 180%. The proton conductivity was measured using an electrochemical test system, and it was 90 mS / cm at 80° C. and a relative humidity of 85%, and 2.1 mS / cm at 80° C. and a relative humidity of 25%.
Embodiment 2
[0117] (1) Orientation of polyether ether ketone film
[0118] At room temperature, soak the polyether ether ketone membrane 2 in deionized water to absorb water, take it out after standing for 12 hours, and dry the surface to obtain a saturated water-containing membrane. Fix the saturated water-containing film in a stretching fixture, place it in a stretching environment at 20°C, and perform biaxial stretching when it is slowly dehydrated to a water content of 35%. After stretching, keep the jig stretched, and move the stretched film into a setting room at 40° C. for 10 minutes of setting treatment. After the setting is finished, the stretched polyetheretherketone film 2 is taken out.
[0119] (2) Performance characterization
[0120] After stretching, the thickness of the polyetheretherketone film 2 is 17.8 microns, the actual stretching ratio is 1.3, and the IEC is 2.2 mmol / g.
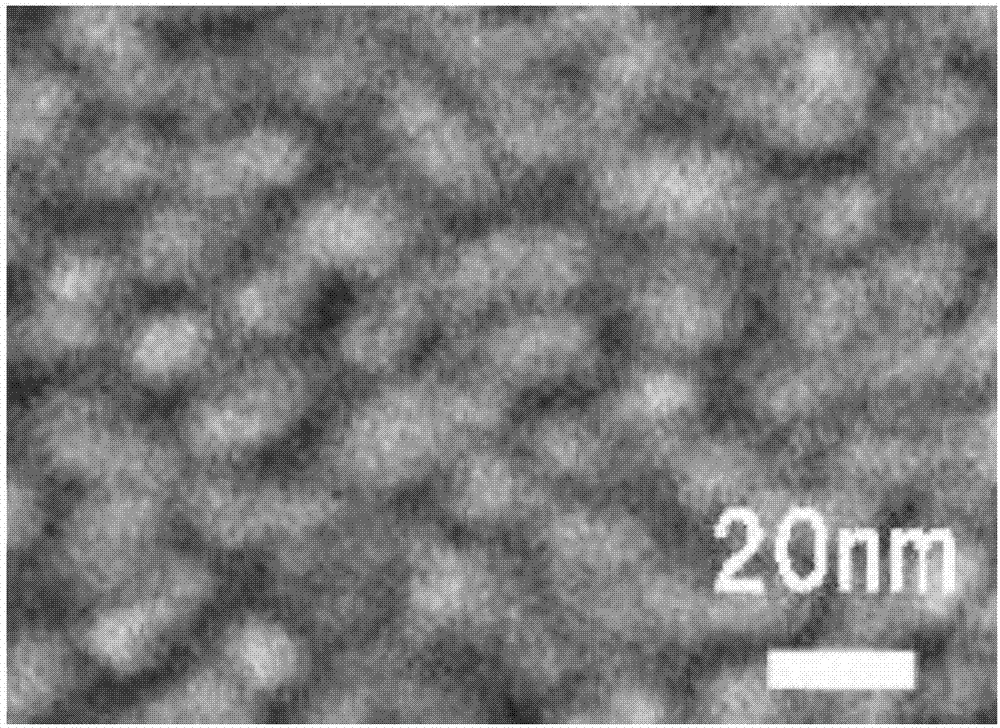
[0121] Observation using a transmission electron microscope shows that the polyether ether ke...
Embodiment 3
[0123] (1) Orientation of the polymer electrolyte membrane
[0124] At room temperature, soak the polymer electrolyte membrane 1 in deionized water to absorb water, take it out after standing for 12 hours, and dry the surface to obtain a saturated water-containing membrane. Fix the saturated water-containing film in a stretching fixture, place it in a stretching environment at 45°C, and perform biaxial stretching when it is slowly dehydrated to a water content of 23%. After stretching, keep the jig stretched, and move the stretched film into a setting room at 45° C. for 10 minutes of setting treatment. After setting, take out the stretched polymer electrolyte membrane.
[0125] (2) Performance characterization
[0126] After stretching, the thickness of the polymer electrolyte membrane is 12.4 microns, the actual stretching ratio is 1.1, and the IEC is 2.2 mmol / g.
[0127] Observation with a transmission electron microscope shows that the polymer electrolyte membrane has a ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com