Tobacco spice prepared by fermenting fructus holboelliae latifoliae by using microorganisms and application thereof
A technology of microbial fermentation and tobacco flavoring, applied in the field of tobacco flavoring, can solve the problems of no public reports of lysobacterium, and achieve the effects of facilitating large-scale industrial production, increasing the richness of aroma, and increasing the sweet and sour feeling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] 1. Cultivation of Lysobacterium C8-1 strain
[0026] (1) Slant culture: inoculate Lysobacterium C8-1 in the slant medium; the slant medium is: glucose 0.5g; yeast extract 0.5g; peptone 0.5g; acid hydrolyzed casein 0.5g; soluble starch 0.5g ; Sodium pyruvate 0.3g; Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.3g; Magnesium sulfate 0.05g; Agar 15g; Distilled water 1000mL, pH7.2;
[0027] (2) Seed culture: pick part of the mycelium from the inclined plane and insert it into the seed medium, and shake the flask for 36 hours. Seed medium: dextrin 120g; soybean powder 40g; yeast extract 2g; tryptophan 0.5g; β-alanine 5g; magnesium sulfate 0.5g; ammonium phosphate 0.2g; ℃.
[0028] 2. Fermentation of Lysobacterium C8-1 strain to prepare tobacco flavor
[0029] Dry and pulverize the August melon, add twice the weight of water, mix evenly, inoculate the activated bacterium liquid of lysobacterium, shake culture for fermentation, the inoculum amount is 15% of the weight of the August melon...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Repeat implementation 1, with the following differences: the added amount of lysobacterium activated bacterial liquid is 5% of August melon weight, and the fermentation time is 24h.
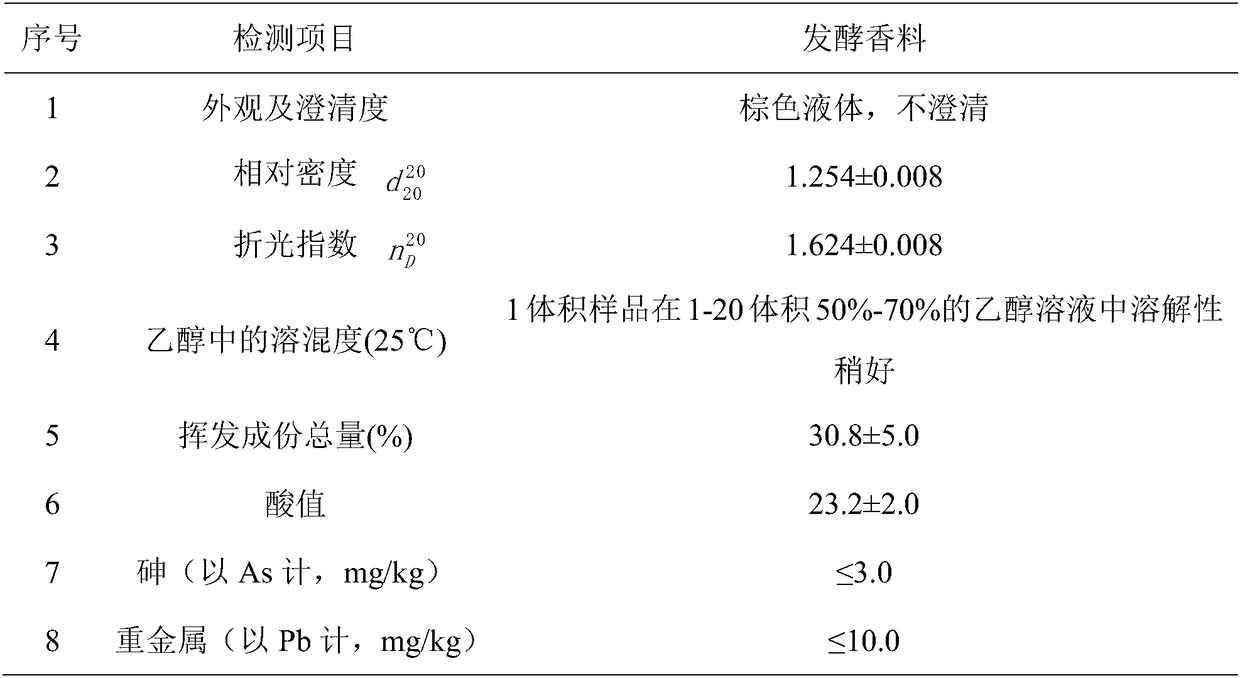
[0042] 1. Product characteristics and physical and chemical properties
[0043] The resulting tobacco flavor was a brown liquid, not clear. The physical and chemical properties of the product are shown in Table 3.
[0044]Table 3 Physicochemical indicators of August melon spices fermented by lysobacteria
[0045]
[0046] 2. Cigarette Flavoring Experiment
[0047] Take 0.1 g of flavoring for tobacco, dilute it 50 times, and evenly spray it in the 50 g group without adding fragrant leaves.
[0048] The results of flavoring showed that the spices fermented by Lysobacterium lysobacter in August melon were significantly different from the control, with more prominent sweet and sour taste, obvious effect of promoting body fluid, reducing miscellaneous gas and pleasant aftertaste. The eva...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Repeat implementation 1, with the following differences: the amount of lysobacterium activated bacterial liquid added is 20% of the August melon weight, and the fermentation time is 48h.
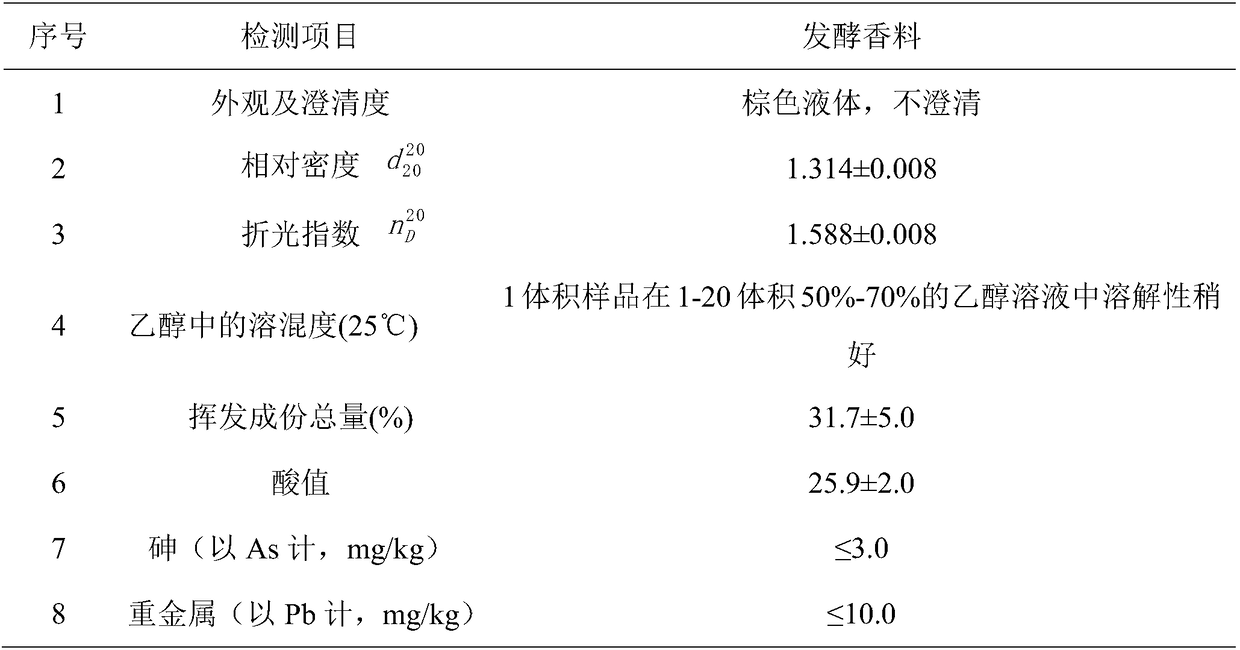
[0054] 1. Product characteristics and physical and chemical properties
[0055] The resulting tobacco flavor was a brown liquid, not clear. The physical and chemical properties of the product are shown in Table 5.
[0056] Table 5 Physicochemical indicators of August melon spices fermented by lysobacteria
[0057]
[0058] 2. Cigarette Flavoring Experiment
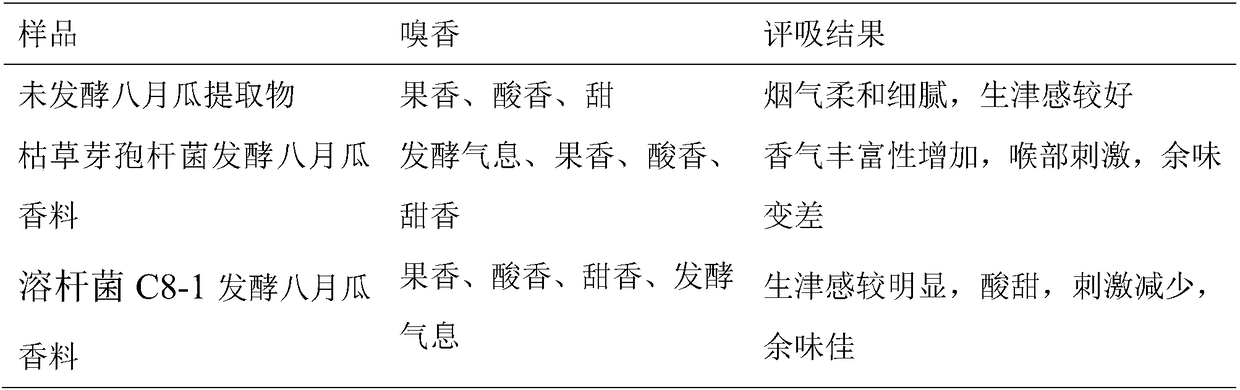
[0059] Take 0.15g of flavoring for tobacco, dilute it 50 times, and evenly spray it in the 50g group without adding fragrant leaves.
[0060] The results of flavoring showed that the spice fermented by Lysobacterium Augustus was significantly different from the control, with obvious sweet and sour taste, soft and delicate smoke, and reduced oral and nasal irritation. The evaluation results are shown in Table 6.
[0061] Ta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com