A Model Parameter Identification Method for Electromechanical Servo System with Limited Rotation Angle
A technology of electromechanical servo system and model parameters, applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large position rotation angle of electromechanical servo system, position drift of electromechanical servo system, exceeding position limit, etc. The effect of convenience, simple structure and high safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0021] Specific implementation mode 1: The specific process of the model parameter identification method of a limited rotation angle electromechanical servo system in this implementation mode is as follows:
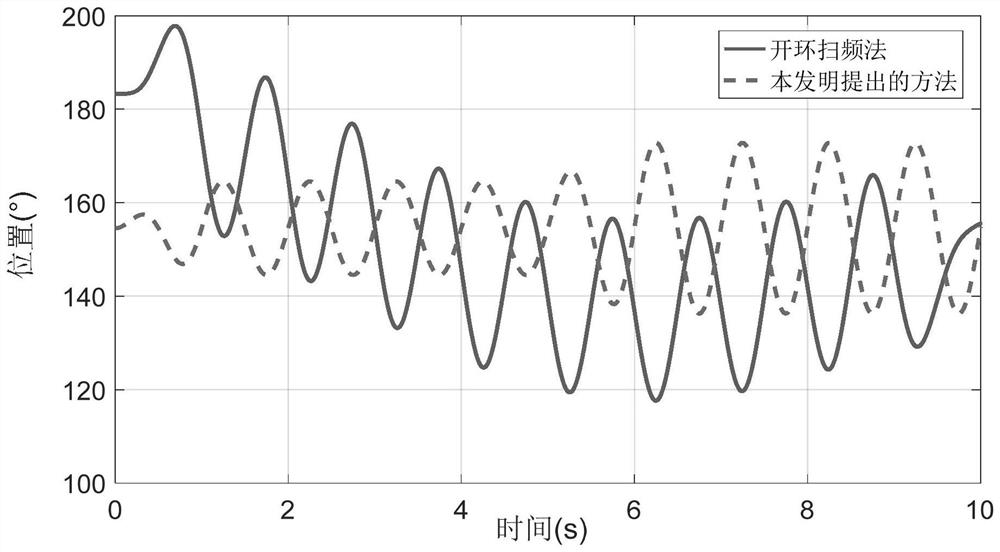
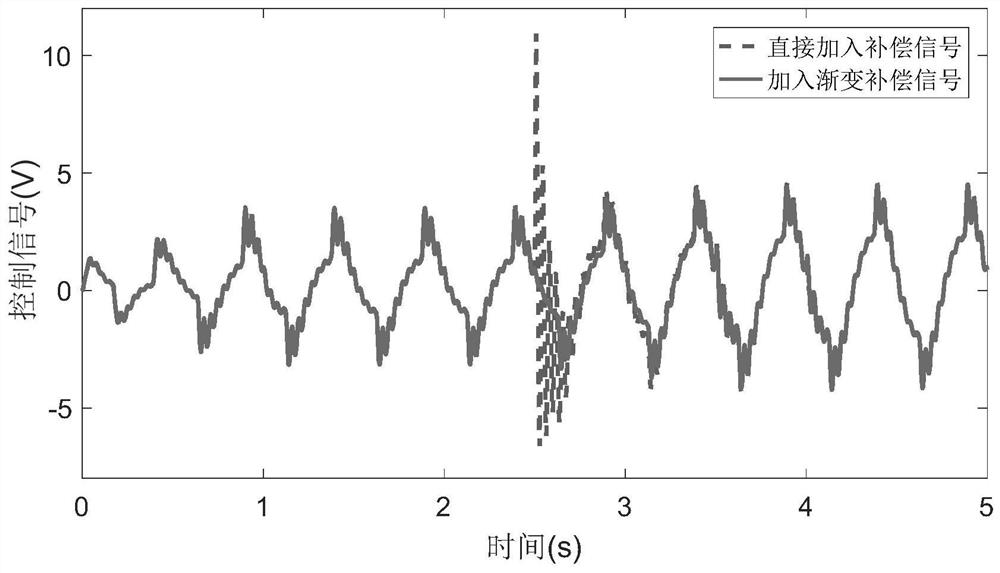
[0022] The invention mainly aims at the problem that the electromechanical servo system with limited rotation angle has position drift, direction is uncertain, and may exceed the limit when the open-loop sinusoidal frequency sweep is used to obtain model parameters, and thus a limited rotation angle is proposed. Model parameter identification method for electromechanical servo systems.
[0023] Step 1, establish the mechanism model of the electromechanical servo system according to the structure of the electromechanical servo system, that is, the open-loop transfer function model G(s) of the electromechanical servo system;
[0024] Step 2. In the closed-loop state of the electromechanical servo system, the input signal amplitude is A r , a sinusoidal signal with a freque...
specific Embodiment approach 2
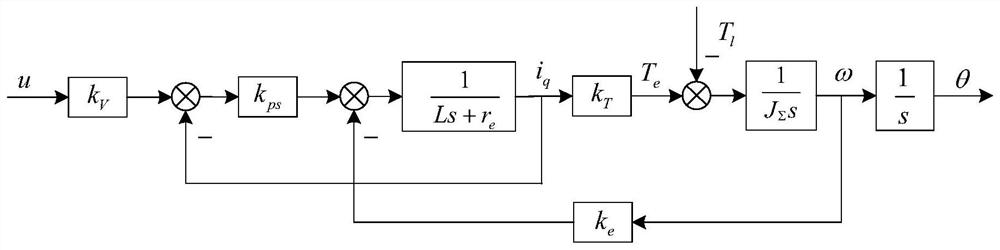
[0032] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: in the step one, according to the structure of the electromechanical servo system ( figure 1 ) to establish the mechanism model of the electromechanical servo system, that is, the open-loop transfer function model G(s) of the electromechanical servo system; the specific process is:
[0033] The mechanism model of electromechanical servo system is:
[0034]
[0035] In the formula, i d ,i q is the direct-axis current and quadrature-axis current in the synchronously rotating d-q coordinate system, d is the direct axis, q is the quadrature axis; ω r is the mechanical angular velocity of the motor; r e is the equivalent resistance of the motor; L is the armature inductance of the motor; J Σ is the total moment of inertia of the shaft system; D is the friction coefficient when the motor rotates; T l is the disturbance torque, including friction torque and fluctuating torq...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0060] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in the step 2, in the closed-loop state of the electromechanical servo system, the input signal amplitude is A r , a sinusoidal signal with a frequency of f, use the correlation identification method to obtain the actual control signal amplitude A at this frequency point u ;
[0061] The specific process is:
[0062] A simple proportional controller is designed to operate the electromechanical servo system in a closed loop. On the premise of ensuring the stability of the system, the structure and control accuracy of the controller do not affect the subsequent steps of the present invention.
[0063] Although it is theoretically possible to control the actual control signal amplitude A at the frequency point f u However, when the system is closed-loop, the input of the closed-loop controller becomes the deviation between the input signal r and the actual position θ, so the actual control...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com