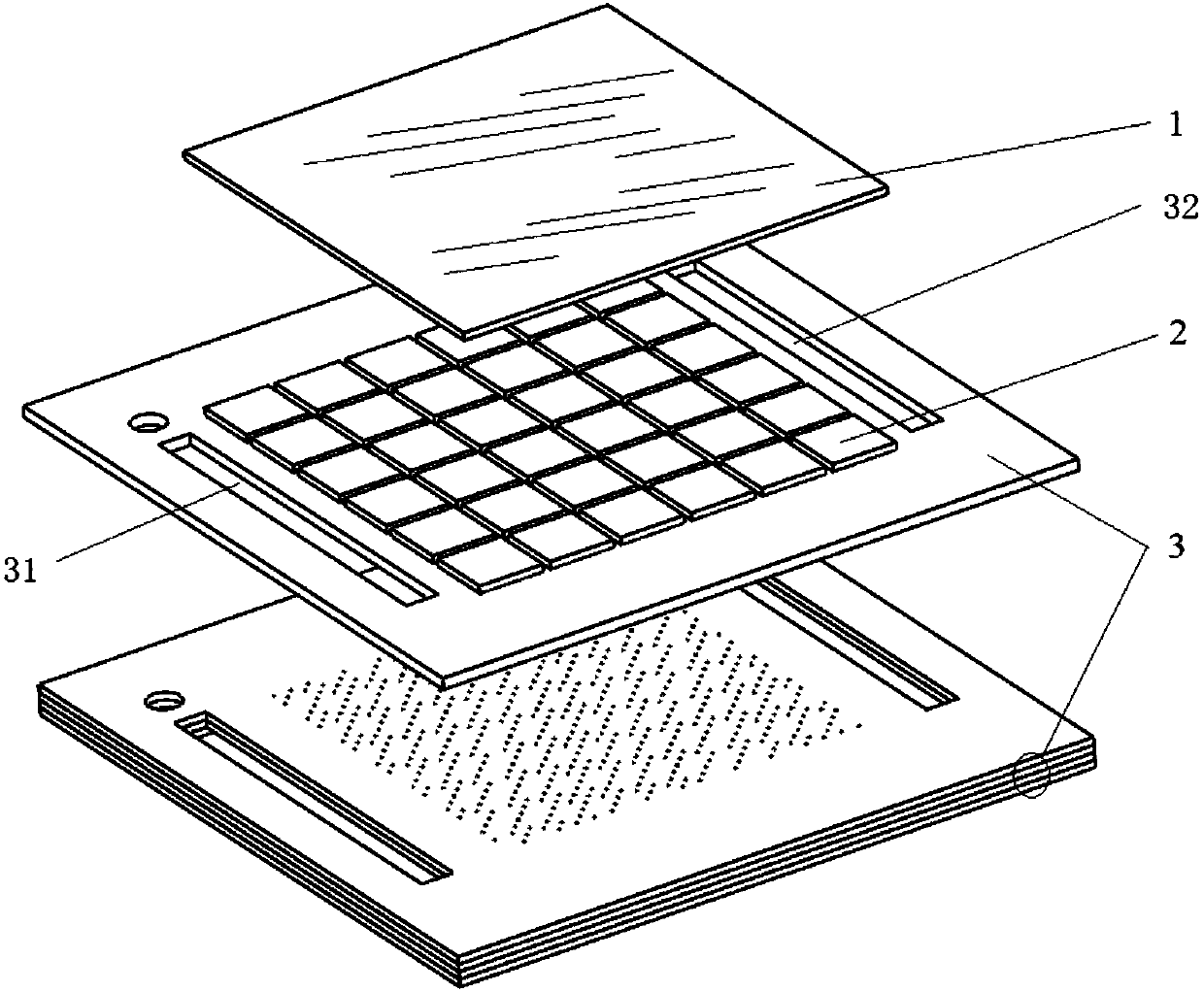
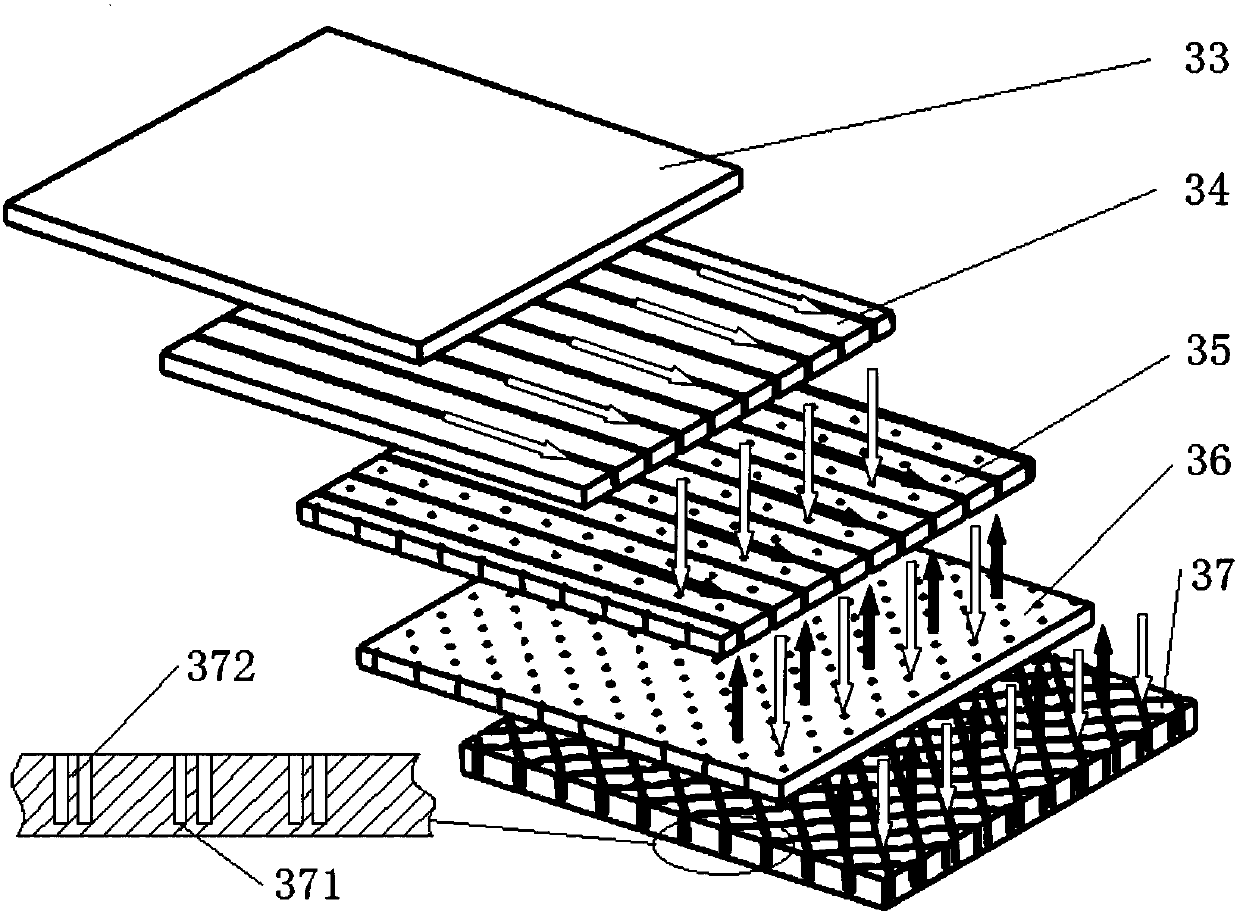
Dense-condensation photovoltaic cell array reducing mismatch loss
A battery array and concentrating photovoltaic technology, applied in the field of solar energy utilization, can solve the problems of large optical loss and DA-CPV system cost increase, and achieve the effect of increasing power output, improving output characteristic curve, improving accuracy and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
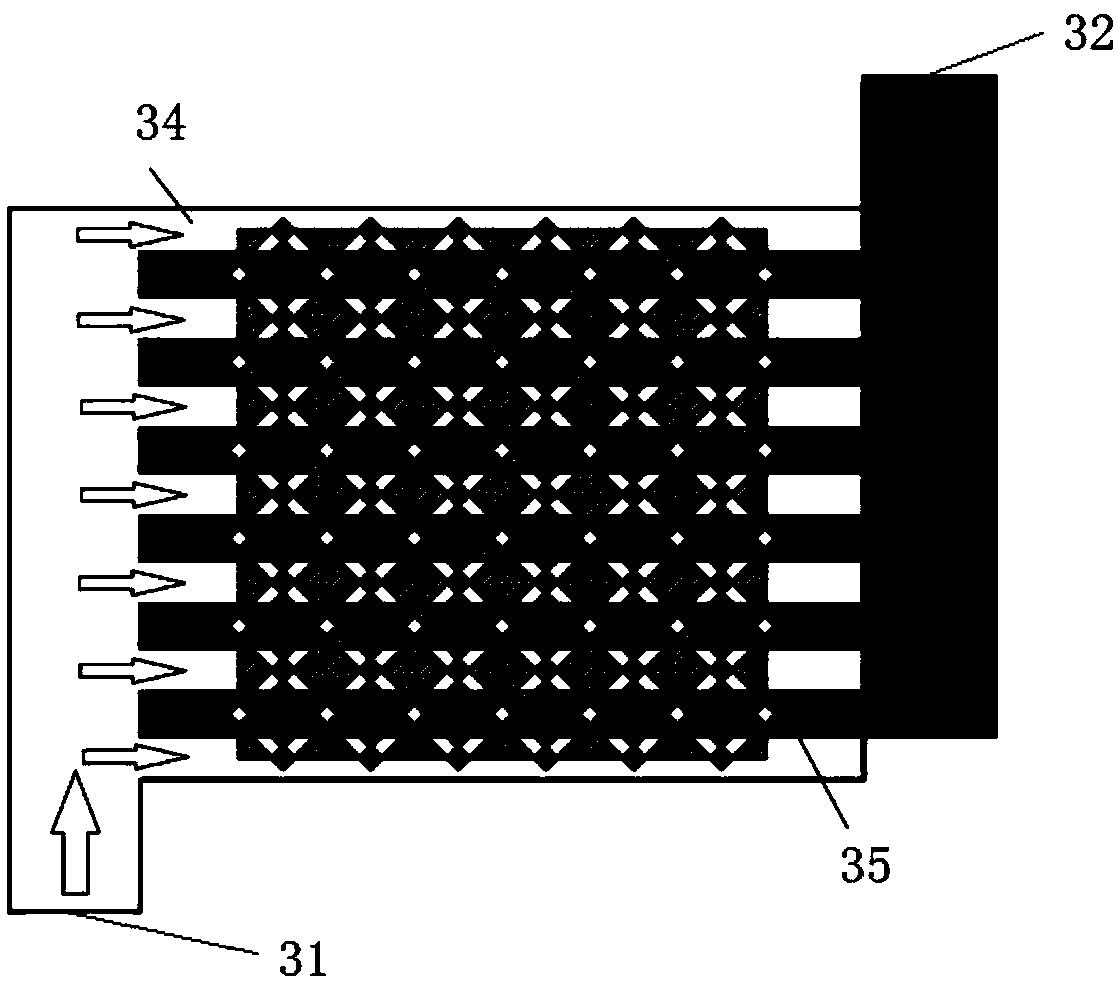
[0043] Preferably, the connections are made in a square-arranged dense array of four-corner rotationally symmetrical connections. This embodiment adopts as Figure 5 Gaussian distribution lighting conditions shown, choose Figure 6 The 6×6 square concentrating photovoltaic dense battery array shown in the figure has a total of 36 square concentrating photovoltaic cells, the size of each battery is 10mm×10mm, arranged into a 6×6 battery array, and each -36 for numbering. The connection method is as Figure 7 As shown, taking the origin of the coordinate axis as the center and the coordinate axis as the boundary, the cell array is divided into 4 sub-modules, and each sub-module contains 9 concentrating cells that are symmetrical to the center of the origin. Connect the batteries numbered 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 13, 14, and 15 in parallel, and name it as a square array. The batteries of 11, 12, 16, 17, and 18 are connected in parallel, named as the third module 233 of the four-corn...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Preferably, the connections are made in a dense array arranged in a square with diagonal rotational symmetry. In this embodiment, the following methods are used: Figure 5 Gaussian distribution lighting conditions shown, choose Figure 6 The 6×6 square concentrating photovoltaic dense battery array shown in the figure has a total of 36 square concentrating photovoltaic cells, the size of each battery is 10mm×10mm, arranged into a 6×6 battery array, and each -36 for numbering. The difference from Example 1 is that the connection method of the dense concentrated photovoltaic cell array is as follows: Figure 9 As shown, in order to adapt to different voltage and current requirements, this embodiment adopts a diagonally rotationally symmetrical connection mode to achieve an effective complementarity with Embodiment 1. Connect the batteries numbered 1, 7, 13, 19, 25, and 31 on both sides of the battery array in parallel, name it a square array, connect the first sub-modul...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Preferably, the connection is made in a circular arrangement of dense arrays containing special-shaped cells with four-corner rotational symmetry. The difference from Embodiments 1 and 2 is that the array is circular in shape and consists of 52 photovoltaic cells. Including square concentrating cells and shaped cells. Each cell is connected to form an array and then used in a concentrated photovoltaic power generation system. Its connection method is as Figure 11 As shown, with the origin of the coordinate axis as the center and the coordinate axis as the boundary, the battery array is divided into four sub-parts, which will be numbered as 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 19, 20 The batteries of , 21, and 22 are connected in parallel, named as a circular arrangement, and the four corners of the special-shaped battery array are rotationally symmetrically connected to the fourth sub-module 254, which will be numbered 3, 4, 8, 9, 10, 15, 16, 17, 18, 23 , 24, 25, and 26 ba...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com