Nanometer zero-valent iron loaded fiber and preparation method and application thereof
A nano-zero valent iron and fiber technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of limited application, difficult separation, secondary pollution of water bodies, etc. Effects of surface area reduction, strong adsorption and reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: nanometer zero valent iron loaded fiber
[0028] Under the effect of nitrogen protection, the slurry with a beating degree of 10 ° SR and the ferrous sulfate solution with a molar concentration of 0.2mol / L are 1:20g / ml according to the dry mass volume ratio of the slurry to the ferrous sulfate solution Mix and react on a magnetic stirrer at a temperature of 30°C and a stirring speed of 400r / min for 2h. After the reaction was complete, an excess of sodium borohydride solution with a molar concentration of 0.2 mol / L was added to the Erlenmeyer flask at a speed of 3 ml / min, and the stirring reaction was continued for 1 h at the same temperature at a speed of 700 r / min. After the reaction is complete, the pulp is washed with distilled water, filtered and then freeze-dried to obtain the desired nanometer zero-valent iron-loaded fiber.
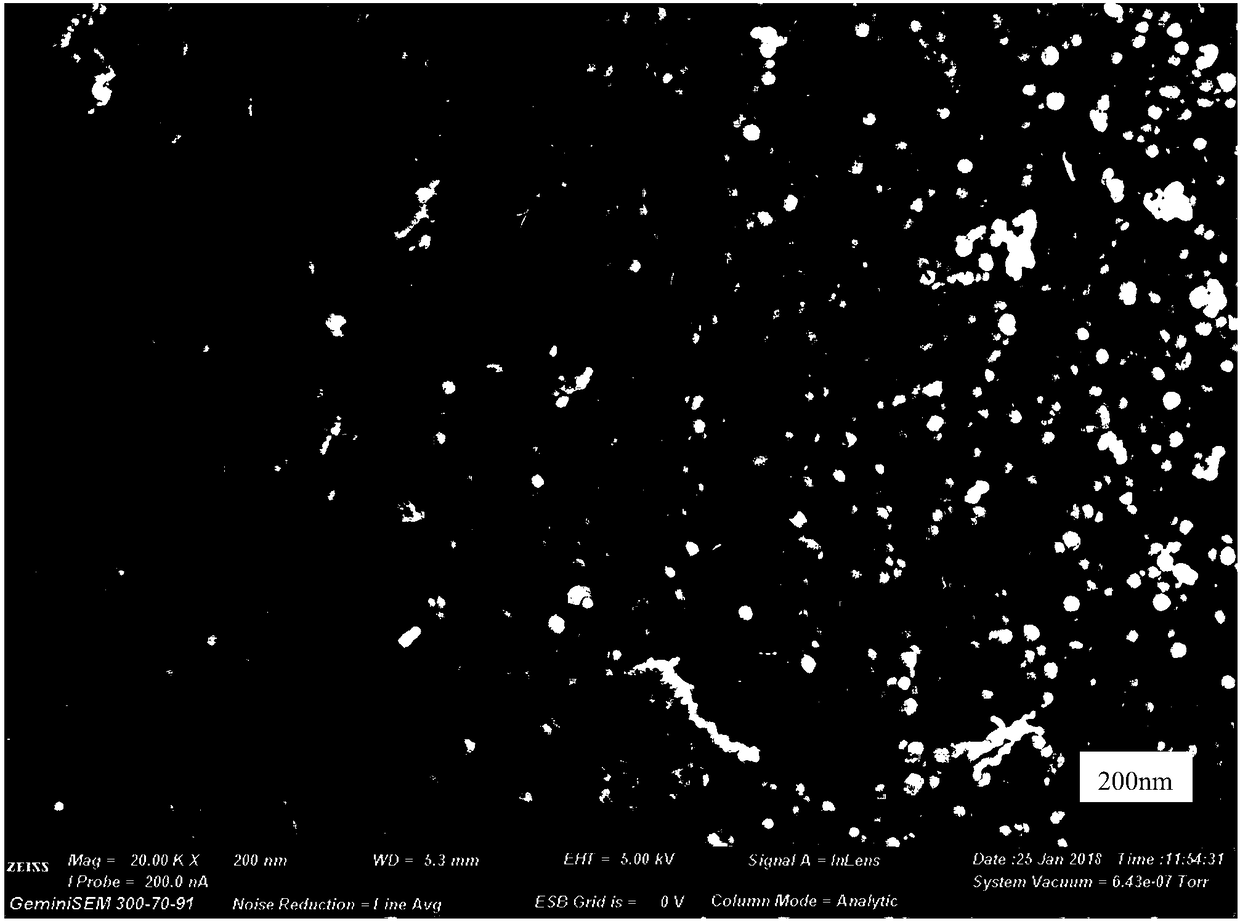
[0029] figure 1 It is a scanning electron micrograph of the nanometer zero-valent iron-loaded fiber prepared in Example 1. ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2: nanometer zero valent iron loaded fiber
[0032] Under the effect of nitrogen protection, the ferrous sulfate solution whose beating degree is 20 ° SR and the molar concentration is 0.4mol / L is 1:40g / ml according to the absolute dry mass volume ratio of the slurry and ferrous sulfate solution Mix and react on a magnetic stirrer at a temperature of 35°C and a stirring speed of 500r / min for 3h. After the reaction was complete, an excess of sodium borohydride solution with a molar concentration of 0.3 mol / L was added to the Erlenmeyer flask at a rate of 5 ml / min, and the stirring reaction was continued for 1.5 h at the same temperature at a rate of 800 r / min. After the reaction is complete, the pulp is washed with distilled water, filtered and then freeze-dried to obtain the desired nanometer zero-valent iron-loaded fiber.
[0033] It can be seen from the scanning electron microscope image and Mapping image of the nano-zero-valent iron-loaded fiber prepared ...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: nanometer zero valent iron loaded fiber
[0035] Under the effect of nitrogen protection, the slurry with a beating degree of 30 ° SR and the ferrous sulfate solution with a molar concentration of 0.6mol / L are 1:60g / ml according to the dry mass volume ratio of the slurry and the ferrous sulfate solution Mix and react on a magnetic stirrer at a temperature of 40°C and a stirring speed of 600r / min for 3h. After the reaction was complete, an excess of sodium borohydride solution with a molar concentration of 0.4 mol / L was added to the Erlenmeyer flask at a speed of 7 ml / min, and the stirring reaction was continued for 2 h at the same temperature at a speed of 800 r / min. After the reaction is complete, the pulp is washed with distilled water, filtered and then freeze-dried to obtain the desired nanometer zero-valent iron-loaded fiber.
[0036] It can be seen from the scanning electron microscope image and Mapping image of the nano-zero-valent iron-loaded fibe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com