Method for degrading contaminants in water body by using nanometer photocatalyst flocculate
A nano-photocatalyst, water pollutant technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, light water/sewage treatment, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of poor treatment effect and low efficiency, and achieve small environmental impact and reduce Cost, effect of good photocatalytic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
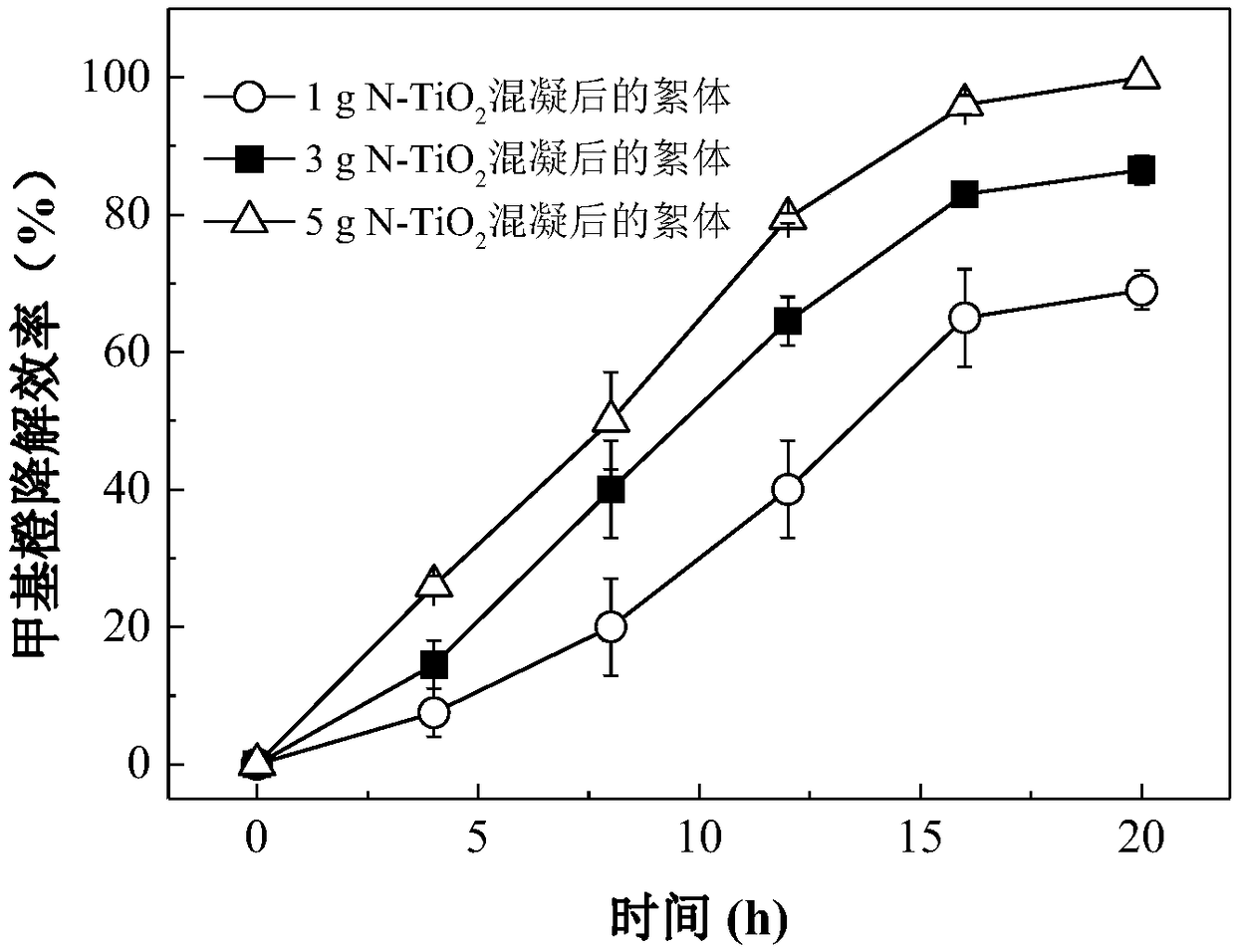
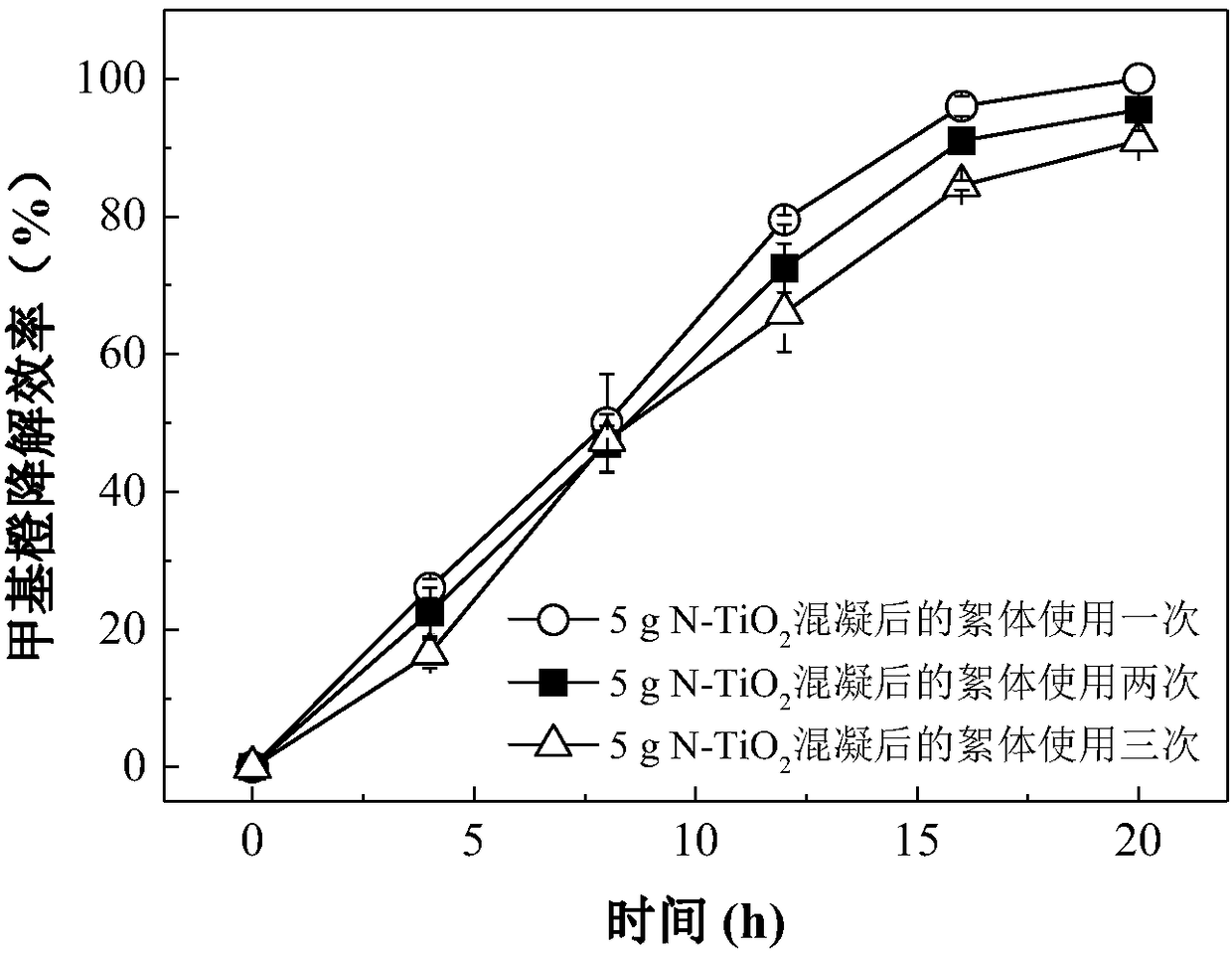
Examples
Embodiment 1
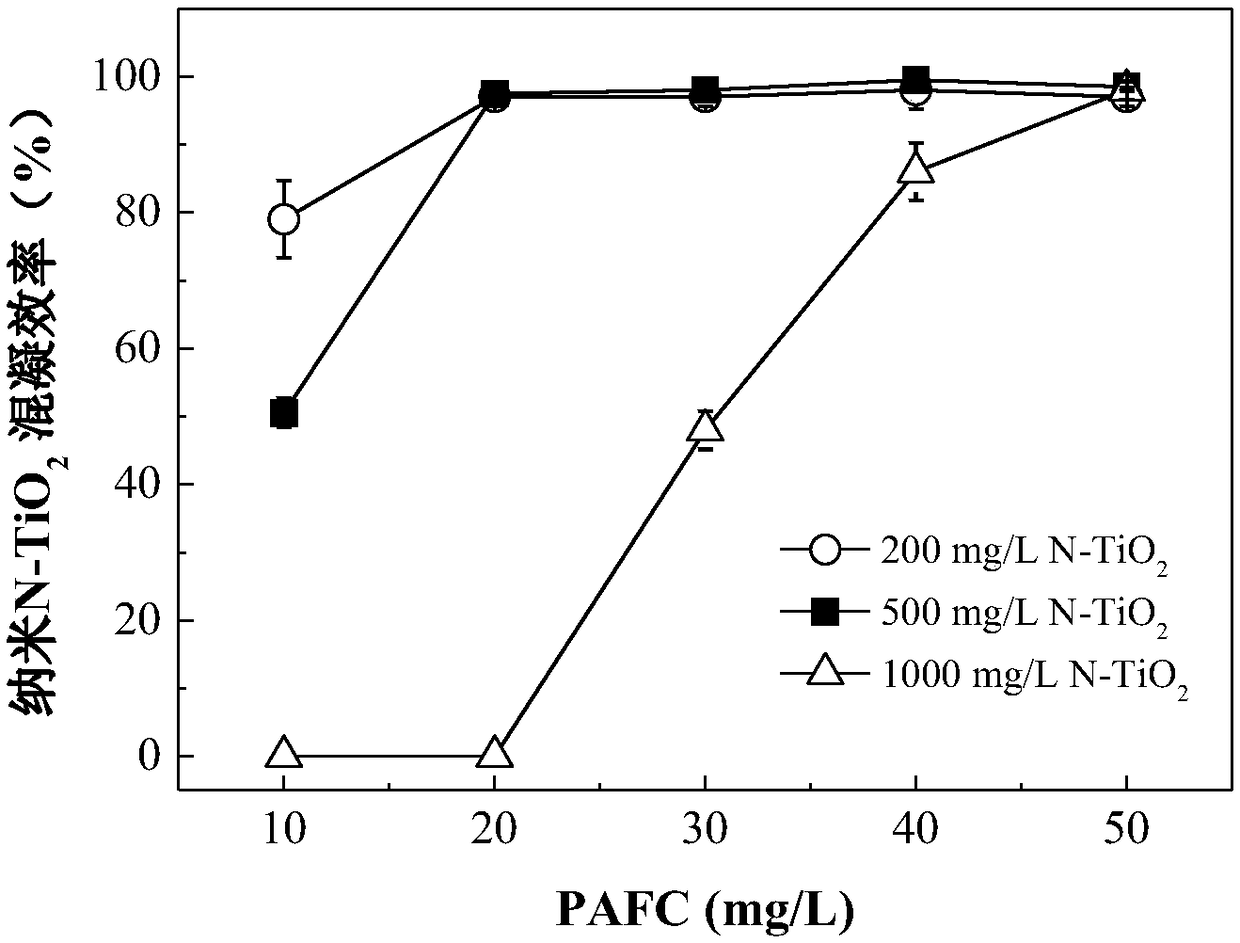
[0064] 200mg of nano-N-TiO 2 Add the powder into 1L of water, add different doses of PAFC, stir rapidly at 250rpm for 1min, and stir slowly at 40rpm for 20min. After the coagulation is completed, let it stand for 20 minutes, and determine the N-TiO by detecting the turbidity change of the supernatant (2cm below the liquid surface). 2 Whether the powder is completely coagulated. When the added PAFC is 20mg / L, N-TiO 2 The powder is fully coagulated, see figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0066] 500mg of nano-N-TiO 2 Add the powder into 1L of water, add different doses of PAFC, stir rapidly at 250rpm for 1min, and stir slowly at 40rpm for 20min. After the coagulation is completed, let it stand for 20 minutes, and determine the N-TiO by detecting the turbidity change of the supernatant (2cm below the liquid surface). 2 Whether the powder is completely coagulated. When the added PAFC is 20mg / L, N-TiO 2 The powder is fully coagulated, see figure 1 .
Embodiment 3
[0068] 1000mg of nano-N-TiO 2 Add the powder into 1L of water, add different doses of PAFC, stir rapidly at 250rpm for 1min, and stir slowly at 40rpm for 20min. After the coagulation is completed, let it stand for 20 minutes, and determine the N-TiO by detecting the turbidity change of the supernatant (2cm below the liquid surface). 2 Whether the powder is completely coagulated. When the added PAFC is 50mg / L, N-TiO 2 The powder is fully coagulated, see figure 1 .
[0069] In summary, in line with the principle of saving coagulants, 500mg of nano-N-TiO 2 The powder was added to 1L of water, and 20mg / L PAFC was added as the optimal coagulation condition.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com