Circulating tumor dissociating DNA mutation detection quality control products and preparation method thereof
A technology for mutation detection and quality control, applied in the fields of clinical laboratory science and biology and medicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Preparation of quality control products for ctDNA mutation detection
[0045] 1. Method
[0046] 1. Cultivate human normal cell-derived cell lines and extract genomic DNA
[0047] (1) Cell culture: human normal cell-derived cell line HEK293T was cultivated in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, which contained 10% fetal bovine serum, 100IU / ml penicillin and 100IU / ml streptomycin; at 37 Cultivate in a constant temperature cell incubator containing 5% CO2. Cell subculture was digested with trypsin, and the cells were expanded to 10 7 ~10 8 and in the logarithmic growth phase.
[0048] (2) Extraction of human genomic DNA: According to the instructions of the kit (QIAmp DNA mini kit, QIAGENE, China), the genomic DNA product of the human normal cell-derived cell line HEK293T was obtained and stored at -20°C.
[0049] 2. Cultivate cell lines derived from human normal cells, and digest the cells with MNase to obtain fragmented genomic DNA
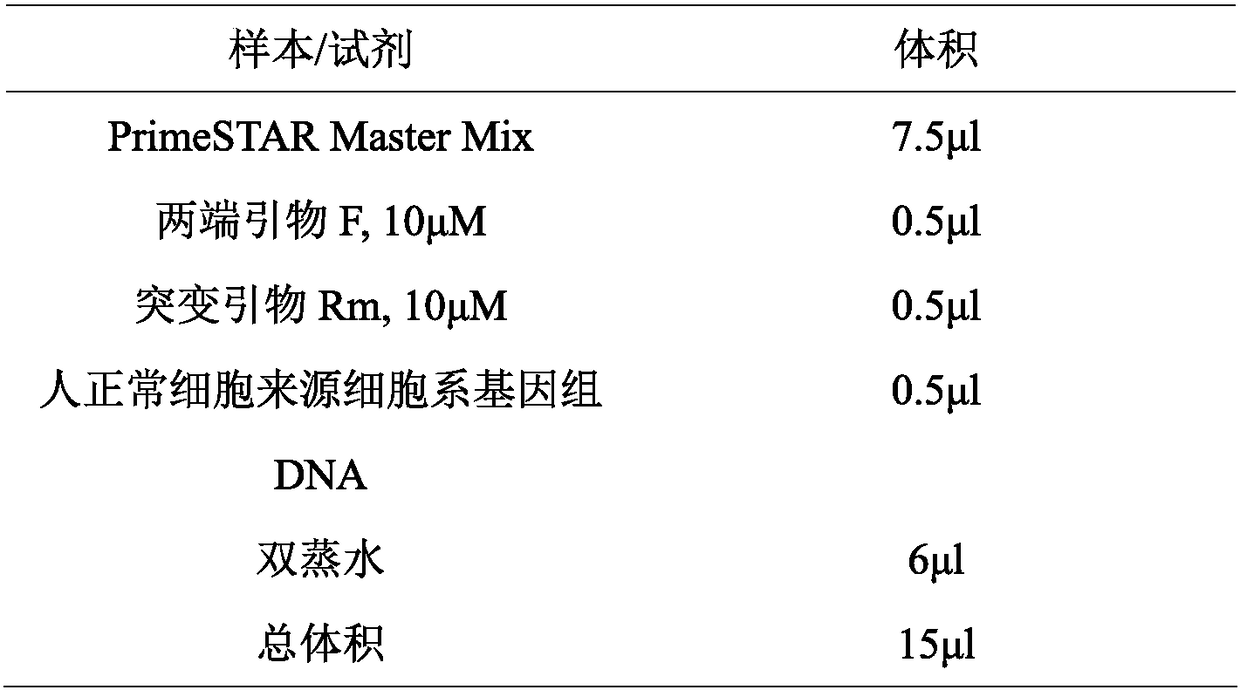
[0050] (...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: Validation of quality control products for ctDNA mutation detection using the dPCR method
[0082] 1. Method
[0083] Validation using the Bio-Rad QX200Droplet Digital PCR System
[0084] Take a set of quality control sample trays obtained in Example 1, and treat it as a conventional ctDNA sample for dPCR testing at Shanghai Austai Medical Laboratory, and obtain the test results through steps such as system preparation, on-board testing, and data analysis.
[0085] In this implementation case, the dPCR detection range is the gene mutation site in the following table:
[0086] Table 7
[0087]
[0088]
[0089] 2. Results
[0090] See Table 8.
[0091] Table 8
[0092]
[0093] The test results of this implementation case show that the Bio-Rad QX200DropletDigital PCR system of Shanghai Austai Medical Laboratory can detect most of the mutations in the quality control sample plate, and the reporting frequency is basically in line with the expectati...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Example 3: Validation of quality control products for ctDNA mutation detection using the ARMS method
[0095] 1. Method
[0096] The Mx 3000P fluorescent PCR instrument of Agilent Company was used for verification.
[0097] Take a set of quality control sample trays obtained in Example 1, and treat it as a conventional ctDNA sample for ARMS testing at Xiamen Aide Medical Laboratory, and obtain the test results through system preparation, on-machine testing, and data analysis.
[0098] In this implementation case, the detection range of ARMS is the gene mutation site in the following table:
[0099] S table 9
[0100]
[0101]
[0102] 2. Results
[0103] See Table 10.
[0104] Table 10
[0105]
[0106] The test results of this implementation case show that Xiamen Aide Medical Laboratory can detect most of the mutations in the quality control sample plate by using the Mx 3000P fluorescent PCR instrument, that is, the ctDNA mutation detection quality contro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com