Drug target point based on mycobacterium tuberculosis ubiquitin ligase PafA and application thereof
A technology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is applied in the field of biomedicine to achieve the effects of growth inhibition, small side effects, and increased success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
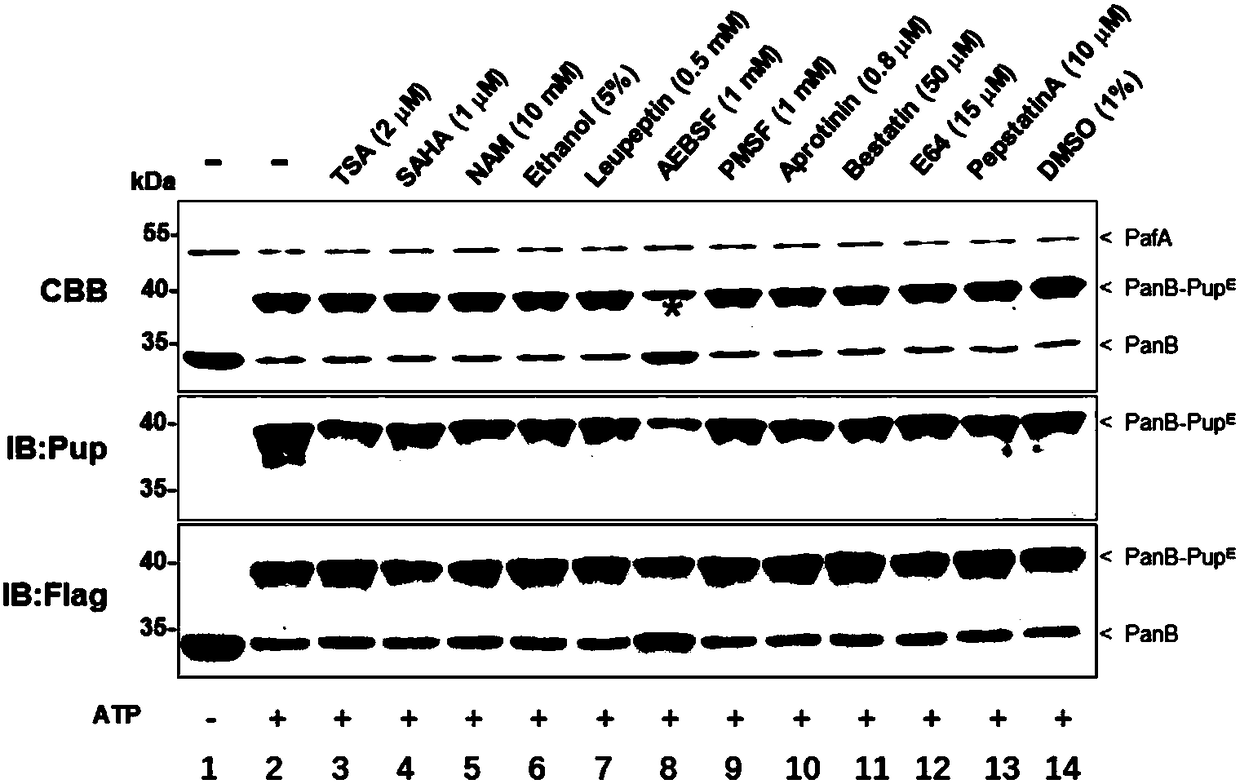
[0027] Example 1. Screening of inhibitors of ubiquitin-like ligation reaction against Mycobacterium tuberculosis ubiquitin-like ligase
[0028] In order to screen for inhibitors against the ubiquitin-like ligation reaction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ubiquitin-like ligase, a ubiquitin-like ligation reaction system was constructed in vitro to facilitate screening. The specific implementation is as follows:
[0029] 1) The Mycobacterium tuberculosis ubiquitin-like ligase PafA required for the construction of the enzymatic reaction (the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No. 1), the substrate protein PanB, and the ubiquitin-like protein Pup E. That is, the corresponding fragment was obtained by PCR from the genome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain (gifted by Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), cloned and connected to PET28a, and a Flag tag was introduced into the C-terminus of the substrate protein PanB to facilitate subsequent detection. ...
Embodiment 2
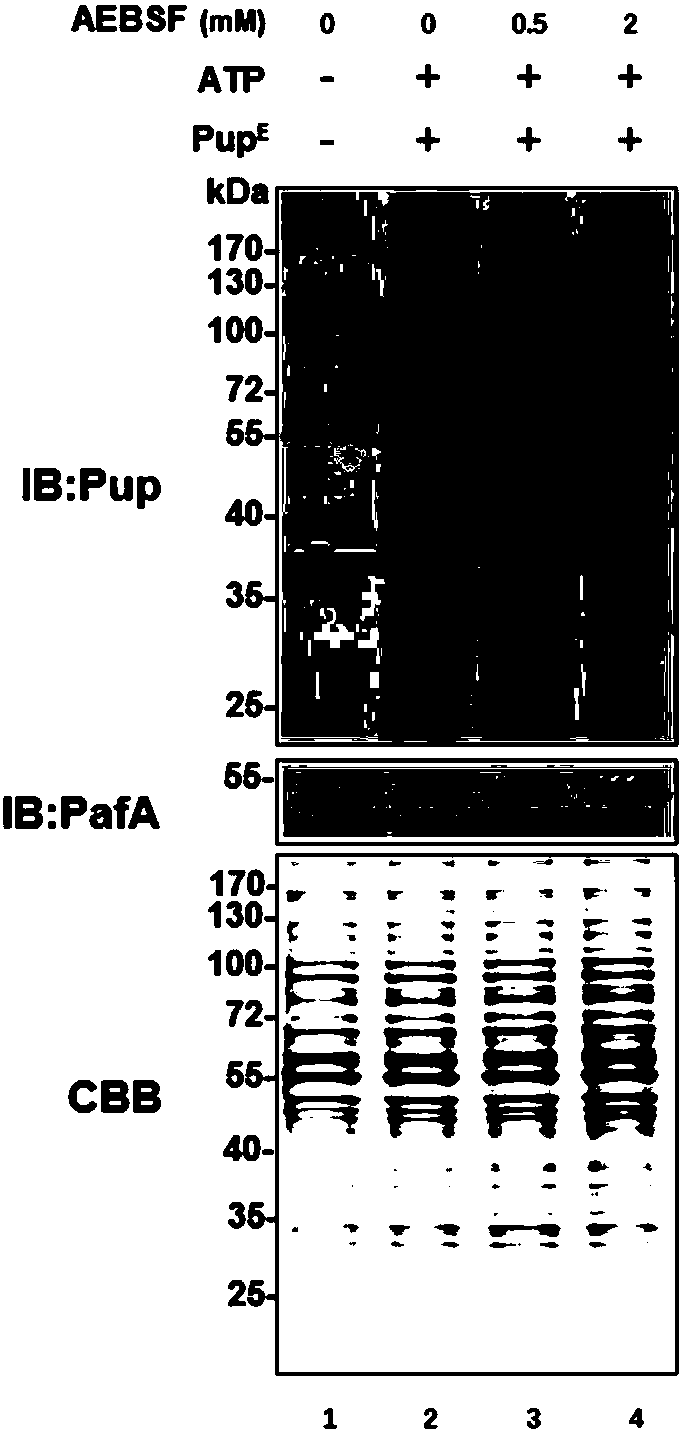
[0041] Example 2. The enzymatic mechanism of the small molecule inhibitor AEBSF inhibiting the enzymatic activity of the ubiquitin-like ligase PafA
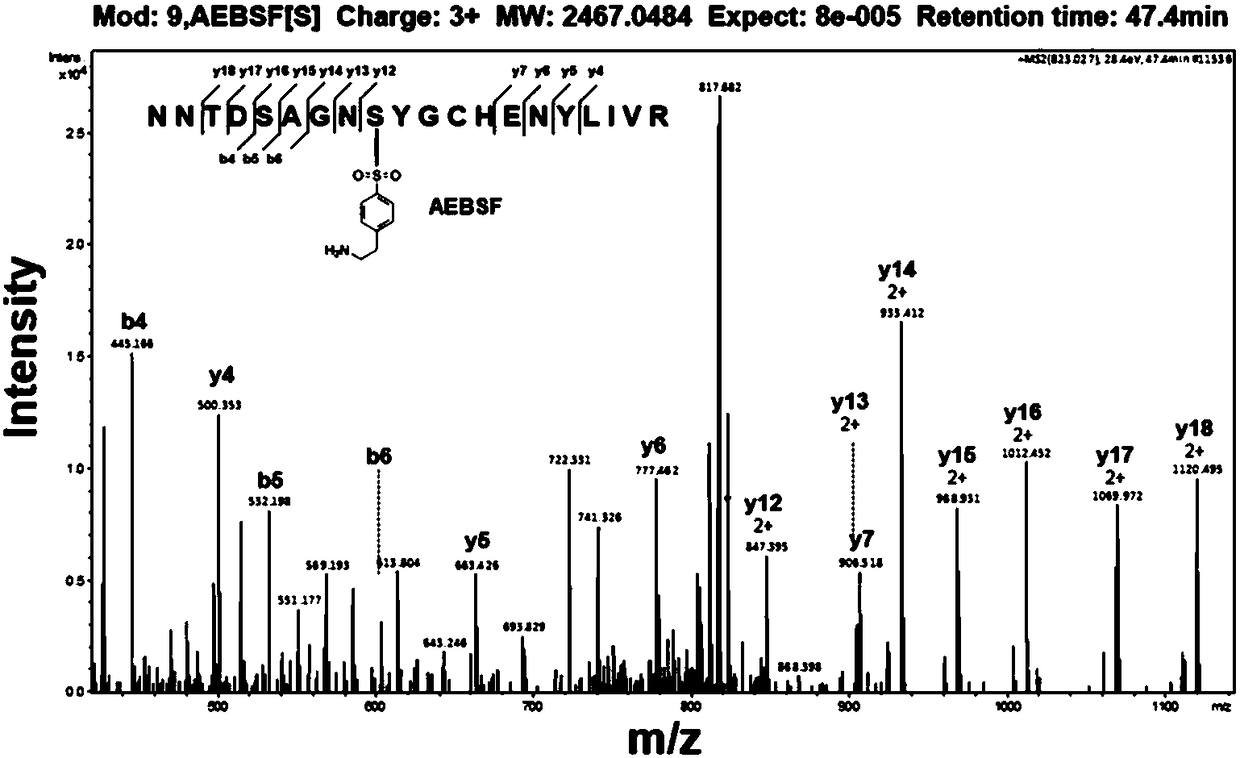
[0042] In order to analyze the enzymatic mechanism of the small molecule inhibitor AEBSF inhibiting the ubiquitin-like ligase PafA, taking into account that AEBSF, as a serine protease inhibitor, can be covalently linked to the serine of the enzyme to inhibit the enzyme activity, we put the ubiquitin-like ligase The ubiquitin ligase PafA (0.5μM) was co-incubated with the small molecule AEBSF (1mM), and then identified by mass spectrometry, it was found that the serine 119 position of the ubiquitin ligase was linked to AEBSF, and the results were as follows image 3 shown.
[0043] In order to prove that serine 119 is involved in the enzymatic mechanism of the small molecule inhibitor AEBSF to inhibit the ubiquitin-like ligase PafA, we mutated serine 119 into alanine and phenyl ring family amino acids, and the mutation to alanin...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3. Screening of small molecule inhibitors that non-covalently bind to the serine region at position 119 of PafA
[0045] To screen small-molecule inhibitors that non-covalently bind to the Ser119 region of PafA, we first performed a local sequence alignment of the ubiquitin-like ligases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Corynebacterium glutamicum , the result is as Image 6 shown. We found that the sequence of serine 119 was highly conserved in the two strains, and this region happened to be located near the pocket of ubiquitin-like ligase binding ubiquitin-like protein Pup. Because the ubiquitin-like ligase structure currently available is only that of Corynebacterium glutamicum, and it is highly conserved with the ubiquitin-like ligase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in this region, we take the use of Corynebacterium glutamicum The ubiquitin-like ligase PafA was docked with small molecule compounds, and we obtained three small molecules with the best compu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com