Method for detecting heterogeneity of mitochondrial genome A3243G site
A mitochondrial genome and site technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of complex methods for the heterogeneity of the mitochondrial genome A3243G site, and achieve the effect of detection, high specificity and accurate detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
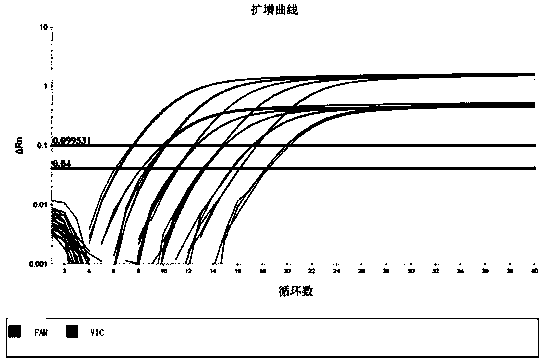
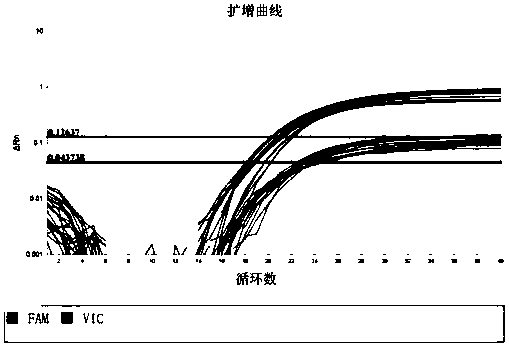
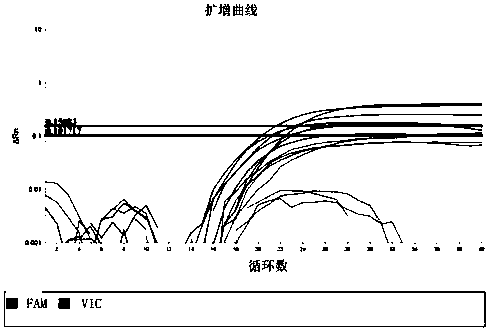
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 1. Extraction of peripheral blood or tissue genomic DNA
[0034] 1. Isolation of Peripheral Blood Leukocytes
[0035] (1) Take 5 mL of cubital venous blood from the patient, anticoagulate with EDTA, and centrifuge at 2500 rpm for 10 min;
[0036] (2) Carefully suck off the upper layer of plasma, add 3 times the volume of red blood cell lysate to the lower layer of blood cell pellet, shake well, and ice-bath for 15 minutes.
[0037] (3) Centrifuge at 2 500 rpm for 10 min, discard the supernatant, and repeat step 2 once.
[0038] (4) Centrifuge at 3 000 rpm for 10 min, discard the supernatant, and obtain white blood cells.
[0039] 2. Extraction of leukocyte or tissue DNA
[0040] (1) Take white blood cells, add 600 μL STE lysis buffer, 10 μL proteinase K and 2 μL RNase A, digest at 55°C for 20 minutes (the extraction of tissue DNA is similar to that of white blood cells, cut it with scissors before digestion);
[0041] (2) After the lysate is cooled to room temperatu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com