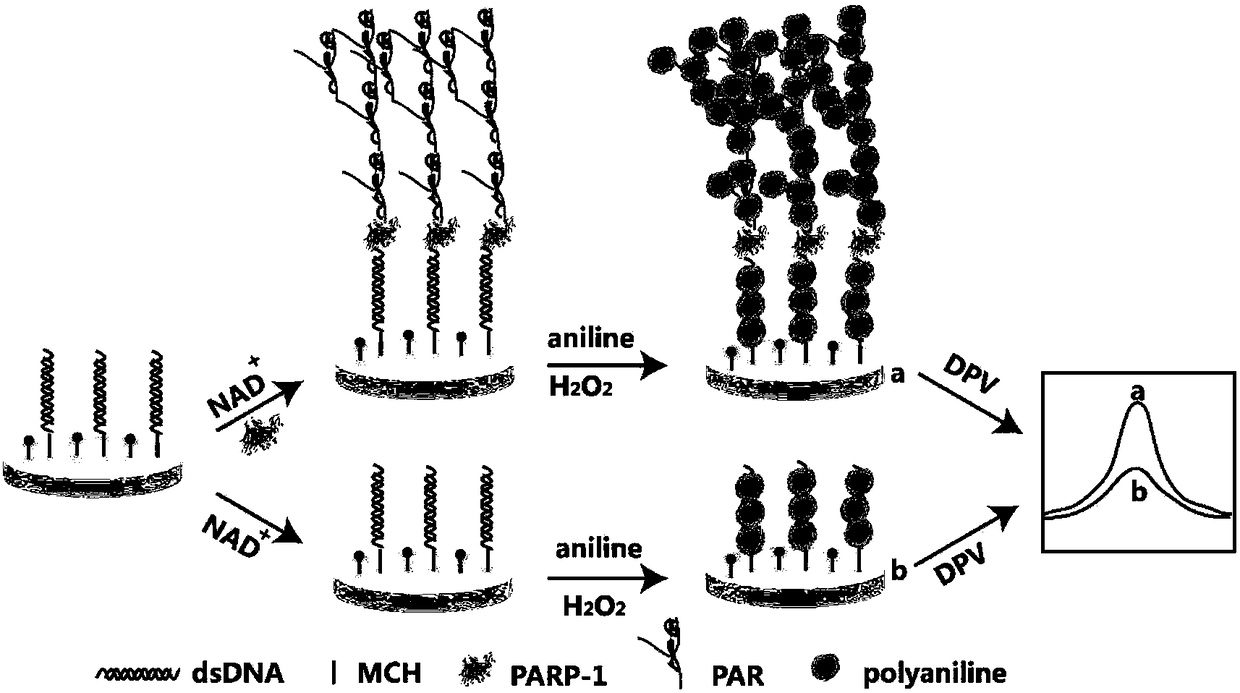
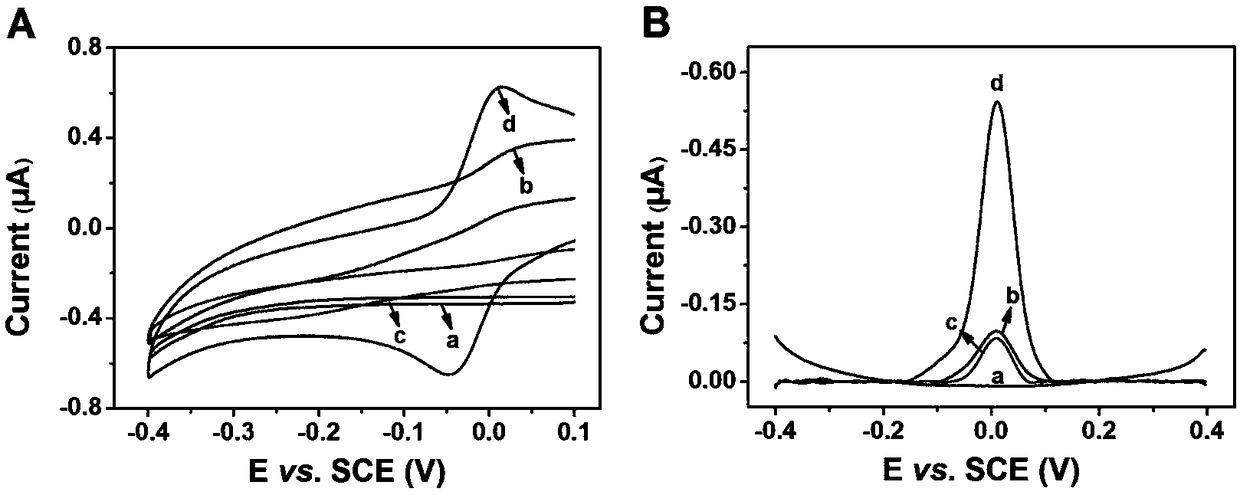
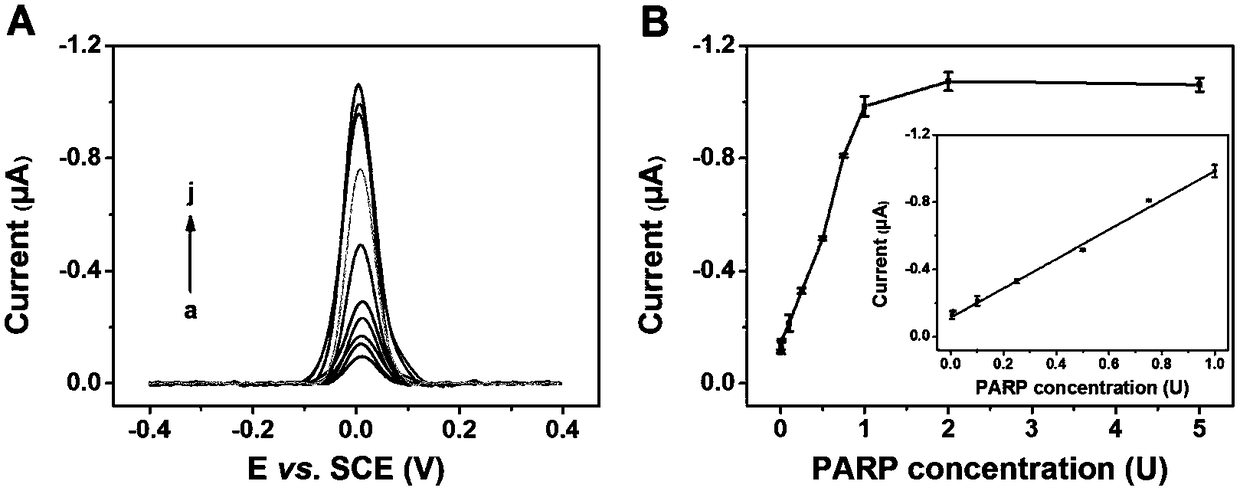
Method for quantitative detection of activity of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 (PARP-1) based on electrochemical sensing electrode with deposited polyaniline
A polyadenosine diphosphate-ribose, quantitative detection technology, applied in the field of biosensing, can solve the problems of high cost, affecting the measurement results, high requirements for instruments, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost and improved sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] The electrochemical sensing electrode based on polyaniline deposition quantitatively detects PARP-1 activity, and the detection steps are:
[0016] 1) Soak the gold electrode in piranha washing solution (H 2 o 2 and concentrated H 2 SO 4 The volume ratio is 3:7), after soaking for 10 minutes and cleaning, polishing with 0.3 μm and 0.05 μm alumina powder, rinsed with ultrapure water, and dried under nitrogen atmosphere to obtain a cleaned electrode;
[0017] 2) Dilute the specific double-stranded DNA-1 with a sulfhydryl group modified at the 5' end in 40-50 μL of fixative solution and 0.5-2 μL of tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) to prepare a final concentration of 0.5-2 μM Then add the prepared sample dropwise to the cleaned electrode surface, cover the beaker, and assemble it overnight at room temperature, then incubate the electrode in 0.5-2mM mercaptohexanol solution for 0.5-1 hour, and rinse with PBS buffer solution Finally, add specific double-stranded DNA-2...
Embodiment 2
[0028]The difference from Example 1 is: different concentrations of PARP (U, 4nM): (a) 0 , (b) 0.05 , (c) 0.1 , (d) 0.3 , (e) 0.5 , (f) 0.75 , ( g) 1 , (h) 2 , (i) 3, the UV-visible light curve obtained, it can be seen that within the range of 0-3 mmol, PARP has a good linear relationship between 0.05 U and 1 U. It can be seen that the sensitivity is greatly improved by the method of the present invention. The invention does not need to prepare complex materials, and has the advantages of low cost, quickness and simplicity. Moreover, the method can be used in the detection of actual samples and has certain clinical significance.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Different from Example 1, a certain amount of benzamide inhibitor is added after step 4), and the electrochemical signal of benzamide inhibiting PARP-1 electrochemical sensor is measured, such as Figure 4 A shows the standard curve diagram of the relationship between electrochemical signal and benzamide concentration after treating 0.5 UPARP-1 with different concentrations of benzamide. IC drawn from the figure 50 The value is 11.51 μM, which is consistent with the previously reported literature results. Therefore, this method can be used to evaluate and screen PARP-1 inhibitors, which is of great significance for the discovery of new anticancer drugs.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com