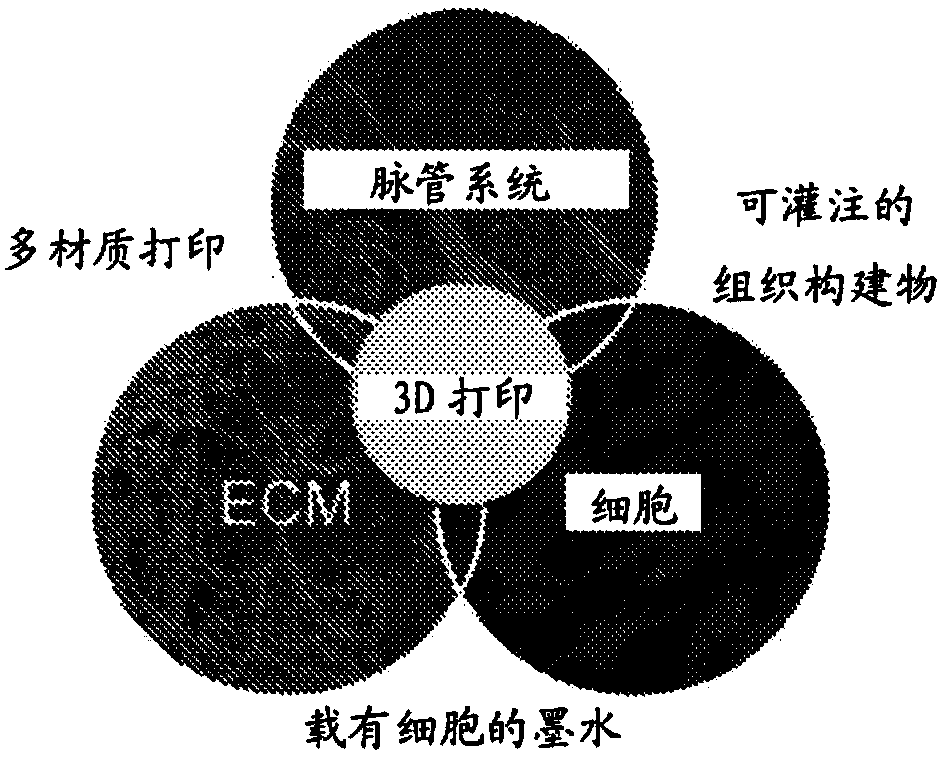
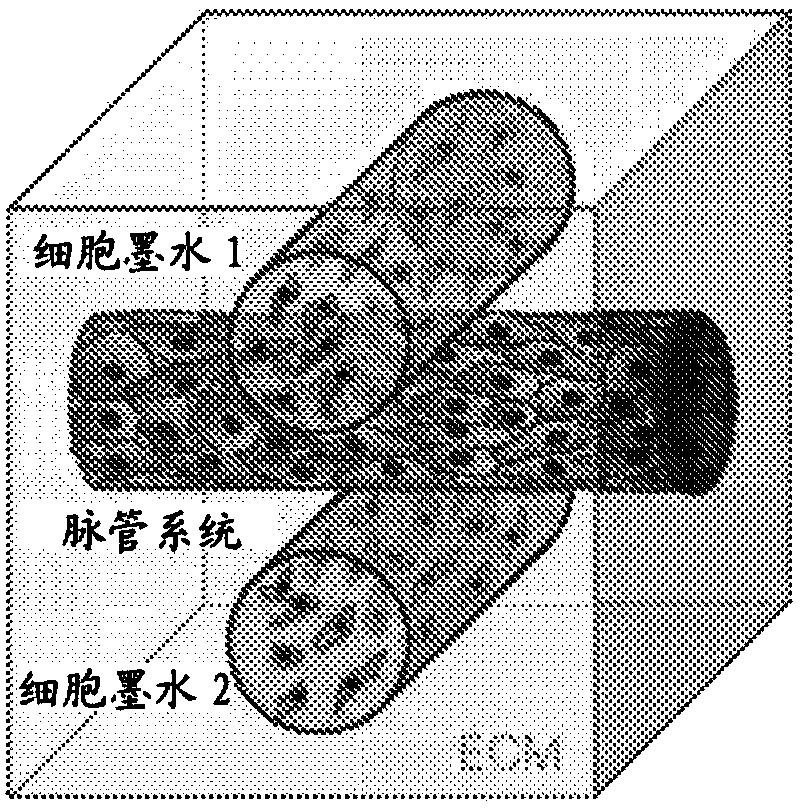
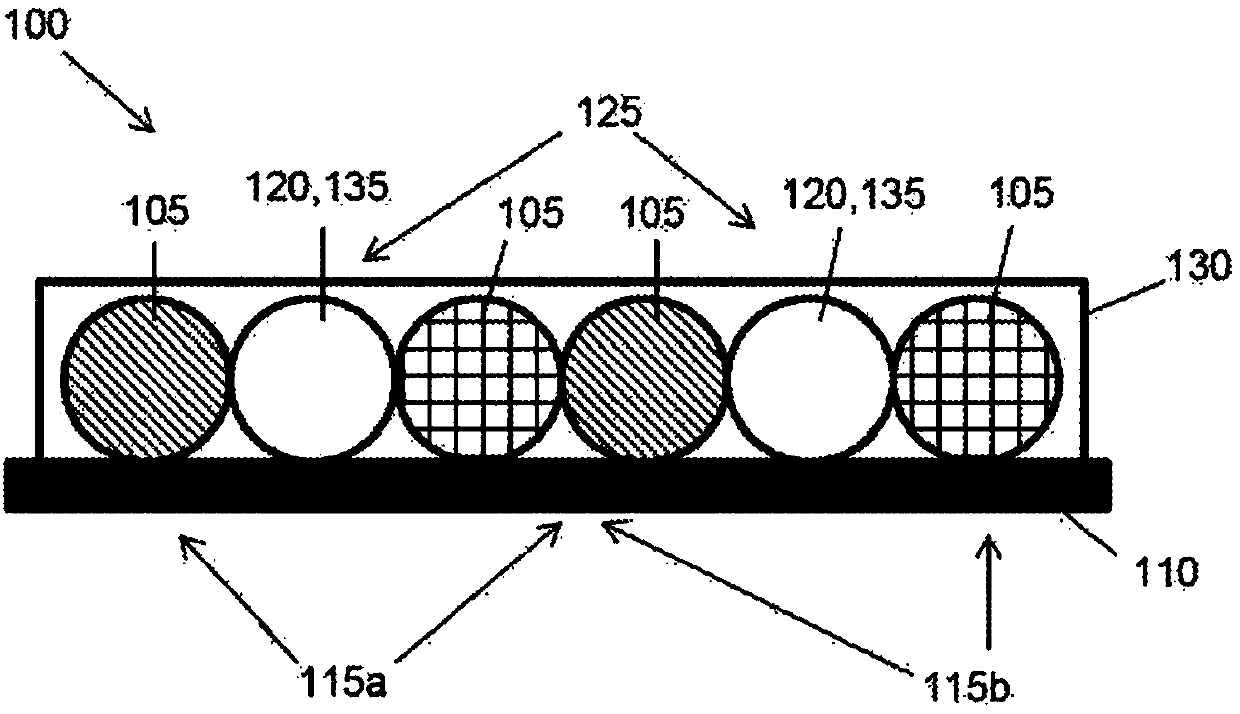
Tubular tissue construct and a method of printing
A tubular and structural technology, which is applied in the device of human tubular structure, tissue regeneration, processing and manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems that hinder the development of 3D tissue engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0284] fugitive ink
[0285] Referring to Figure 6A, a high concentration (40wt%) of Pluronic F127A (which was used when the applied shear stress exceeded the shear yield stress (τ y ) (e.g., in printing) exhibits a strong shear-thinning response, and when the applied shear stress is less than τ y The platform shear elastic modulus (G')) which when (for example, after printing) exceeds the shear viscosity modulus (G") was chosen as the fugitive ink for the exemplary system. The elasticity of the fugitive ink was found to be in the range of 22 °C is about 2x 10 4 Pa, as shown in Figure 6B. Below the CMT (approximately 4°C), the ink liquefies and its elasticity decreases by orders of magnitude, facilitating its removal from tissue constructs.
[0286] As noted above, the sacrificial monofilaments formed from escaped ink may include one or more other cells, growth factors, drugs, and the like. For example, endothelial, epithelial, and / or other cells can be dispersed in the ...
Embodiment 2
[0318] Example 2: 3D bioprinting of thick living tissue
[0319] A central issue in the construction of thick living tissues is the design of bio-, sacrificial and elastic inks for multi-material 3D bioprinting.
[0320] method
[0321] Solution preparation :
[0322] Matrix and ink precursor solutions were prepared prior to generation of tissue engineered constructs. A 15 wt / v% gelatin solution (type A, 300 bloom, from pigskin, Sigma) was produced by warming to 70°C in DPBS (1X Dulbelco's phosphate-buffered saline without calcium and magnesium) (unless otherwise indicated), the gelatin powder was then added to the solution while stirring vigorously. The gelatin was completely dissolved by stirring at 70° C. for 12 h (unless otherwise indicated), then the pH was adjusted to 7.5 using 1 M NaOH. The warmed gelatin solution was sterile filtered and stored in aliquots at 4°C for later use (<3 months).
[0323] Prepare fibrinogen solution (50 mg·mL -1 ): Freeze-dried bovi...
Embodiment 3
[0385] Example 3: Bioprinting of coiled 3D renal proximal tubules on a perfusion chip
[0386] Extracellular matrix preparation and rheology
[0387] ECM comprised gelatin and a fibrin network prepared as described in Example 2 above.
[0388] Ink rheology measurements were performed using a controlled stress rheometer (DHR-3, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE) with a 40 mm diameter, 2" cone and plate geometry. Shear storage modulus (C) and loss modulus (G") measured at a frequency of 1 Hz and a vibration stress (γ) of 0.01. Time scanning was performed by rapidly placing a premixed ECM solution containing thrombin on a Peltier plate maintained at 37°C.
[0389] ink preparation
[0390] Two inks are required for 3D bioprinting of perfusable PT models. Both inks were prepared as described in Example 2 above.
[0391] Bioprinting of 3D perfusable proximal tubule constructs
[0392] The 3D PT construct was built using a custom-designed multi-material 3D bioprinter equippe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com