3D culture, passage, cryopreservation, recovery and identification method for in-vitro organoids based on small intestines of different segments of mice
An organoid and small intestine technology, which is used in the fields of resuscitation and identification, passaging, cryopreservation, and in vitro organoid 3D culture. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
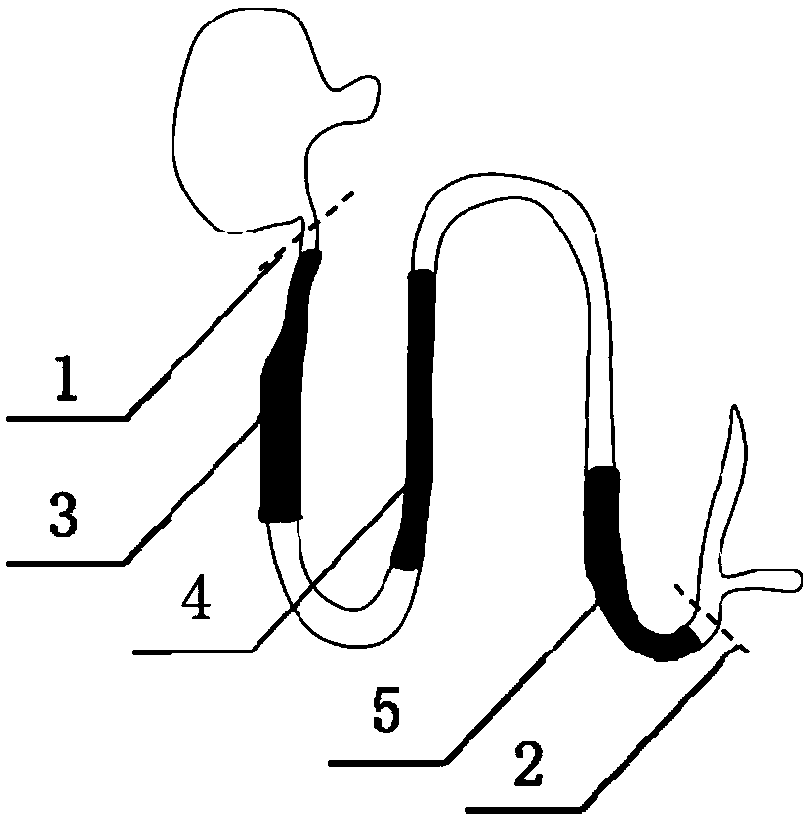
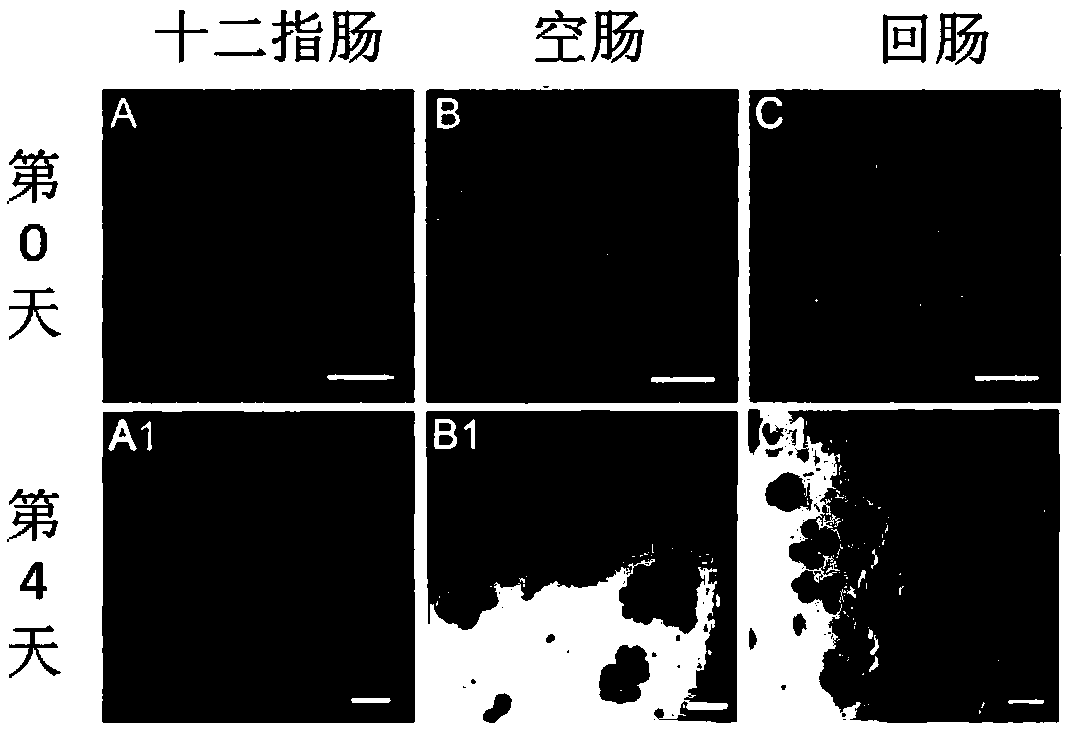
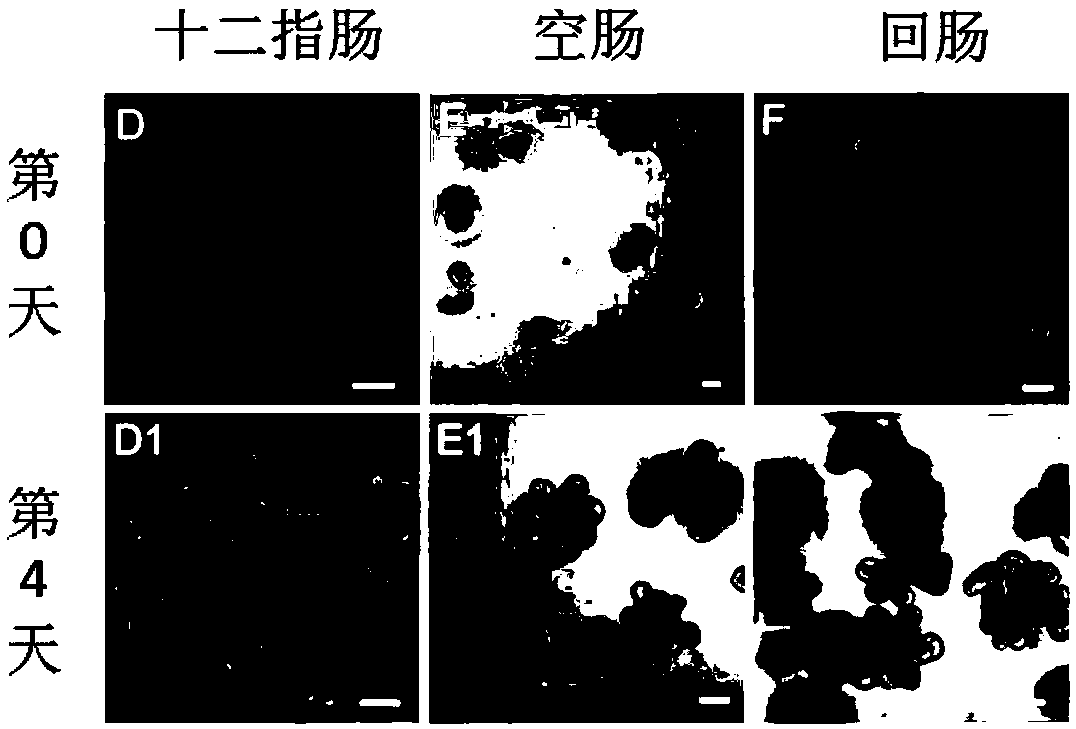
[0037] Step 1. Euthanize a 9-week-old male C57BL / 6 mouse with carbon dioxide and dislocate the cervical vertebrae; wet the abdomen of the mouse with 70% ethanol solution, and cut the abdominal cavity of the mouse to the extracranial genitalia by dissecting , cut the bilateral abdominal muscle tissue and extend the incision to the ribs, cut the duodenum from the pyloric sphincter, pull the small intestine out of the abdominal cavity and cut off the small intestine at the ileum and cecum; put the collected small intestine in pre-cooled Place it on ice in a phosphate buffer solution without calcium and magnesium ions; remove the residual mesentery of the small intestine with ophthalmic forceps, cut the small intestine longitudinally from the duodenum along the longitudinal axis, and use pre-cooled calcium and magnesium ion-free phosphate Wash with salt buffer solution to remove the chyme in the intestinal tract to obtain the cleaned small intestine; divide the cleaned small intest...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com