Patents
Literature
46 results about "Immunofluorescent labeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Immunofluorescent labeling is a straight-forward technique for assessing the presence and subcellular localization of an antigen or a protein. Several labeling methods are available depending on the biological sample, cell preparation, and availability of antibodies against the target.
Gold nanoparticle flower or quantum dot composite probe for living cell immunofluorescent labeling and photothermal treatment
InactiveCN104416152AImprove stabilityEffective orientationMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryHigh concentrationGold ball
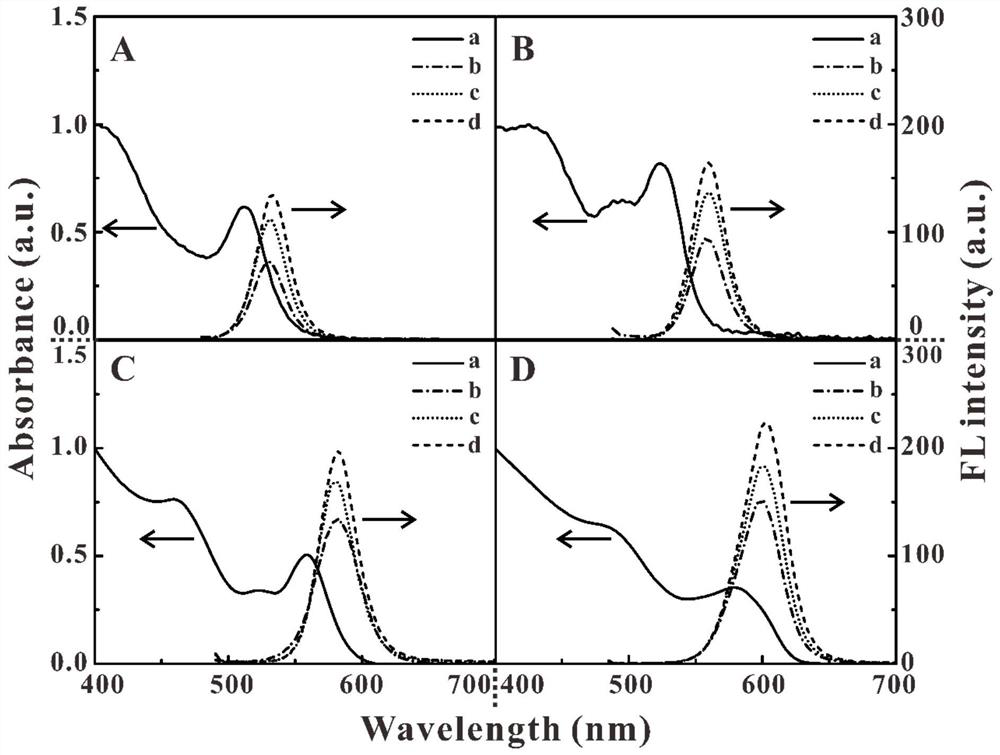
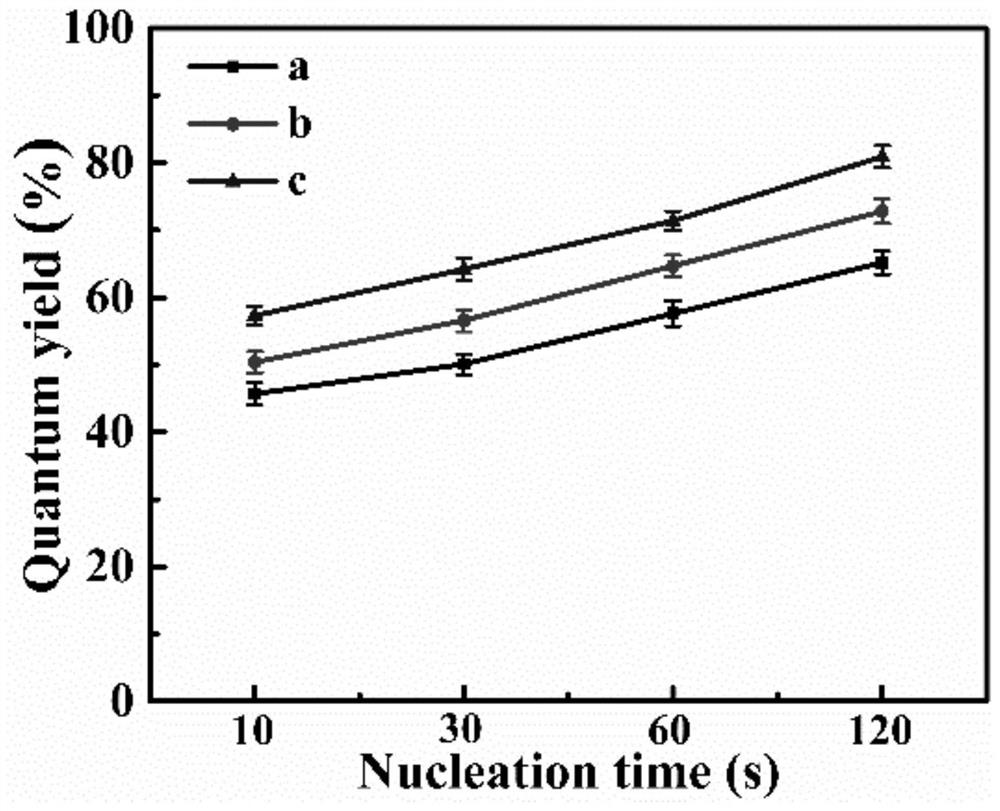
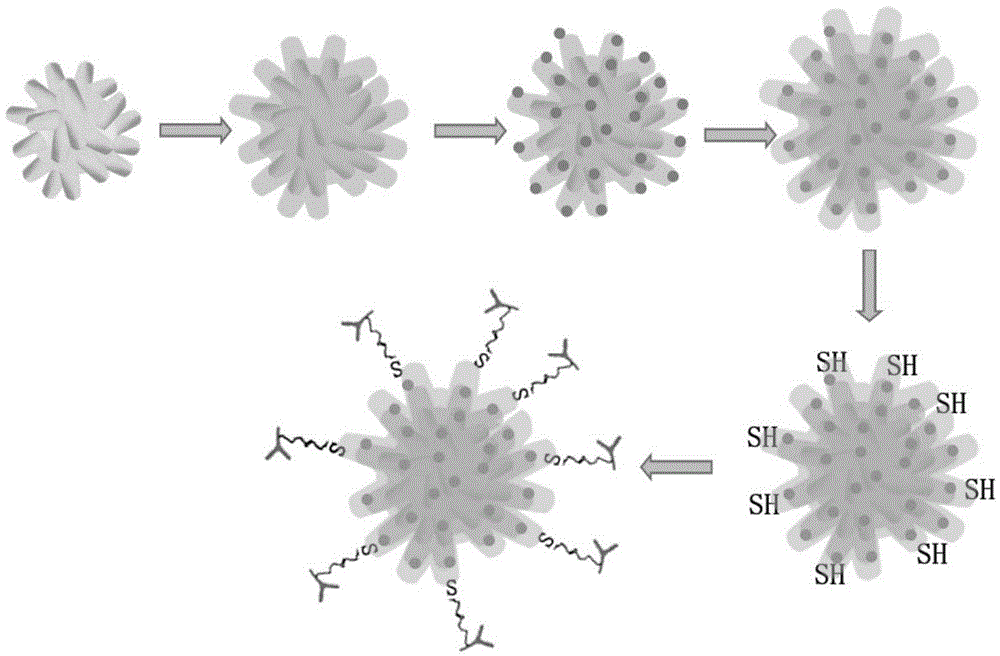
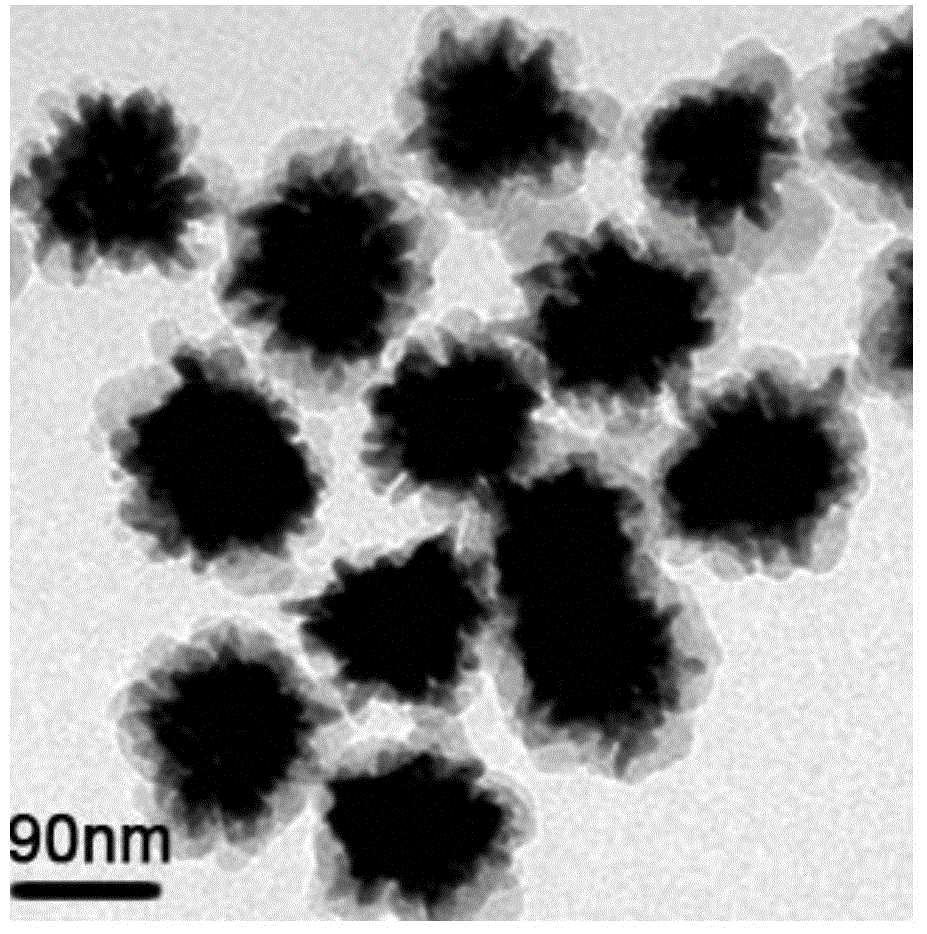
The present invention provides are a gold nanoflower structure and a preparation method therefor. The gold nanoflower structure is a gold nanoflower particle, with round-head columns being uniformly distributed at the periphery thereof, obtained by using gold octahedrons, gold balls or gold tetrahedrons as seed crystals and reducing chloroauric acid by using weak reductant in an environment of high-concentration polyvinylpyrrolidone. In addition, also provided in the present invention are a gold nanoflower / quantum dot composite probe for living cell immunofluorescent labeling and photothermal therapy, a preparation method therefor and a use thereof. In comparison with traditional probes, the probe, incorporates the features of photothermal therapy and fluorescent labeling, and is capable of killing cancer cells in an effective and directional way. Two light sources are adopted to bring a tremendous photothermal conversion efficiency and a greater enhancement on fluorescence intensity of quantum dots respectively, thus mutual interference of two effects are avoided tactfully. The coating of silicon dioxide averts the biotoxicity of the gold nanoflower and the quantum dot effectually, enabling the surface of the composite probe to be easily functionalized and also imparting an extraordinarily excellent biocompatibility to the composite probe.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
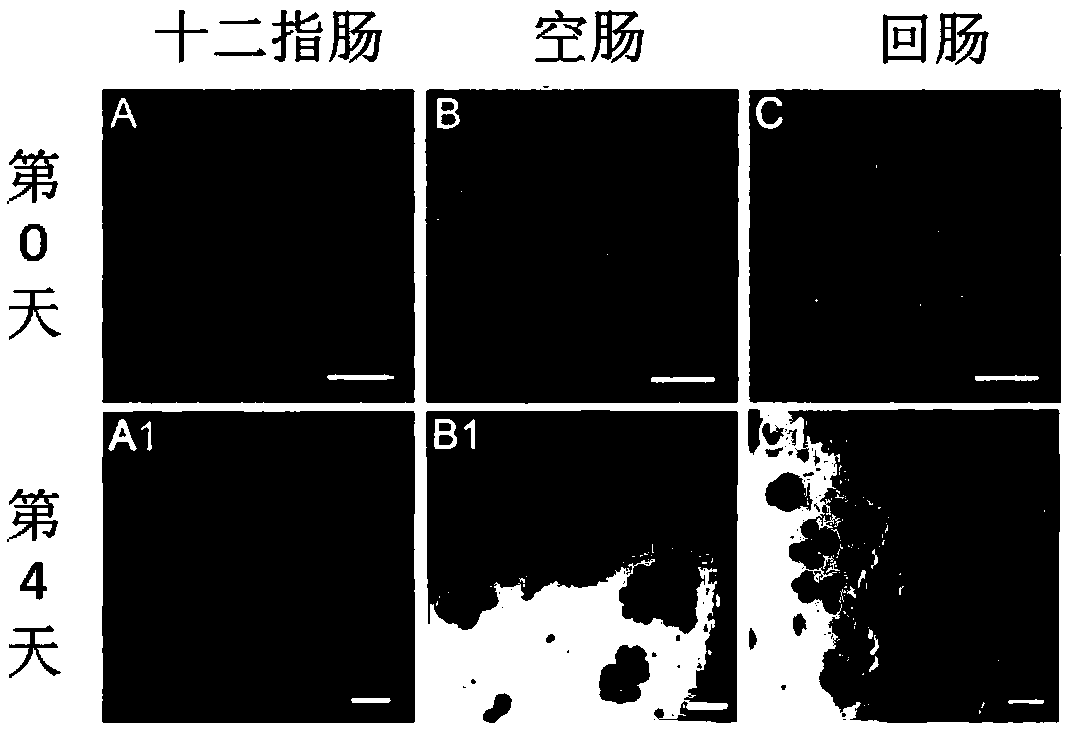
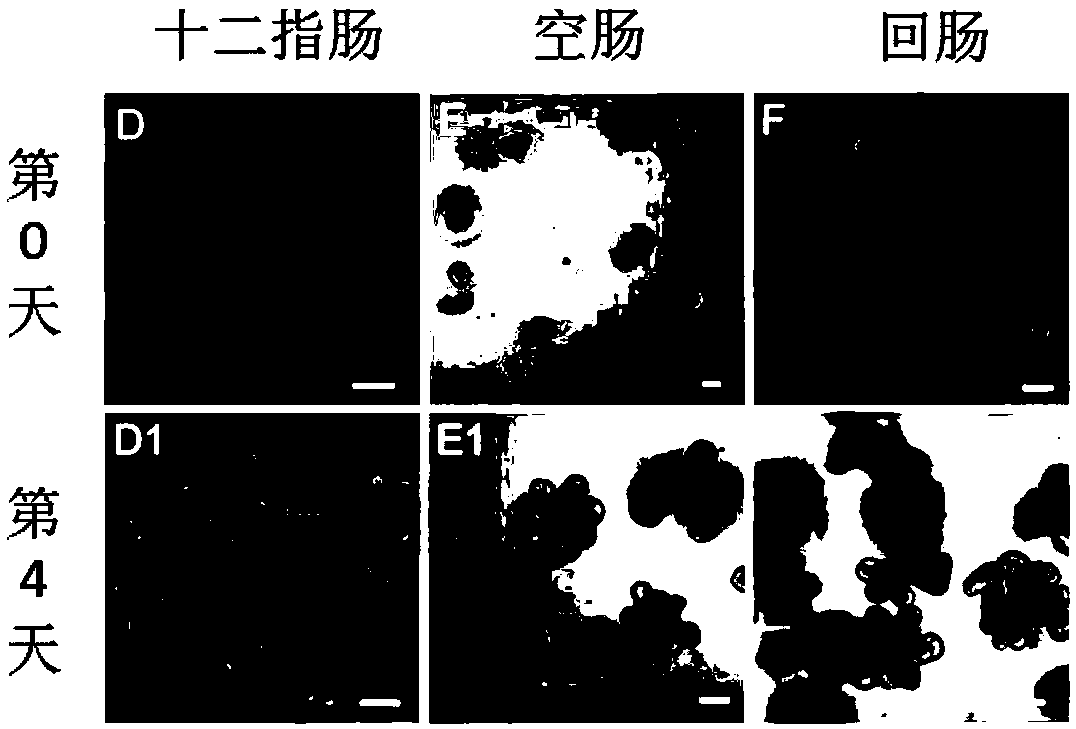
3D culture, passage, cryopreservation, recovery and identification method for in-vitro organoids based on small intestines of different segments of mice
InactiveCN108728399ASignificant advantagesSignificant progressGastrointestinal cellsDead animal preservationIntestinal structureImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention discloses a 3D culture, passage, cryopreservation, recovery and identification method for in-vitro organoids based on small intestines of different segments of mice. The method comprisesthe following steps: (1) separating recesses of duodenum, jejunum and ileum segments of mice; (2) performing 3D culture on the recesses of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum segments of mice, and forming organoids; (3) performing passage on organoids of small intestines of mice; (4) performing cryopreservation on the organoids of small intestines of mice; (5) performing recovery on the organoids ofsmall intestines of mice; (6) preparing frozen sections of the organoids of small intestines of mice; and (7) performing immunofluorescence labeling and identification on the frozen sections of the organoids of small intestines of mice. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention optimizes a recess extraction manner, an in-vitro culture system and a culture medium based on the recesses of the small intestines containing stem cells, and comprises the steps of complete culture, passage, cryopreservation, recovery and identification. The small intestine organoids obtained by the method are capable of performing repeated passage, and the passage organoids have character stability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Immune fluorescent marking method for naked plant pollen tube microtubule skeleton and its use
InactiveCN101074952AOmit the closing stepStable storageFluorescence/phosphorescenceImmunofluorescent labelingIMMUNE FLUORESCENCE
An immune-fluorescence labeling method of micro-pipe frame at pollen tube on gymnosperm includes fixing pollen tube of gymnosperm on fixing liquid for 40-60min, washing pollen tube, placing pollen tube in enzyme solution for carrying out enzymolysis of 30-40 min under temperature of 20-30deg.c, washing pollen tube, setting pollen tube in Triton X-100 to penetrate there for 1-3h, washing pollen tube, adding anti-beta-tubulin single clone antibody to carry out hatching for 1-3h, washing pollen tube, adding fluorescence label to carry out shielded hatching for 1-3h for making micro-pipe frame be immune-fluorescence labeled.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
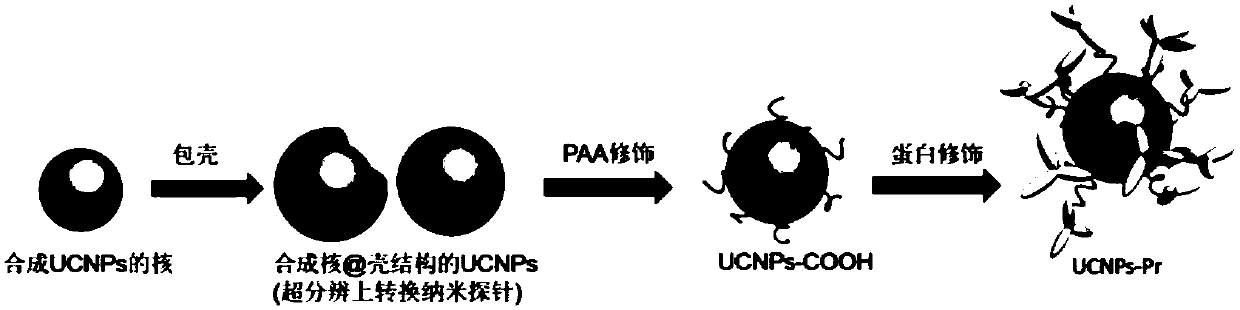
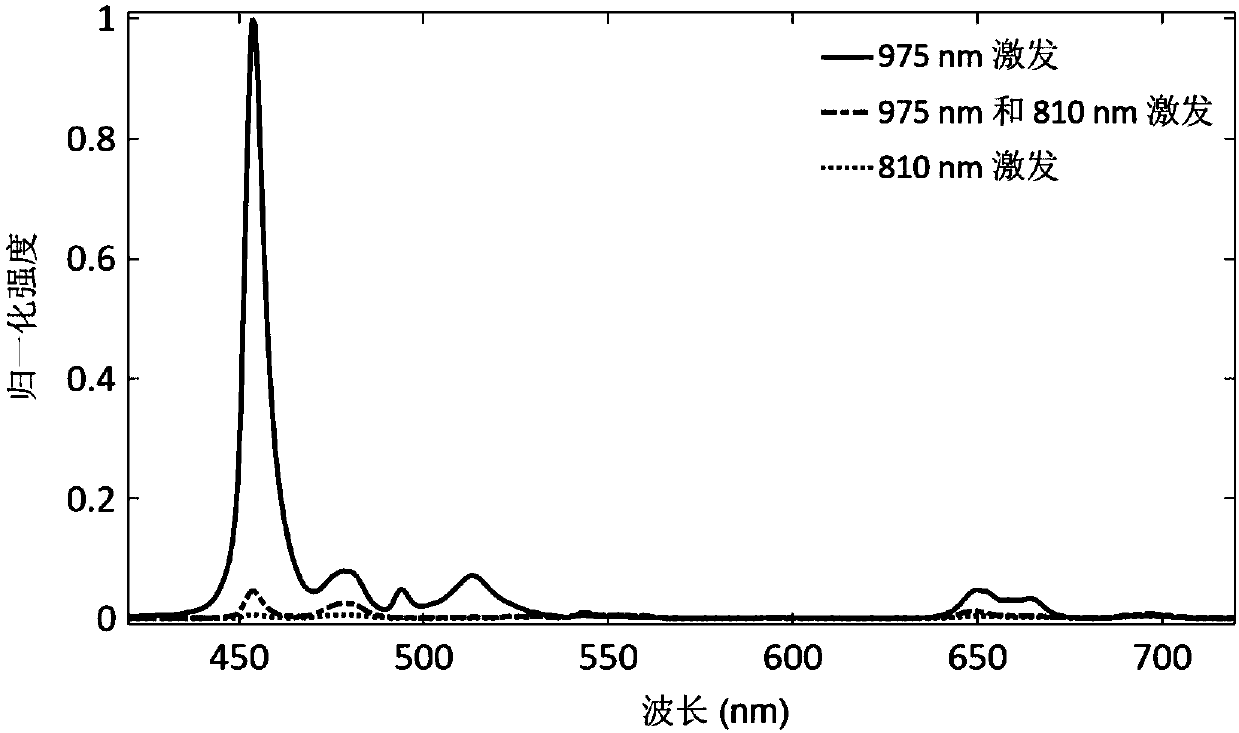
Upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107629792AAchieve super-resolution optical imagingGood photochemical stabilityNanoopticsFluorescence/phosphorescenceImmunofluorescent labelingSubcellular structure
The invention discloses an upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe has a core@shellstructure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing rare-earth upconversion nano-particles with controllable particle size and excellent dispersion property by adopting a solvothermal method; performing surface modification by polyacrylic acid; and finally performing protein modification. The upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe is applied to immunofluorescent labeling of a subcellular structure of cells, so that fluorescent super-resolution imaging of the subcellular structure is realized. Compared with the traditional fluorescein-based super-resolution optical imaging method, the method disclosed by the invention is a fluorescence zero-bleaching and zero-flicker super-resolution microscopic imaging method based on the upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe, and biological samples can be observed for a long time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
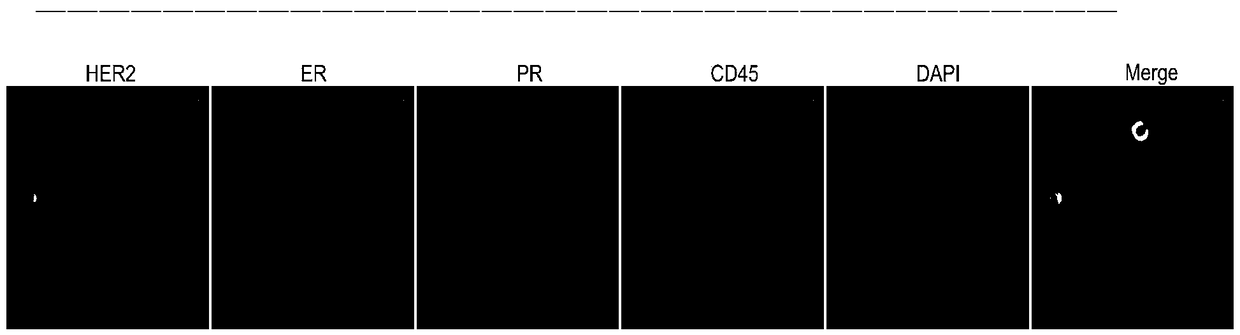
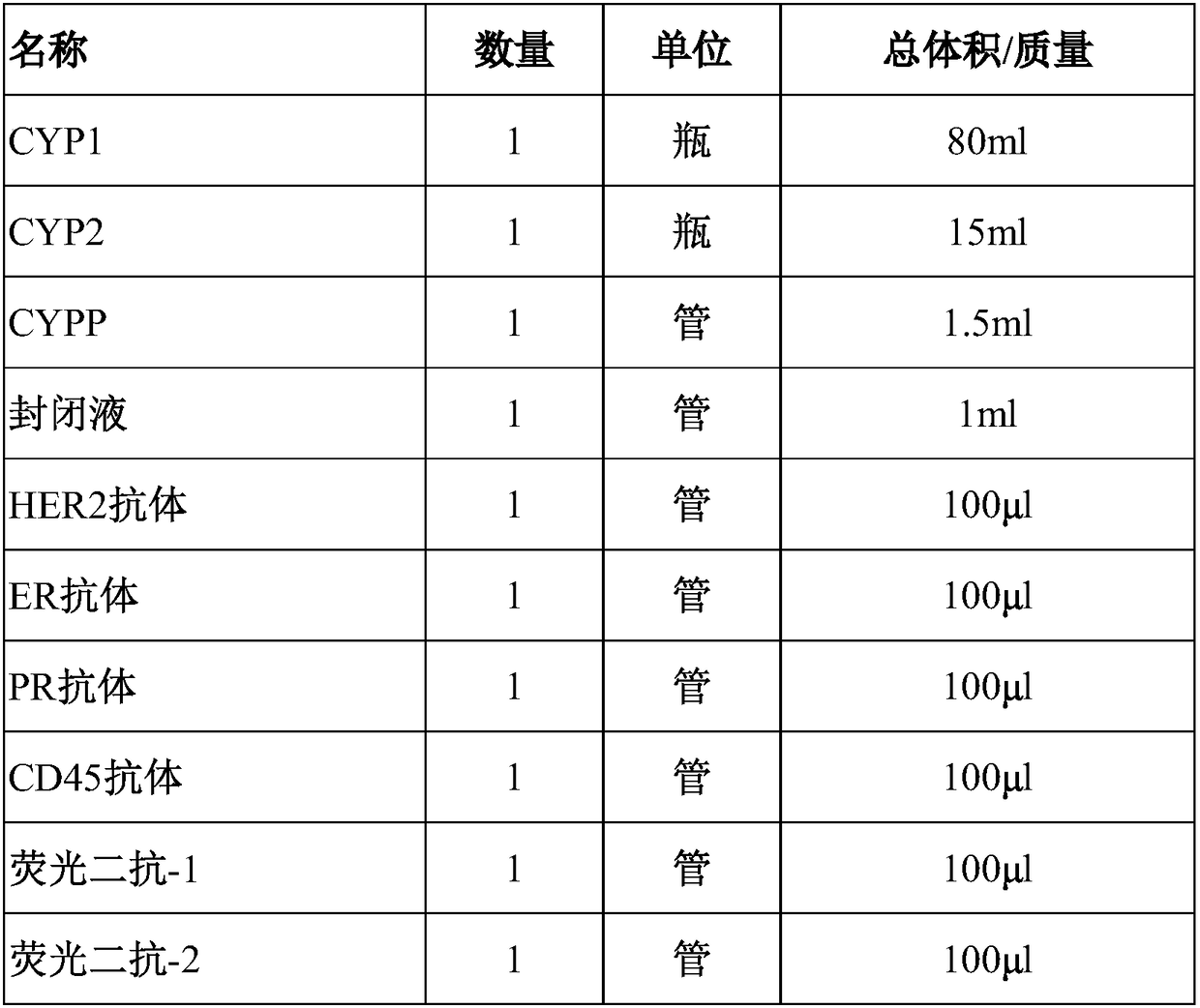
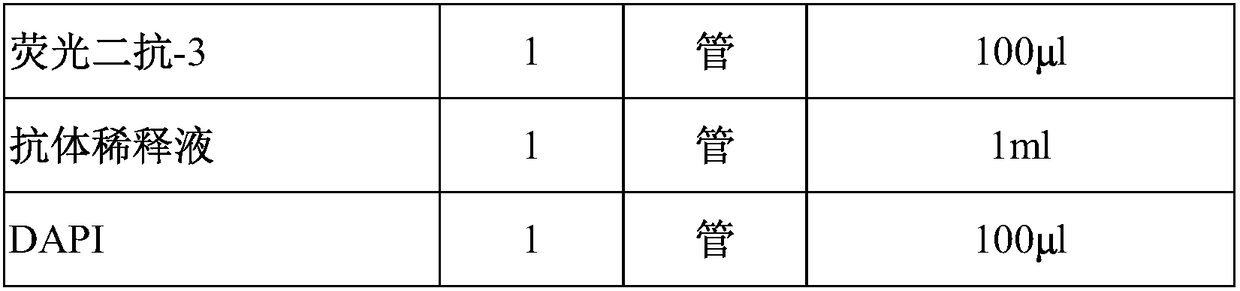
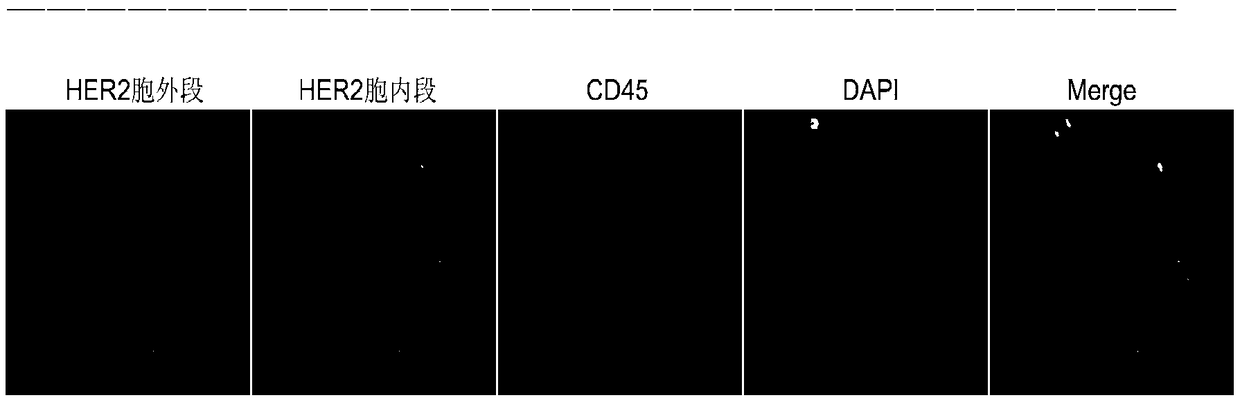
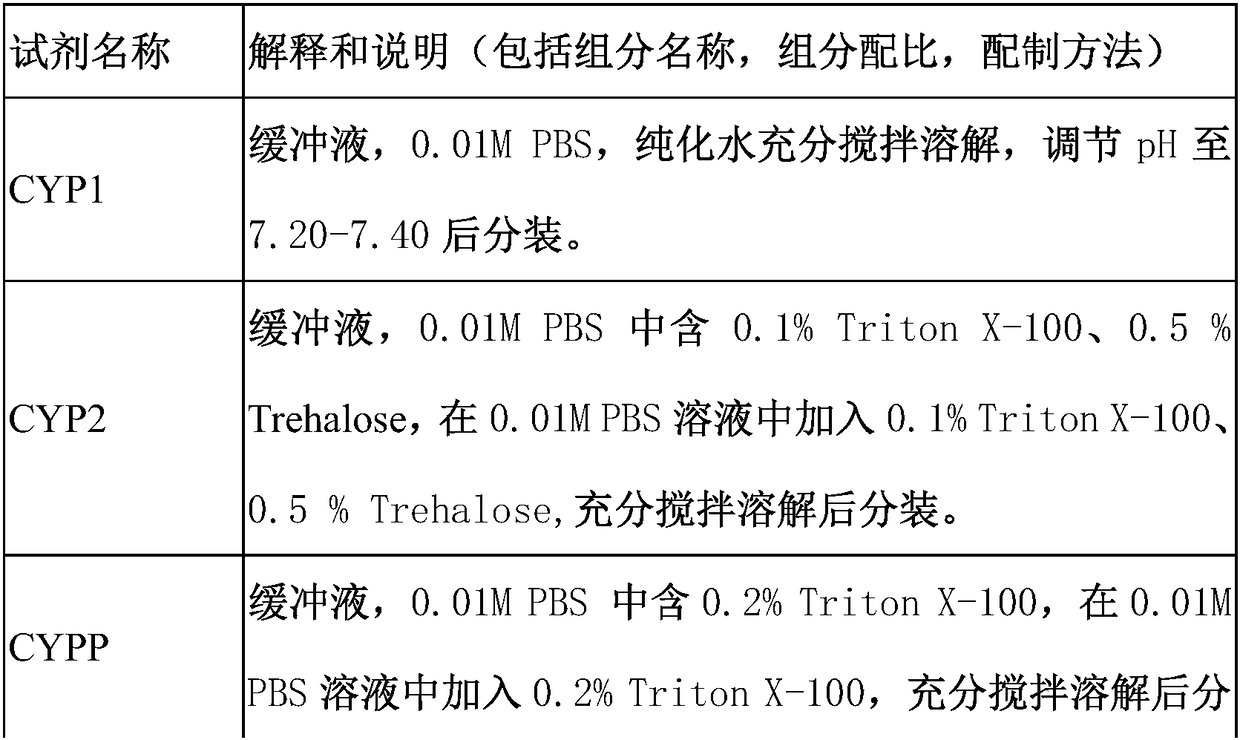
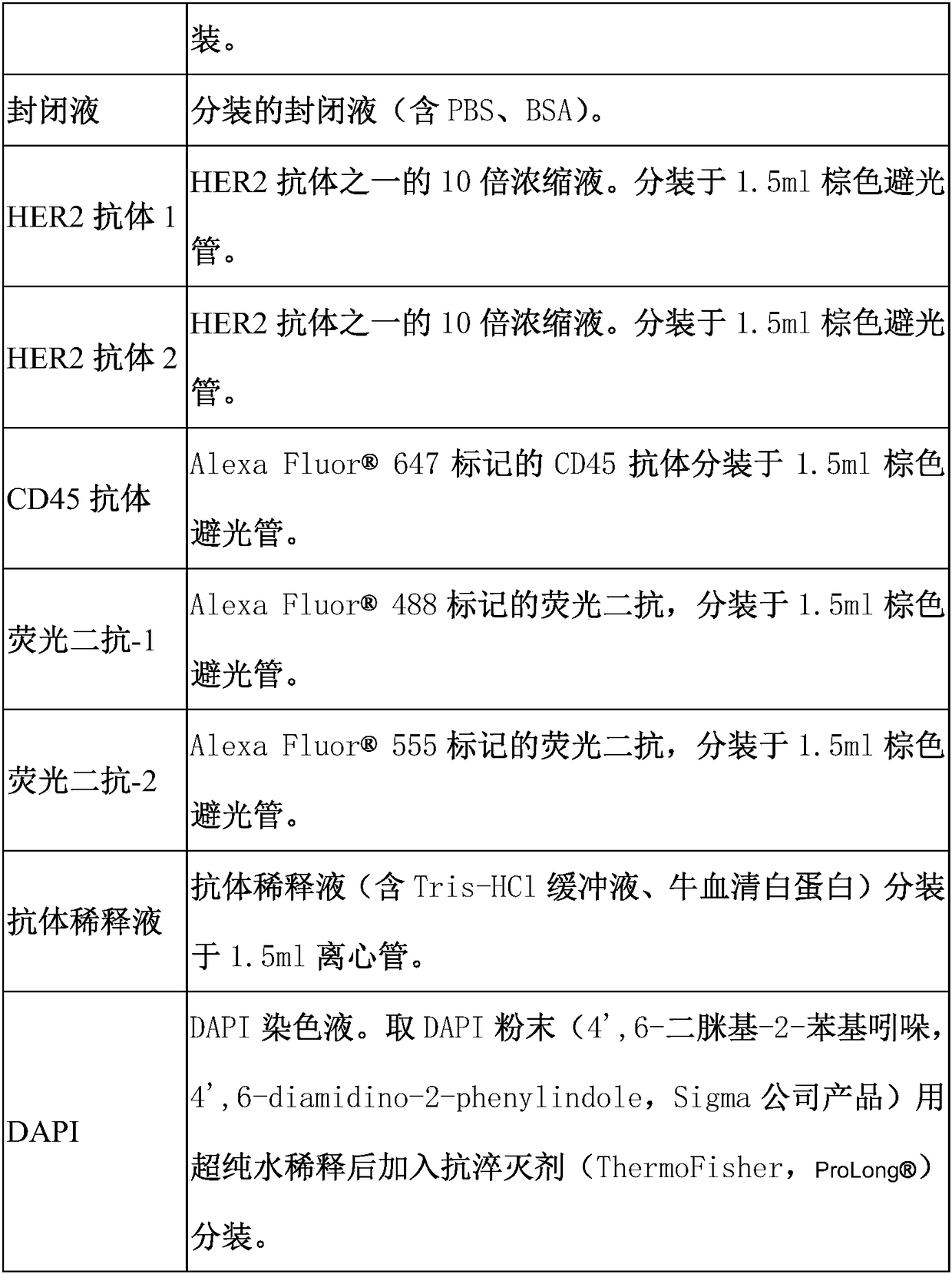
Immunofluorescent kit for detecting circulating tumor cells HER2, ER and PR and application of immunofluorescent kit
InactiveCN109187978APrecise Medication GuidanceGood choiceDisease diagnosisBiological testingProtein targetImmunofluorescence
The invention relates to an immunofluorescent kit for detecting circulating tumor cells HER2, ER and PR and an application of the immunofluorescent kit. A detection principle of a method disclosed bythe invention is as follows: firstly, enriching circulating tumor cells and other rare cells, and then, detecting the expression of target proteins in the enriched cells in cells by using an immunofluorescene detection method according to an antigen-antibody reaction principle. According to the kit, a common antigen CD45 of a target cell and a leukocyte is fluorescently labeled, and the cells withpositive target proteins and negative CD45 are screened, so that the circulating tumor cells with positive specific proteins in the blood are interpreted and counted.
Owner:北京莱尔生物医药科技有限公司
Immunofluorescence label reagent kit
InactiveCN101149372ASimple and fast operationImprove stabilityBiological testingFluorescenceImmunofluorescent labeling
This invention discloses to a kind of immunofluorescence mark reagent box. It is a reagent box applied for the aspects of immunity mark which uses the green fluorescence protein (GFP) as the indicator, the staphylococcus protein A (SPA) as the antibody. It also discloses the preparation method of the reagent. This invention can applied wide range in the field such as the immunity fluorescence mark, immunity histochemistry, biochemistry analysis, antibody test, protein chip and so on. It can replace the exist product efficiently, its operation is more simple, stability, delicacy and reliability, it is especially the same with the high flux analysis which analyze by the fluorescence analysis instrument.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV AT WEIHAI
Immunofluorescent kit for detecting different loci of HER2 antigen and application of immunofluorescent kit
InactiveCN109187977AAccurately reflectEasy to get materialsDisease diagnosisBiological testingProtein targetImmunofluorescence
The invention relates to an immunofluorescent kit for detecting different loci of an HER2 antigen and an application of the immunofluorescent kit. A detection principle of the method disclosed by theinvention is as follows: firstly, enriching non-humoral rare nucleated cells, and then, detecting the expression of target proteins in the enriched cells in cells by using an immunofluorescene detection method according to an antigen-antibody reaction principle. According to the kit, a common antigen CD45 of a target cell and a leukocyte is fluorescently labeled, and the cells with positive targetproteins and negative CD45 are screened, so that the non-humoral rare nucleated cells with positive specific proteins in the blood are interpreted and counted.
Owner:北京莱尔生物医药科技有限公司
Method for analyzing tar-induced cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) damage on basis of quantitative analysis of high content technology
InactiveCN106970051AHigh-throughput detectionOvercome deficienciesFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh resolution imagingImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention discloses a method for analyzing tar-induced cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) damage on the basis of quantitative analysis of the high content technology. The method includes the steps of 1), cell culture; 2), cell contamination; 3), immunofluorescent labeling of gamma H2AX; 4), quantitative analysis of high content technology. The method has the advantages that automatic imaging is performed by the aid of a high content imaging system, tar-induced gamma H2AX protein of DNA double-strand fracture markers is quantitatively analyzed, cells are detected directly and rapidly, and sample processing is facilitated; distribution of gamma H2AX in cell nucleuses can be observed directly and image materials are stored and reanalyzed conveniently through high-resolution imaging, the tar-induced gamma H2AX in each cell nucleus can be quantitatively analyzed, and detection results are more sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
Multi-color immunofluorescence labelling method and imaging method
The invention discloses a multi-color immunofluorescence labelling method and an imaging method, and relates to the technical field of immunofluorescence. The multi-color immunofluorescence labellingmethod comprises a plurality of fluorescence labelling steps and crosslinking fixing steps of incubating a sample with a crosslinking fixative after each fluorescent labelling step. The crosslinking fixative comprises acetone, paraformaldehyde and PBS buffer. According to the multi-color immunofluorescence labelling method, various kinds of different fluorescent dyes can be labelled on various kinds of antigen markers in the sample. The labelled sample can be used for confocal microscopy imaging to display various kinds of different colors, and the colors are clear, bright and uncolored. The method provides a basis for scientific research workers to simultaneously observe the properties, positioning and content of various kinds of antigens.
Owner:姜云瀚
Shortcut method for separation and purification of embryonic cranial neural stem cells
InactiveCN103031271AAchieve separationEfficient separationNervous system cellsEmbryonic cellsOligodendrocyteNeurulation
The invention provides a method able to realize separation, amplification and purification of embryonic cranial neural stem cells rapidly and simply. The invention uses the thermal conversion polymer N-isopropylacrylamide and polyethylene glycol to conduct three-dimensional culture on neural cells, and makes use of the characteristic that neural stem cells can proliferate in a gel environment and form neurospheres to achieve the purposes of separation and purification of the neural stem cells. The formed neurospheres are subjected to immunofluorescent labeling determination, which shows that about 93% of the cells are Nestin positive, so that the method is simple and effective for separation and purification of neural stem cells. The embryonic neural stem cells separated and purified by the method can differentiate in vitro to form neurons, oligodendrocytes and Glias.
Owner:北京清美联创干细胞科技有限公司
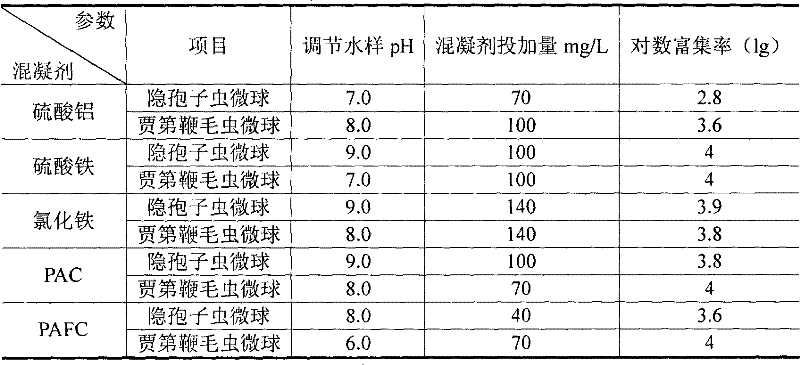
Method for enriching Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts and Giardia Lamblia sporocysts in water
InactiveCN102191307AEfficient enrichmentReduce investmentMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCryptosporidium parvumImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention relates to a method for enriching Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts and Giardia Lamblia sporocysts in water. The method comprises the following steps: adding an inorganic metal salt coagulant into a bulk water sample, stirring, coagulating, precipitating, collecting precipitate alumen ustum in a small-volume container, adding acidic solution into the small-volume container to dissolve the alumen ustum, centrifuging, removing supernate and thus, enriching the Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts and Giardia Lamblia sporocysts in water. In the invention, the problems of low Cryptosporidium parvum oocyst and Giardia Lamblia sporocyst enrichment rate, instability, high operation requirement and expensive filtering equipment and consumable items of the conventional method for enriching Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts and Giardia Lamblia sporocysts. The method does not need expensive apparatus and equipment and medicines and greatly reduce capital investment. The method is simple in operation, easy to master, time-saving and labor-saving, reduces cost of enrichment of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts and Giardia Lamblia sporocysts in water, improves enrichment efficiency and is a novel method which clears the preliminary work for subsequent steps of immunomagnetic separation, immunofluorescence label microscope counting, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) qualitative detection, nano probe gene chip detection and Real-time PCR quantitative detection and the like.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
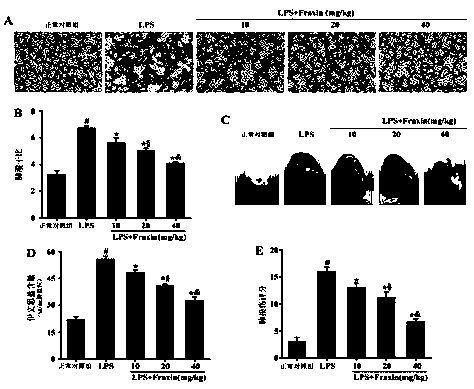
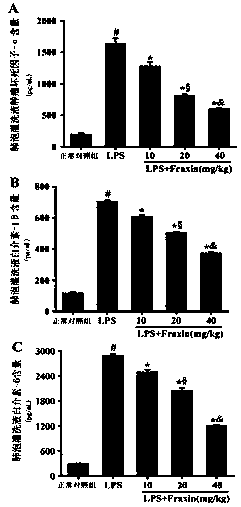
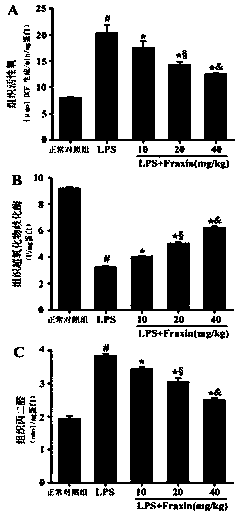
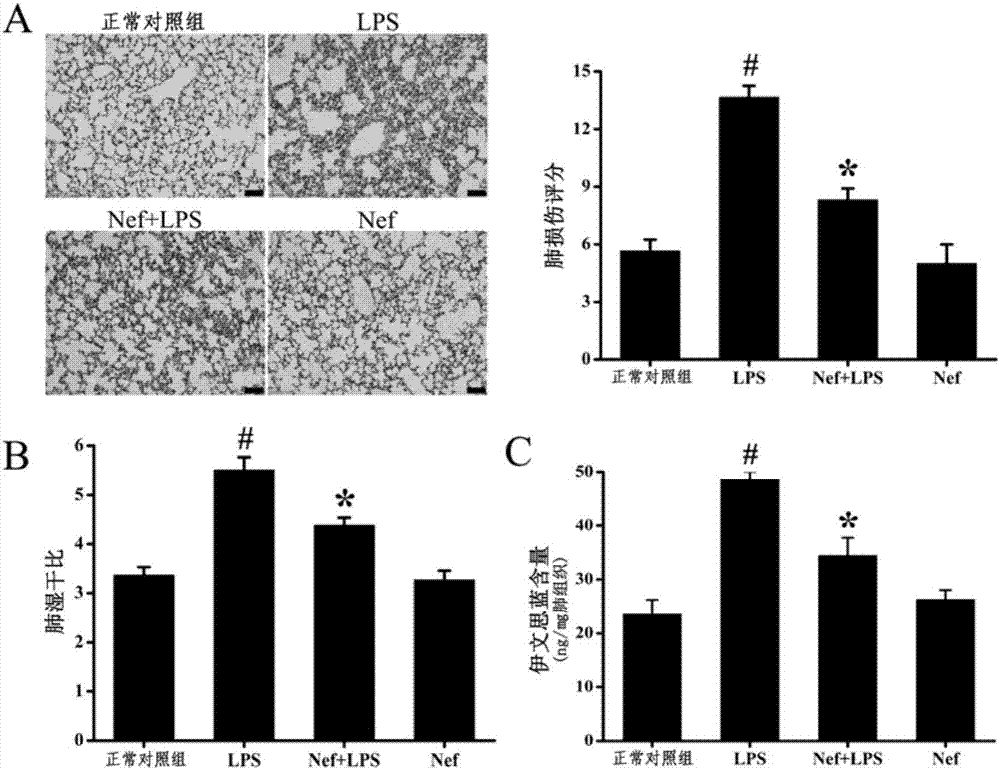
Application of fraxin in preparation of drugs for preventing or treating acute respiratory distress syndrome
InactiveCN108403708AInhibitionInhibition of activationOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderFraxinusInflammatory factors
The invention provides application of fraxin in preparation of drugs for preventing or treating an acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The fraxin is a coumarins compound which is extracted from dry barks of oleaceae fraxinus chinensis, Fraxinus szaboana Lingelsh or Fraxinus stylosa Lingelsh. Existing researches show that the fraxin has effects of resisting inflammation, reducing blood uricacid, resisting bacteria and inducing diuresis. On the basis of constructing an anima damage model of acute respiratory distress syndrome, by HE, Evan blue staining, fluorescence probes, immunofluorescent labeling, western blotting and the like, it verifies that the fraxin can reduce generation and releasing of reactive oxygen (ROS), inhibit generation and releasing of inflammatory factors and inhibit activation of signal paths MAPKs, therefore, degradation of a blood vessel endothelial polysaccharide coating is relieved, and vascular permeability is relieved to prevent or treat ARDS.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Immunofluorescent labeling method for protein in living cell
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for detecting protease-4 of human airway trypsin sample by using flow cytometry
ActiveCN105758783ARelieve painImprove complianceIndividual particle analysisBiological testingProteinase activityImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention discloses a method for detecting protease-4 of a human airway trypsin sample by using flow cytometry. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting a marrow or peripheral blood sample; (2) performing immunofluorescent labeling; (3) performing detection with a becton dickinson caliber. According to the detection method disclosed by the invention, a few of marrow cells canbe used as samples, and peripheralblood can be also used as a sample, so that pain of a patient in a sample collecting process can begreatly relieved, and the compliance of the patient is improved. Furthermore, the operation steps in the detection method disclosed by the invention are simple and convenient, and the detection period is short; the detection can be completed within only several hours; the detection period is greatly shortened, the progress of relevant researches can be accelerated favorably, and the time cost is reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Monoclonal antibody of anti-perkinsus membrane protein, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102766209AAids in location analysisQuick checkTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsImmunofluorescenceImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention provides a monoclonal antibody of anti-perkinsus membrane protein (MOE). The monoclonal antibody of the anti-perkinsus membrane protein (MOE) is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain IAQ1101 of the anti-perkinsus membrane protein (MOE) with an accession number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) No.6180. The invention also provides a preparation method and application of the monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody of the anti-perkinsus membrane protein (MOE) is obtained by a genetic engineering technology and an immunological method; by labeling the monoclonal antibody with fluorescence, the immunofluorescence labeling technology is utilized to quickly and accurately detect infected perkinsus in shellfish, accordingly, a reliable immunological detection method is provided for the rapid identification of a port.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
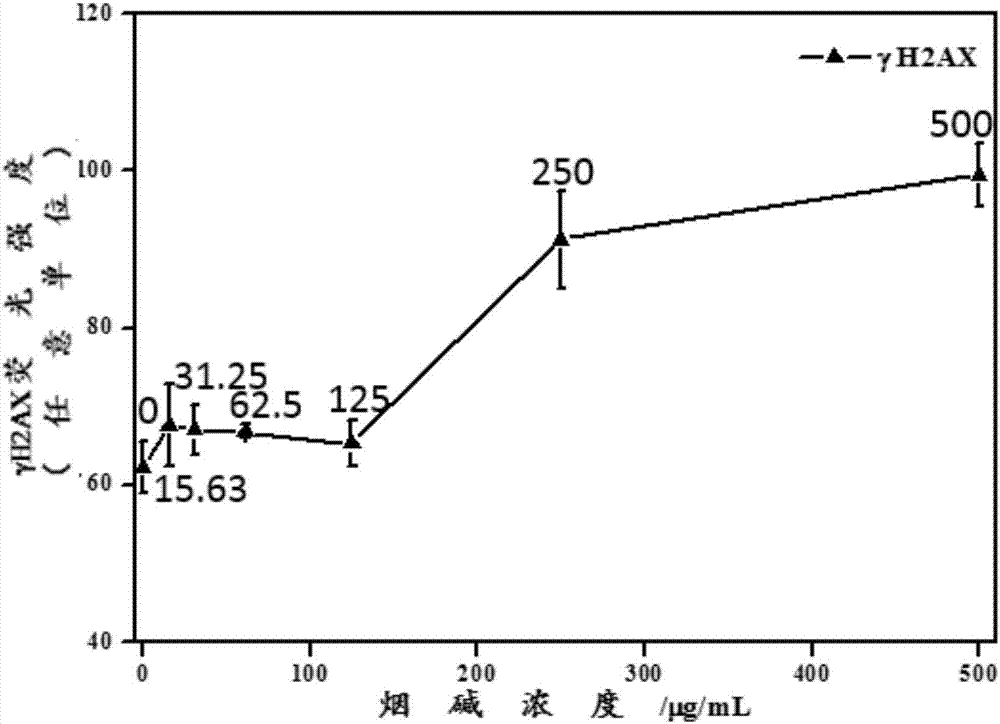
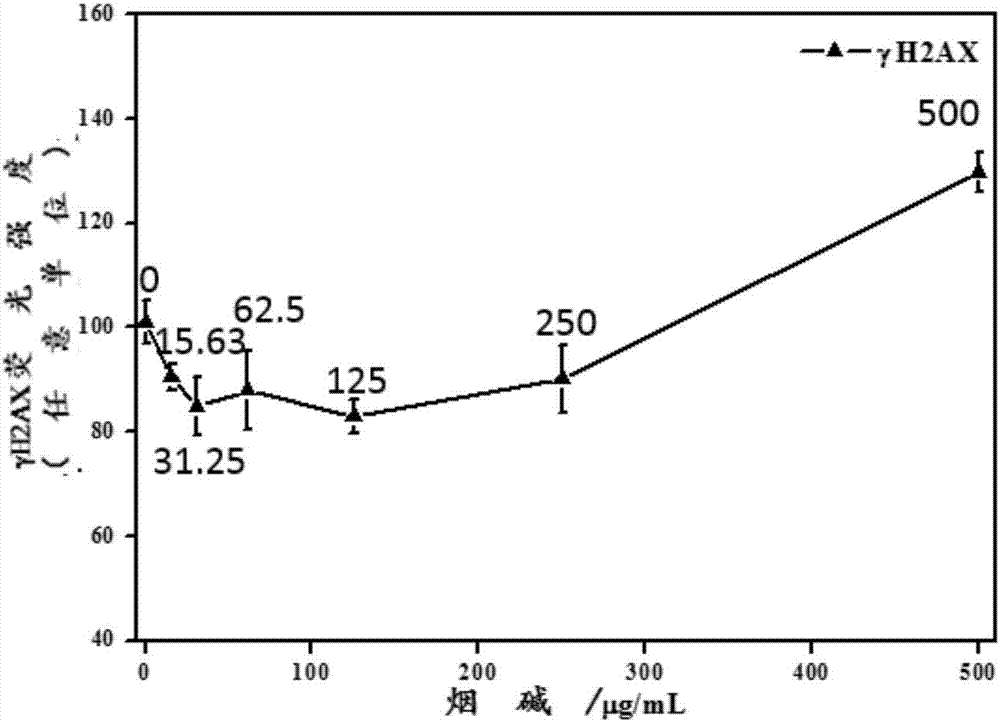
Method for quantitatively analyzing nicotine-induced cell DNA damage based on high content technology
InactiveCN107153054ASmall amount of sampleHigh detection throughputFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh resolution imagingImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing nicotine-induced cell DNA damage based on the high content technology. The method includes the steps of firstly, culturing cells; infecting the cells; thirdly, performing immunofluorescent labeling of gamma H2AX; fourthly, performing high-content-technology quantitative analysis. The method has the advantages that a high-content imaging system is used to perform automatic imaging, DNA double-strand break marker gamma H2AX protein generated by nicotine induction is quantitatively analyzed, direct and fast cell detection is achieved, and sample processing convenience is achieved; the high-resolution imaging allows the distribution of the gamma H2AX in each cell nucleus to be able to be observed directly and image data to be convenient to store and reanalyze, the nicotine-induced gamma H2AX in each cell nucleus can be quantitatively analyzed, and the detection result is sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
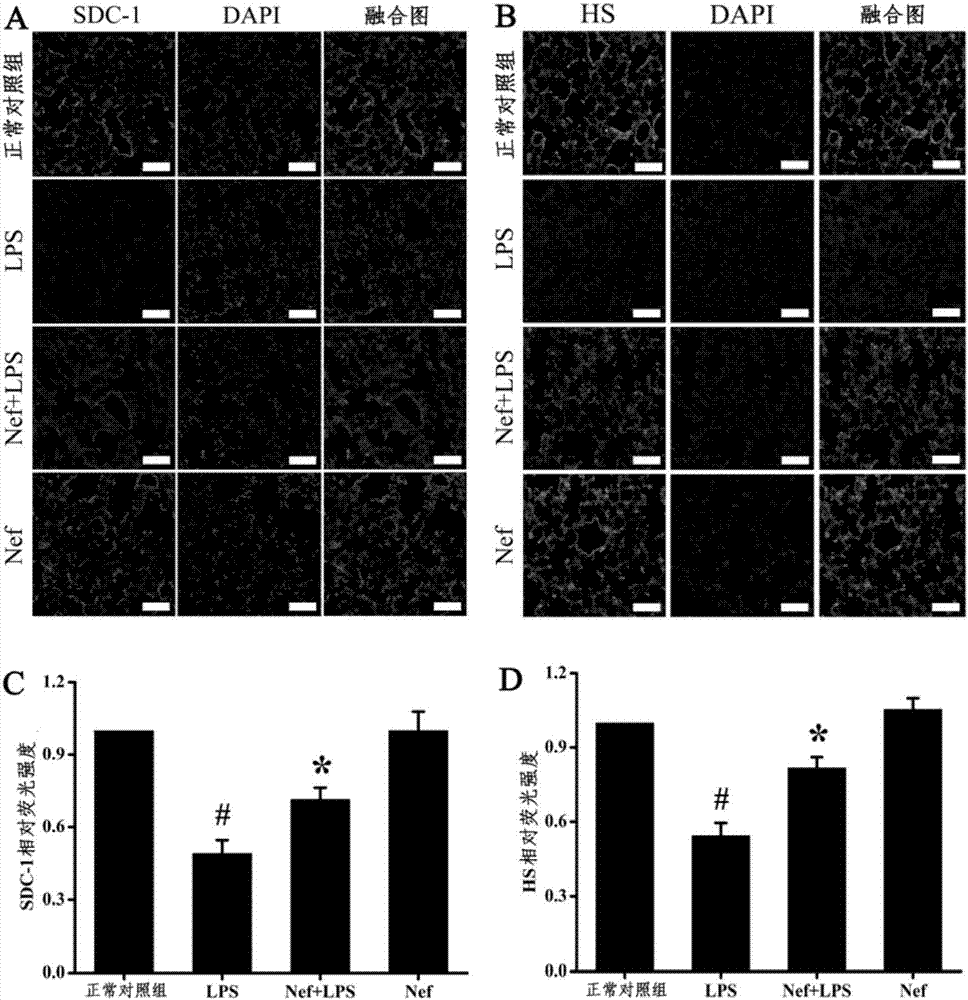
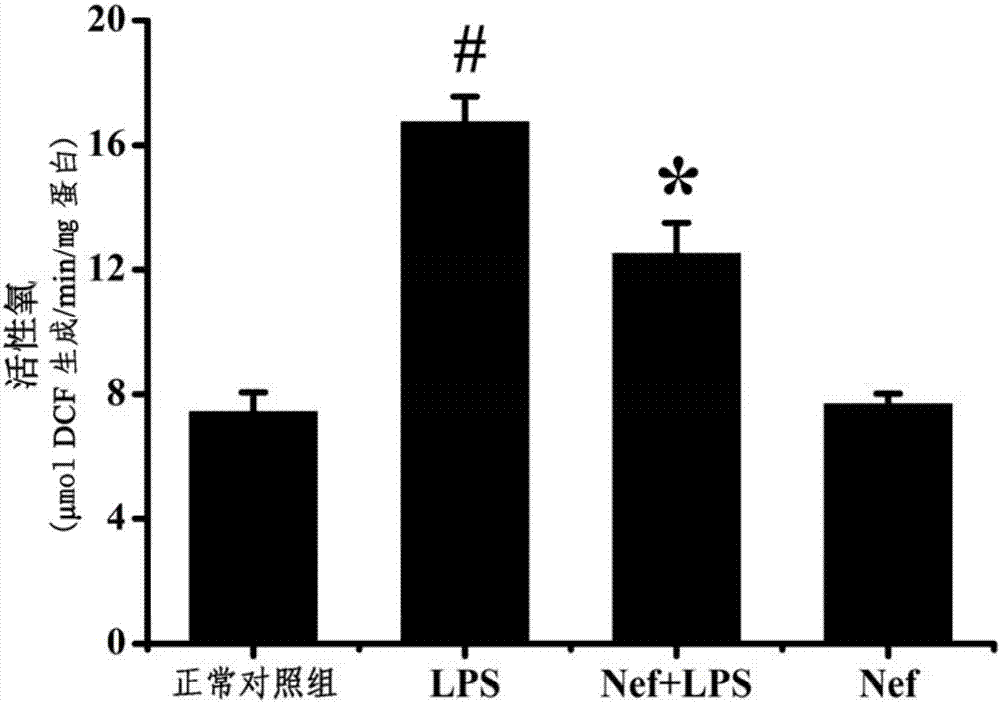
Application of neferine in preparation of drugs for preventing or treating acute respiratory distress syndrome
The invention provides an application of neferine in the prevention or treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The neferine is alkaloid extracted from natural plants and has antioxidant activity. Based on the construction of animal and cell damage models of acute respiratory distress syndrome, by HE, Evan blue staining, fluorescent probe, immunofluorescence labeling and the like, it is verified that the neferine can reduce the production and release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce the degradation of vascular endothelium polysaccharide coating (Glycocalyx), thus the occurrence and development of ARDS are inhibited, and ARDS is prevented or treated.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Same-section multi-target protein immunohistochemical or immunofluorescent labeling method
The invention provides a same-section multi-target protein immunohistochemical or immunofluorescent labeling method. The method comprises the following steps of: unfolding slices in corresponding liquid in the process of slicing a tissue wax block, selecting two continuously connected slices in the process of catching a target slice, placing the back surface of the first slice upwards in the process of catching the slice by employing a glass slide, and placing the front surface upwards in the process of catching the second slice, so that the condition that the surfaces of the two tissue slice for staining belong to the same slicing surface is ensured; and respectively performing immunohistochemical or immunofluorescent staining on different target proteins for two slices from the same slicing surface, performing overlap comparison on the tissue staining result in a same area, so as to realize existential analysis of a same cell or tissue site multi-target protein. The effect of performing multi-target protein labeling on the same cell or tissue site to be detected is achieved.
Owner:FUZHOU MAIXIN BIOTECH CO LTD
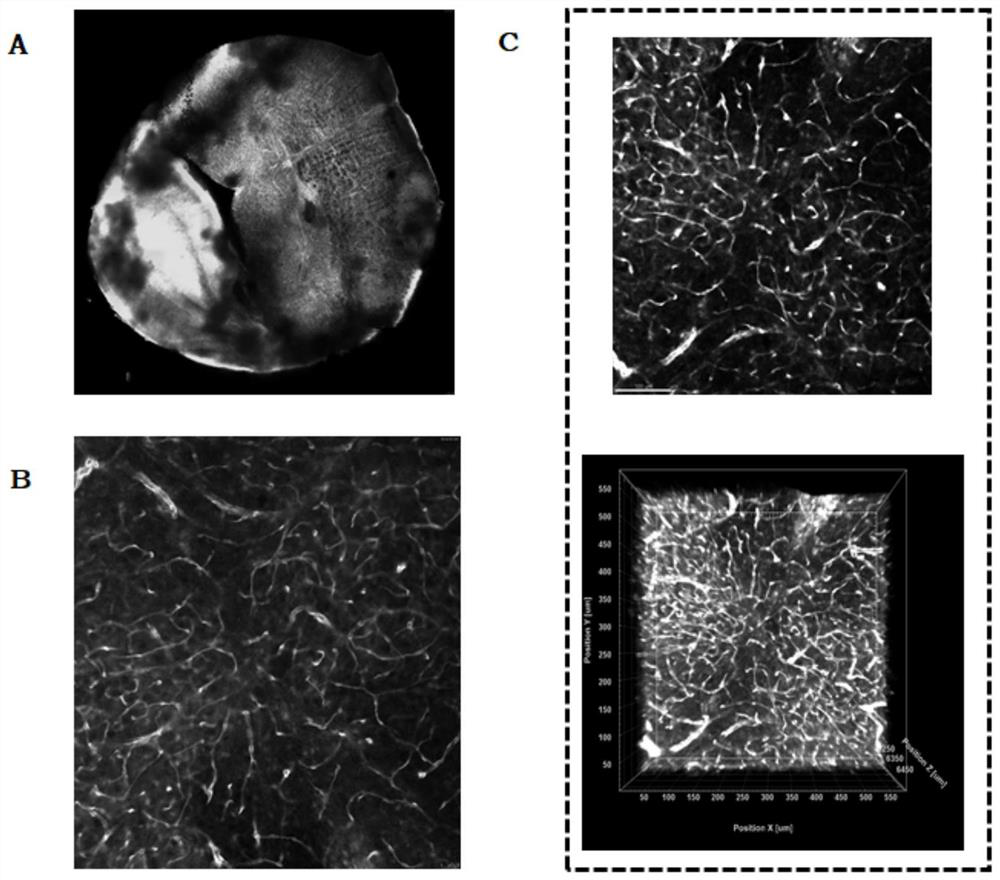
Precise immunofluorescence labeling method for integral tissue sample
PendingCN112834737AImprove permeabilitySolve the problems of low permeability and poor compatibility of fluorescent proteinsMaterial analysisAgainst vector-borne diseasesImmunofluorescenceImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention provides a precise immunofluorescence labeling method for a whole tissue sample, which comprises the following steps: fixing, pretreatment, transparentizing treatment, confining liquid confining, freeze thawing and primary antibody incubation, and secondary antibody incubation. Freeze thawing and ultrasonic incubation are adopted, so that the permeability of an optical transparentizing agent and the compatibility of fluorescent protein are increased, the resolution of a fluorescence image is increased, the permeability of a large tissue sample is realized, and the overall immunolabeling of an organ is achieved.
Owner:佳维斯(武汉)生物医药有限公司
Method for quantitatively detecting 1,3-butadiene-induced cell DNA damage in combination with gas-liquid interface exposure system and high-content technology
ActiveCN107121553AImprove effectivenessImprove accuracyBiological testingHigh resolution imagingImmunofluorescent labeling
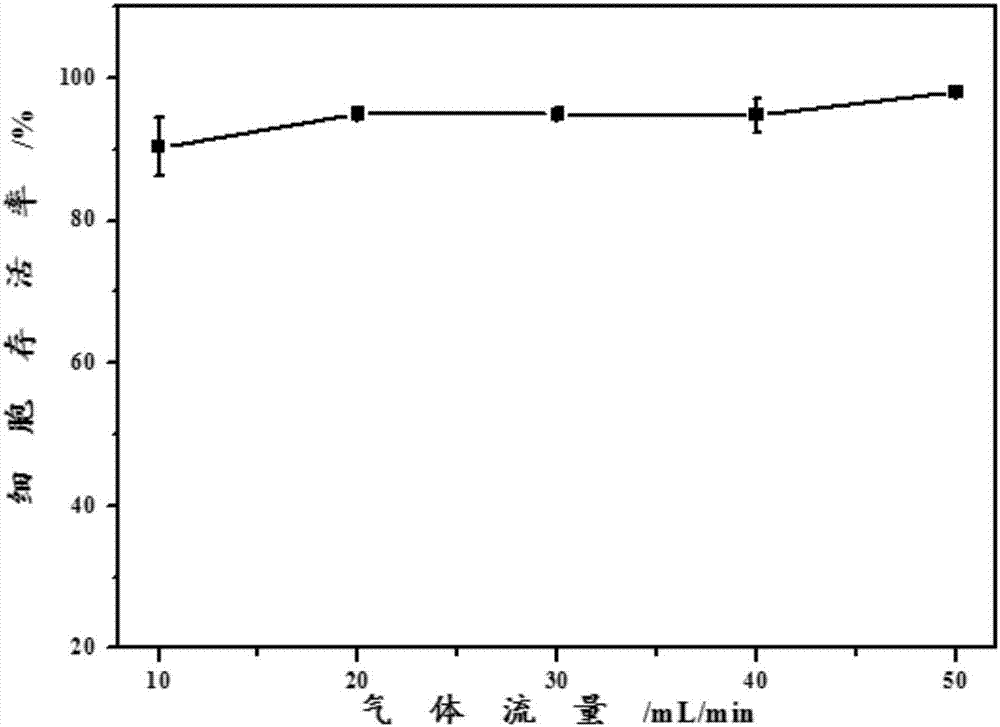
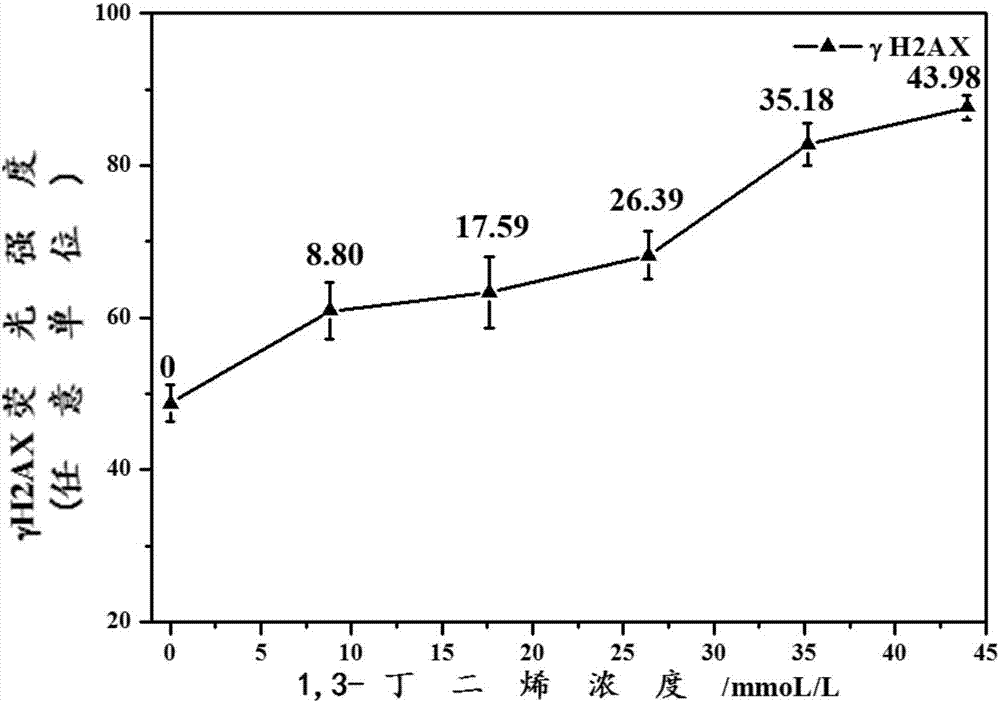
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting 1,3-butadiene-induced cell DNA damage in combination with a gas-liquid interface exposure system and a high-content technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1) cell culture; 2) 1,3-butadiene exposure through a gas-liquid interface exposure mode; 3) immunofluorescent labeling of gamma H2AX; 4) high-content detection. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the efficient exposure of gaseous 1,3-butadiene to wall-attached cells in vivo is realized by adopting the in-vitro gas-liquid interface exposure mode, so that the exposure efficiency of the 1,3-butadiene is improved; a high-content imaging system is utilized for automatic imaging, 1,3-butadiene-induced DNA double-chain fracture maker gamma H2AX proteins are quantitatively analyzed, and the direct and quick detection of the cells is realized, so that the sample treatment is more convenient; through high-resolution imaging, not only can the distribution of the gamma H2AX in cell nucleuses be directly observed, but also image data is convenient to store and re-analyze, and the quantitative analysis on the 1,3-butadiene-induced gamma H2AX in each of the cell nucleuses can be realized, so that detection results are more sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
Immunofluorescence labeling method for proteins in living cells
The present invention discloses an immunofluorescence labeling method for proteins in living cells, and relates to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises following steps: a cell smear is treated through 0.2% TritonX-100 for 10-15 minutes, is washed with 0.01 M PBS for 3-5 minutes, is washed for 3-5 times, is digested with a 0.01 trypsin solution at 37-40 degree Celsius for 12-15 min, iswashed with the 0.01 M PBS for 3 - 5 minutes, is washed for 3 - 5 times, then is blocked with normal rabbit serum, is added with FITC-goat-anti-mouse iGg, is incubated at 37-40 degree Celsius for 30-40 minutes, is washed with the 0.01 M PBS for 3 - 5 minutes, with BrdU used as a protein marker, and after fixed with cross-linking fixative, is observed under a fluorescence microscope. The method canobserve and detect a morphological structure, molecular and ion number of the living cells in real time, can simultaneously study a plurality of target proteins on one specimen, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:陈彩丽
Non-enveloped virus quantum dot marking method and application
PendingCN105717084AImprove performanceImprove efficiencyFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell specificImmunofluorescent labeling
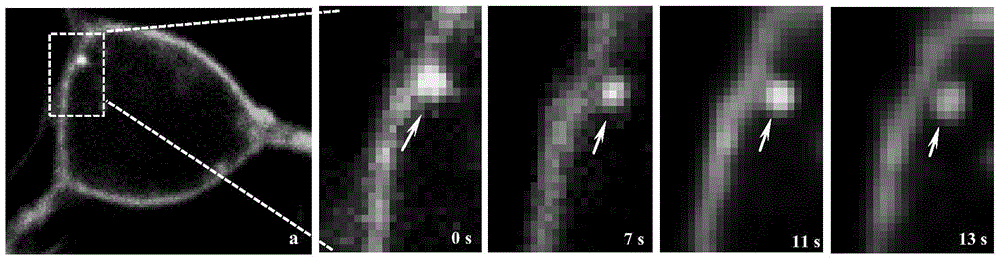
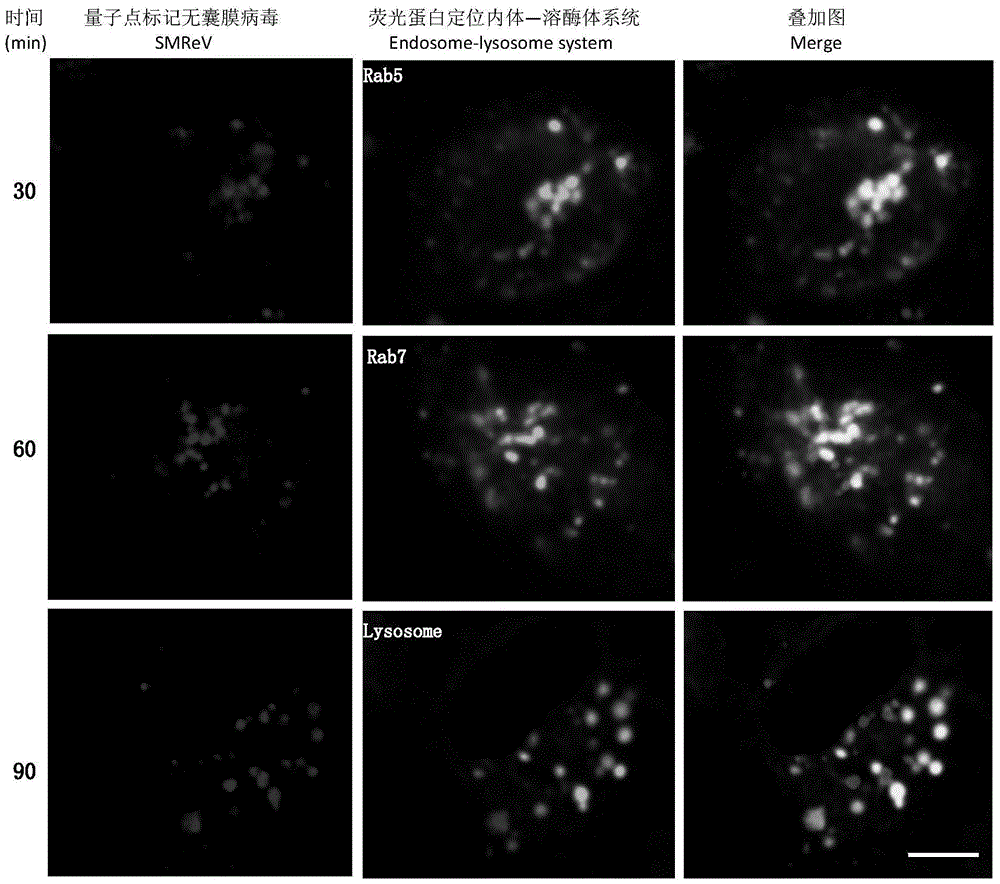
The invention discloses a non-enveloped virus quantum dot marking method and application.The method comprises the steps that biotinylation virus suspension is centrifuged, and biotinylation non-enveloped viruses of the uniform structure are obtained; the viruses are inoculated into susceptible cells, quantum dots are added for incubation, and non-enveloped viruses marked with the quantum dots can be obtained.By means of the marked non-enveloped viruses, non-enveloped virus outer capsid protein immunofluorescence marking and cell specific component fluorescent protein positioning, dynamic tracking of a non-enveloped virus living body in the invasion process and positioning of interaction components of the non-enveloped viruses and host cells are achieved.The method can also be used for monitoring the host cell invasion path of the viruses in real time, and is particularly applicable to identifying the interaction components of fish non-enveloped viruses and host cells and also applicable to screening, research and development of fish reovirus resistance preparations.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
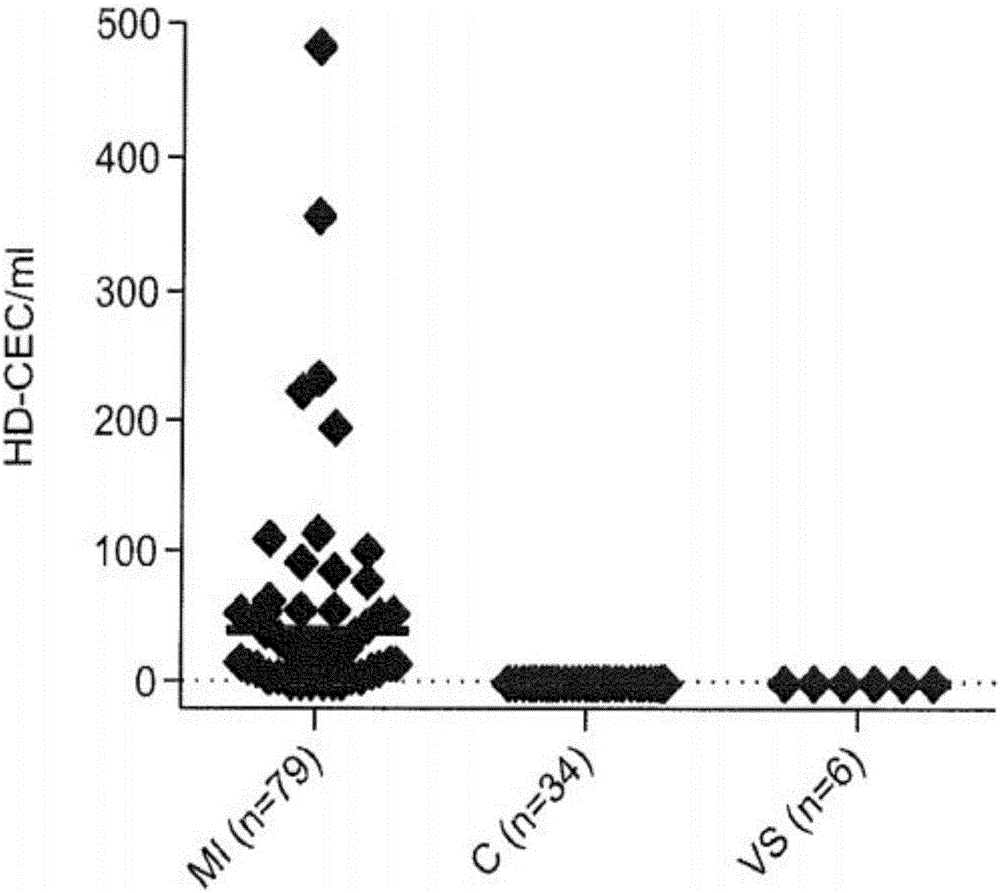
Methods for the detection and quantification of circulating endothelial cells
PendingCN106170542AVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsCirculating endothelial cellImmunofluorescent labeling
The disclosure provides methods for detecting circular endothelial cells (CECs) in a non- enriched blood sample. The present disclosure is based, in part, on the unexpected discovery that CECs can be detected in non-enriched blood samples. The present disclosure is further based, in part, on the discovery that CECs can be detected in non-enriched blood samples by combining the detection of one or more immunofluorescent markers in the nucleated cells of a non-enriched blood sample with an assessment of the morphology of the nucleated cells. The present disclosure is further based, in part, on the discovery that CECs can be detected in non-enriched blood samples by comparing the immunofluorescent marker staining and morphological characteristics of CECs with the immunofluorescent marker staining and morphological characteristics of WBCs. The methods disclosed herein serve to classify human subject in myocardial infarction (MI) patients or healthy controls.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
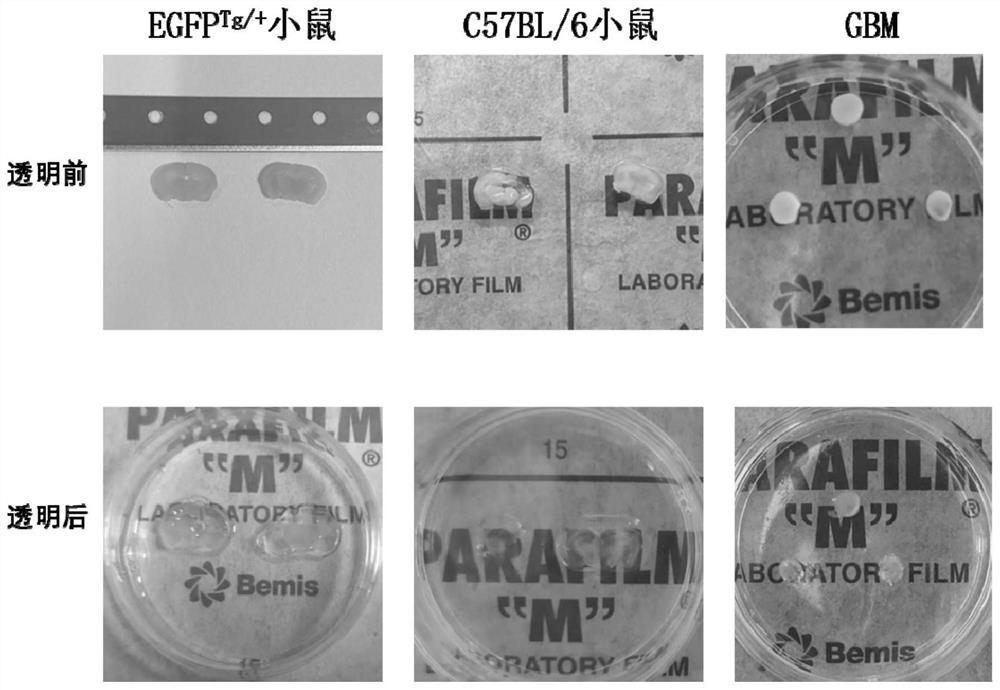
Application of combination of tissue transparentizing method and histological method to detection of bacteria in tumor
PendingCN113640520AAvoid pollutionReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingImmunofluorescent labelingBiology
The invention relates to the technical field of detection, and particularly discloses application of combination of a tissue transparentizing method and a histological method in detection of bacteria in tumors. According to the invention, a tissue transparentizing method and a traditional histological method are combined for use, so that the limitation (several microns) on the thickness of a sample can be broken so as to avoid potential pollution on the surface of a thin slice, and a high-resolution and integral three-dimensional image of a large-size tissue sample can be completely constructed so as to achieve three-dimensional visualization of bacteria in tumors; and a tissue with a thickness of 500 microns is selected, optical transparency is achieved through a tissue transparentizing method, and a traditional histological method (such as an immunofluorescence labeling method) is combined for labeling bacteria in the tumor tissue, so that a more accurate experiment result is obtained, and a solid foundation is laid for researching the direct interaction between the microbial population and the tumor cells in the tumor microenvironment.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
An immunochromatographic detection method based on near-infrared luminescent rare earth nanomaterials
ActiveCN110514825BGood light stabilityImprove stabilityBiological testingQuantum efficiencyImmunofluorescence
The invention discloses an immunochromatographic detection method based on a near-infrared luminescent rare earth nano-material, which uses the near-infrared luminescent rare earth nano-material as animmunofluorescent marker to mark and recognize antibodies for performing immunochromatographic detection. The near-infrared luminescent rare earth nano-material has the following characteristics: (1)both the excitation light and the emission light are located in the near-infrared light region from 700 to 1700 nm; (2) the excitation wavelength is less than the emission wavelength, and the excitation light is a positive Stokes shift luminescence, and the Stokes shift is greater than 150 nm; (3) the fluorescence quantum efficiency is higher than 1%; (4) the fluorescence lifetime is greater than10 microseconds; and (5) the light stability is better than organic dyes. By using the immunochromatographic detection method based on the near-infrared luminescent rare earth nano-material disclosedby the invention for immunochromatographic detection, the stability of the fluorescent marker is better, the fluorescence emission is stronger, and the detection result has better repeatability.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
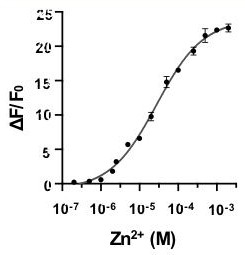
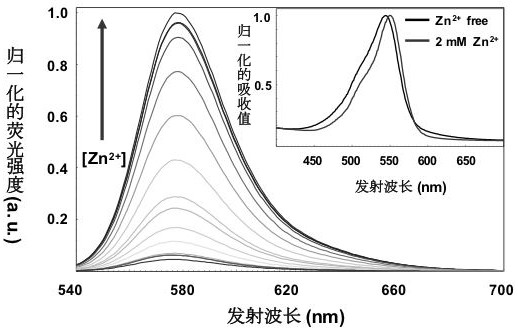
Rhodamine fluorescent dye containing water-soluble substituent as well as preparation method and application of rhodamine fluorescent dye
The invention discloses a rhodamine dye containing a water-soluble substituent and a functional derivative (a zinc ion probe and an antibody labeled dye) of the rhodamine dye. The rhodamine dye has a structure as shown in a general formula I. After the N-site of a parent nucleus of the dye is connected with different water-soluble substituents, the biocompatibility of the parent nucleus of the dye is greatly improved; and specifically, non-specific staining in cells is remarkably reduced, cell apoptosis signals do not appear any more, phototoxicity is remarkably reduced (the zinc ion probe), labeling efficiency is improved, observation time is prolonged (the antibody labeled dye) and the like. The fluorescent dye disclosed by the invention can be applied to the fields of observing insulin release of in-vitro live pancreas islets, immunofluorescence labeling and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
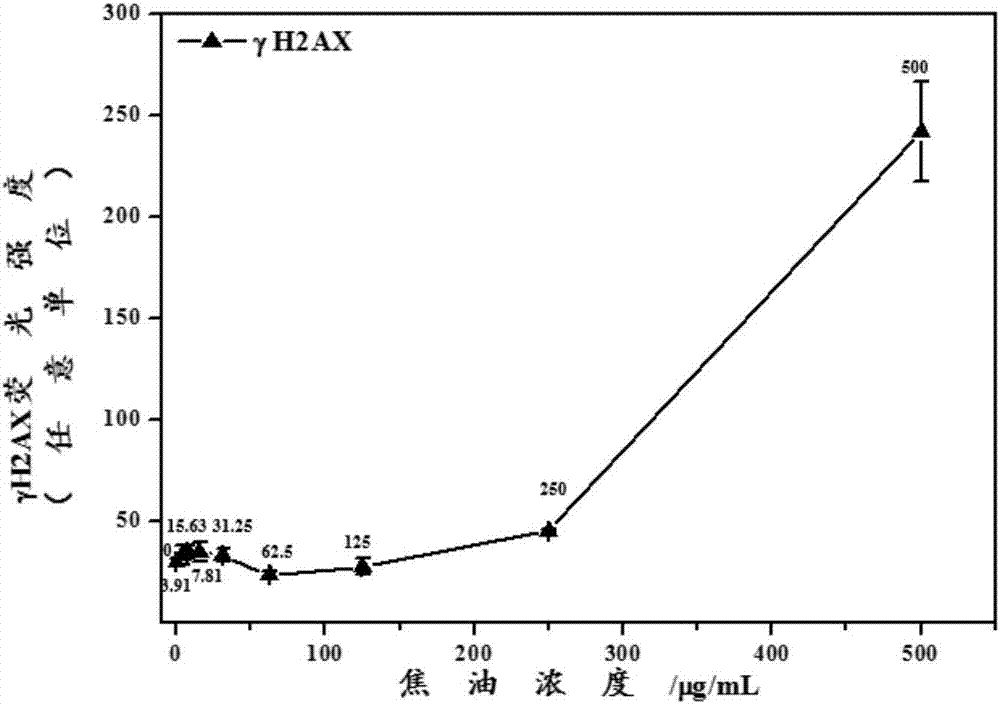
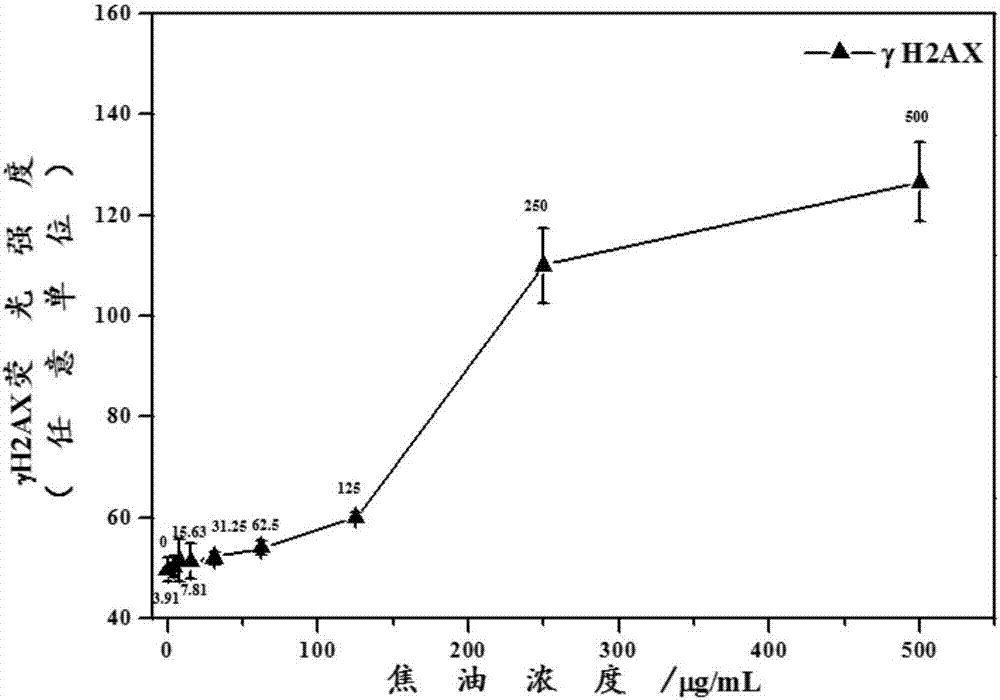
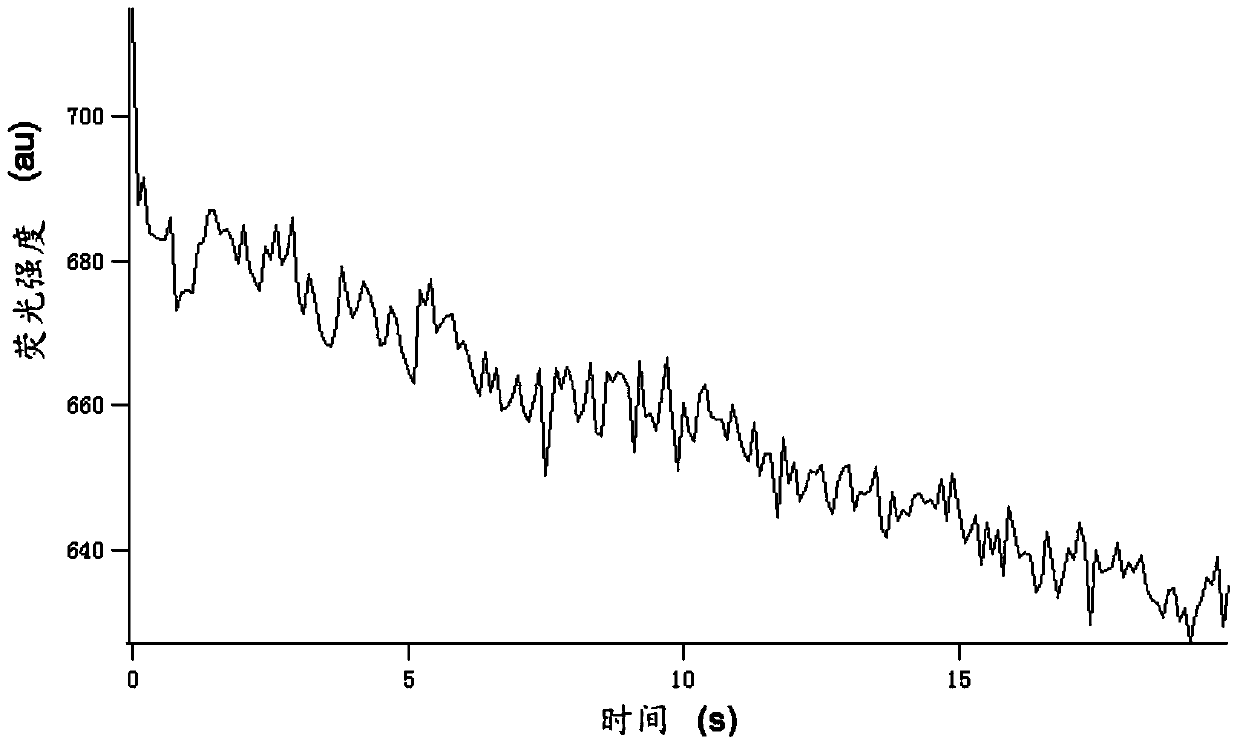
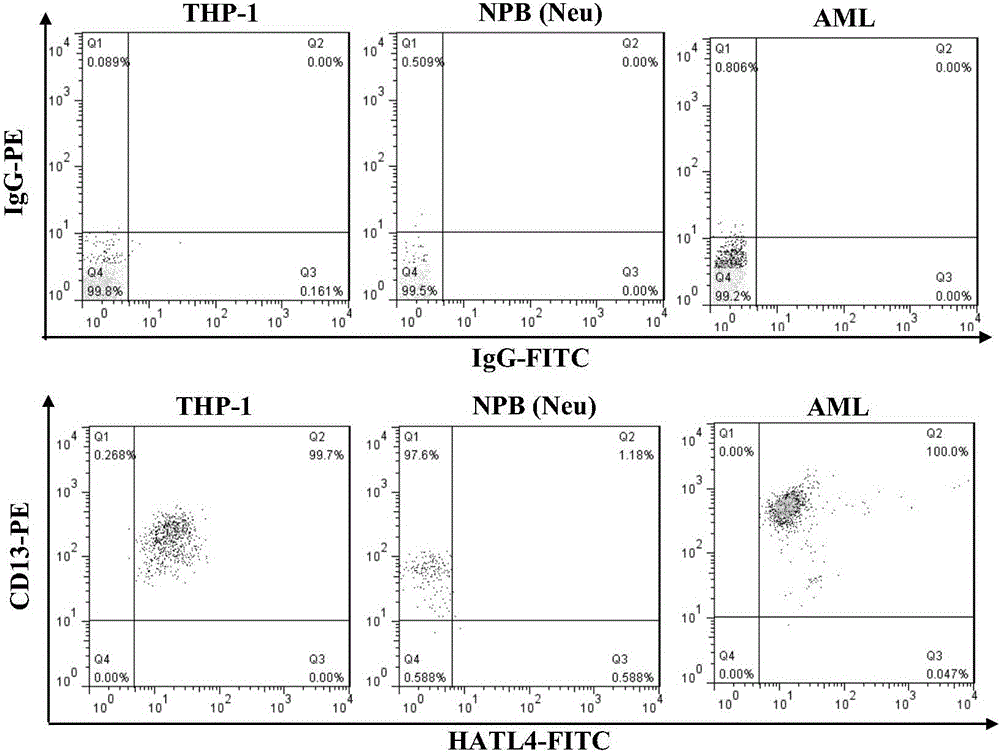
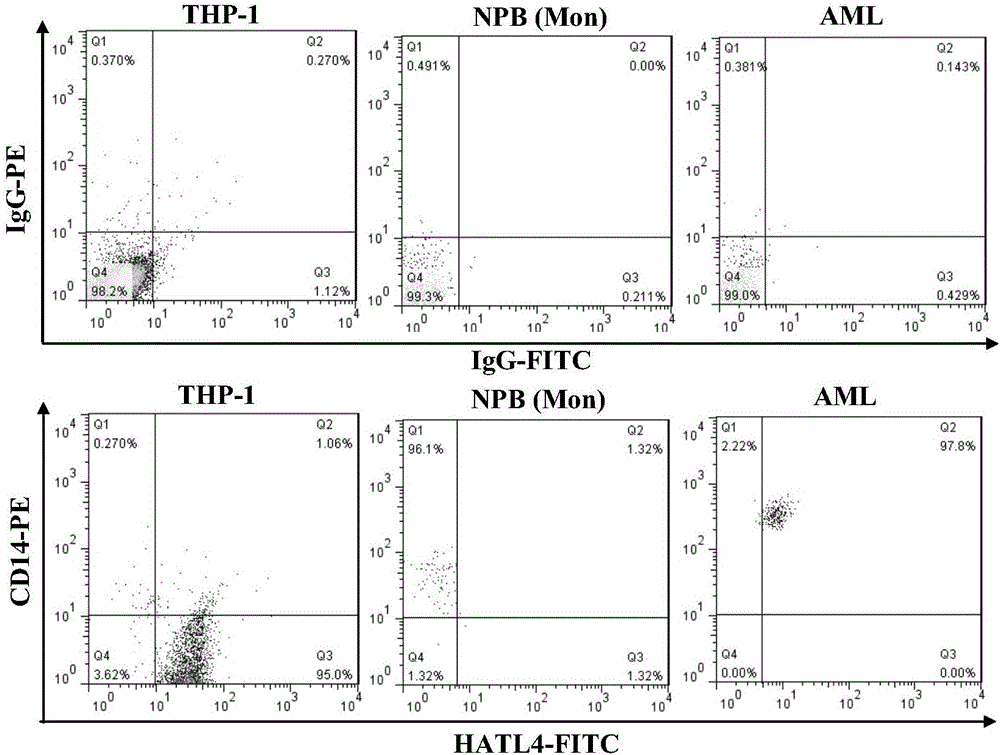
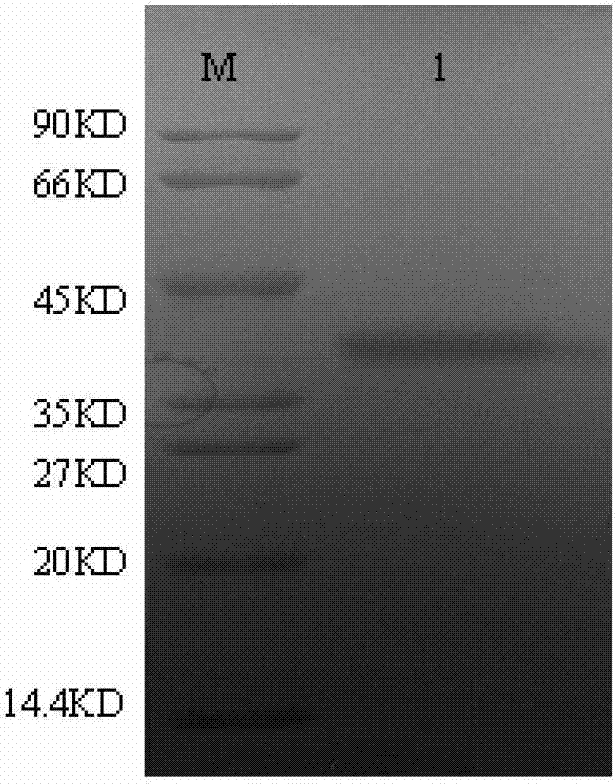
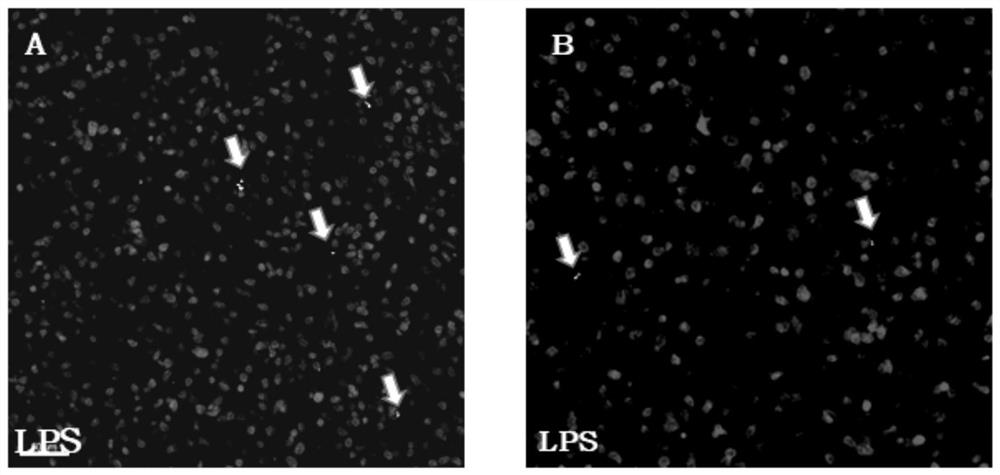
Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique
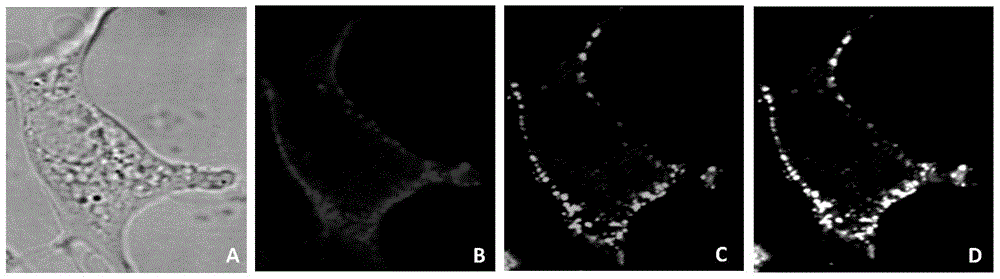
InactiveCN107064086AGood effectLess cellsFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh resolution imagingImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on a high connotation technique. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing cell culture; 2) infecting cells; 3) performing immunofluorescent labeling for gamma H2AX; and 4) performing quantitative analysis by adopting the high connotation technique. The method has the advantages that a high connotation imaging system is utilized for automatically imaging and quantitatively analyzing the gamma H2AX protein of a DNA double-strand breaking mark induced by benzo[a]pyrene, the direct and quick detection for cells is realized, and the sample treatment is more convenient; and due to high-resolution imaging, the distribution of gamma H2AX in a cell nucleus can be directly observed, the image data can be conveniently stored and analyzed, and the quantitative analysis for gamma H2AX, induced in each cell nucleus, of benzo[a]pyrene, can be realized, so that the detection result is more sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
Immunofluorescence method for locating woody plant pollen tube protein and kit thereof
InactiveCN108318679APositioning directlyEffective positioningMaterial analysisSucroseImmunofluorescent labeling
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Prognostic evaluation method for hepatocellular carcinoma through Telocytes
InactiveCN114034722ASolve the problem of the possibility of prognostic evaluation indicatorsPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceParanasal Sinus CarcinomaStaining
The invention relates to the technical field of clinical medicine, in particular to a prognostic evaluation method for hepatocellular carcinoma through Telocytes, which comprises the following steps: taking a postoperative tumor specimen of a hepatocellular carcinoma patient, preparing a frozen section or a paraffin section from a cancer cell para-tissue within a range of 1-2cm from the tumor, carrying out immunofluorescent staining by using CD34 (highly glycosylated I-type transmembrane glycoprotein) / CD117 (III-type transmembrane kinase receptor protein) / PDGFR (platelet-derived growth factor receptor) / vimentin (waveform fibrin) indexes, taking CD34 + / CD117 + / PDGFR + / vimentin-cells as TCs cells, putting para-carcinoma tissues into a general stationary liquid for an electron microscope, performing slicing, and observing the morphology of the TCs cells under a transmission electron microscope. According to the prognostic evaluation method for the hepatocellular carcinoma through the Telocytes, multiple groups of double immunofluorescence markers are adopted, and the cell morphology and the telomere number are observed, so that accurate indexes for prognostic evaluation of patients can be provided for clinicians, and the problem of probability of prognostic evaluation indexes of the patients with the hepatocellular carcinoma is solved.
Owner:许莹
A kind of nanometer fluorescent probe solution and application of hepatic cell labeling below freezing point
ActiveCN113061427BPerformance is not affectedGuaranteed steady stateMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsFluoProbesImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention belongs to the field of biological imaging of nanomaterials, and discloses a nano fluorescent probe solution for liver cell labeling below freezing point and its application. The nano fluorescent probe solution includes nano fluorescent probes dispersed therein as a dispersoid; The needle includes nano fluorescent particles and targeting molecules coupled on the surface of the nano fluorescent particles, the targeting molecules can be used to target specific cells in the liver; and the nano fluorescent probe solution also includes antifreeze substances, the concentration of the antifreeze substances satisfies the nano Fluorescent probe solutions remain liquid at temperatures below freezing. In the present invention, by improving the detailed structure and composition of the nano fluorescent probe solution, the specific liver cells of the pre-selected cell type can be used as the target cells, and based on the nano fluorescent probe, the liver cells can be immunofluorescently labeled below freezing point , has the characteristics of rapidity, simplicity and high efficiency, and is especially suitable for use as a fluorescent marker in liver micro-optical section tomography.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com










![Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a030fdd0-712b-4383-933c-044a172bd1a0/HDA0001247233460000011.png)
![Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a030fdd0-712b-4383-933c-044a172bd1a0/HDA0001247233460000012.png)
![Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a030fdd0-712b-4383-933c-044a172bd1a0/HDA0001247233460000021.png)