Piston-cylinder refrigerating device based on memory alloy thermoelastic effect
A memory alloy and refrigeration device technology, applied in piston pumps, refrigerators, refrigeration components, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable heat controllable transmission, free heat loss, and low heat exchange efficiency, so as to improve circulation rate and reduce natural loss , Improve the effect of heat transfer rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
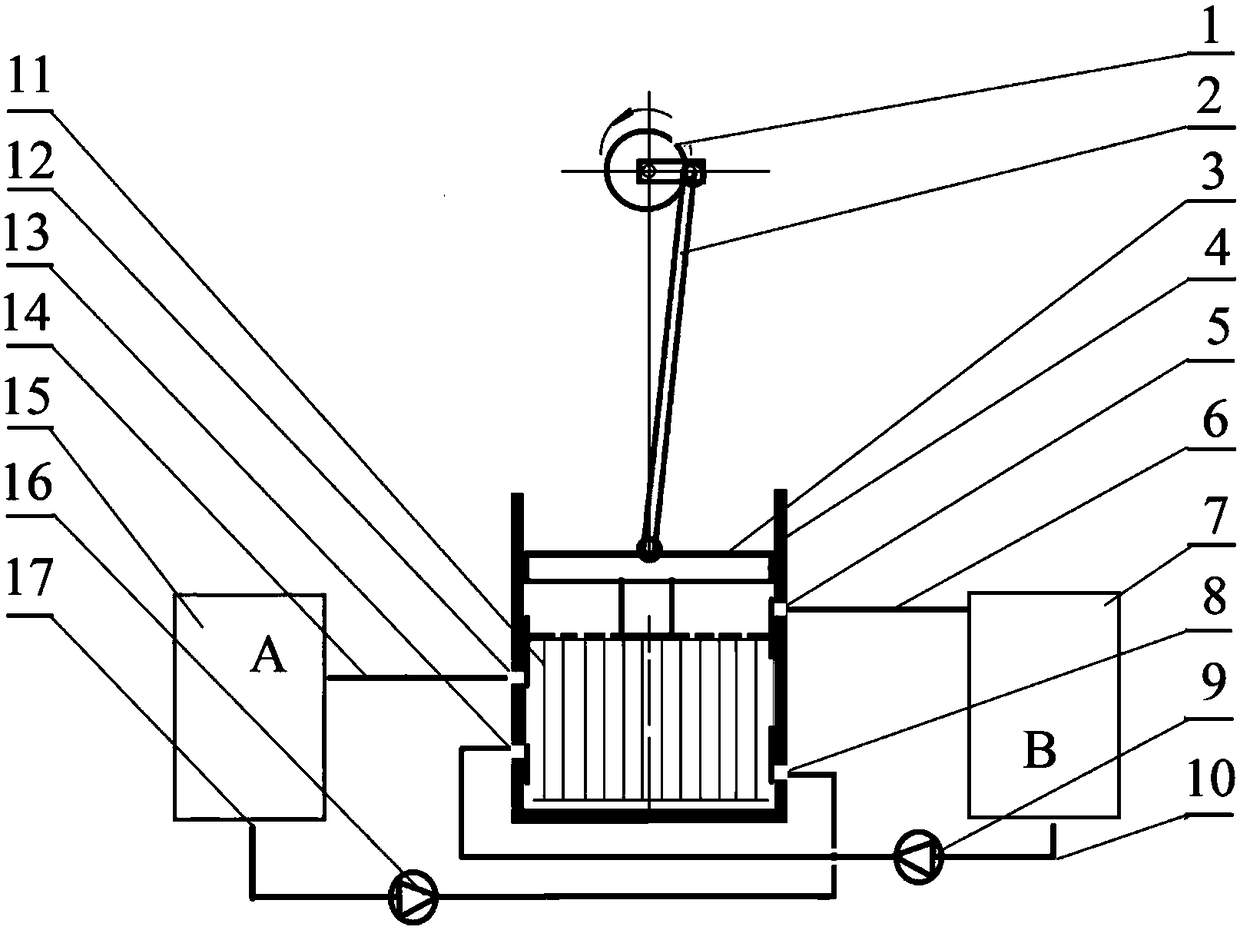
[0021] Step 1, install the motor power system. The output shaft of the motor (1) is perpendicular to the central axis of the hydraulic cylinder (4). One end of the crank connecting rod (2) is installed on the output shaft of the motor, and the other end is installed on the top of the piston (3), and the two ends of the crank connecting rod are hinged. The rotary motion of the output shaft of the motor is converted into the linear reciprocating motion of the piston in the hydraulic cylinder through the crank connecting rod. The frequency of the linear reciprocating motion of the piston is adjusted by the motor speed, and the stroke of the linear reciprocating motion of the piston is adjusted by the eccentricity of the crank connecting rod. The stroke of the linear reciprocating motion of the piston is selected as 30 mm. Adjust the distance between the motor and the hydraulic cylinder so that when the connecting rod is at the lowest position, the space height between the lower...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0025] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the loading method of the memory alloy is compression loading. The memory alloy thermoelastic effect cooling body is processed into a compression spring, and the free length of the spring is 60mm. Adjust the distance between the motor and the hydraulic cylinder so that when the connecting rod is at the highest position, the space height between the lower surface of the piston and the inner bottom surface of the hydraulic cylinder is 60mm.
[0026] Correspondingly, when the piston is in the second half cycle, the memory alloy compression spring induces martensitic phase transformation, releasing the latent heat of phase transformation. Along with refrigeration system operation, the water temperature in A container (15) constantly reduces, and the water temperature in B container (7) raises gradually.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com