Method for controlling extension of lateral branches of cut chrysanthemum
A technology for cut chrysanthemum and side branches is applied in the field of controlling the elongation of side branches of cut chrysanthemum, can solve the problems of affecting the quality of cut flowers, increase production cost, restrict efficient production of cut chrysanthemum, etc., and achieves easy operation, reduced frequency and intensity, and shortened and reduced number of chrysanthemums. and the effect of length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] This embodiment relates to a method for controlling the growth of side branches of cut chrysanthemum by regulating the ratio of red light and far-red light, including the following steps:
[0041] 1) Rooting culture
[0042] A. Cut the top tip of the mother plant of 'Shenma' as cuttings, keep 3-5 unfolded leaves on the cuttings, 4-6 cm in length, and the cut is close to the lower end of the node.
[0043] B. Soak the cut cuttings in water with 1000 times of chlorothalonil solution to absorb water for 10-15 minutes, then dip them in rooting agent for cutting. The cutting matrix is a 1:1 mixture of vermiculite and perlite, and spray water immediately after cutting. Keep the humidity of the slotting bed at about 90%, the temperature of the slotting bed is above 18°C, and take root after 15 days.
[0044] 2) Colonization culture
[0045] Transfer the rooted "Shenma" seedlings into a 12cm×12cm nutrient cup / pot for planting; put the above-mentioned planted cuttings under ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This embodiment relates to a method for controlling the growth of side branches of cut chrysanthemum by regulating the ratio of red light and far-red light. Compared with Example 1, the difference is that in the step 3), the ratio of red light and far-red light is adjusted 0.50:1.
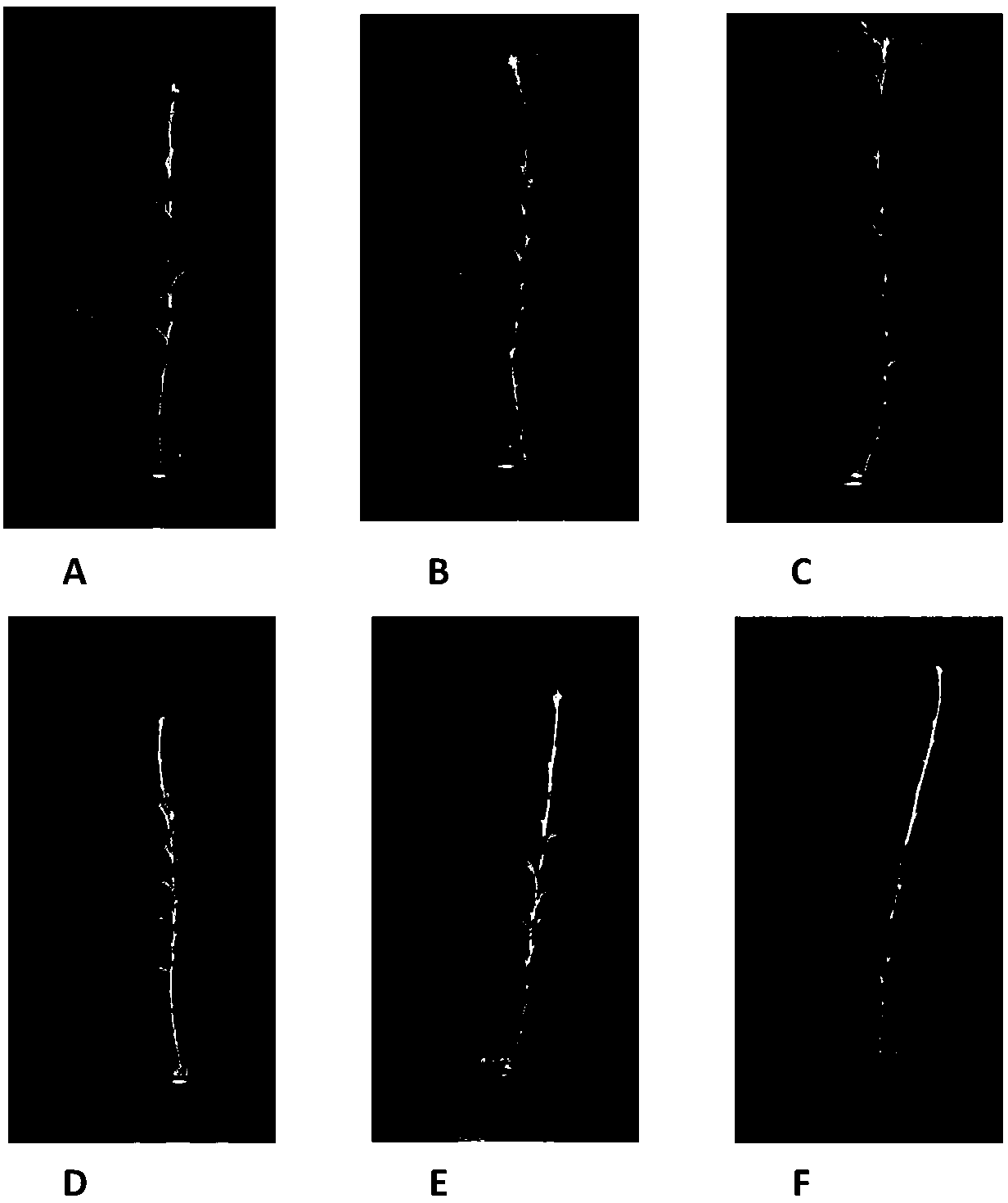
[0052] The data after statistical growth one month, axillary bud germination and elongation are suppressed, and axillary bud germination number is 48.8% of comparative example 1, and length is 59.2% of comparative example 1 (see attached figure 1 B and figure 1 E).
Embodiment 3
[0054] This example relates to a method for controlling the growth of side branches of cut chrysanthemums by regulating the ratio of red light and far-red light. Compared with Example 1, the difference is that in step 3) some of the axillary buds of "Shenma" start to germinate and elongate. For a long time (at this time, "Shenma" grows to about 45cm), adjust the optical density ratio of red light and far-red light to 0.08:1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com