Temperature sensitive hydrogel composition including nucleic acid and chitosan
A temperature-sensitive hydrogel and composition technology, which is applied in the directions of medical preparations containing active ingredients, drug delivery, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as composition differences, and achieve the effect of improving retention and adhesion time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059]
[0060] In order to prepare the nucleic acid-chitosan hydrogel, the nucleic acid and chitosan stock solutions (stock solutions) of the concentrations corresponding to the examples in the following Table 1 were prepared. At this time, nucleic acid was added to 200 mM sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate buffer solution, and dissolved using a heating stirrer at 65° C. for 1 hour or more.
[0061] Chitosan was dissolved with 100 mM acetic acid.
[0062] The nucleic acid and chitosan stock solutions prepared according to the concentrations in Table 1 below were mixed at a weight ratio of 1:1, and stirred in a heating stirrer at 60° C. for 1 hour. Afterwards, the temperature was lowered to normal temperature and stirred for 1 hour, thereby preparing the nucleic acid-chitosan hydrogel.
Embodiment 2
[0067]
[0068] Nucleic acid-chitosan-hyaluronic acid hydrogels were prepared by the following procedure.
[0069]The nucleic acid was dissolved in a 200 mM sodium phosphate dibasicdodecahydrate buffer solution to a concentration of 2.2% by weight. At this time, it was melt|dissolved using the heating stirrer of 65 degreeC for 1 hour or more.
[0070] Chitosan was dissolved in 100 mM acetic acid to a concentration of 0.4% by weight.
[0071] Sodium hyaluronate was dissolved in 200 mM sodium phosphate dibasicdodecahydrate buffer solution so as to have a concentration of 2% by weight. At this time, after dissolving for 30 minutes using a heating stirrer at 40° C., the temperature was lowered to normal temperature while stirring.
[0072] The prepared 2.2 wt% nucleic acid and 0.4 wt% chitosan solution were mixed at a weight ratio of 9:1, and stirred in a heating stirrer at 65° C. for 10 minutes. In the nucleic acid-chitosan mixed solution, further add 2% by weight of sodium ...
experiment example 1
[0080]
[0081] The hydrogel compositions of Example 1, Example 2, Comparative Example 1, and Comparative Example 2 were used to verify gelation, gel stability, and solubility.
[0082] After mixing each composition, observe the transparency and gelation state of each composition for three days with the naked eye. The gelation is verified by whether there is viscoelasticity, and the stability of the gel is verified by whether there is a precipitate and whether stratification occurs. to verify.
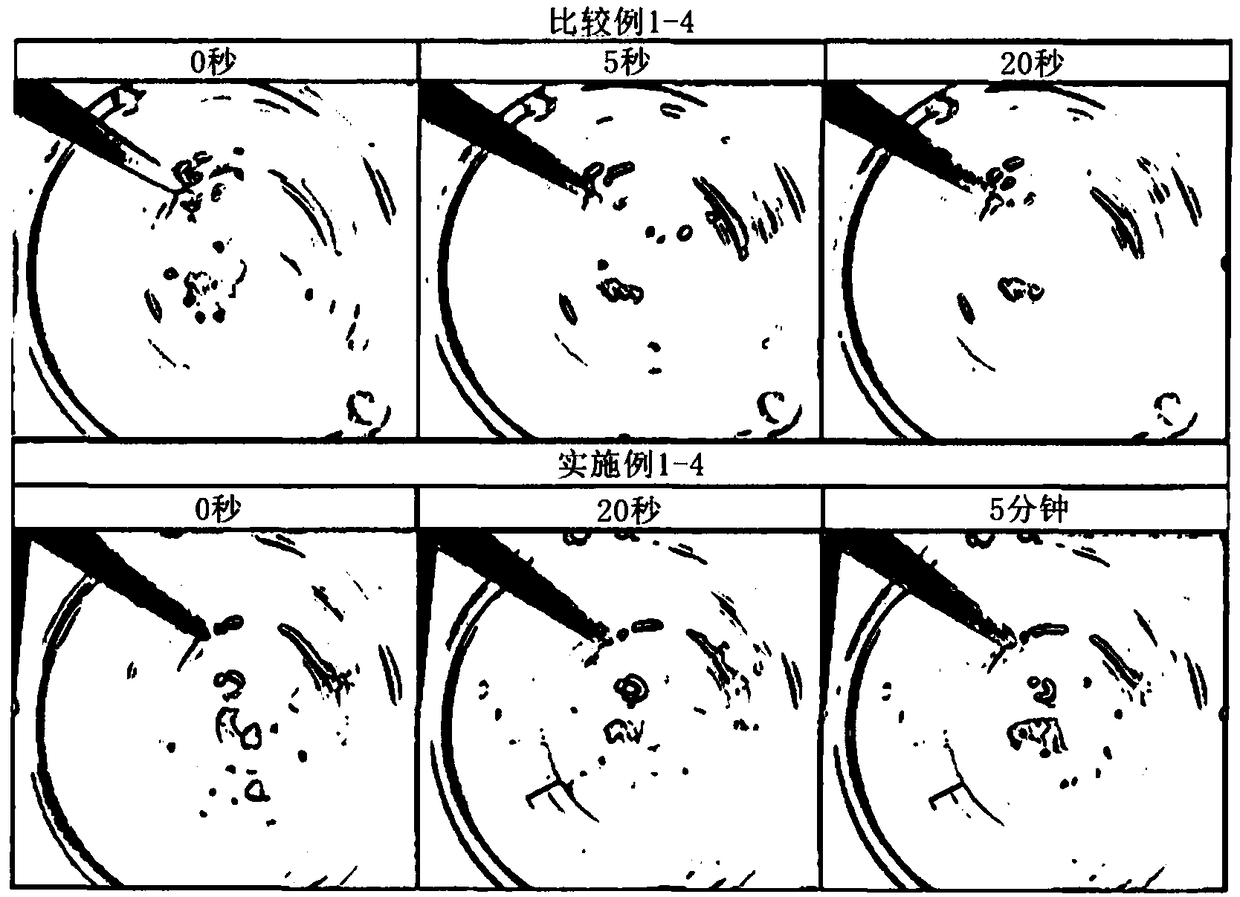
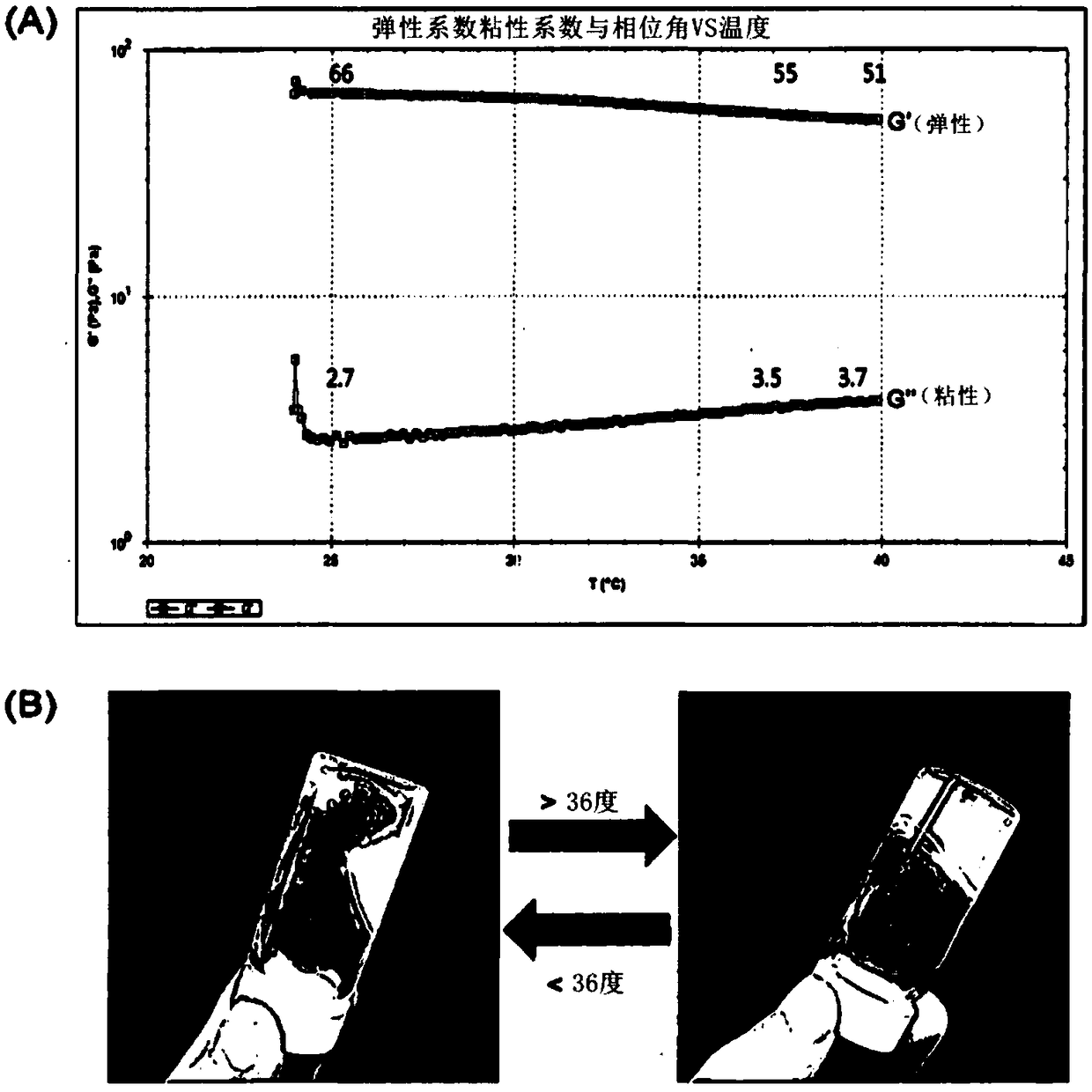
[0083] In terms of gel solubility, when the hydrogel compositions of Example 1, Example 2, Comparative Example 1, and Comparative Example 2 were titrated in an aqueous solution at 37.5°C to gel, and then maintained at 37.5°C Stir at 400 rpm for 5 minutes while confirming whether the gel is dissolved. The results are shown in Table 3, figure 1 and figure 2 .
[0084] [table 3]
[0085]
[0086] From the table 3 and figure 1 It can be seen that the temperature-sensitive hydro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| osmolarity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com