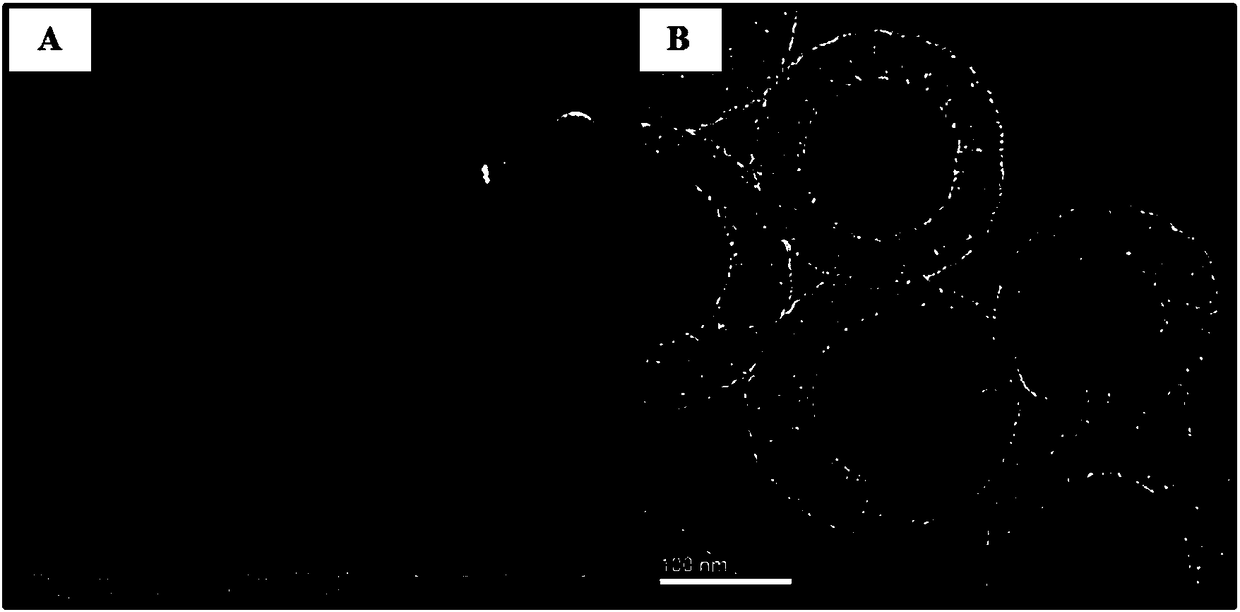
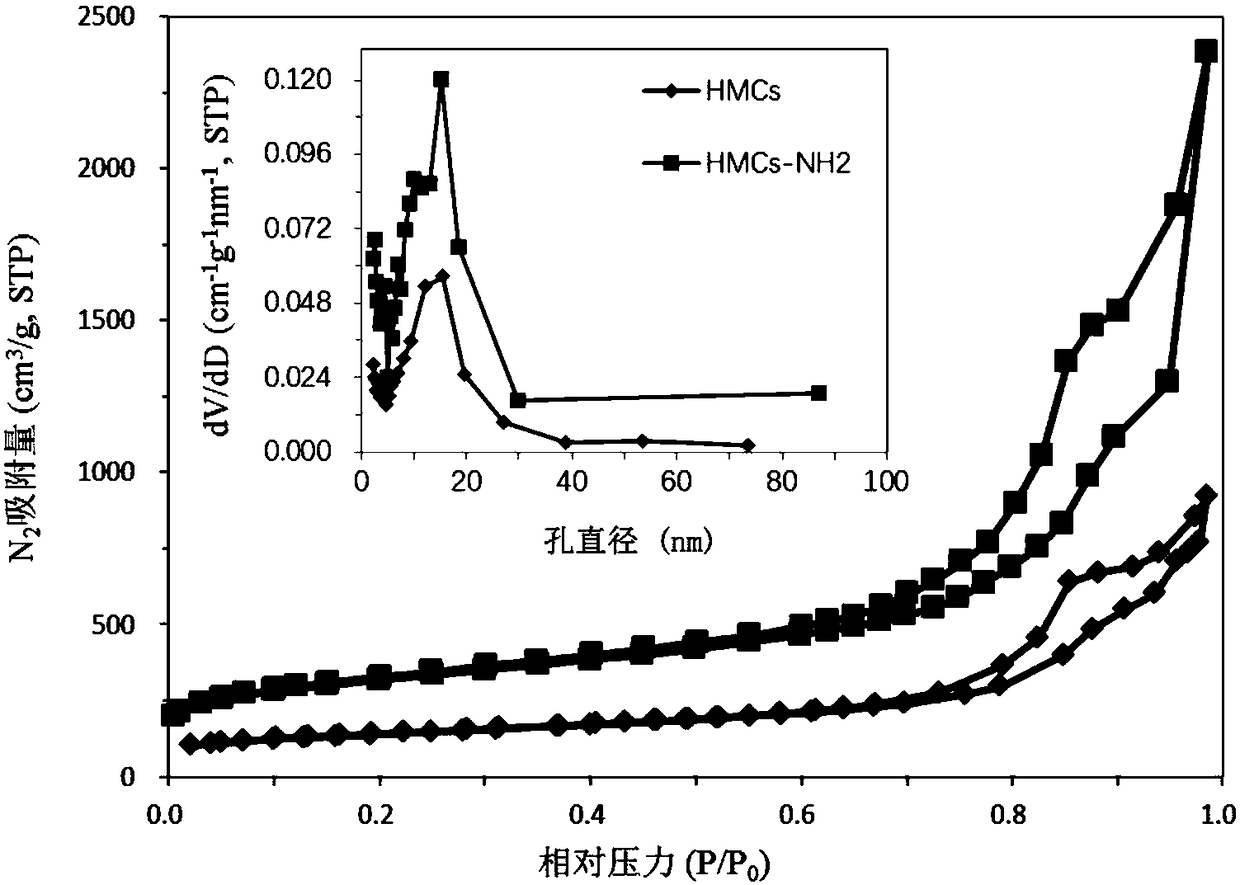
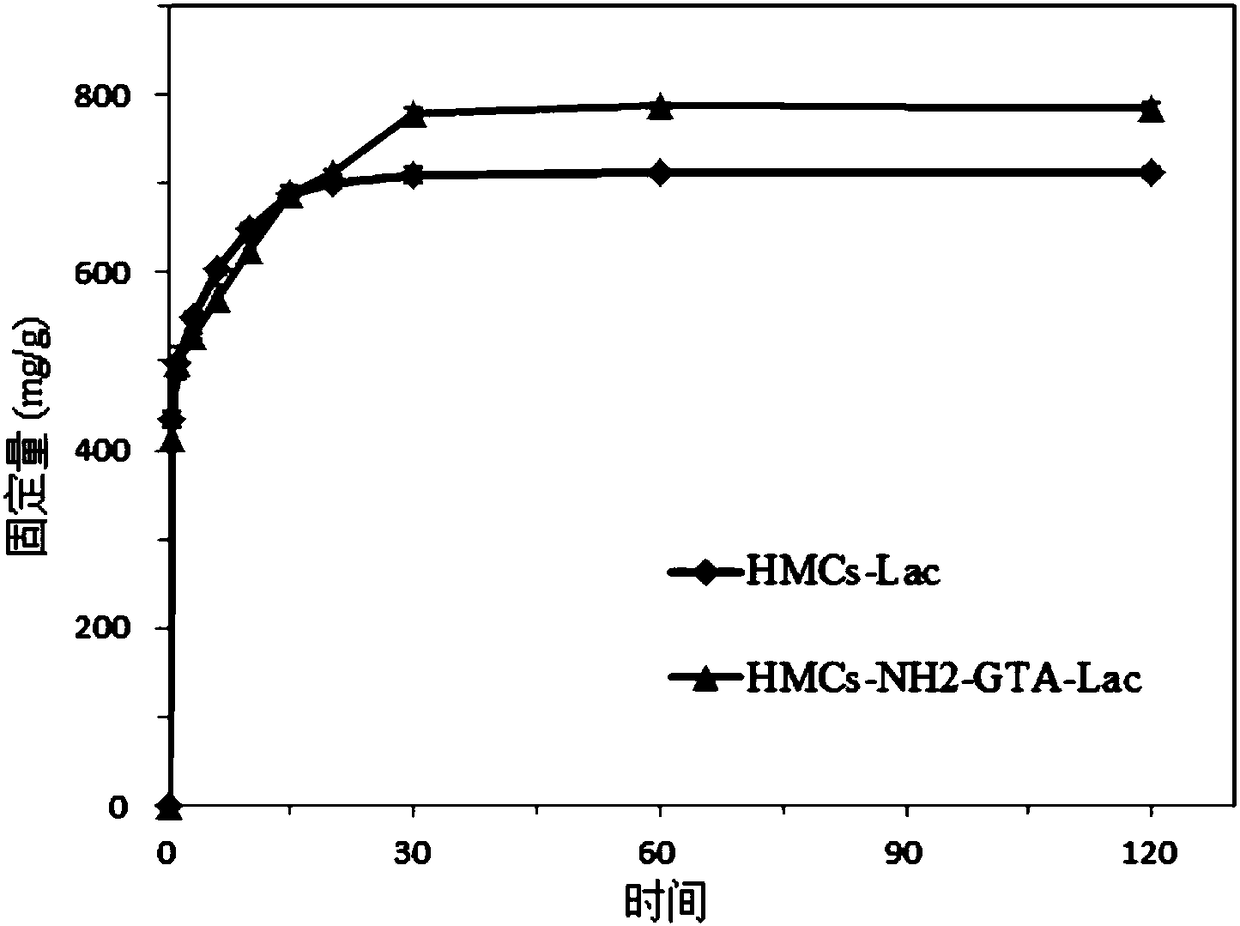
Method of removing antibiotic from water body with hollow mesoporous carbon immobilized laccase
A technology for immobilizing laccase and mesoporous carbon, applied in the direction of immobilizing on or in inorganic carriers, chemical instruments and methods, natural water treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low immobilization efficiency and instability, and achieve stable protection performance, improve efficiency, and improve the effect of transmission capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] A kind of hollow mesoporous carbon immobilized laccase (HMCs-Lac and HMCs-NH) of the present invention 2 -GTA-Lac) removes the method for tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH) in water body, comprises the following steps:
[0045] Take 20 mg of hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccase and add it to 100 mL of citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution (0.1 M, pH=4.5) containing 50 mg / L tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH), and place each mixture at 30 ° C. In a shaking incubator at 150 rpm for 3 hours, the removal of tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH) was completed.
[0046] Among them, the structure of the hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccase can be that the laccase is directly physically adsorbed in the hollow cavity of the hollow mesoporous carbon (referred to as HMCs-Lac), and the laccase utilizes glutaraldehyde, through covalent cross-linking Hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccase immobilized on hollow mesoporous carbon (HMCs-NH 2 -GTA-Lac) both.
[0047] ...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Two kinds of hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccases (inactivated HMCs-Lac and inactivated HMCs-NH 2 -GTA-Lac) and two kinds of hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccases (HMCs-Lac and HMCs-NH 2 -GTA-Lac) removes the application research of tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH) pollutant in the water body, concrete steps are as follows:
[0086] Two hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccases (inactivated Cs-Lac and inactivated HMCs-NH 2 -GTA-Lac) and two non-inactivated hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccases (HMCs-Lac and HMCs-NH 2 -GTA-Lac) each 20mg was added to 100mL citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution (0.1M, pH=4.5) containing 50mg / L tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH) The shaking incubator was removed for 3 hours, during which samples were taken at different times to determine the remaining concentration of TCH.
[0087] The concentration of TCH was measured at 357 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (UV-2550; Shimadzu company, Japan).
[0088...
Embodiment 3
[0093] A kind of method utilizing hollow mesoporous carbon immobilized laccase of the present invention to remove ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (CPH) in water body may further comprise the steps:
[0094] Take 20 mg of hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccase and add it to 100 mL of citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution (0.1M, pH=4.5) containing 50 mg / L ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (CPH), and place each mixture in 30° C., 150 rpm in a shaking incubator for 3 hours to complete the removal of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (CPH).
[0095] Among them, the structure of hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccase can be that laccase is directly physically adsorbed in the hollow cavity of hollow mesoporous carbon (referred to as HMCs-Lac), and laccase is immobilized by covalent cross-linking using glutaraldehyde. Hollow mesoporous carbon immobilized laccase (HMCs-NH 2 -GTA-Lac) both. The preparation method of the above two hollow mesoporous carbon-immobilized laccases with dif...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com