A low fluid loss secondary cross-linked gel modifier
A technology of secondary cross-linking and adjusting the displacement agent, which is applied in the drilling compositions, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems such as difficulty in effectively plugging fracture channeling channels, poor injection ability, and difficulty in gel formation, etc. The effect of reliable synthesis principle, reduced economic feasibility and convenient on-site configuration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
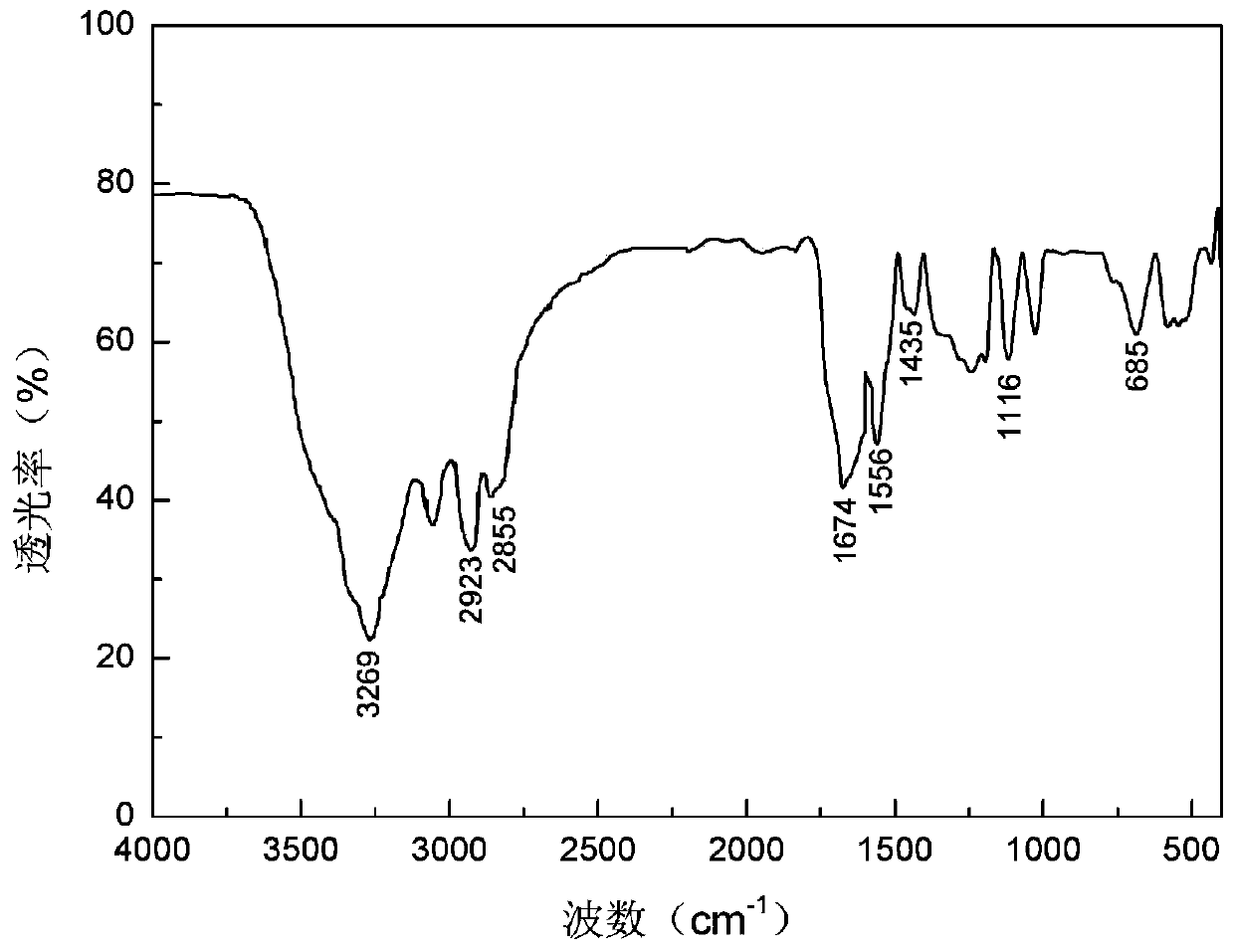
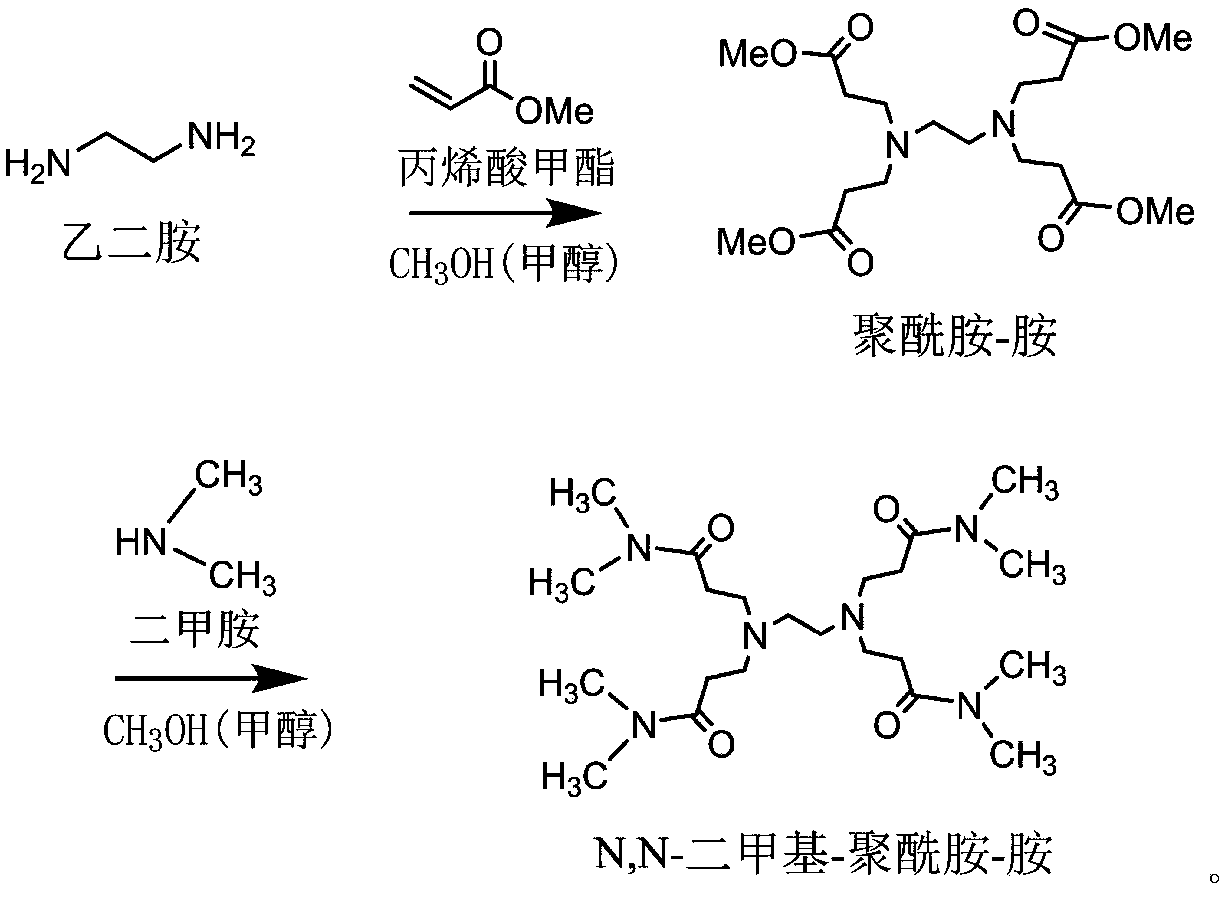
[0026] N, the preparation steps of N-dimethyl-polyamido-amine are as follows:
[0027] Step 1. Dissolve 17.2g of methyl acrylate in 80ml of methanol and add it to a three-necked bottle with a magnetic rotor under ice-salt bath conditions. Turn on the magnetic stirrer. When the solution of methyl acrylate in the three-necked bottle is cooled When the temperature reaches 0-2°C, slowly add 3.3g of ethylenediamine dropwise into the methanol solution of methyl acrylate under the stirring condition of rotating speed of 90-120r / min. The reaction was slowly stirred for at least 48 hours under the conditions, and then the reactant was subjected to two-stage vacuum distillation at 40°C to remove excess methyl acrylate and methanol (recycling of methanol) to obtain a colorless transparent liquid, which is polyamide- Amine, yield 95%; Step 2, dissolving 11.4g of polyamide-amine in 60ml of methanol, ice-salt bath conditions, adding to a three-necked bottle with a magnetic rotor, turning on...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Using the N,N-dimethyl-polyamide-amine prepared in Example 1 as an activator, a secondary cross-linked gel control agent based on partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide, the component ratio is: partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM) 0.25-0.35%, N,N-dimethyl-polyamide-amine 0.05%, hexamethylenetetramine 0.07%, phenol and formaldehyde mixture 0.25%, and the rest is water or brine.
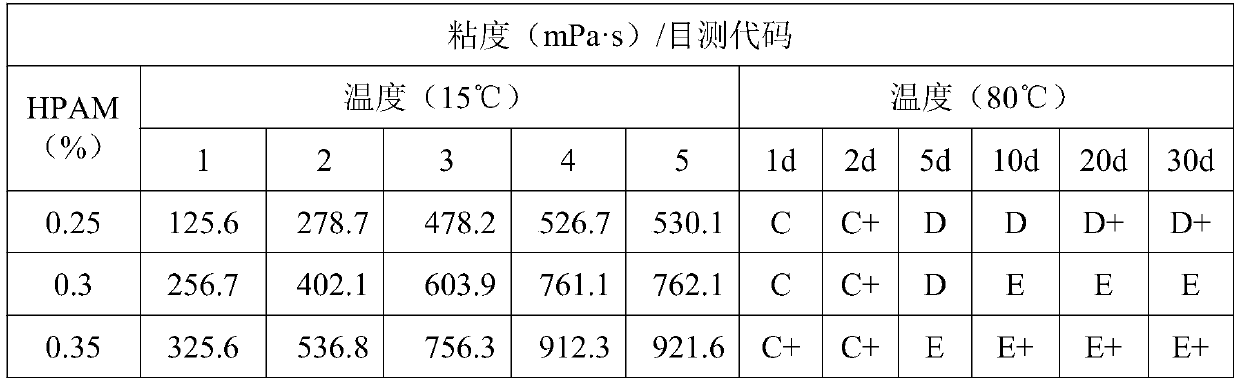
[0032] After configuring the displacing agent into a gel base liquid, observe at 15°C for 6 hours to test the relationship between the viscosity and time of the primary cross-linking system; The gel code method was used to determine the relationship between the strength of the secondary gel and time. The measurement results are shown in Table 1. It can be seen that under the condition of 15°C, the primary gelation time is 4 hours, and the secondary gelation is carried out at 80°C for 20 days to form a final gel. The concentration of HPAM used is 0.25-0.35%, and the final gelation strength co...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Using the N,N-dimethyl-polyamide-amine prepared in Example 1 as the activator, the secondary cross-linked gel regulating agent based on the hydrophobic association polymer, its component ratio is: hydrophobic association polymer (HAPAM) 0.25-0.4%, N,N-dimethyl-polyamide-amine 0.03%, hexamethylenetetramine 0.10%, phenol and formaldehyde mixture 0.30%, and the rest is water or brine.
[0040] After configuring the displacing agent into a gel base liquid, observe the relationship between the viscosity and time of the primary cross-linking system at 20°C for 5 hours; then let the primary gel system stand at 90°C The glue code method was used to measure the relationship between the strength of the secondary gel and time, and the results are shown in Table 3. It can be seen that at 20°C, the first gelation time is 4h, and the second gelation is 30d at 90°C to form a final gel. The concentration of HAPAM used is 0.25-0.4%, and the final gelation strength code is F-G . Refer ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| core plugging rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com