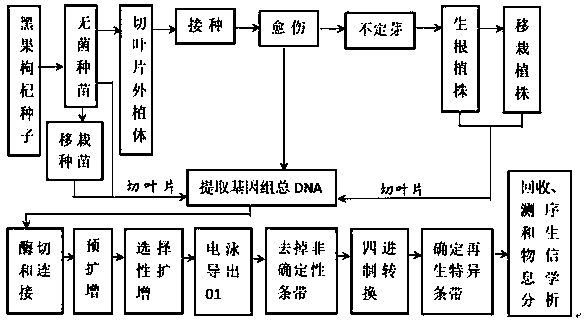
Method for screening MSAP sites relevant to regeneration in vitro of lycium ruthenicum
A technology of black fruit Lycium barbarum and in vitro regeneration, applied in the field of plant epigenetics, can solve the problems of limited establishment and application, unclear molecular mechanism of callus, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Example 1 A method for screening MSAP sites related to in vitro regeneration of Lycium barbarum
[0062] 1. Obtain sterile seedlings
[0063] Put the mature seeds of wolfberry black fruit in warm water at 37 ℃ for 24 hours; soak the seeds in 70-75% alcohol in a sterile ultra-clean workbench for 30 s-1min, and quickly soak the seeds in 0.2% mercuric chloride aqueous solution 2 min; after rinsing with sterile water for 4 times, blot the water on the surface of the seeds and inoculate them horizontally on 1 / 2MS solid medium without any plant growth regulator (add 0.45% agar and 2% sucrose, pH The value was adjusted to 5.8 with 1M KOH, autoclaved at 121°C for 16 minutes), and the seeds and medium must be in close contact. The inoculated materials were cultured at 25 °C under the photoperiod conditions of "light 12 h / dark 12 h", and the light was 3000 lx.
[0064] 2. Inoculation of leaf explants to obtain callus and regenerated plants
[0065] When the seeds inoculated in...
Embodiment 2
[0132] Example 2 A method for screening MSAP sites related to in vitro regeneration of Lycium barbarum
[0133] 1. Obtain sterile seedlings
[0134] Put the mature seeds of wolfberry black fruit in warm water at 37 ℃ for 24 hours; soak the seeds in 70-75% alcohol for 30 s-1 min in a sterile ultra-clean workbench, and quickly place the seeds in 0.1% mercuric chloride aqueous solution Soak for 5 min; after rinsing with sterile water for 5 times, blot the water on the surface of the seeds and inoculate them horizontally in 1 / 2MS solid medium without any plant growth regulator (add 0.45% agar and 2% sucrose, Adjust the pH value to 5.8 with 1M KOH, autoclave at 121°C for 16 minutes), pay attention to the close contact between the seeds and the medium; place the inoculated material at 25°C, under the photoperiod conditions of "light 12 h / dark 12 h" For cultivation, the light is 3000 lx.
[0135] 2. Inoculation of leaf explants to obtain callus and regenerated plants
[0136] When...
Embodiment 3
[0201] Example 3 A method for screening MSAP sites related to in vitro regeneration of Lycium barbarum
[0202] 1. Plant sterile seeds to obtain sterile seedlings
[0203] Put the mature seeds of wolfberry black fruit in warm water at 37 ℃ for 24 hours; soak the seeds in 70-75% alcohol for 30 s-1 min in a sterile ultra-clean workbench, and quickly place the seeds in 0.2% mercuric chloride aqueous solution Soak for 2 min; after rinsing with sterile water for 4 times, blot the water on the surface of the seeds and inoculate them horizontally in 1 / 2MS solid medium without any plant growth regulator (add 0.45% agar and 2% sucrose, Adjust the pH value to 5.8 with 1M KOH, autoclave at 121°C for 16 minutes), pay attention to the close contact between the seeds and the medium; place the inoculated material at 25°C, under the photoperiod conditions of "light 12 h / dark 12 h" For cultivation, the light is 3000 lx.
[0204] 2. Inoculation of leaf explants to obtain callus and regenerate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com