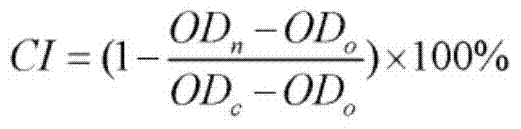Patents
Literature
38 results about "High content imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
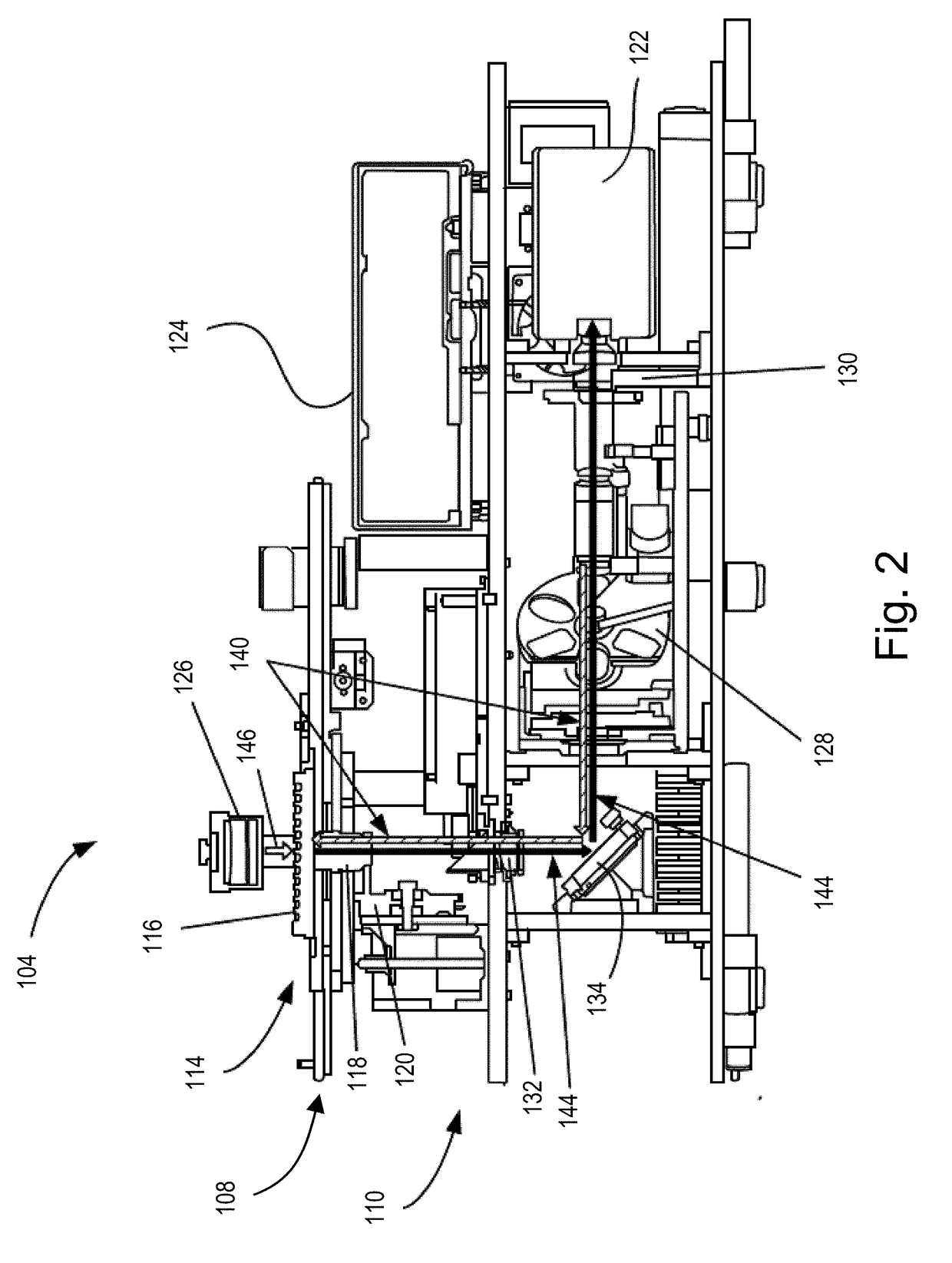
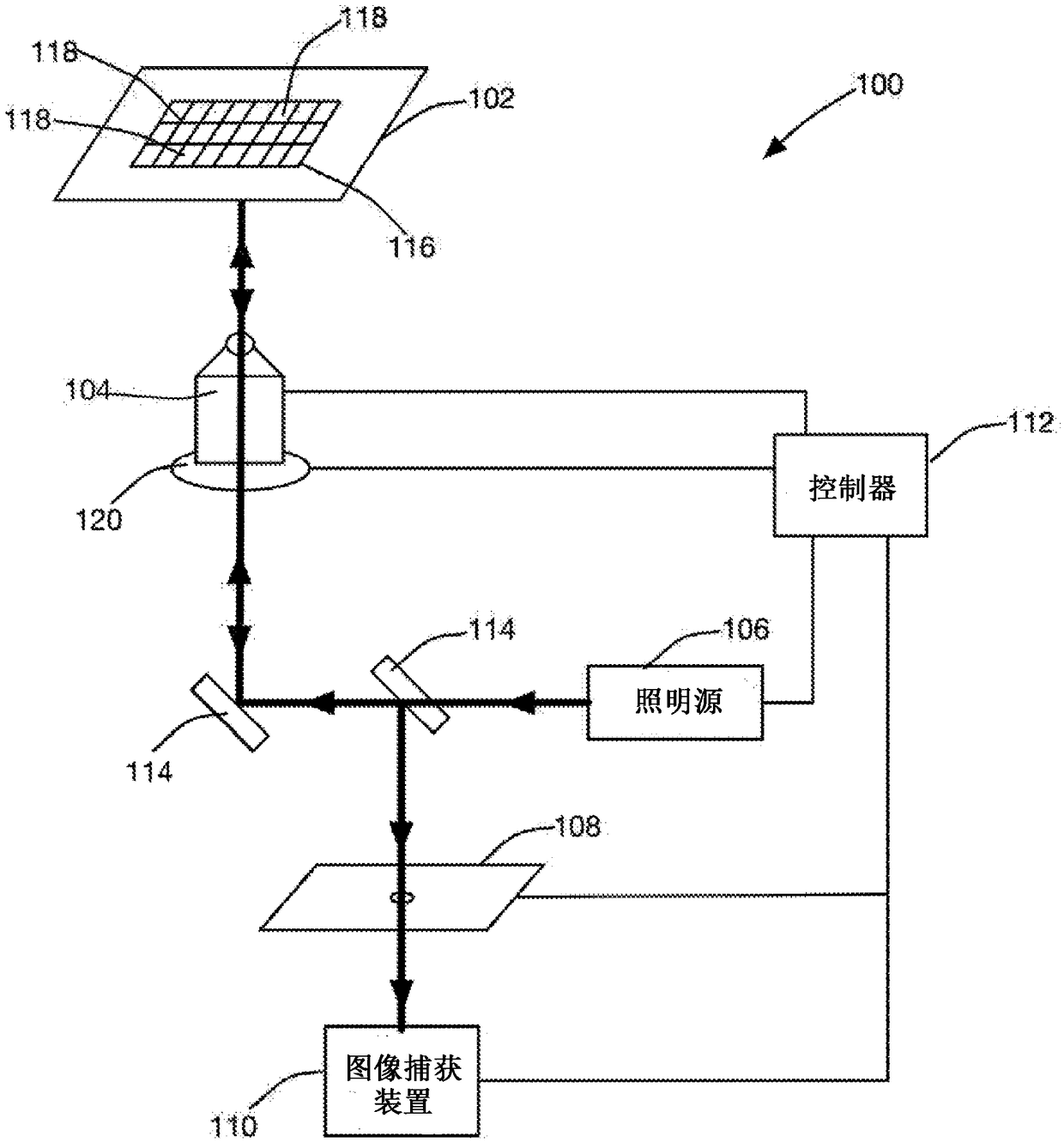
High content imagers (HCI) at the present time typically consist of an automated microscope or components of a microscope in a box supplied with image analysis software and commonly have image management packages to store images on a server/data storage system.
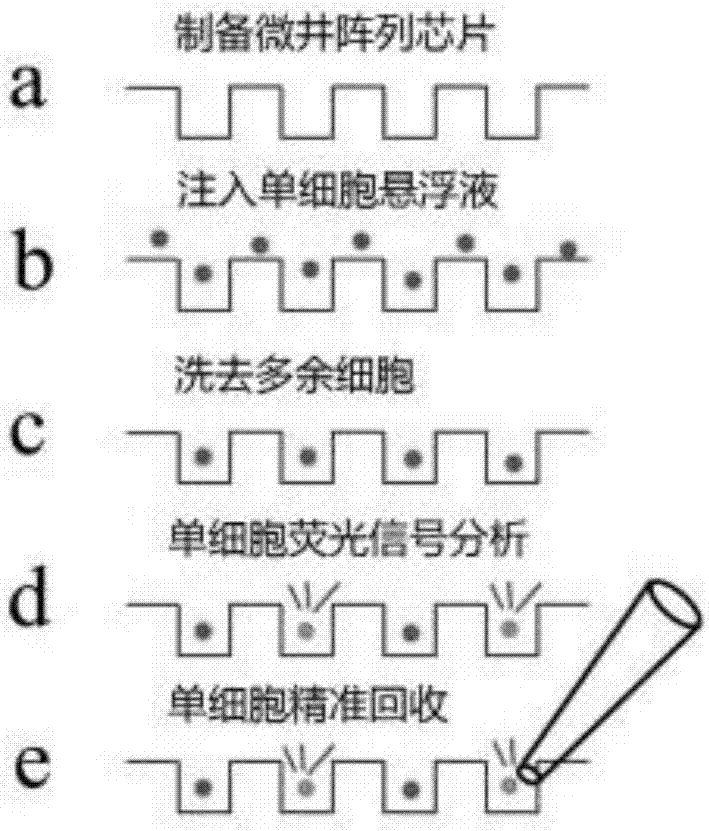
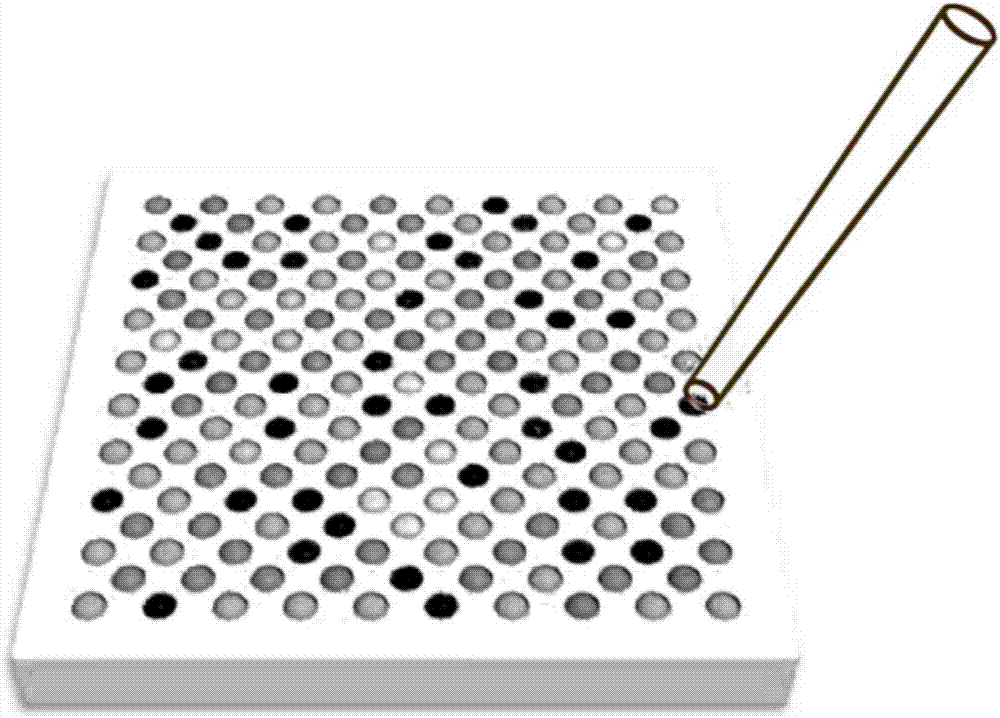
Efficient capturing, high-content imaging and whole transcriptome analyzing device and method for single cell
InactiveCN107389642AEfficient captureReduce consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh fluxHigh throughput imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of single-cell capturing and analysis and in particular relates to an efficient capturing, high-content imaging and whole transcriptome analyzing device and method for a single cell. The device is used for capturing the single cell; the device comprises a polydimethylsiloxane micro-well array chip and a cell culture plate substrate or a cell culture dish substrate; the micro-well array chip is fitted to the cell culture plate substrate or the cell culture dish substrate. The invention provides the device and method, which can be used for simultaneously carrying out single-cell high-throughput imaging analysis, whole transcriptome analysis of the target single cell and deep exploration of heterogeneity between the single cells from a whole transcriptome level of the single cells.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
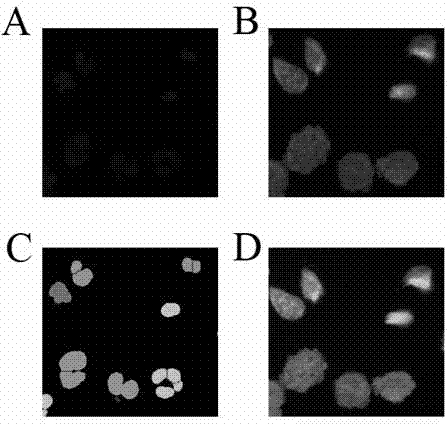
In-vitro cell micronuclei method for detecting total particulate matters of main stream smoke of cigarettes
ActiveCN104122189ALong storage timeThe detection process is fastImage analysisPreparing sample for investigationTotal particulate matterBiology
The invention discloses an in-vitro cell micronuclei method for detecting total particulate matters of main stream smoke of cigarettes. The method comprises the steps of seeding cells on a 96-hole plate for cigarette smoke contamination, directly fixing, dyeing, and feeding the cells into a high-connotation imaging system for detection; setting fluorescence intensity parameters of main nucleuses and the micronuclei of the cells according to the difference between a fluorescence value of cell nucleuses and a background fluorescence value, measuring the sizes of the main nucleuses and the micronuclei of the cells so as to set nucleus diameter parameters, and setting distance parameters according to distances between the cell nucleuses; performing analysis on images according to the setting, and selecting the number of binucleated cells with the micronuclei and the total number of the binucleated cells from a result lead-out column so as to calculate the micronucleus rate. According to the method, the number of required cells is small, the cells are not need to be used, and micronuclei sheets are not required to be manufactured; furthermore, the in-vitro cell micronuclei method is high in detection speed, large in sampling quantity and high in accuracy.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Automated imaging of chromophore labeled samples
ActiveUS20150323462A1Improve abilitiesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPlanar light sourcesDifferential absorptionFluorophore
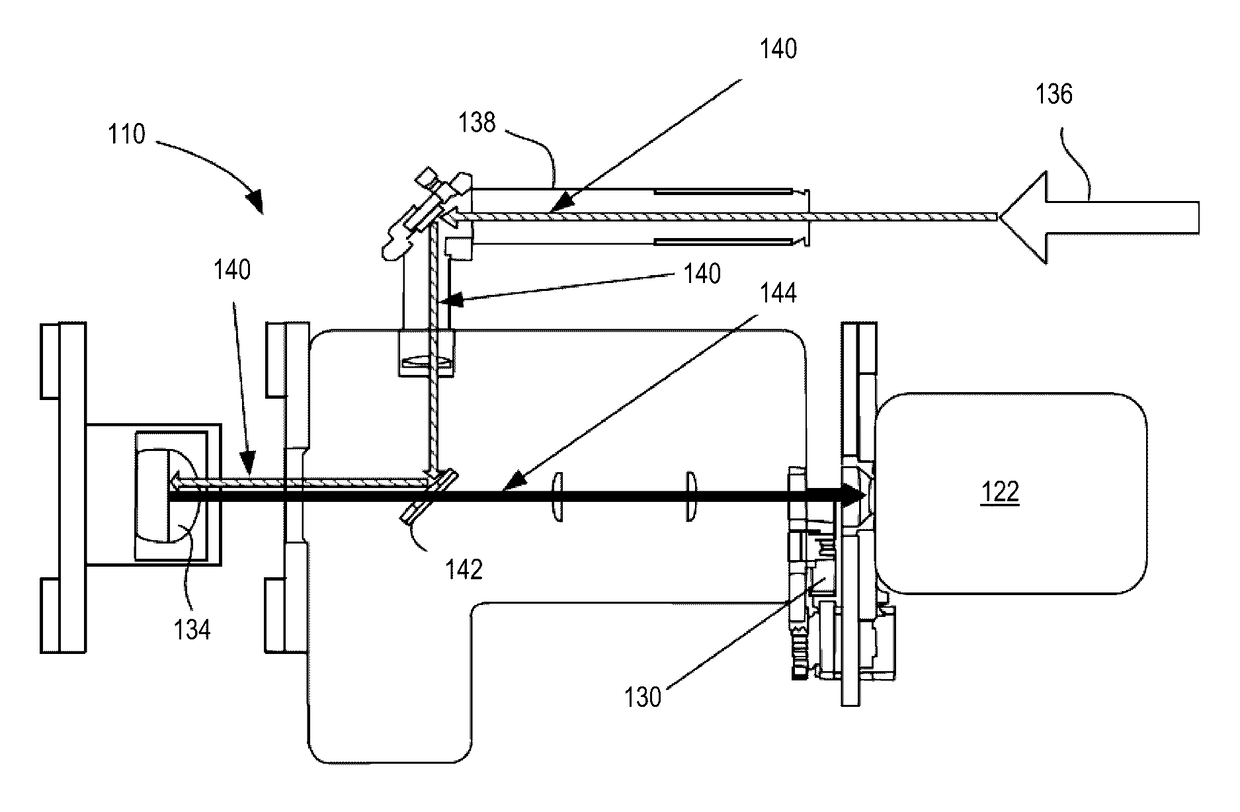
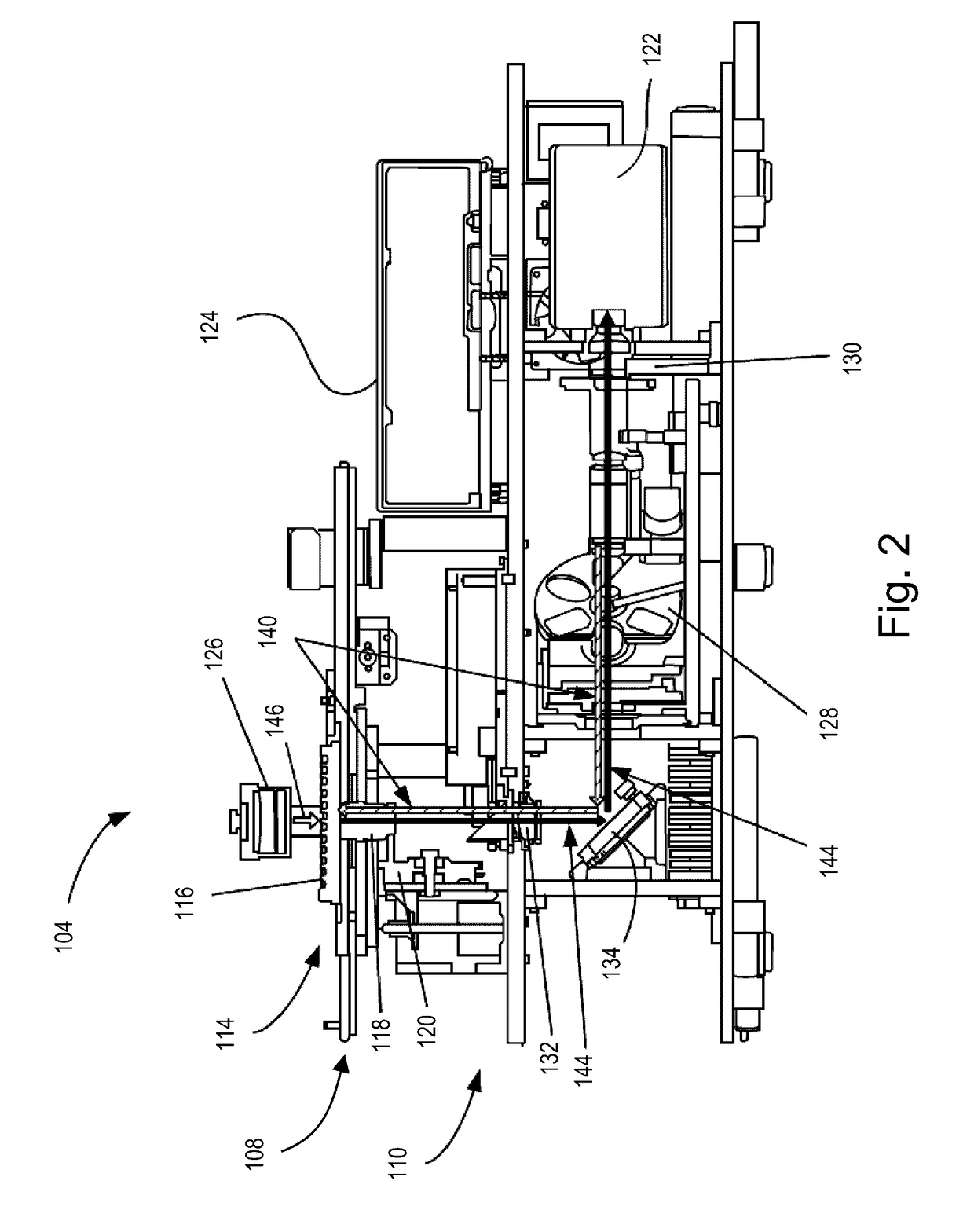
A system and method that images biological samples and uses chromophores to analyze the imaged samples. The chromophore analysis can be done by itself or in conjunction with fluorophore analysis in High Content Imaging systems. To perform chromophore analysis the biological samples can be labeled with different chromophores and imaged using transmitted light that is at least partially absorbed by the chromophores. To also perform fluorophore analysis the samples can also be labeled with fluorophores that are excited by excitation light. The chromophore analysis and fluorophore analysis can be performed separately or concurrently using a High Content Imaging system. The system provides the expanded capability by illuminating the chromophore-labeled samples with transmitted light of different wavelengths and automatically detecting the images which represent the differential absorption of the colored lights by the sample.
Owner:CELLOMICS
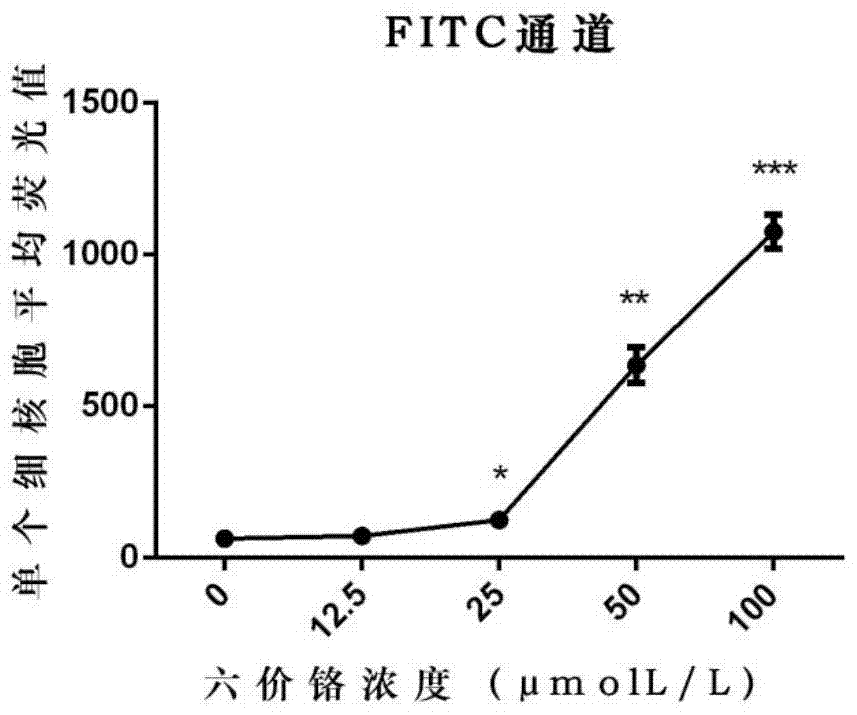
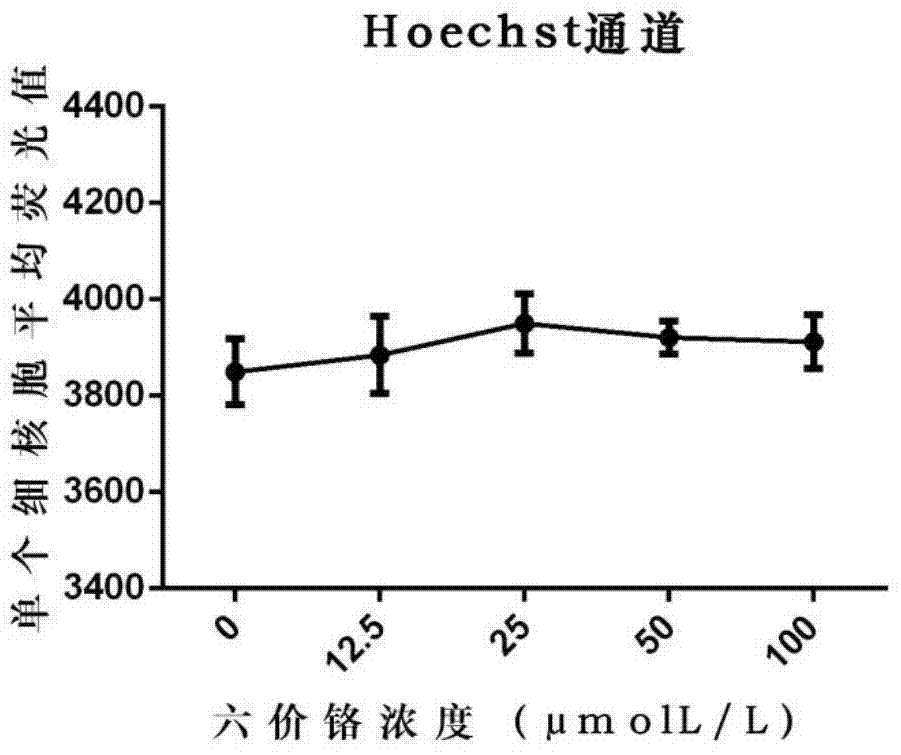
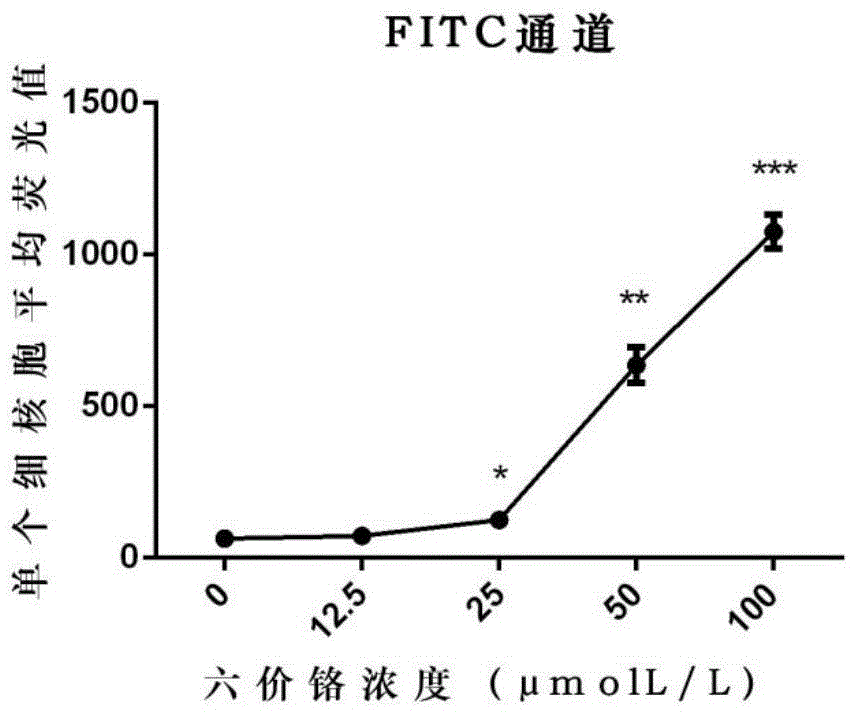
Evaluation method for measuring cell DNA damage caused by soluble heavy metal
ActiveCN104931473AFast and accurate simultaneous detectionThe target is accurate and intuitiveFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell stainingHigh content imaging
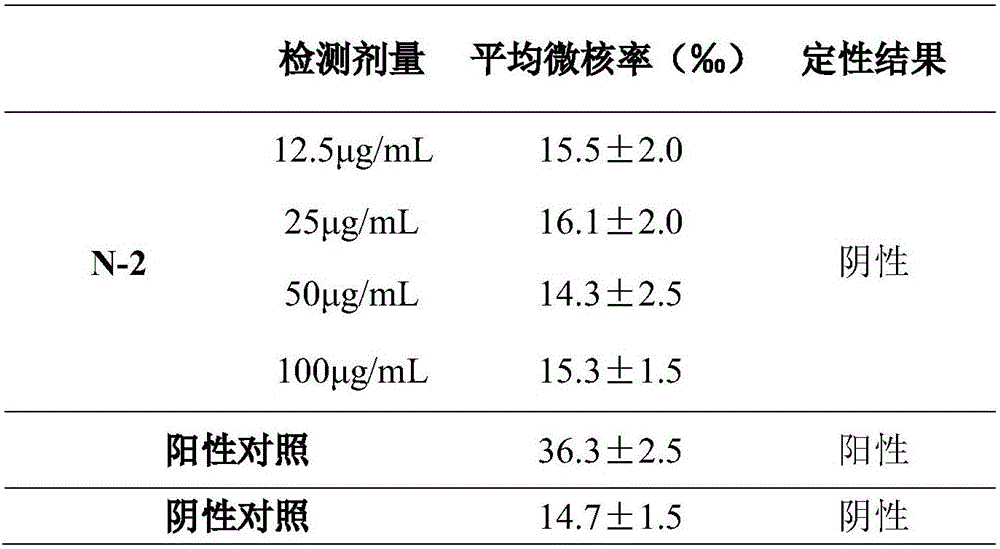
The invention relates to an evaluation method for measuring cell DNA damage caused by soluble heavy metal. The method includes the following steps that firstly, tested cells are processed through a soluble heavy metal solution; secondly, the processed tested cells are fixed and are subjected to cell permeabilization; thirdly, the tested cells having been subjected to cell permeabilization are dyed; fourthly, detection is performed through a high-content imaging system and analysis is performed. The evaluation method for measuring the cell DNA damage caused by the soluble heavy metal is convenient to operate, high in sensitivity and high in detection speed and has high specific pertinence, and research on the genetic toxicity of the heavy metal is supplemented and expanded.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
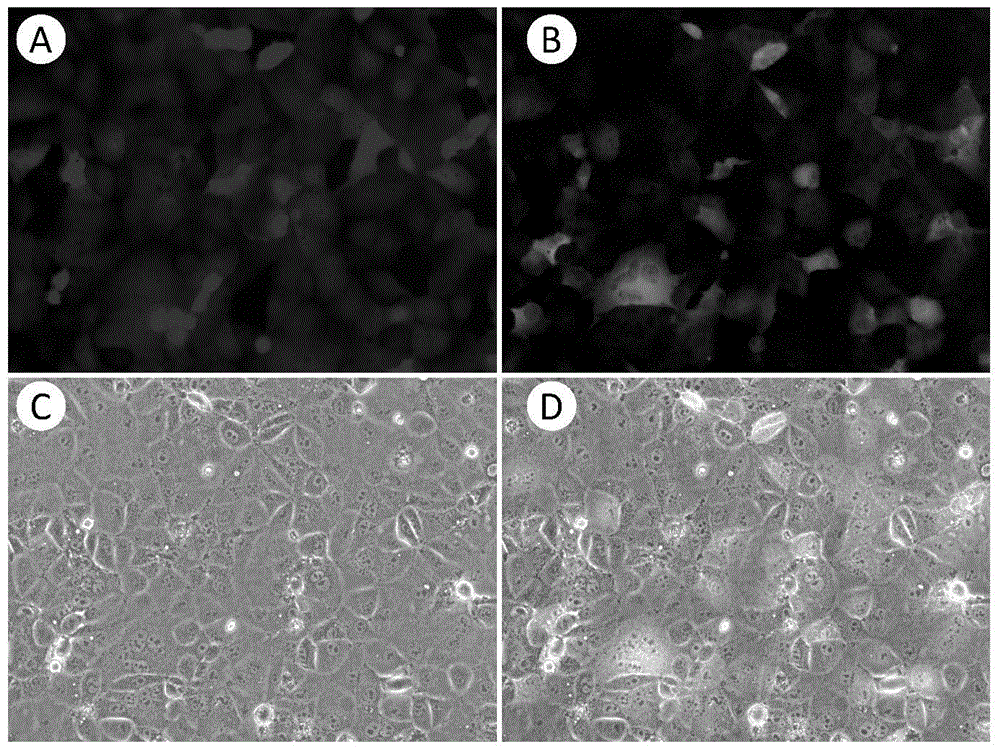
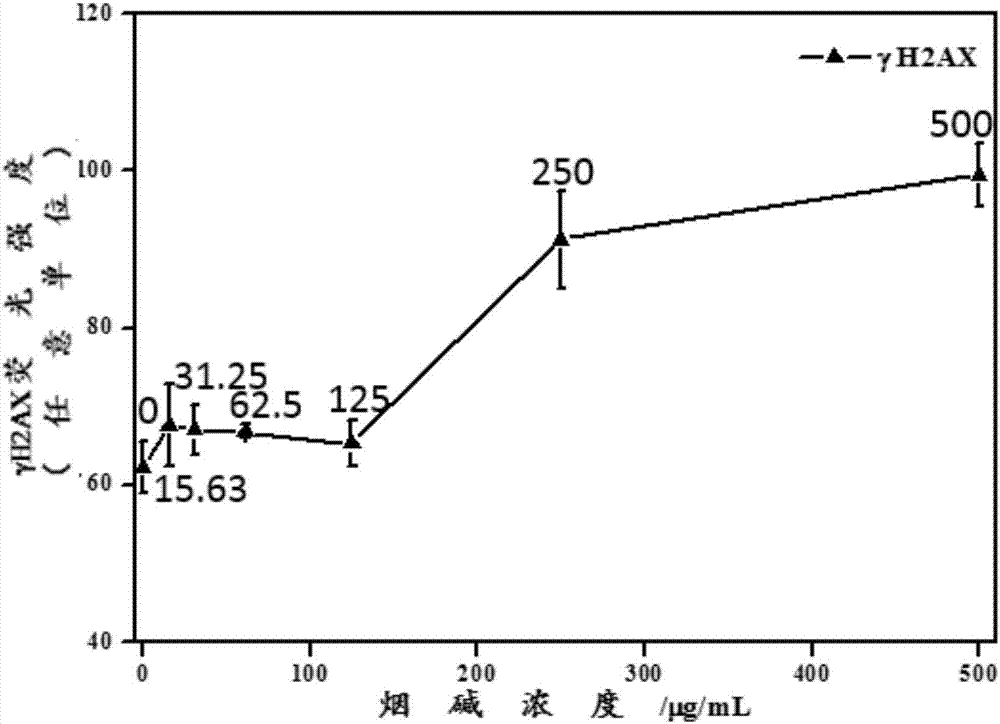
Method of detecting influence on human oral cell [gamma] H2AX level due to tobacco chewing gum
InactiveCN106367468AEasy to crushIncrease contact areaMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisMeasuring instrumentCell culture media
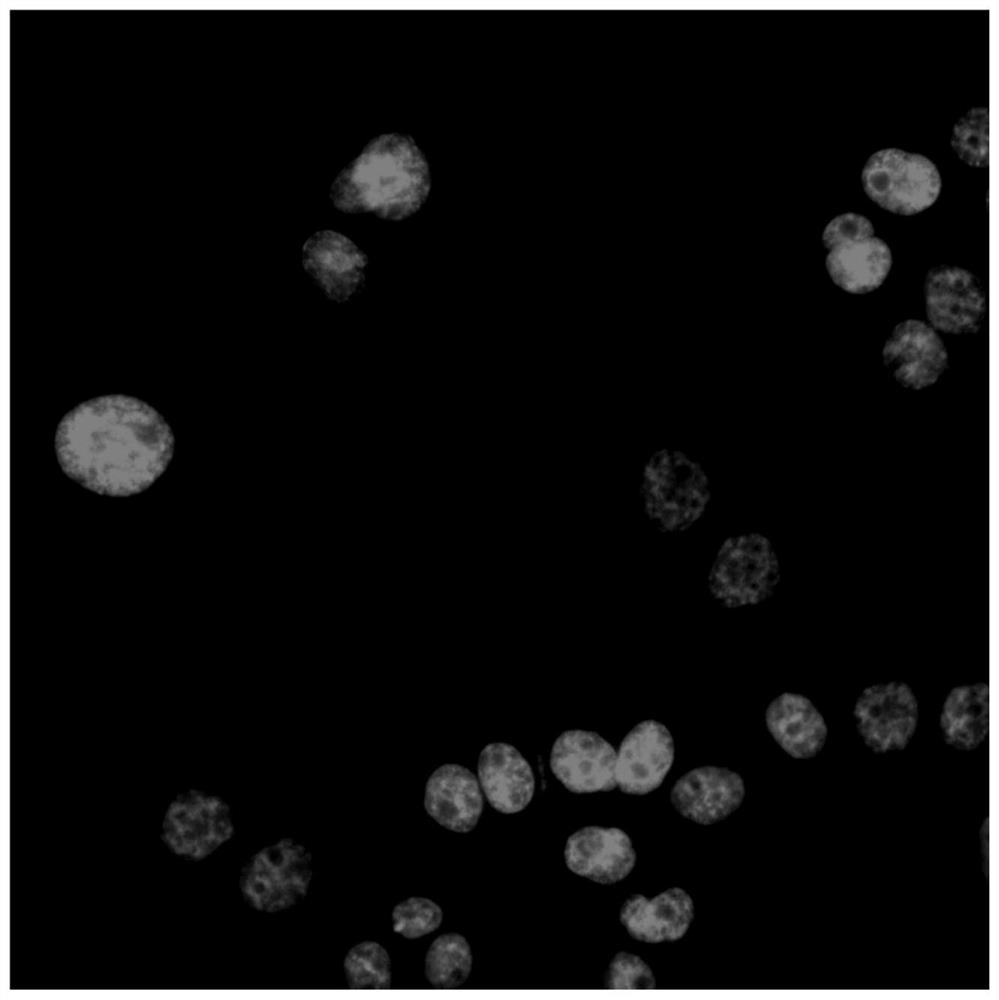
The invention discloses a method of detecting influence on human oral cell [gamma] H2AX level due to tobacco chewing gum. The method includes the steps of: 1) freezing to-be-tested tobacco chewing gum in liquid nitrogen; 2) instantly crushing the tobacco chewing gum by means of a crusher; 3) freezing the crushed tobacco chewing gum in the liquid nitrogen; 4) soaking the crushed tobacco chewing gum in artificial saliva; 5) centrifugally separating an extract liquid; 6) detecting a supernatant liquid by means of an osmotic pressure measuring instrument and regulating the osmotic pressure to be consistent with that of a cell culture medium; 7) measuring the content of nicotine in the extract liquid; 8) culturing human oral mucosa epithelial cells as a detection object; 9) adding the extract liquid of the tobacco chewing gum to the cultured human oral mucosa epithelial cells; and 10) culturing the cells for 4 hours, and detecting the change situation of the [gamma] H2AX of the cells by means of a high-content imaging instrument.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Application of bifluorescence reporting system in tumor stem cell targeted drug screening and method thereof
InactiveCN104593512AImprove filtering effectMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisScreening effectGreen fluorescent protein
The invention discloses application of a bifluorescence reporting system in tumor stem cell targeted drug screening and a method thereof. Red and green fluorescence proteins are utilized to respectively mark colony tumor cells and tumor stem cells, and the targeting properties of the drug for the tumor cells and tumor stem cells can be respectively evaluated by using a high-content imaging system. No targeted drug screening methods for tumor stem cells exist at present. The tumor stem cell screening method established by the invention is hopeful to be used for screening novel antineoplastic drugs for tumor stem cells, thereby enhancing the screening effect of the antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
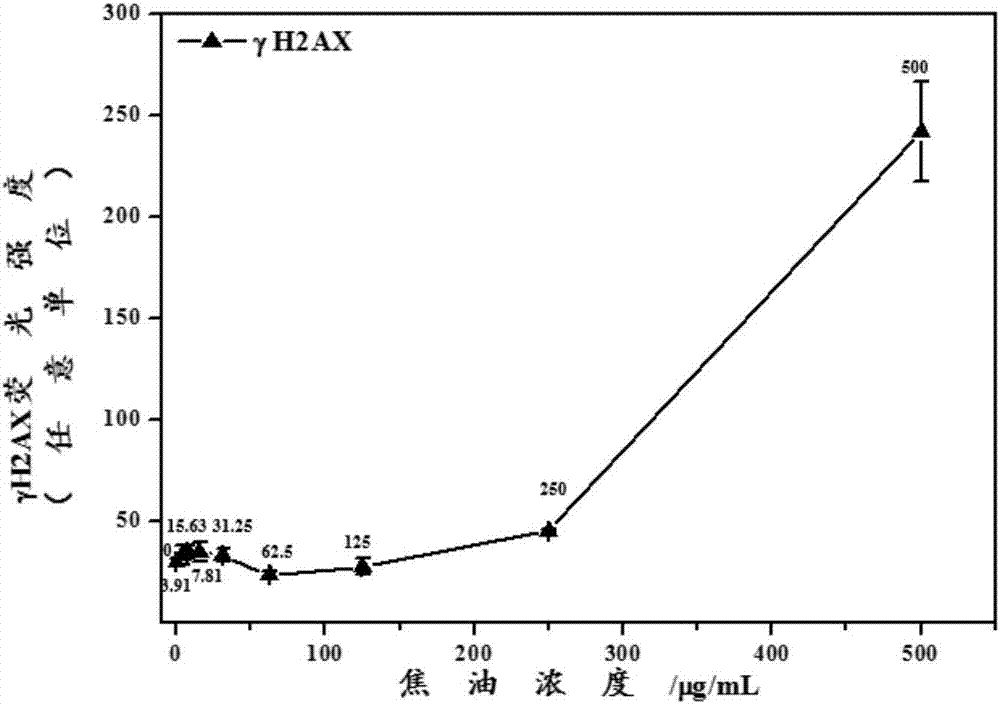
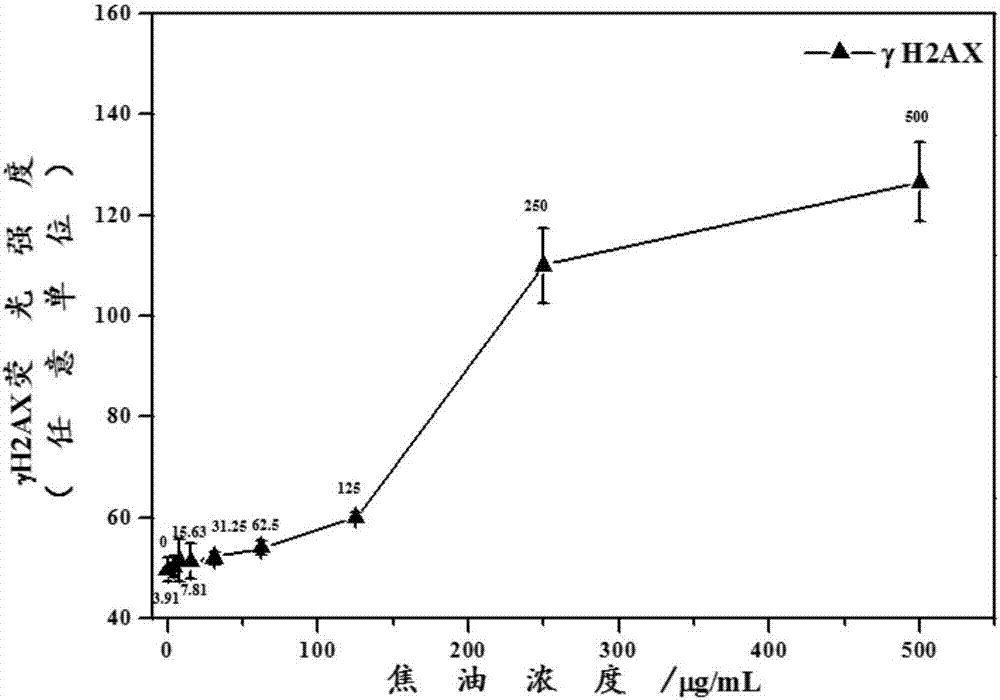
Method for analyzing tar-induced cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) damage on basis of quantitative analysis of high content technology
InactiveCN106970051AHigh-throughput detectionOvercome deficienciesFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh resolution imagingImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention discloses a method for analyzing tar-induced cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) damage on the basis of quantitative analysis of the high content technology. The method includes the steps of 1), cell culture; 2), cell contamination; 3), immunofluorescent labeling of gamma H2AX; 4), quantitative analysis of high content technology. The method has the advantages that automatic imaging is performed by the aid of a high content imaging system, tar-induced gamma H2AX protein of DNA double-strand fracture markers is quantitatively analyzed, cells are detected directly and rapidly, and sample processing is facilitated; distribution of gamma H2AX in cell nucleuses can be observed directly and image materials are stored and reanalyzed conveniently through high-resolution imaging, the tar-induced gamma H2AX in each cell nucleus can be quantitatively analyzed, and detection results are more sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
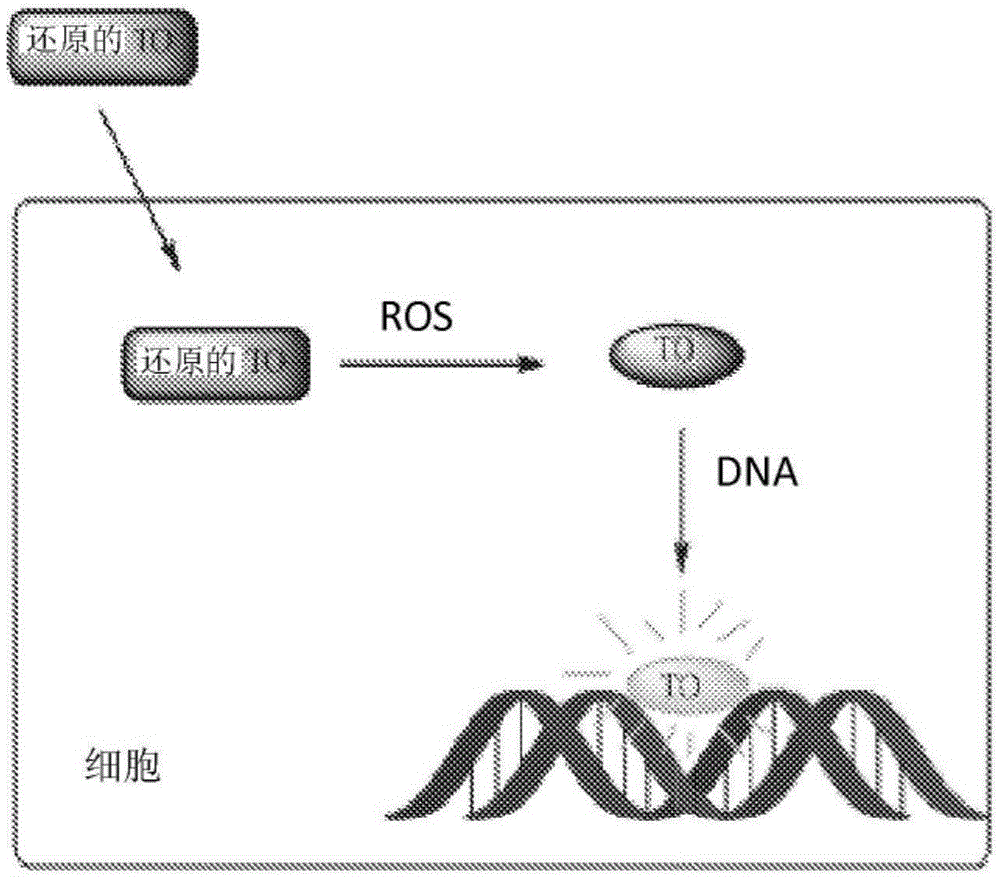
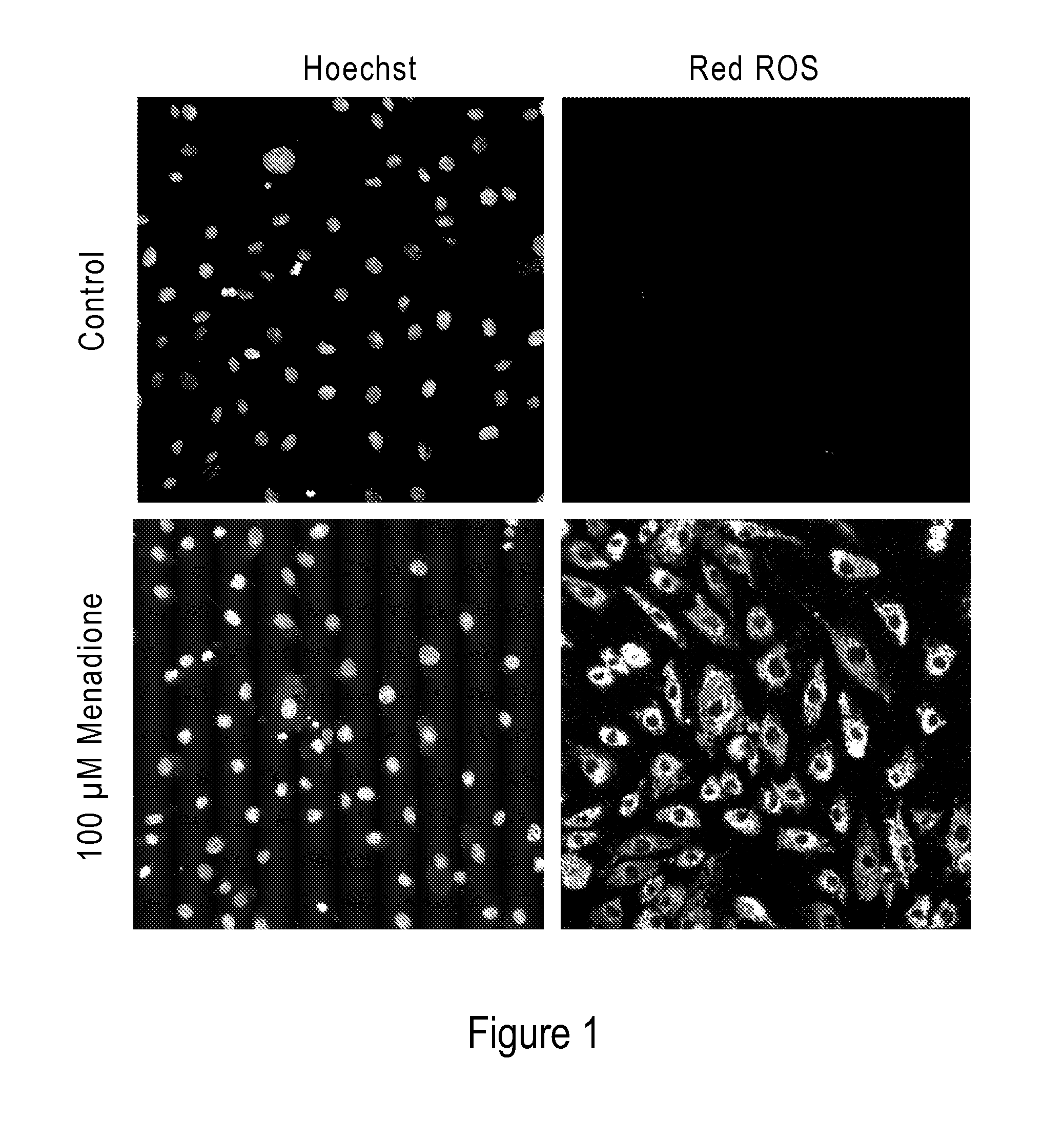
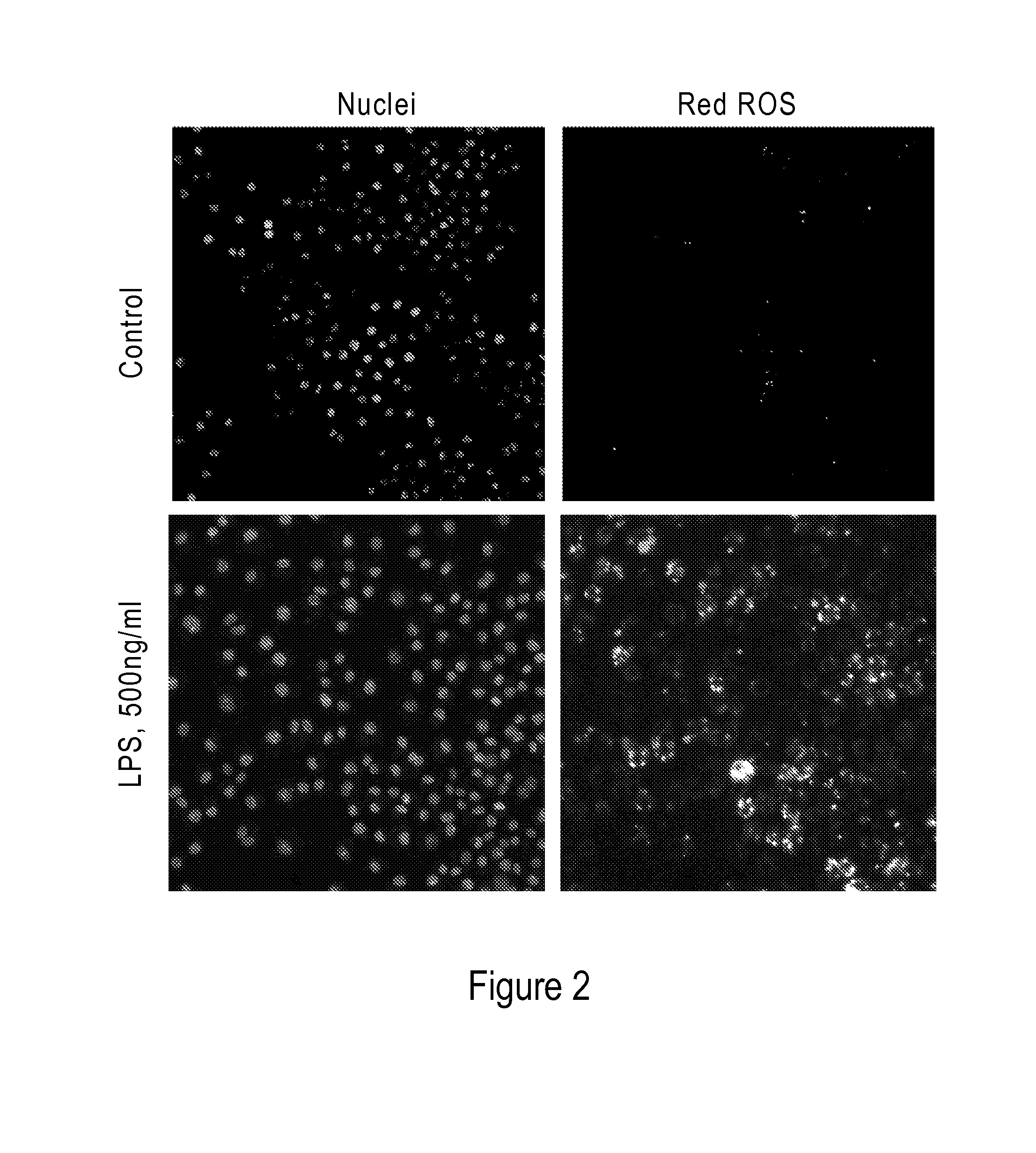
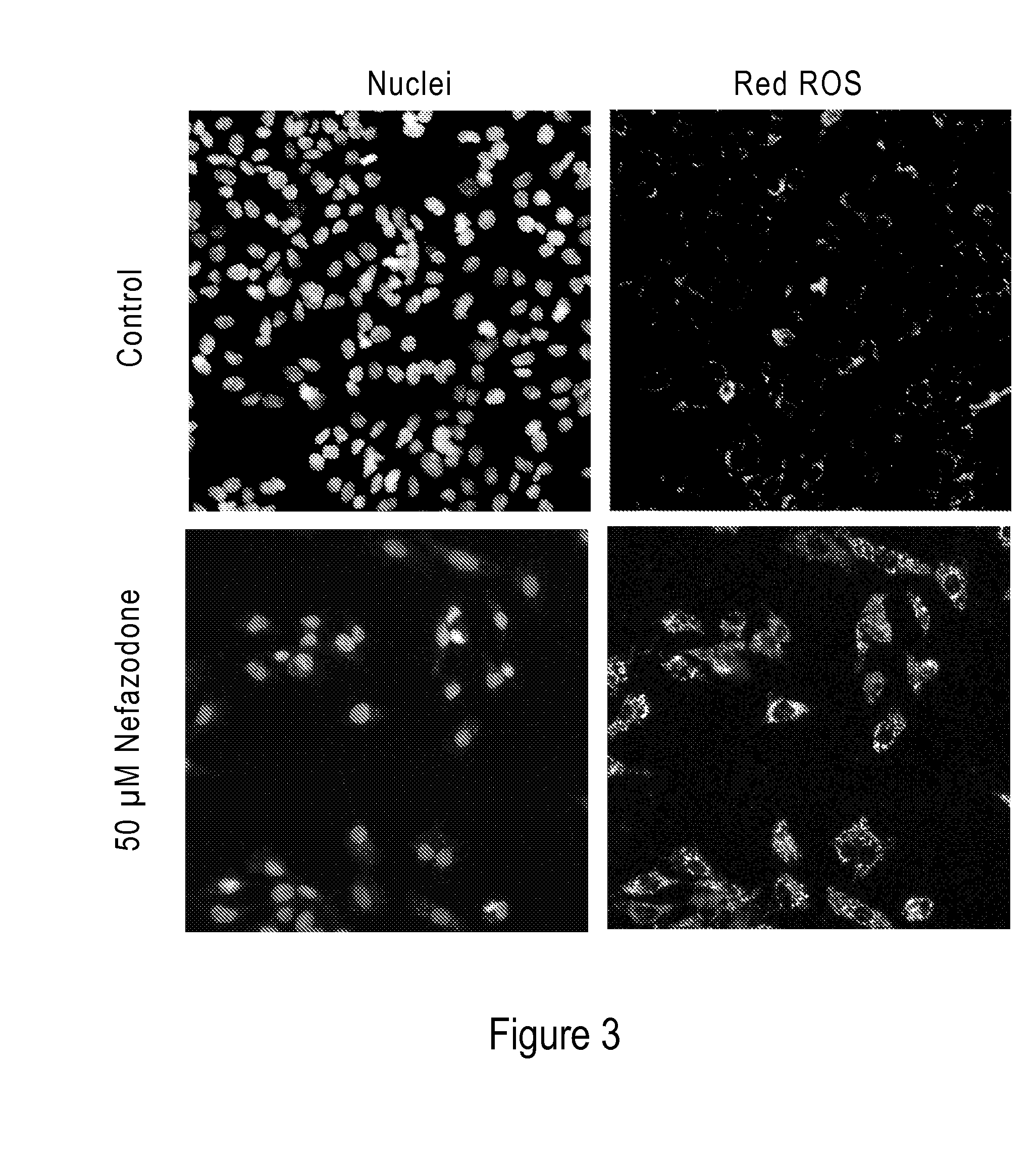
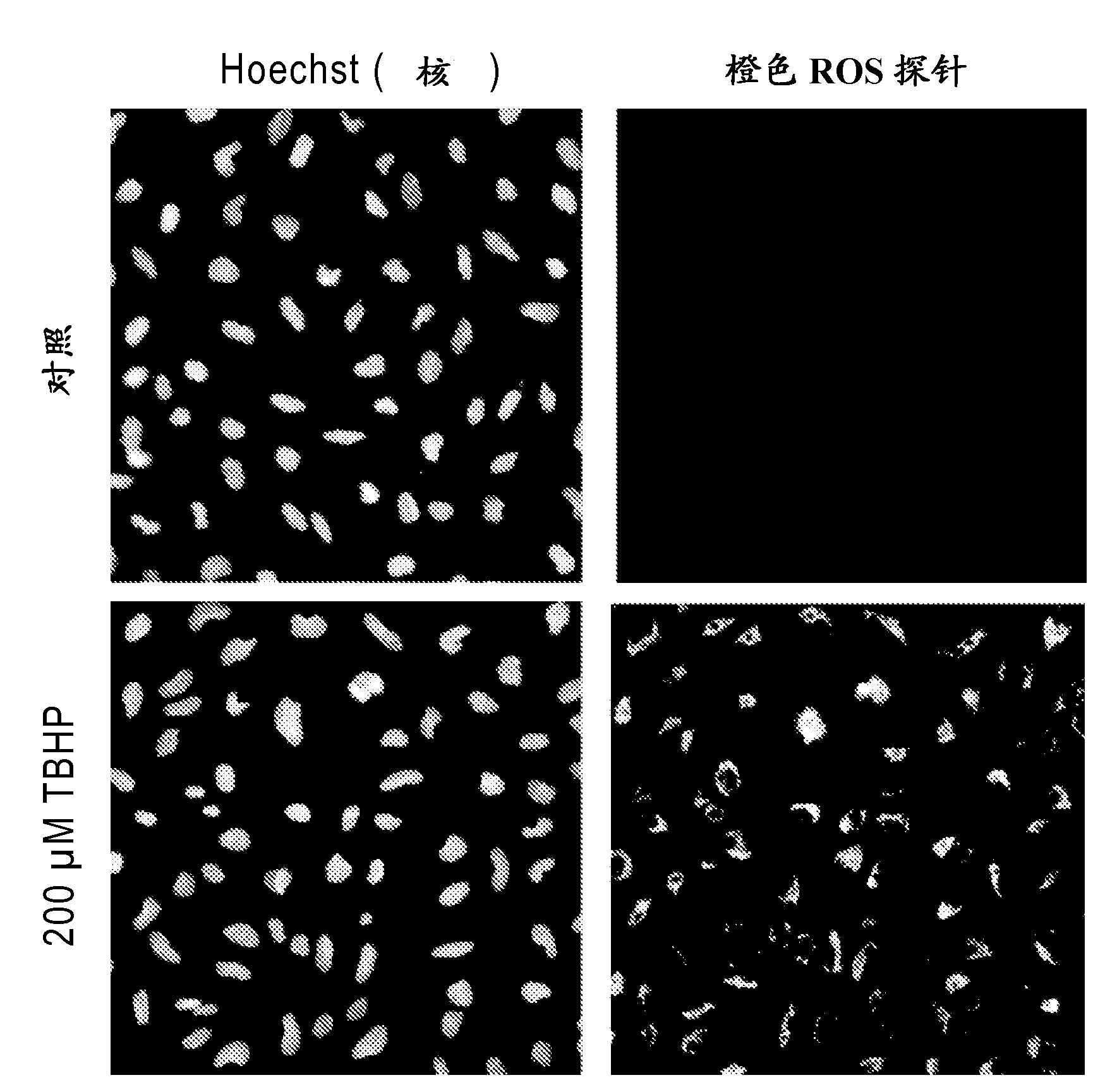
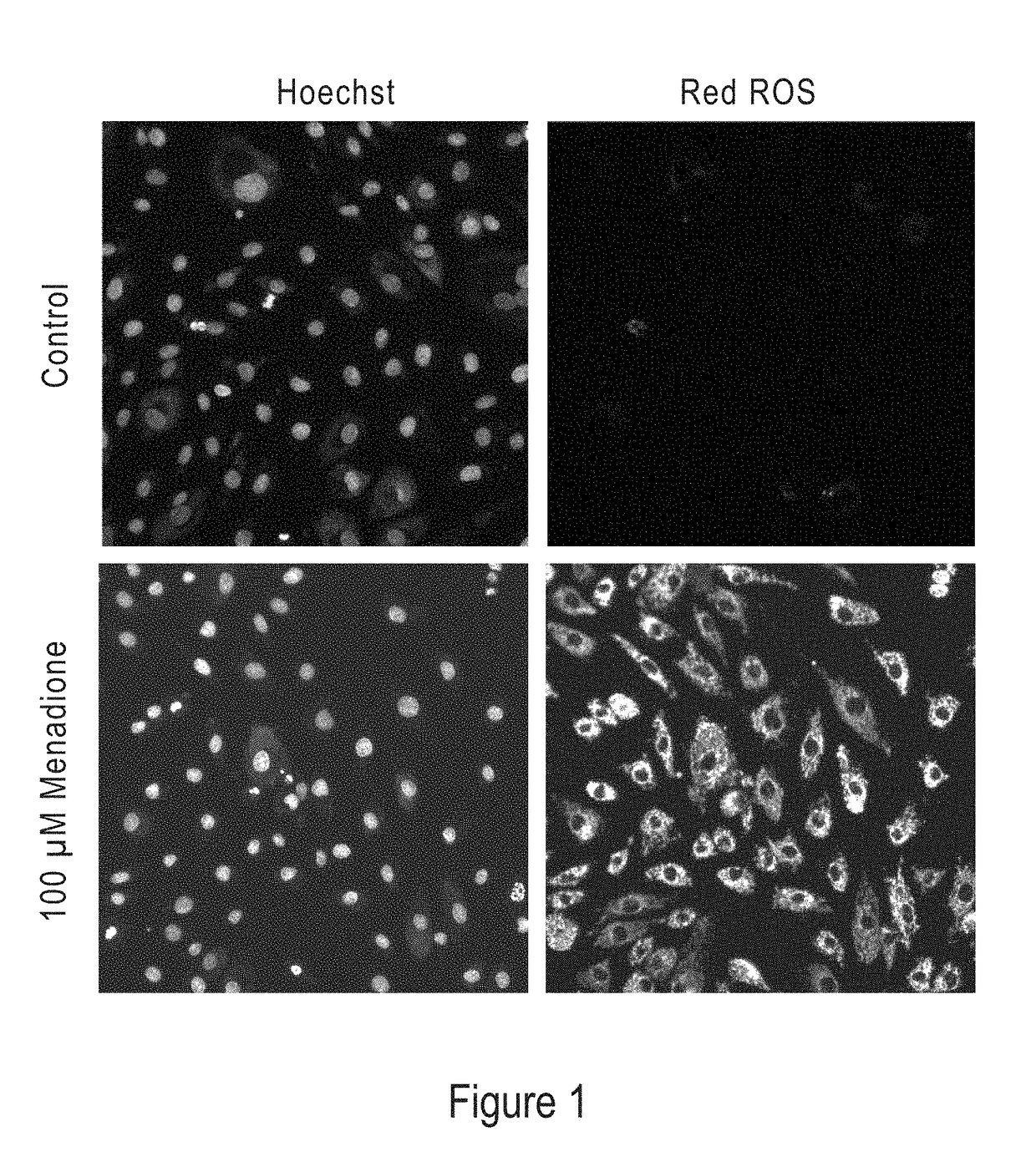
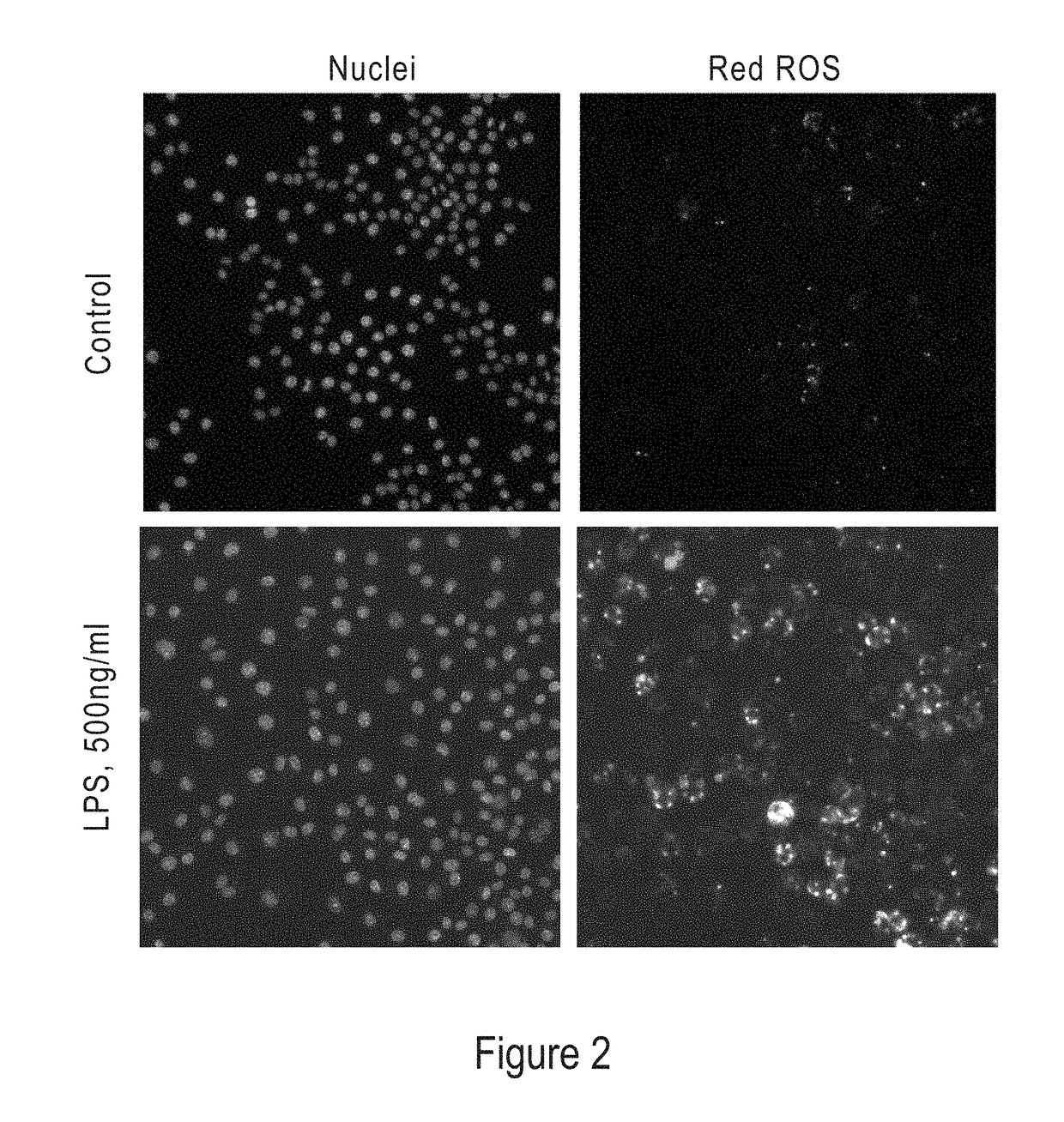
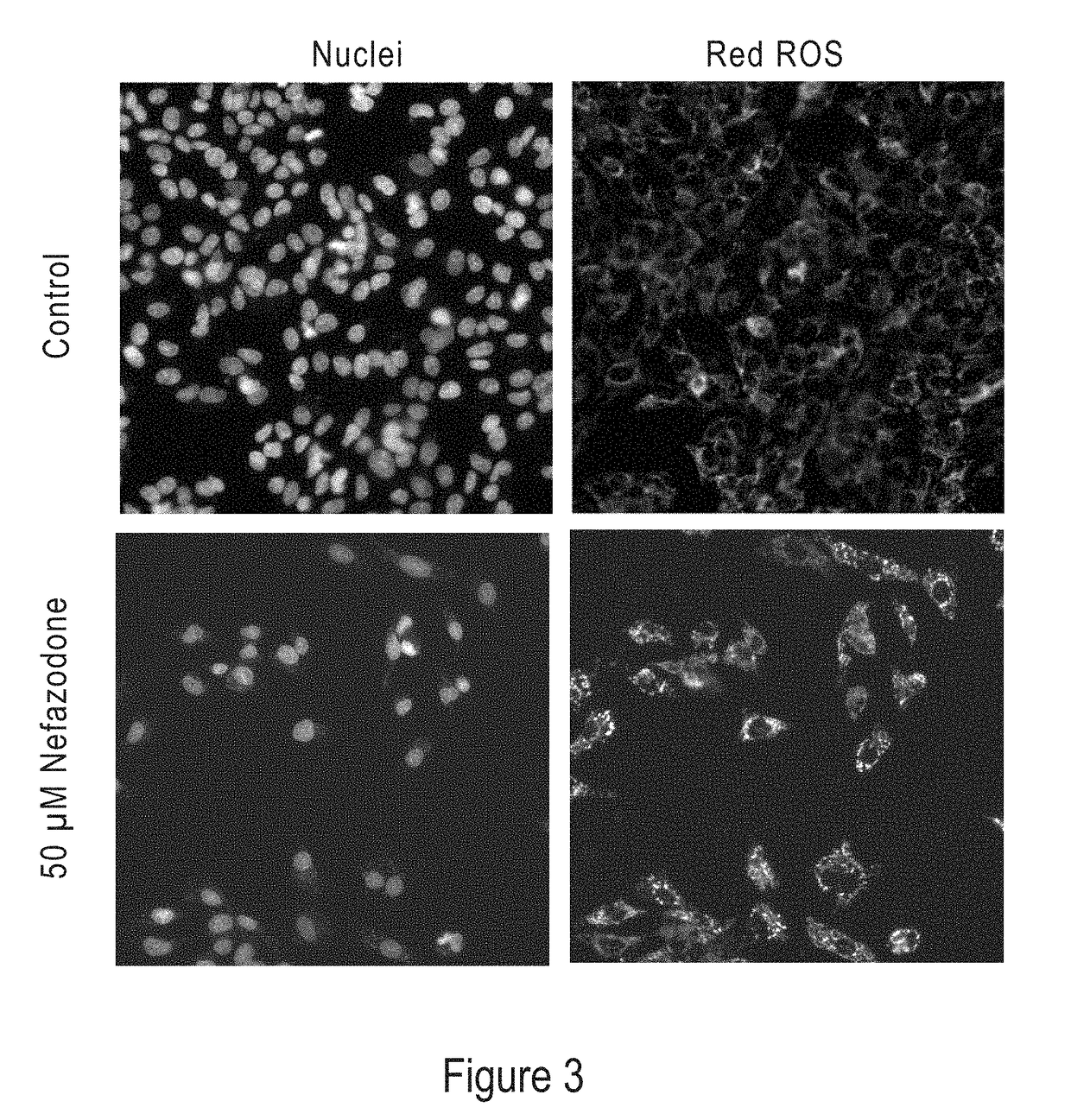
Modified Hydrocyanine Dyes for the Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species
InactiveUS20130287689A1Useful measurementMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryOxidative stressHigh content imaging
The present invention is directed to compounds, compositions, methods, and kits for detecting reactive oxygen species (ROS) by conventional fluorescence microscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, flow cytometry, and / or high content imaging. The compounds disclosed herein are novel reduced dyes, including Cy-based hydrocyanine dyes and Cy-based deuterocyanine dyes, which dyes are probes for detecting ROS and measuring oxidative stress in cells either in vitro and / or in vivo. Also described herein are processes for preparing novel reduced dyes, i.e., ROS probes, for use in the disclosed compositions, methods and kits.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Automated imaging of chromophore labeled samples
A system and method that images biological samples and uses chromophores to analyze the imaged samples. The chromophore analysis can be done by itself or in conjunction with fluorophore analysis in High Content Imaging systems. To perform chromophore analysis the biological samples can be labeled with different chromophores and imaged using transmitted light that is at least partially absorbed by the chromophores. To also perform fluorophore analysis the samples can also be labeled with fluorophores that are excited by excitation light. The chromophore analysis and fluorophore analysis can be performed separately or concurrently using a High Content Imaging system. The system provides the expanded capability by illuminating the chromophore-labeled samples with transmitted light of different wavelengths and automatically detecting the images which represent the differential absorption of the colored lights by the sample.
Owner:CELLOMICS
Automated imaging of chromophore labeled samples
ActiveUS9683939B2Planar light sourcesDiffusing elementsHigh resolution imagingDifferential absorption
A system and method that images biological samples and uses chromophores to analyze the imaged samples. The chromophore analysis can be done by itself or in conjunction with fluorophore analysis in High Content Imaging systems. To perform chromophore analysis the biological samples can be labeled with different chromophores and imaged using transmitted light that is at least partially absorbed by the chromophores. To also perform fluorophore analysis the samples can also be labeled with fluorophores that are excited by excitation light. The chromophore analysis and fluorophore analysis can be performed separately or concurrently using a High Content Imaging system. The system provides the expanded capability by illuminating the chromophore-labeled samples with transmitted light of different wavelengths and automatically detecting the images which represent the differential absorption of the colored lights by the sample.
Owner:CELLOMICS
System and method for automatically analyzing phenotypical responses of cells
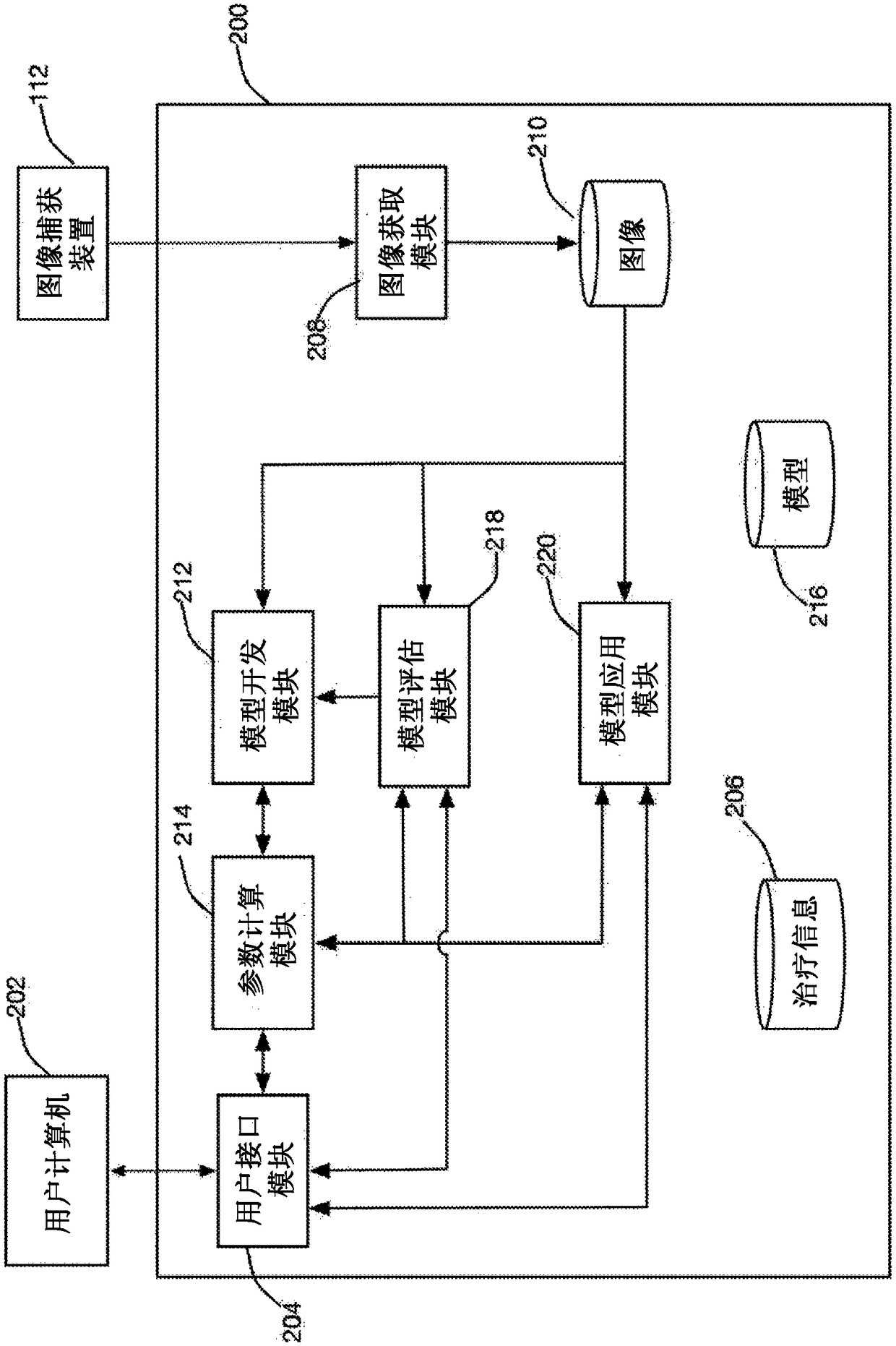
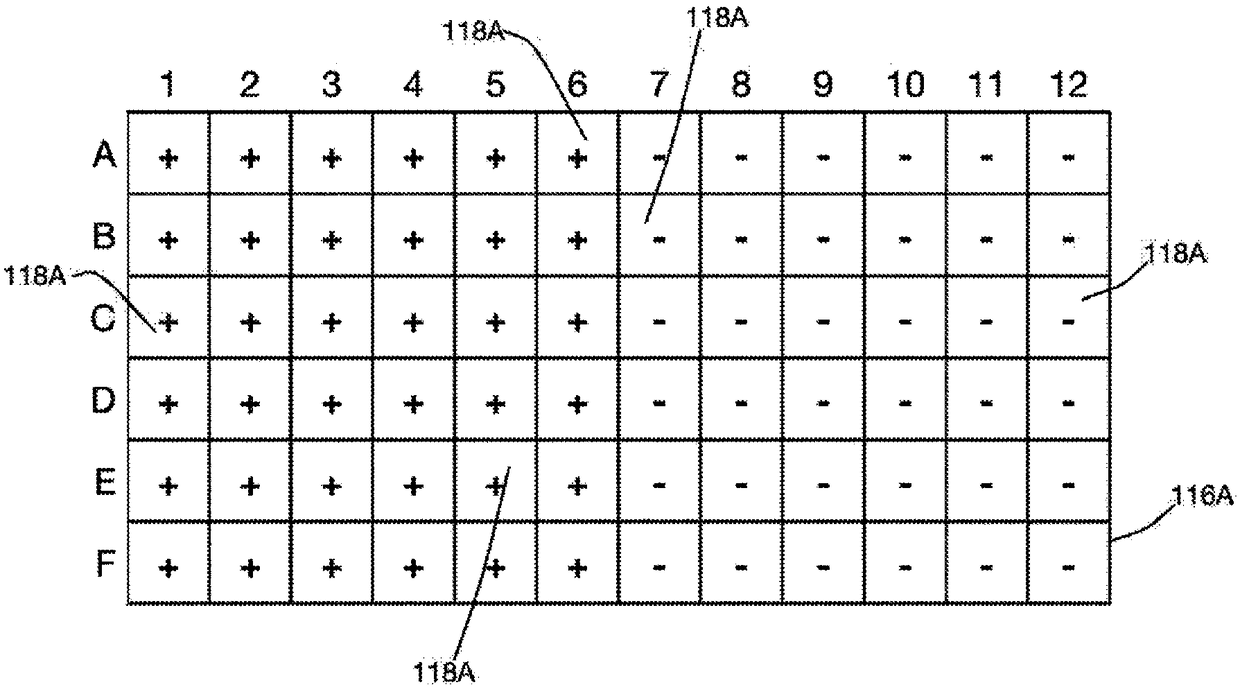
A system and a method to analyze a phenotypical response of cells to a treatment are disclosed in which a model development module receives images of a plurality of reference cell carriers and treatment information associated with the plurality of reference cell carriers, identifies parameters of cells in the image that distinguish those reference cell carriers to which the treatment has been applied from other reference cell carriers, and trains a model using the identified parameters. A high-content imaging system includes an image capture device, and the image acquisition module receives from the image capture device a plurality of images of cell carriers to be evaluated. The model application module applies the trained model to the plurality of images of the cell carriers to be evaluated to predict a concentration of the treatment applied to each of the cell carriers evaluated.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Method for detecting influence of gum-based type tobacco product on human oral cavity in vitro micronucleus
InactiveCN106244662AEasy to crushIncrease contact areaMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisOral mucosal epithelial cellCell culture media
The invention discloses a method for detecting the influence of a gum-based type tobacco product on the human oral cavity in vitro micronucleus. The method comprises: (1) placing a gum-based type tobacco product to be detected in liquid nitrogen, and freezing; (2) immediately crushing the frozen gum-based type tobacco product by using a crusher; (3) re-freezing; (4) soaking the crushed gum-based type tobacco product by using artificial saliva; (5) carrying out centrifugal separation on the extraction solution; (6) determining the supernatant through an osmotic pressure determining instrument, and adjusting the osmotic pressure to achieve the same osmotic pressure of a cell culture medium; (7) determining the nicotine content in the extraction solution; (8) culturing human oral mucosal epithelial cells as the detection object; (9) adding the extraction solution to the cultured human oral mucosal epithelial cells; and (10) after the incubation, detecting the cell in vitro micronucleus condition by using a high-content imaging instrument.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
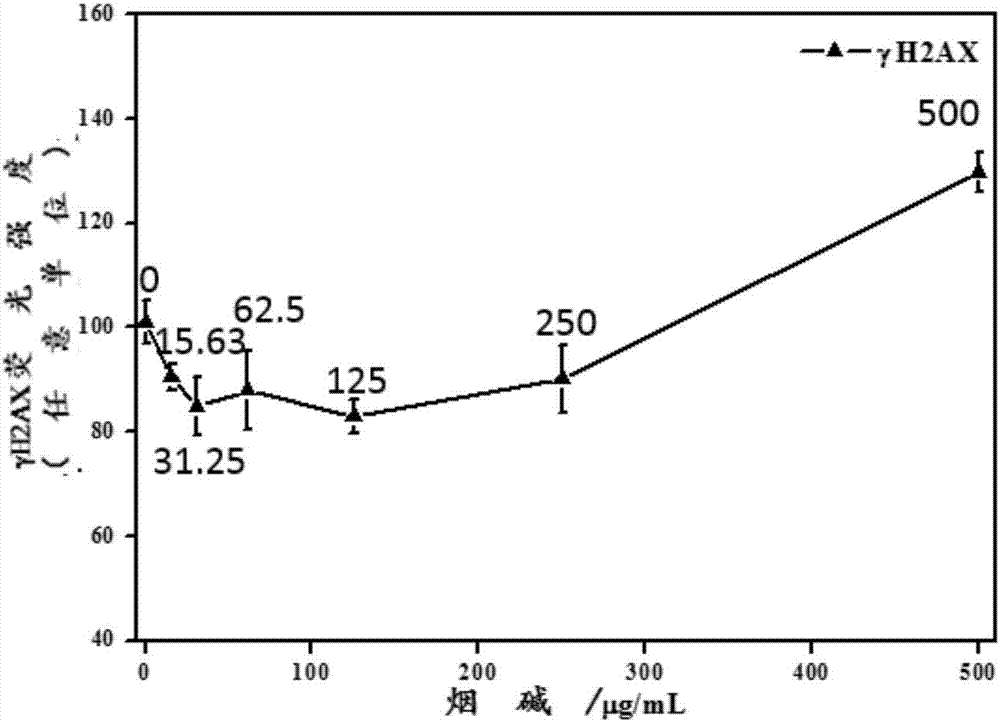
Method for quantitatively analyzing nicotine-induced cell DNA damage based on high content technology
InactiveCN107153054ASmall amount of sampleHigh detection throughputFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh resolution imagingImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing nicotine-induced cell DNA damage based on the high content technology. The method includes the steps of firstly, culturing cells; infecting the cells; thirdly, performing immunofluorescent labeling of gamma H2AX; fourthly, performing high-content-technology quantitative analysis. The method has the advantages that a high-content imaging system is used to perform automatic imaging, DNA double-strand break marker gamma H2AX protein generated by nicotine induction is quantitatively analyzed, direct and fast cell detection is achieved, and sample processing convenience is achieved; the high-resolution imaging allows the distribution of the gamma H2AX in each cell nucleus to be able to be observed directly and image data to be convenient to store and reanalyze, the nicotine-induced gamma H2AX in each cell nucleus can be quantitatively analyzed, and the detection result is sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
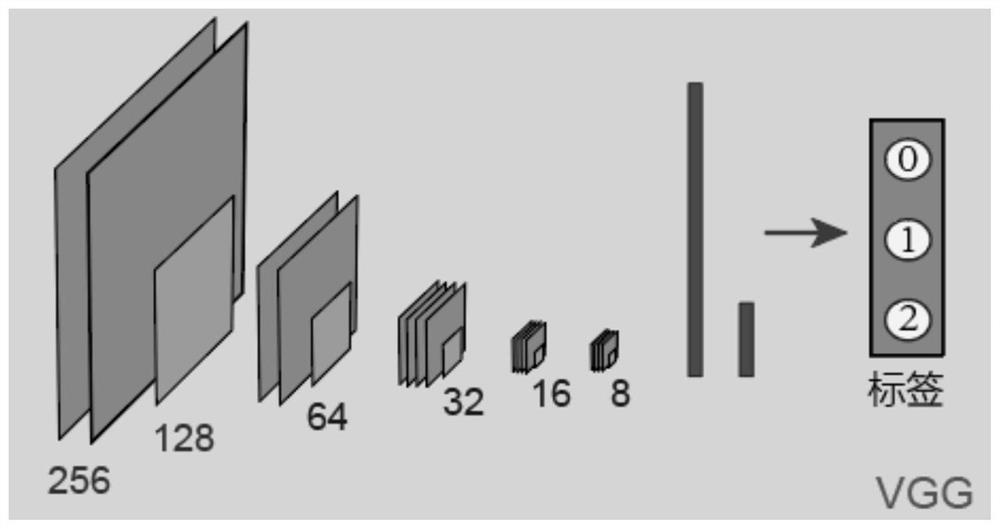
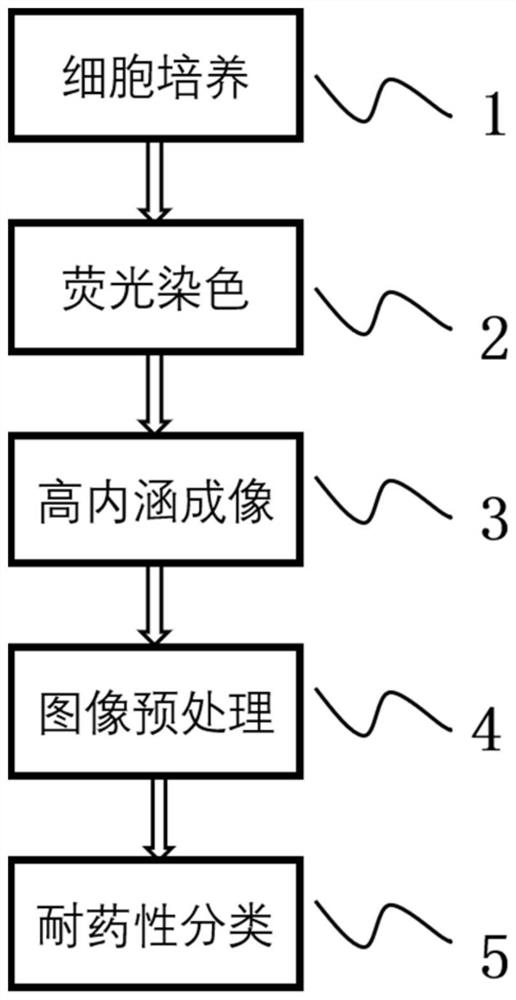
Cell drug resistance detection method based on high content imaging, medium and electronic equipment
PendingCN112507821AImprove recognition accuracyAccurately identify drug resistanceCharacter and pattern recognitionIndividual particle analysisNerve networkFluorescent staining
The invention relates to a cell drug resistance detection method based on high content imaging, a medium and electronic equipment. The cell drug resistance detection method comprises the following steps: carrying out fluorescence staining on cells to be detected; performing high-content imaging on the dyed to-be-detected cells to obtain a corresponding high-content image; preprocessing the high content image; and taking the preprocessed image as the input of a trained drug resistance classification and identification model based on the convolutional neural network, and detecting the drug resistance category to which the to-be-detected cell belongs. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of simplicity, reliability, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF MEDICINE & HEALTH SCI +1
Method for quantitatively detecting 1,3-butadiene-induced cell DNA damage in combination with gas-liquid interface exposure system and high-content technology
ActiveCN107121553AImprove effectivenessImprove accuracyBiological testingHigh resolution imagingImmunofluorescent labeling
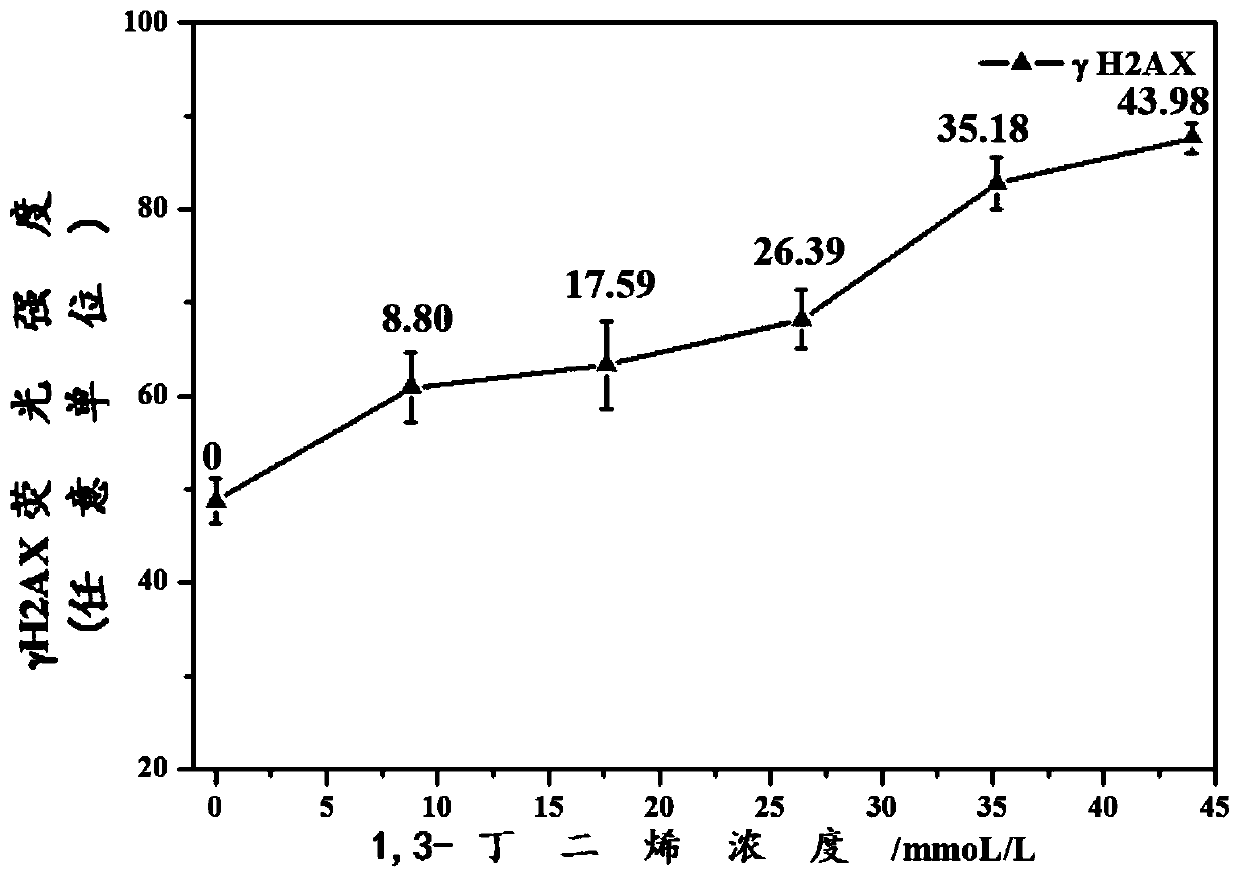
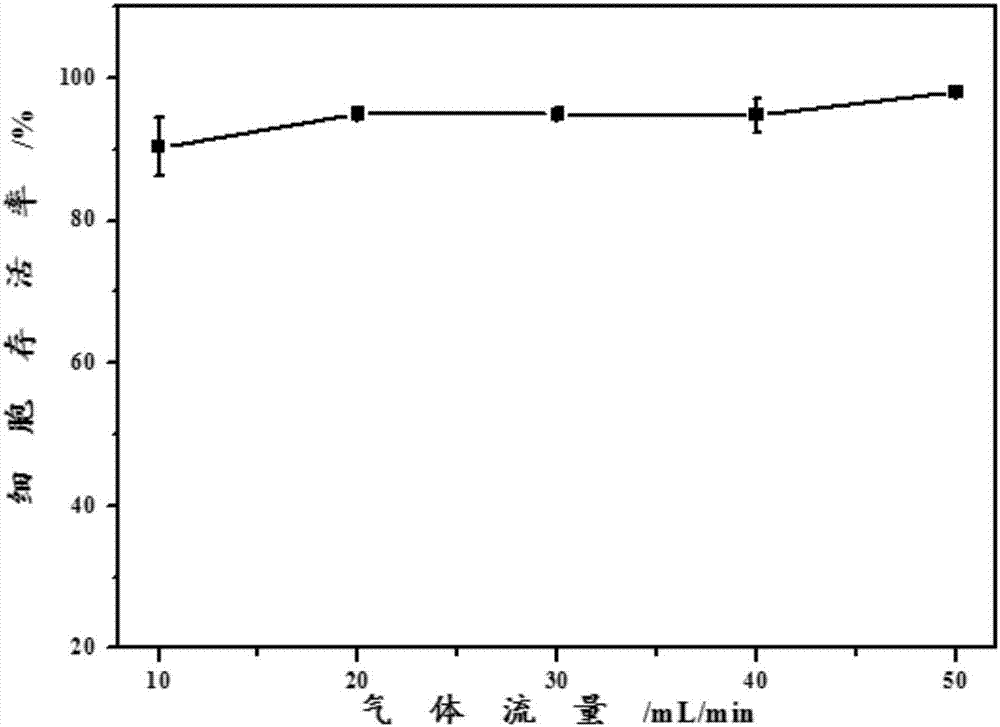
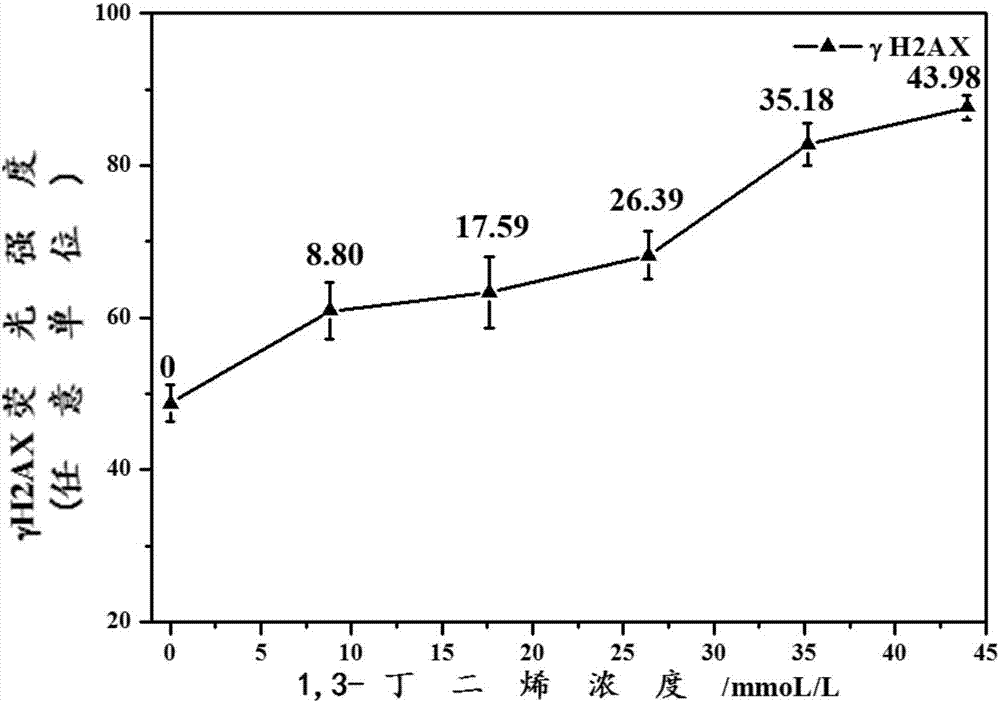
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting 1,3-butadiene-induced cell DNA damage in combination with a gas-liquid interface exposure system and a high-content technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1) cell culture; 2) 1,3-butadiene exposure through a gas-liquid interface exposure mode; 3) immunofluorescent labeling of gamma H2AX; 4) high-content detection. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the efficient exposure of gaseous 1,3-butadiene to wall-attached cells in vivo is realized by adopting the in-vitro gas-liquid interface exposure mode, so that the exposure efficiency of the 1,3-butadiene is improved; a high-content imaging system is utilized for automatic imaging, 1,3-butadiene-induced DNA double-chain fracture maker gamma H2AX proteins are quantitatively analyzed, and the direct and quick detection of the cells is realized, so that the sample treatment is more convenient; through high-resolution imaging, not only can the distribution of the gamma H2AX in cell nucleuses be directly observed, but also image data is convenient to store and re-analyze, and the quantitative analysis on the 1,3-butadiene-induced gamma H2AX in each of the cell nucleuses can be realized, so that detection results are more sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
Modified hydrocyanine dyes for the detection of reactive oxygen species
ABSTRACT Described herein are compounds, compositions, methods, and kits for detecting reactive oxygen species (ROS) by conventional fluorescence microscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, flow cytometry, and / or high content imaging. The compounds disclosed herein are novel reduced dyes, including Cy-based hydrocyanine dyes and Cy-based deuterocyanine dyes, which dyes are probes for detecting ROS and measuring oxidative stress in cells either in vitro and / or in vivo. Also described herein are processes for preparing novel reduced dyes, i.e., ROS probes, for use in the disclosed compositions, methods and kits.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Modified Hydrocyanine Dyes for the Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species
The present invention is directed to compounds, compositions, methods, and kits for detecting reactive oxygen species (ROS) by conventional fluorescence microscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, flow cytometry, and / or high content imaging. The compounds disclosed herein are novel reduced dyes, including Cy-based hydrocyanine dyes and Cy-based deuterocyanine dyes, which dyes are probes for detecting ROS and measuring oxidative stress in cells either in vitro and / or in vivo. Also described herein are processes for preparing novel reduced dyes, i.e., ROS probes, for use in the disclosed compositions, methods and kits.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
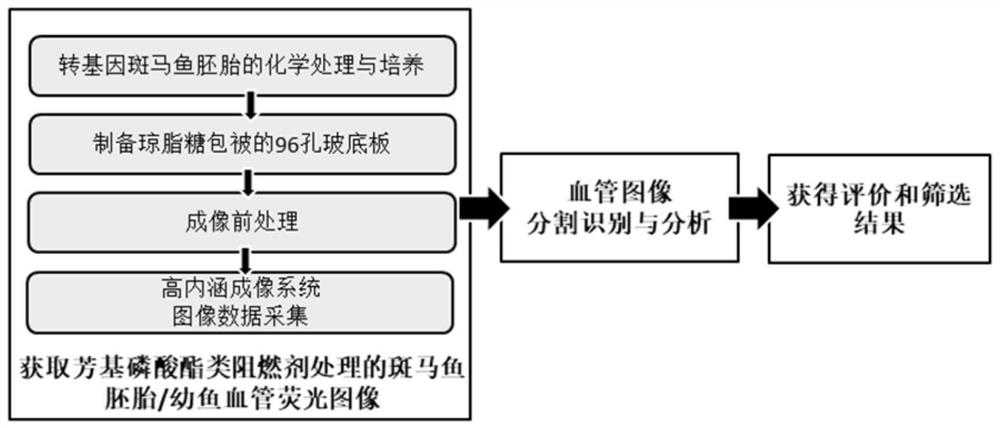
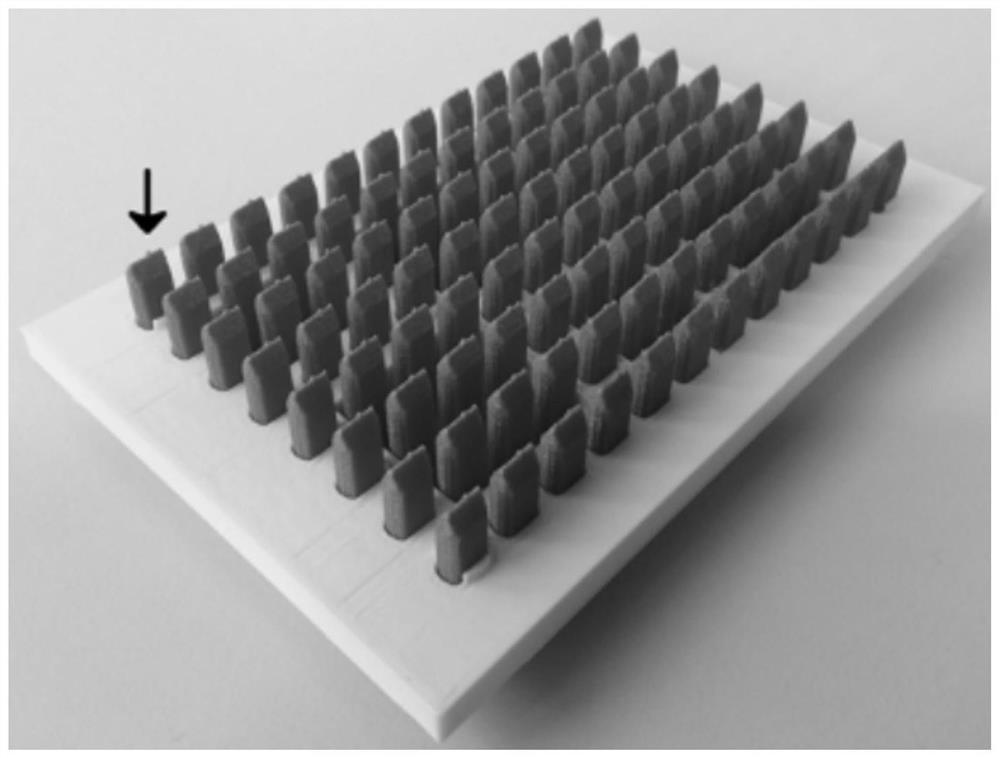
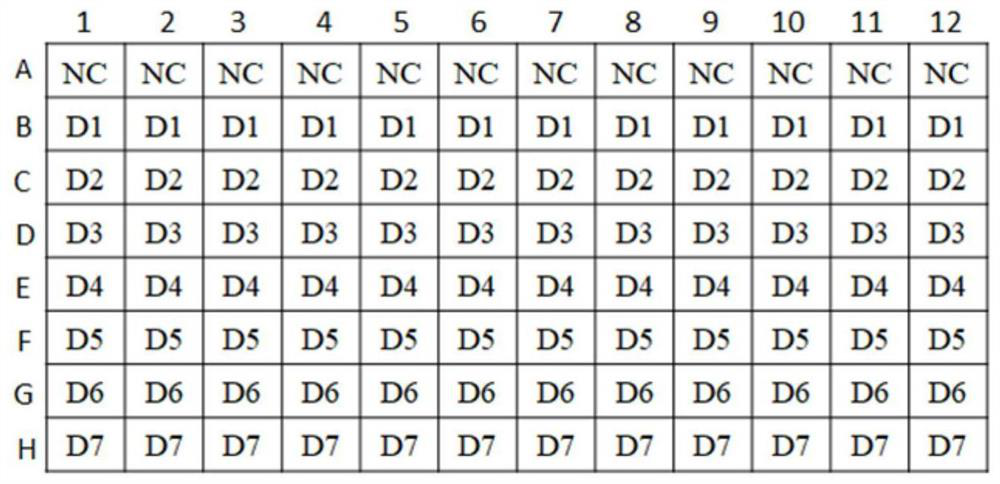
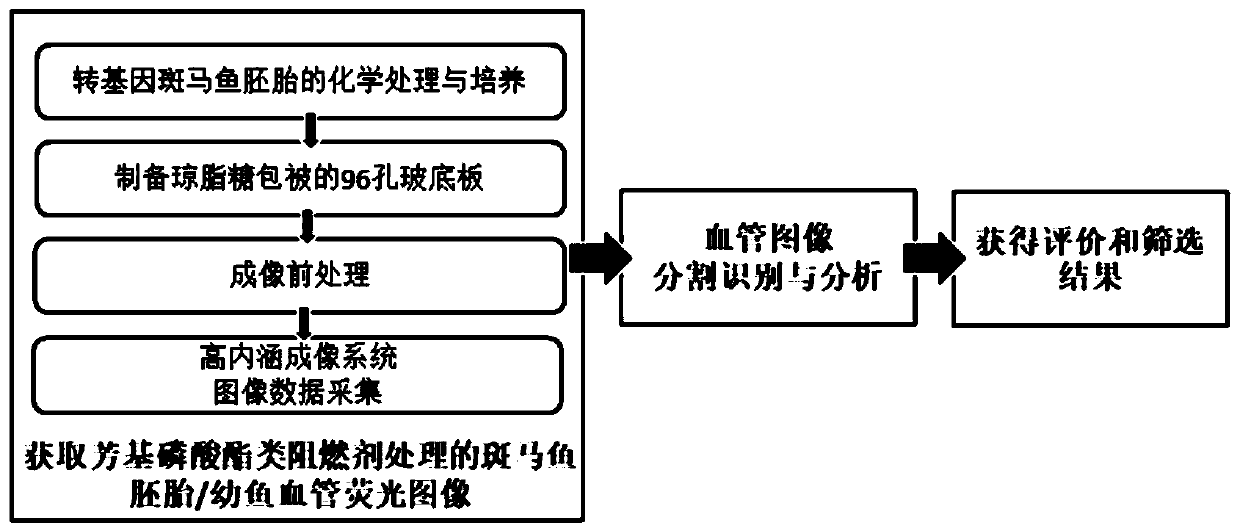
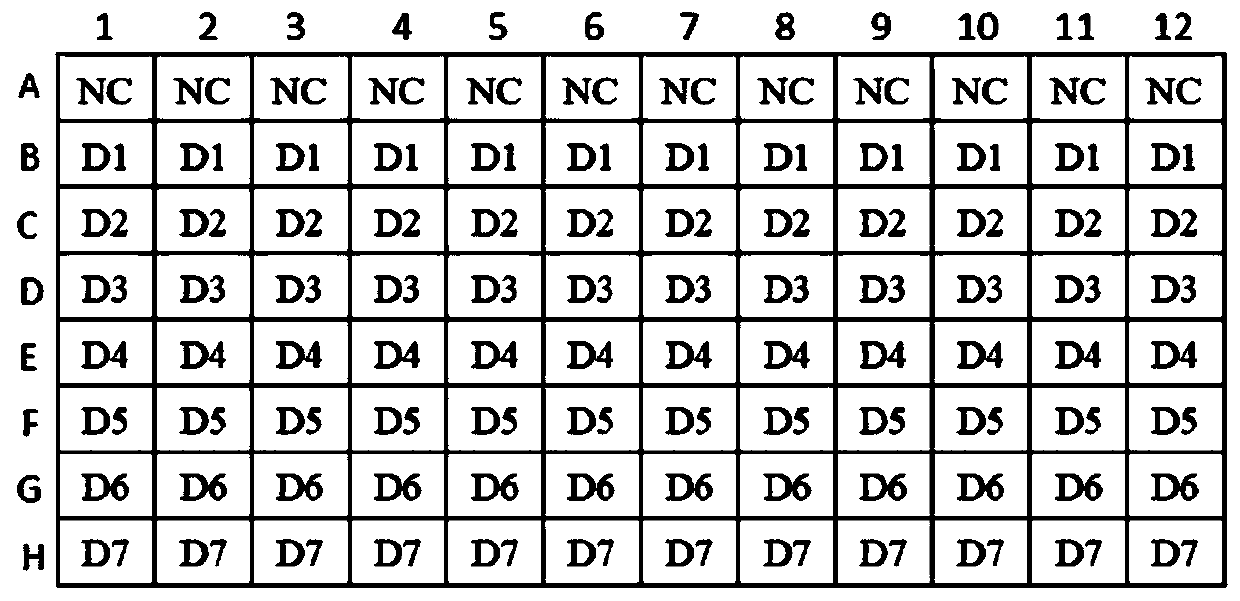
Method for evaluating vascular toxicity of aryl phosphate flame retardant based on high-content imaging system
ActiveCN110956625AImprove throughputRapid Vascular Toxicity AssessmentImage enhancementImage analysisJuvenile fishFish embryo
The invention discloses a method for evaluating vascular toxicity of an aryl phosphate flame retardant based on a high-content imaging system. The method comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring azebra fish embryo / juvenile fish vascular fluorescence image treated by the aryl phosphate flame retardant; 2) performing blood vessel image segmentation identification and analysis; and 3) obtaining evaluation and screening results. Vascular images of transgenic zebra fish embryos / juvenile fishes marked by specific vascular fluorescence are collected, and polyvascular parameters are analyzed to realize evaluation and screening of the vascular development toxicity of the aryl phosphate flame retardants. The method comprises the steps that a hardware system is responsible for obtaining blood vessel image data and is composed of a high-content imaging system and a 96-hole glass bottom plate matched with agarose coating; and the software system is used for semi-automatic identification and multi-parameter output analysis of a target blood vessel, and relates to software such as Photoshop, Matlab and GraphPad Prism. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high flux and stable result, and can quickly and accurately evaluate and screen the vascular development toxicity of the aryl phosphate flame retardant with multiple parameter indexes.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
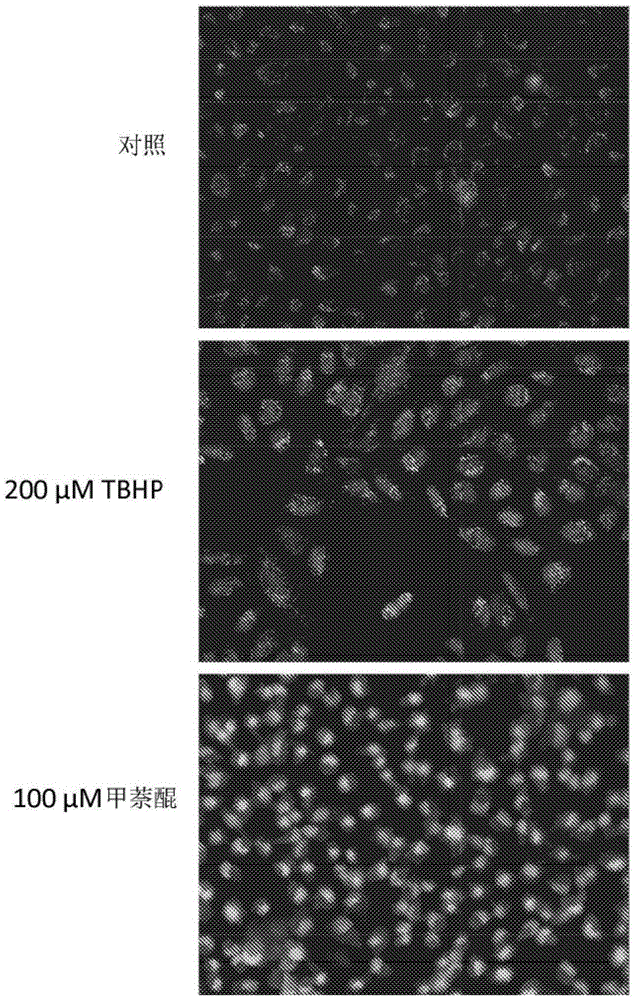
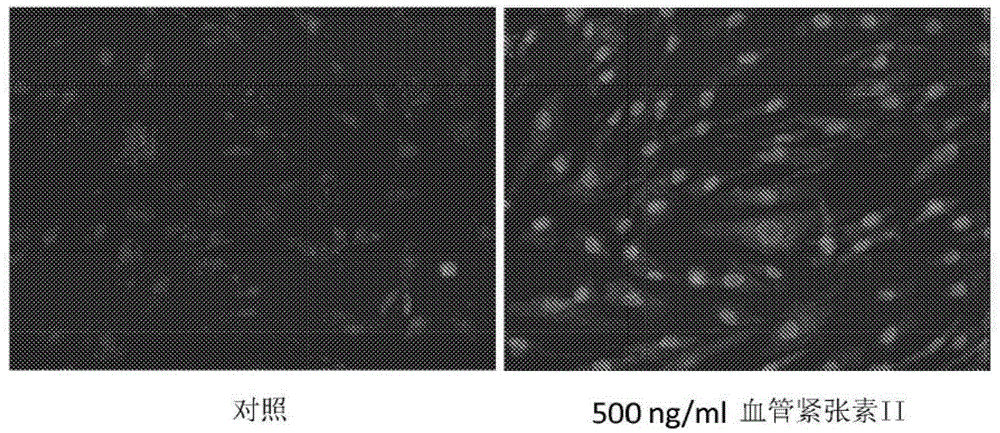
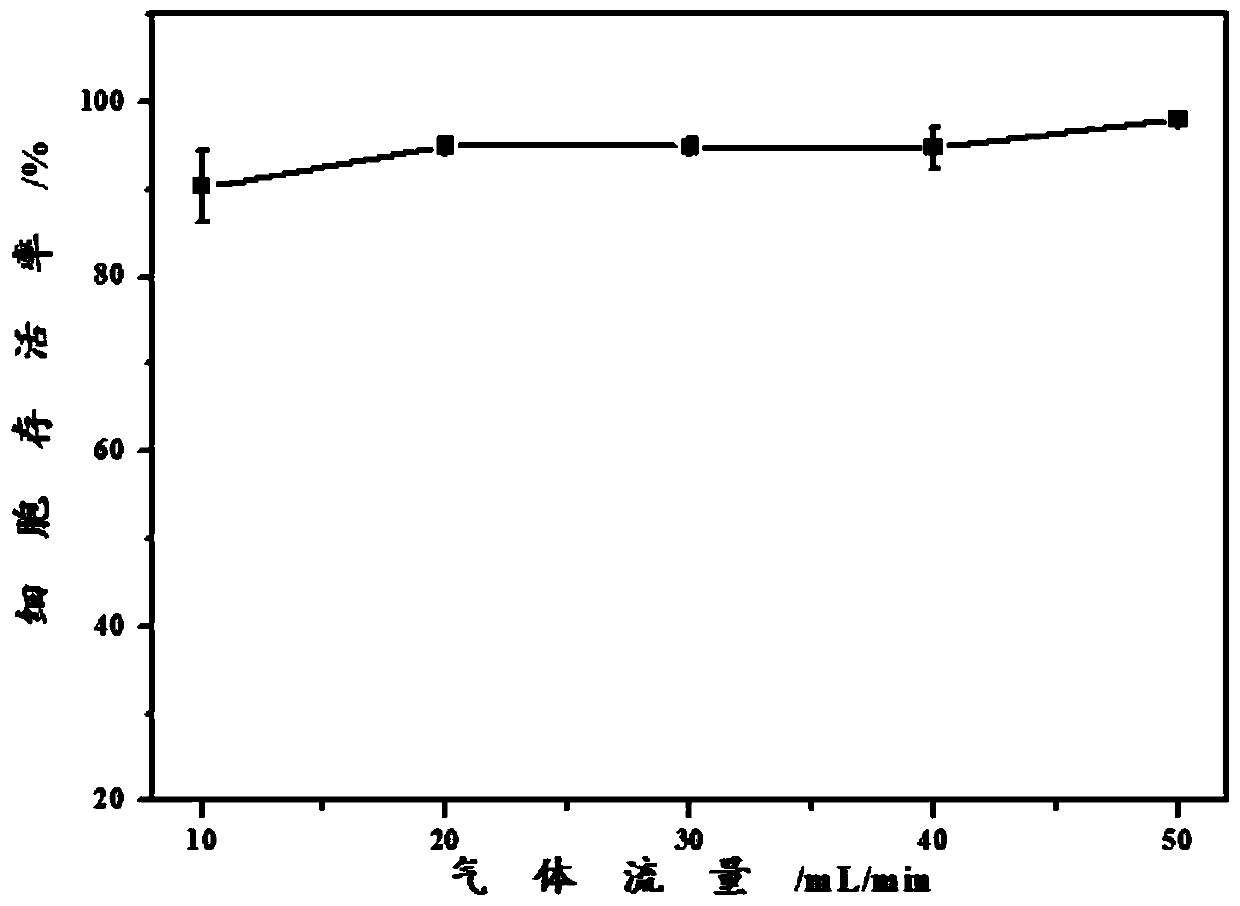
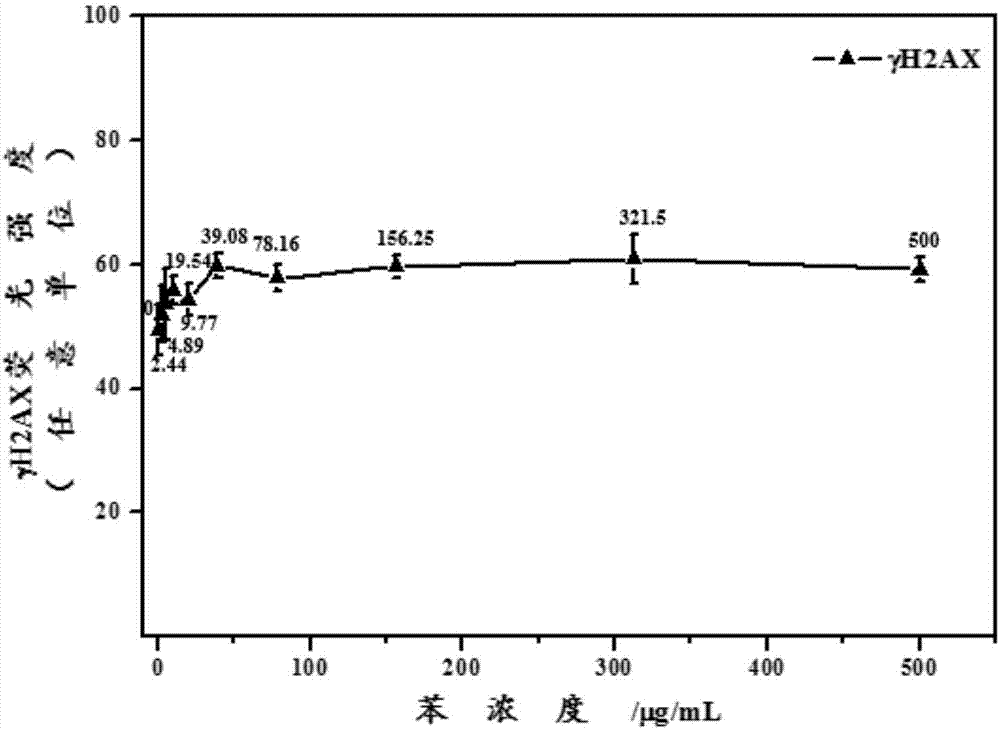
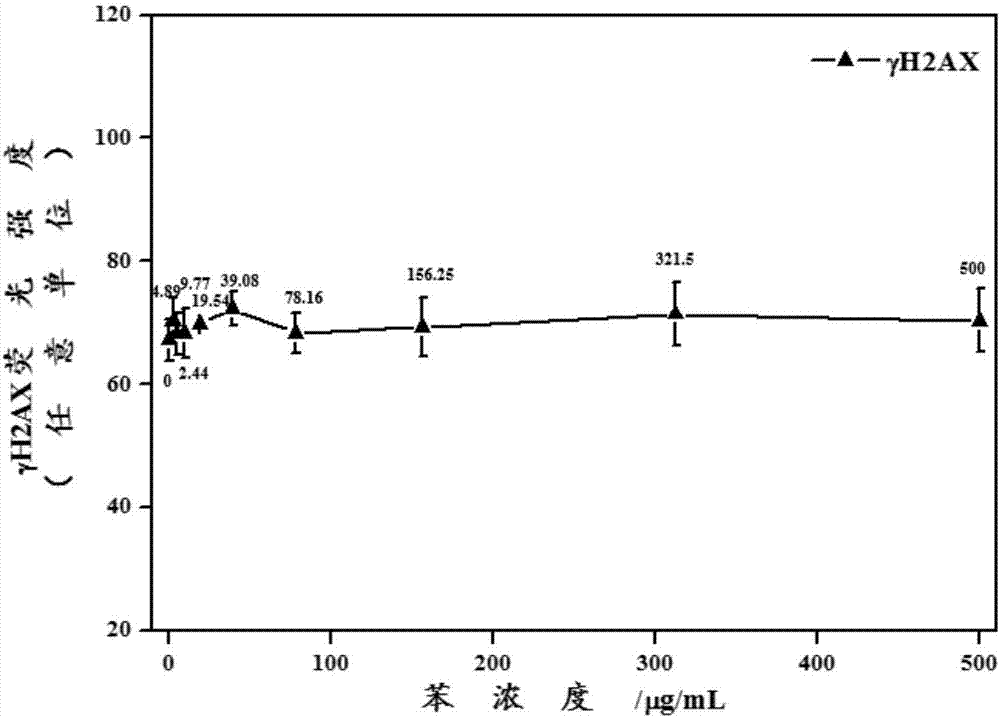
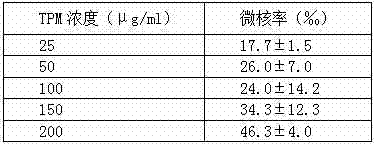
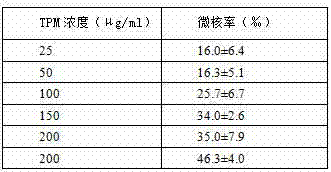
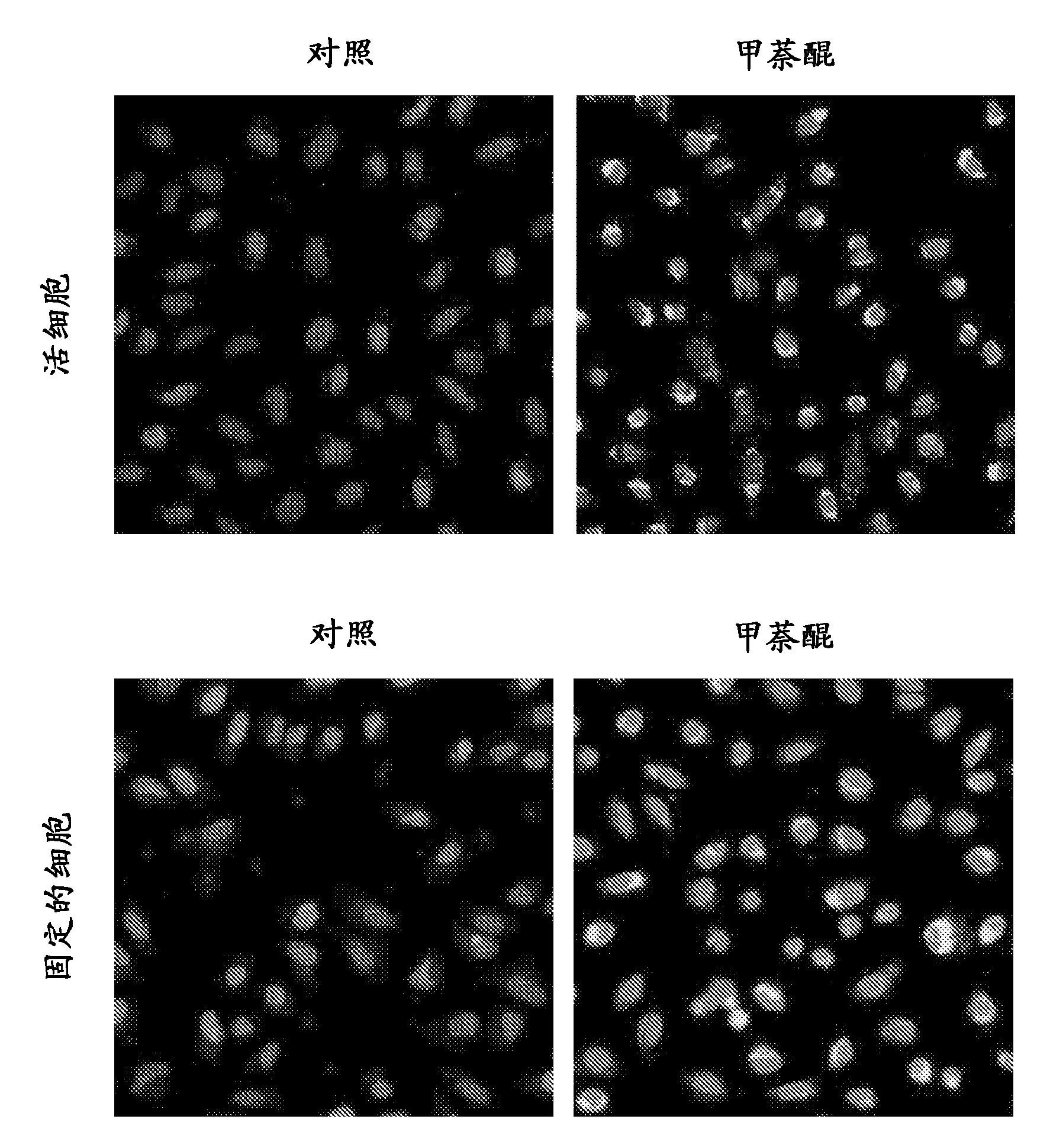
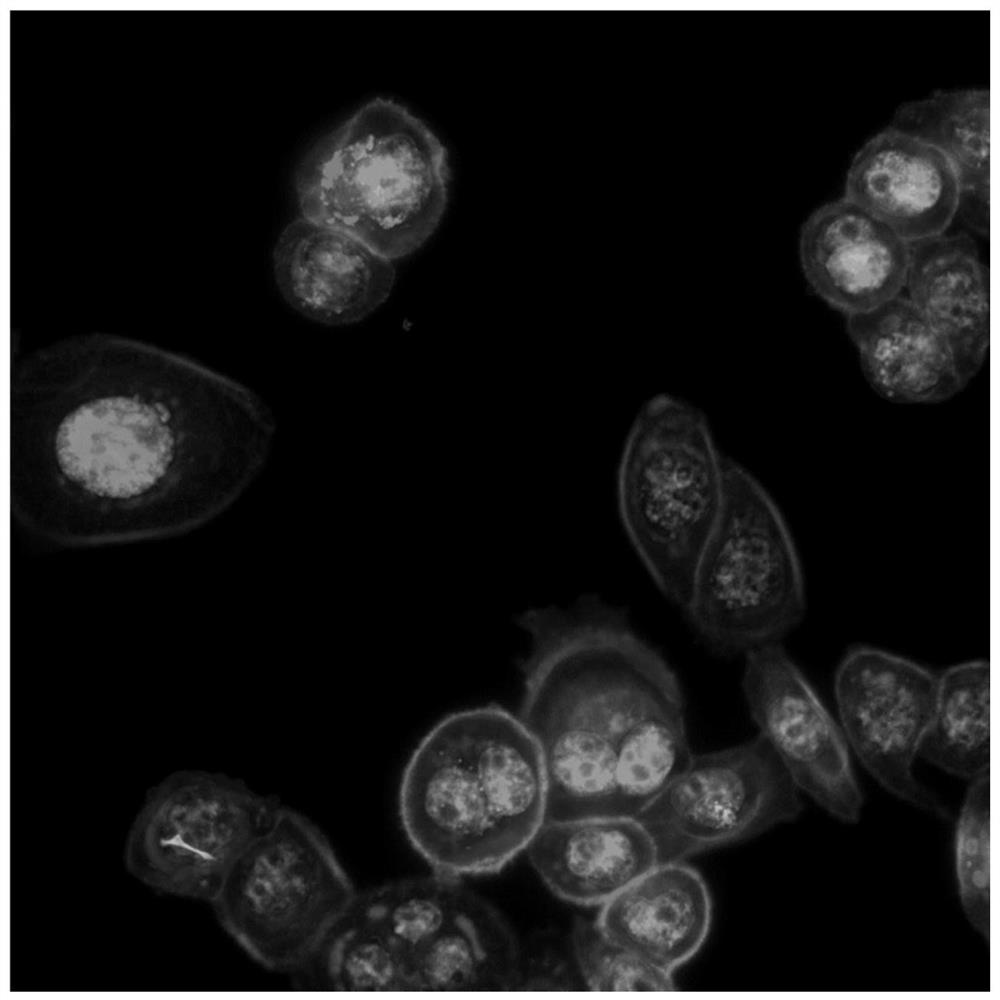
Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique
InactiveCN107064086AGood effectLess cellsFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh resolution imagingImmunofluorescent labeling
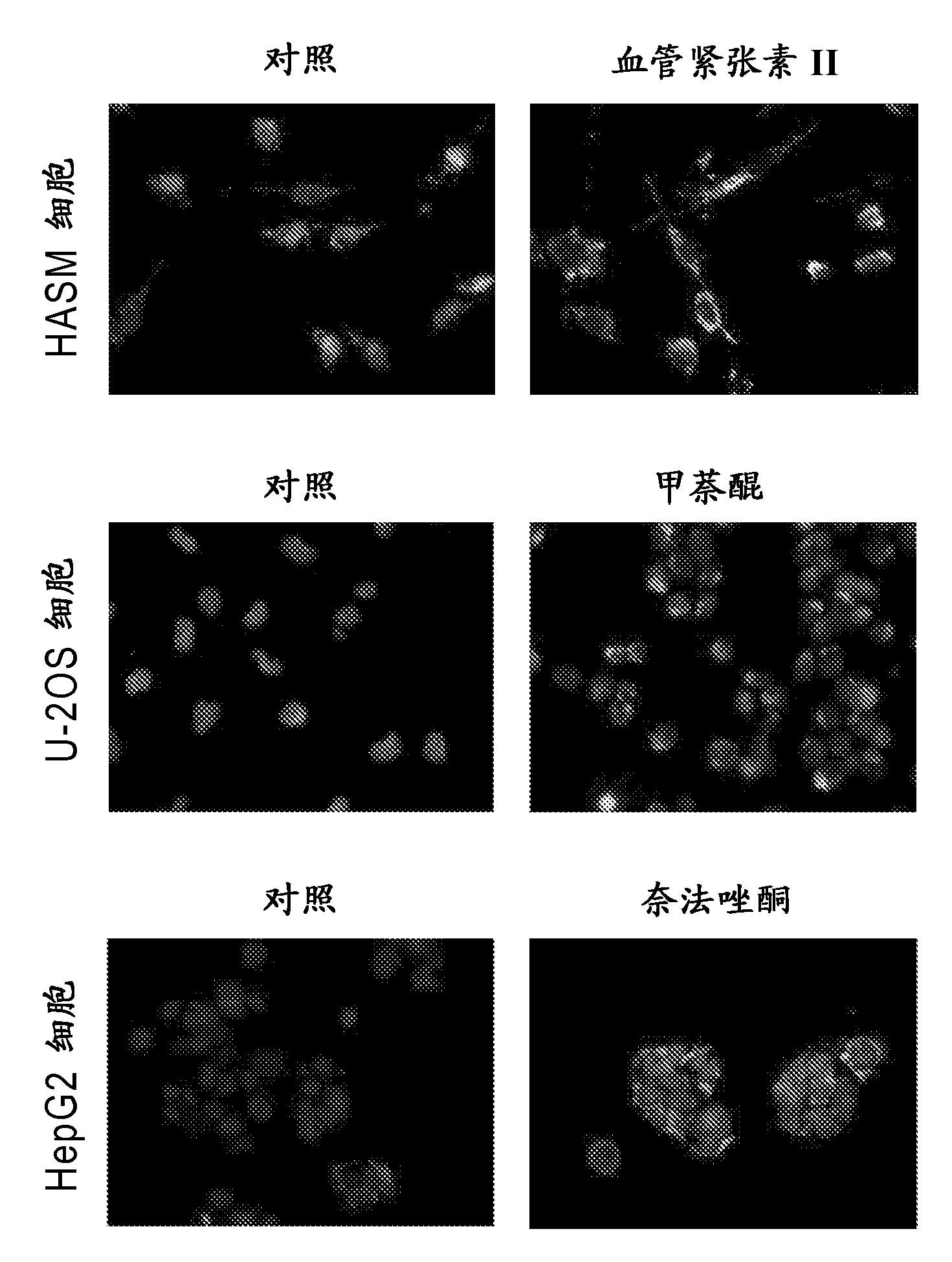
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on a high connotation technique. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing cell culture; 2) infecting cells; 3) performing immunofluorescent labeling for gamma H2AX; and 4) performing quantitative analysis by adopting the high connotation technique. The method has the advantages that a high connotation imaging system is utilized for automatically imaging and quantitatively analyzing the gamma H2AX protein of a DNA double-strand breaking mark induced by benzo[a]pyrene, the direct and quick detection for cells is realized, and the sample treatment is more convenient; and due to high-resolution imaging, the distribution of gamma H2AX in a cell nucleus can be directly observed, the image data can be conveniently stored and analyzed, and the quantitative analysis for gamma H2AX, induced in each cell nucleus, of benzo[a]pyrene, can be realized, so that the detection result is more sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
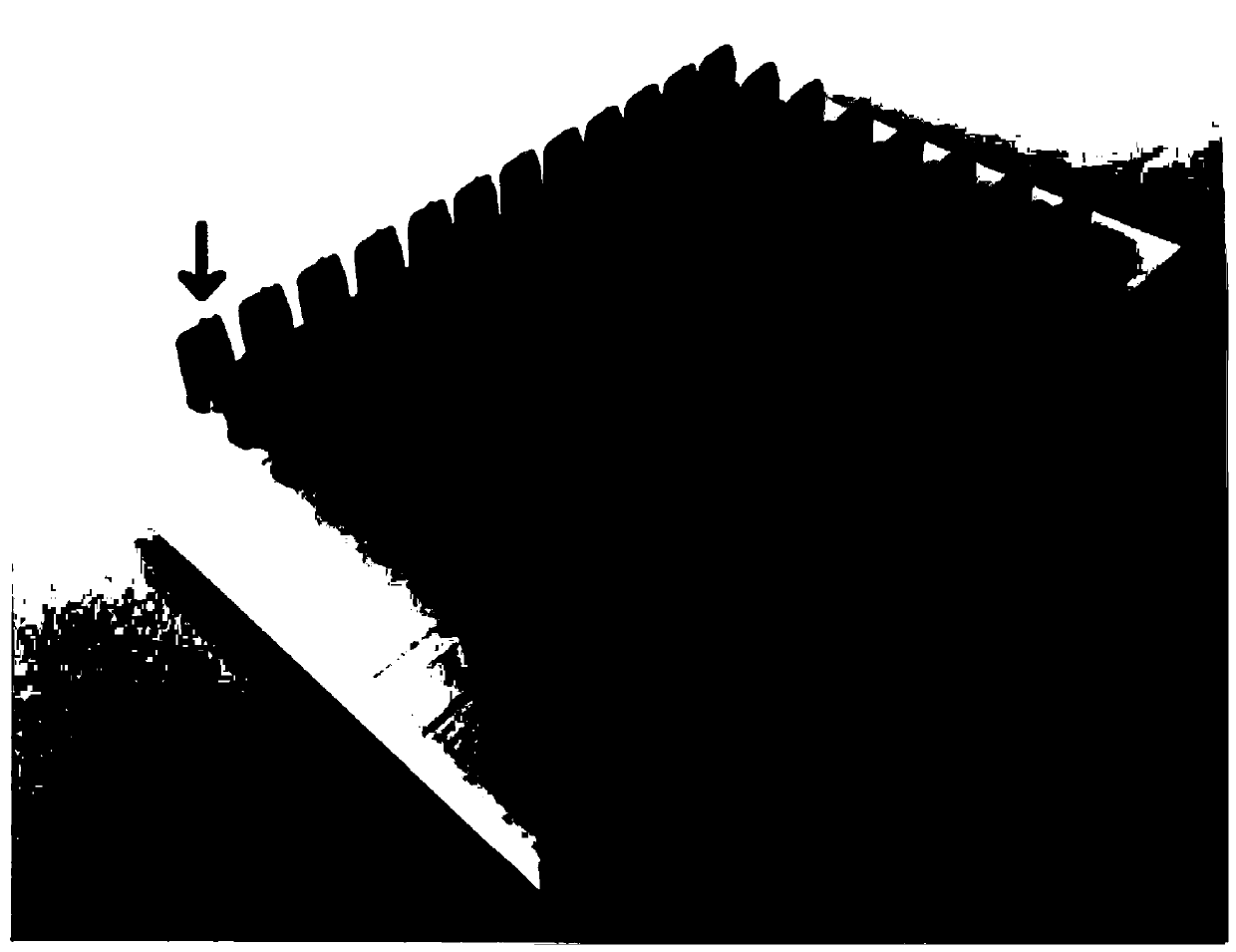
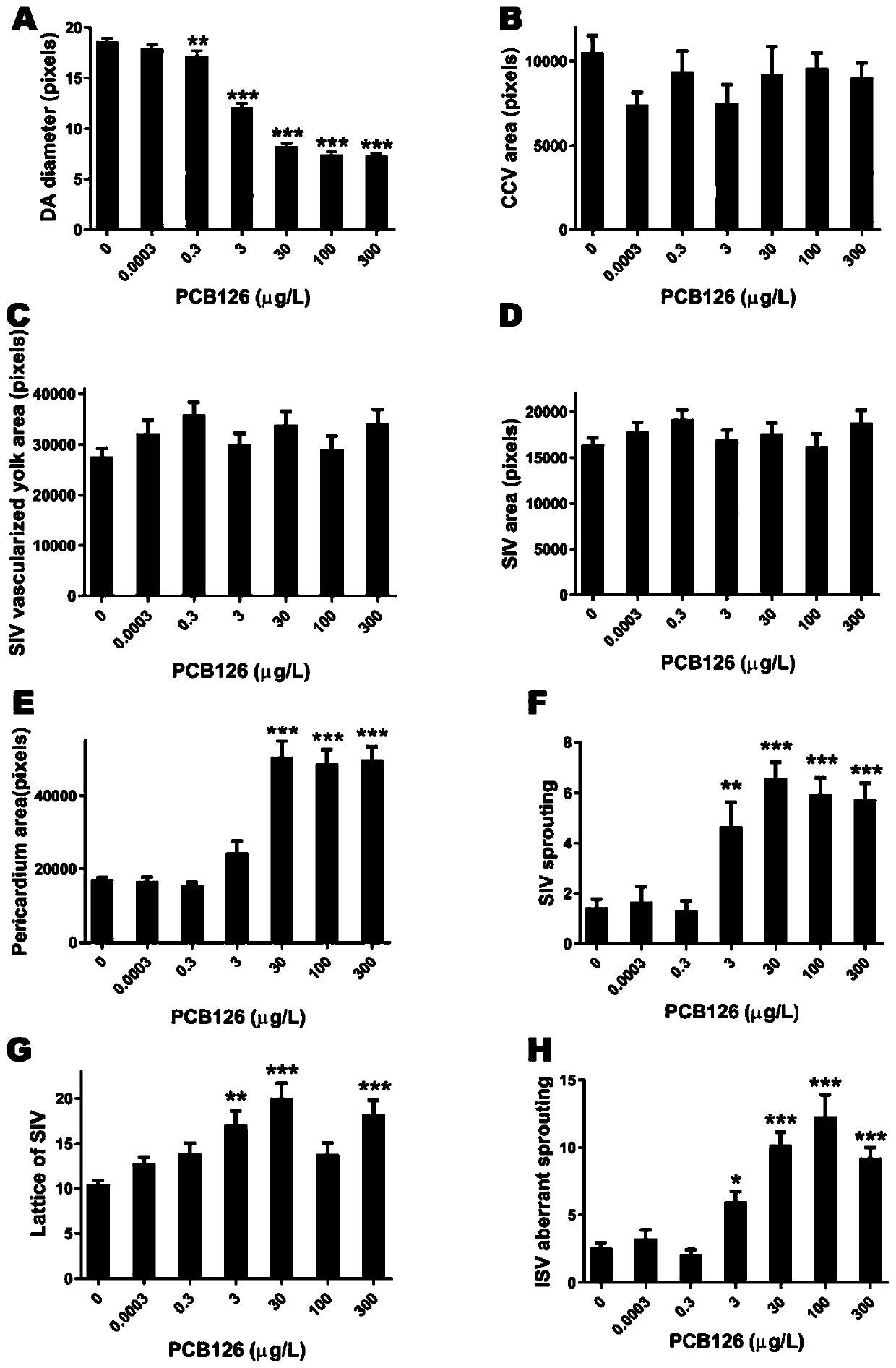
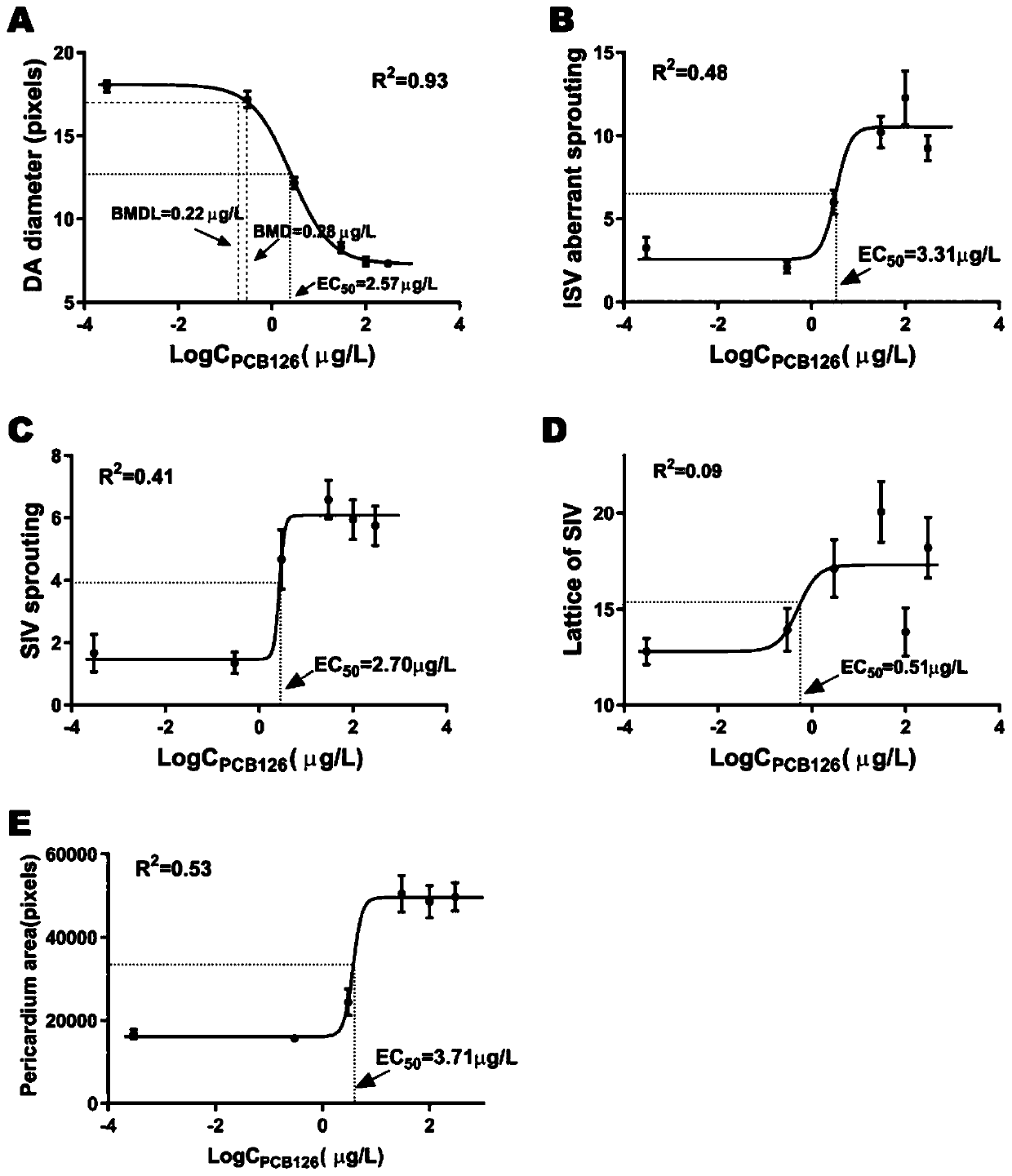
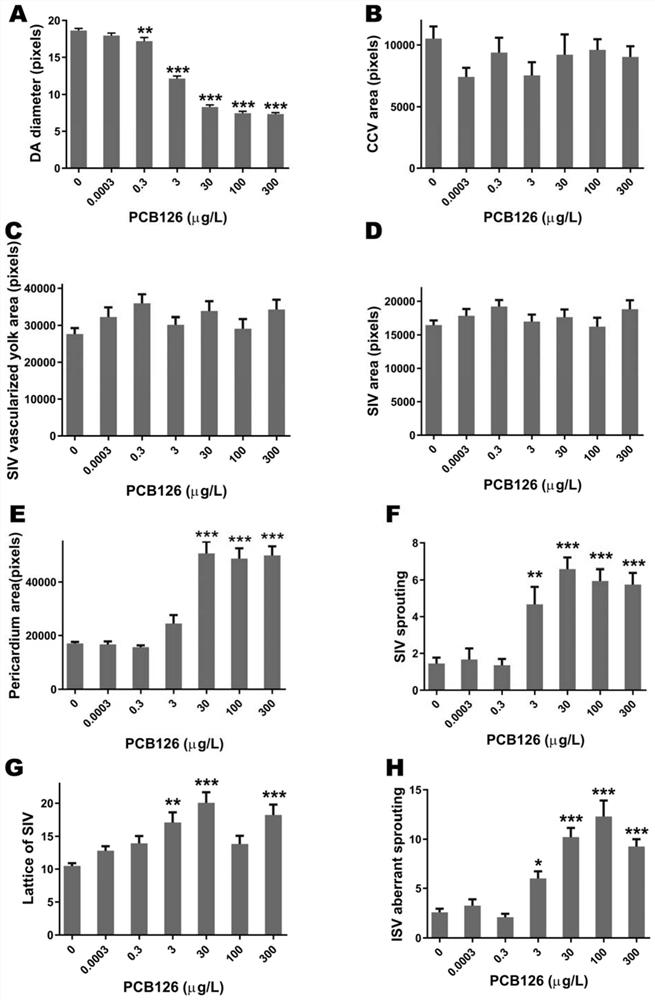
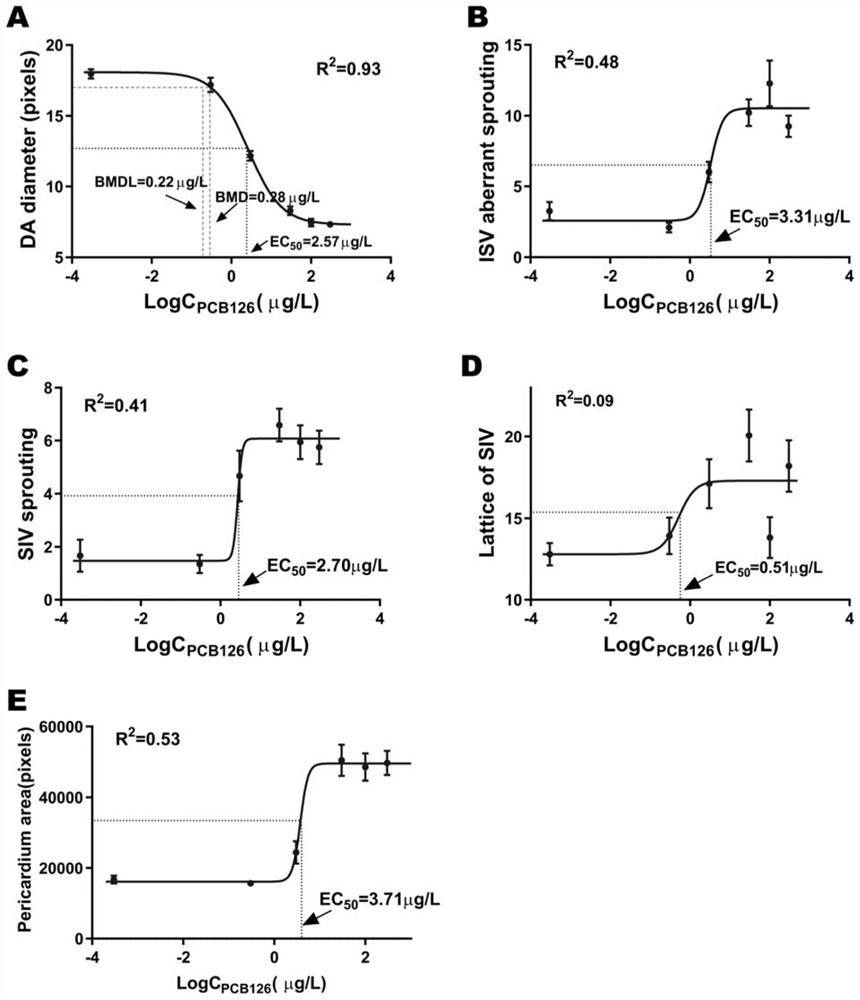
Application of diameter of aorta dorsalis of juvenile zebrafish as effect marker in detection of PCB126 cardiovascular toxicity, and detection method
ActiveCN110702658AProtect healthPromote social and economic developmentFluorescence/phosphorescenceAnimal scienceJuvenile fish
The invention discloses an application of a diameter of aorta dorsalis of a juvenile zebrafish as an effect marker in detection of PCB126 cardiovascular toxicity, and a detection method. The diameterof aorta dorsalis of the juvenile zebrafish is obtained through subjecting a roe of the juvenile zebrafish to PCB126 contamination treatment within 2 hours of fertilization, fixing a posture after culturing the roe, performing image acquisition and carrying out measurement. The juvenile zebrafish is a transgenic juvenile zebrafish of which vascular endothelial cells are labeled with green fluorescence. The juvenile zebrafish is cultured in an illumination constant-temperature incubator with the temperature of 26.5 DEG C in a 14h / 10h light and dark cycle, and is cultured to 72 hpf. The image acquisition is performed by adopting a high-content imaging system for layer scanning to obtain a juvenile zebrafish blood vessel fluorogram. The measurement is carried out by measuring the diameter ofthe aorta dorsalis by using Photoshop software, corresponding original data is recorded by means of EXCEL, and then software GraphPad Prism is used for statistical analysis. The application is beneficial to characterizing cardiovascular toxicity caused by low-dose PCB126 exposure at an ambient level, and provides a technical method and a reference basis for environmental monitoring and evaluationas well as formulation of related technical standards.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
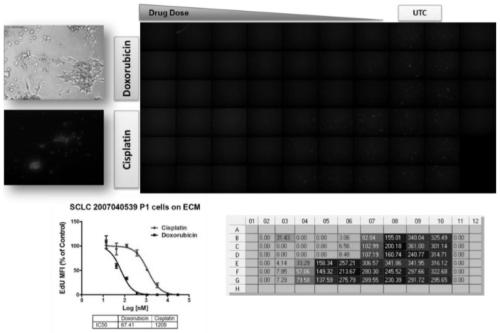
Method for testing proliferative response of drug to tumor cell derived from patient
PendingCN110029141AReliable simulationPredicted responseCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDrug testing methodsCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention relates to use of a 3D cell culture technology in an in-vitro drug test method, and more particularly to a method for testing a proliferative response of a drug to tumor cell derived from a patient, which can reliably screen the candidate drugs by predictive proliferation assay for efficacy and / or mechanism of action. The method comprises the steps of: (1) obtaining cells from a biopsy or tumor resection material; (2) culturing the obtained cells on a 3D extracellular matrix; (3) treating the tumor cells cultured on the 3D extracellular matrix with drug treatment; (4) performinghigh-content imaging on the processed tumor cells; and (5) evaluating the high-content imaging of the processed tumor cells, and testing the proliferative response of the drug to the tumor cells derived from the patient.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIODURO BIOLOGICS
An evaluation method for the determination of cell DNA damage caused by soluble heavy metals
ActiveCN104931473BFast and accurate simultaneous detectionThe target is accurate and intuitiveFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell stainingHigh content imaging
The invention relates to an evaluation method for measuring cell DNA damage caused by soluble heavy metal. The method includes the following steps that firstly, tested cells are processed through a soluble heavy metal solution; secondly, the processed tested cells are fixed and are subjected to cell permeabilization; thirdly, the tested cells having been subjected to cell permeabilization are dyed; fourthly, detection is performed through a high-content imaging system and analysis is performed. The evaluation method for measuring the cell DNA damage caused by the soluble heavy metal is convenient to operate, high in sensitivity and high in detection speed and has high specific pertinence, and research on the genetic toxicity of the heavy metal is supplemented and expanded.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Modified nucleic acid-binding cyanine dyes for detection of reactive oxygen species
Disclosed herein are compounds, compositions, methods, and kits for detecting reactive oxygen species (ROS) by conventional fluorescence microscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, flow cytometry, and / or high content imaging. The compounds disclosed herein are novel reduced nucleic acid binding cyanine dyes, which dyes are probes for detecting ROS and measuring oxidative stress in cells either in vitro and / or in vivo. Also described herein are processes for preparing novel reduced dyes, i.e., ROS probes, for use in the disclosed compositions, methods and kits.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
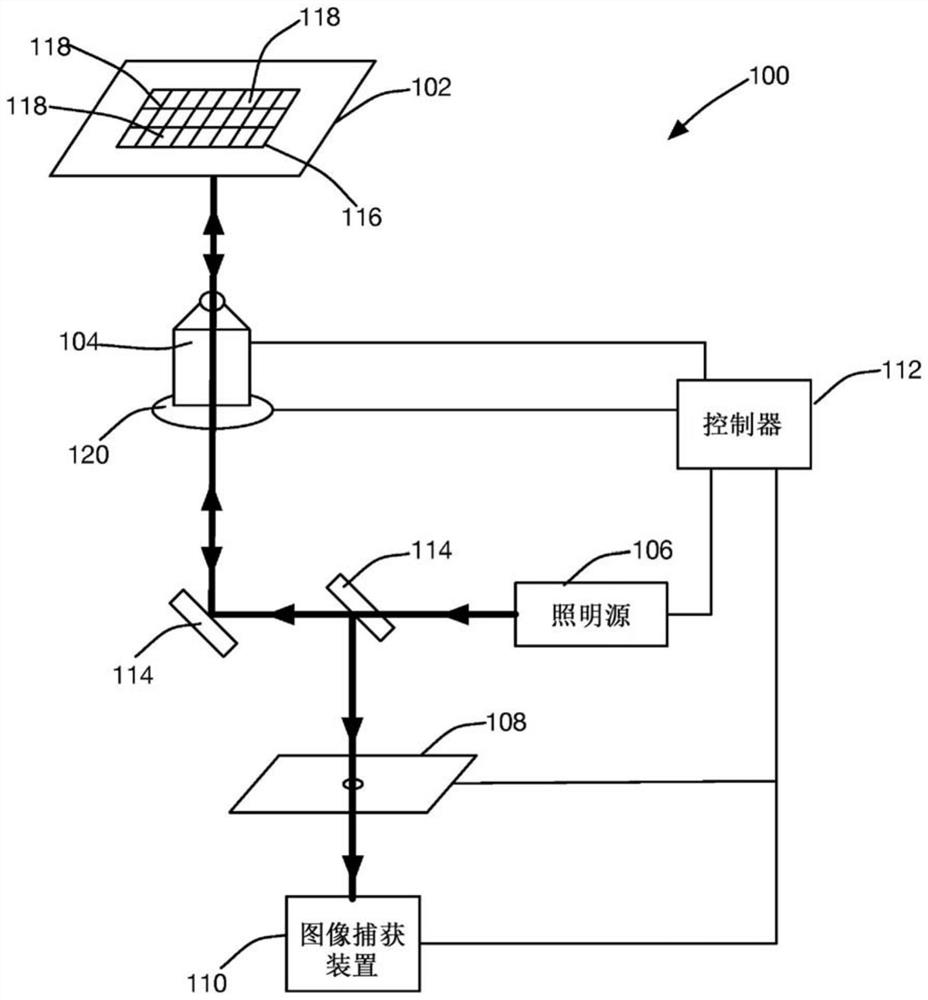
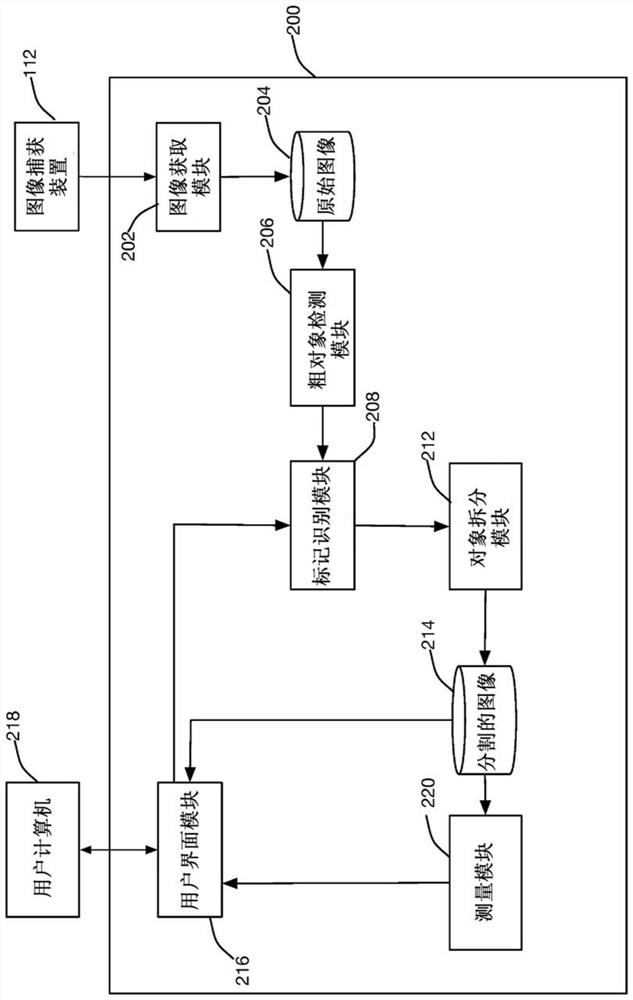
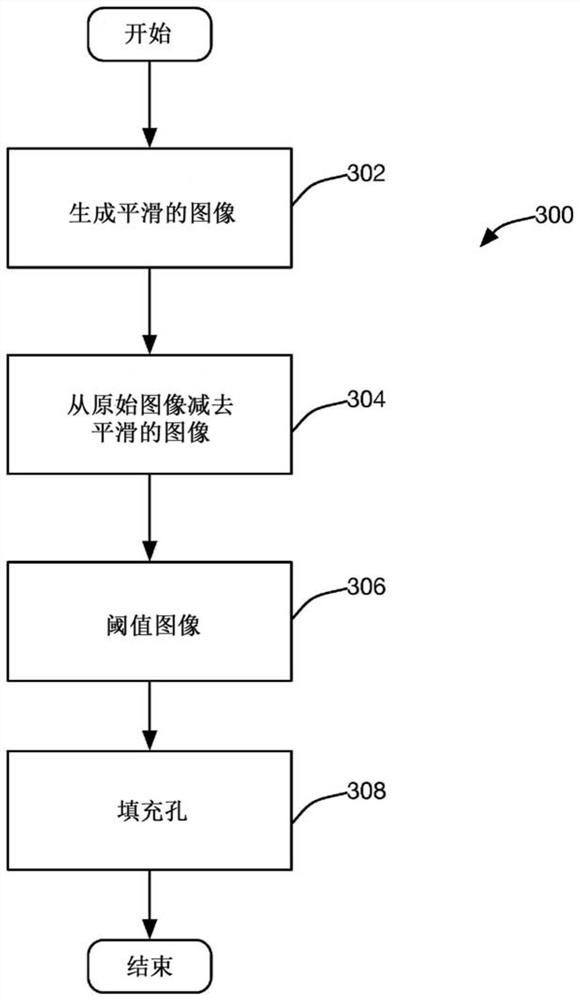
Systems and methods for segmentation of three-dimensional microscope images
A system and method for segmenting an image captured from an image capture device of a high-content imaging system includes an image capture module that receives an image captured by the image capture device. A coarse object detection module generates a coarsely segmented image, wherein each pixel of the coarsely segmented image is associated with a corresponding pixel in the captured image and identified as one of an object pixel and a background pixel. The marker identification module selects at least one marker pixel from the pixels of the coarsely segmented image, wherein each marker pixel is an object pixel in a continuous group of object pixels in the coarsely segmented image, and the object pixel is relatively Neighboring pixels to the set of object pixels are farthest from background pixels. an object splitting module comprising a plurality of processors operating in parallel to associate each object pixel of a coarsely segmented image with a marker pixel, wherein, in the coarsely segmented image, where the object pixel is associated with the The distance-based measure between marker pixels is smaller than the distance-based measure between the object pixel and any other marker pixel.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
A method for quantitative detection of cellular DNA damage induced by 1,3-butadiene using an air-liquid interface exposure system combined with high-content technology
ActiveCN107121553BImprove effectivenessImprove accuracyBiological testingHigh resolution imagingImmunofluorescent labeling
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting 1,3-butadiene-induced cell DNA damage in combination with a gas-liquid interface exposure system and a high-content technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1) cell culture; 2) 1,3-butadiene exposure through a gas-liquid interface exposure mode; 3) immunofluorescent labeling of gamma H2AX; 4) high-content detection. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the efficient exposure of gaseous 1,3-butadiene to wall-attached cells in vivo is realized by adopting the in-vitro gas-liquid interface exposure mode, so that the exposure efficiency of the 1,3-butadiene is improved; a high-content imaging system is utilized for automatic imaging, 1,3-butadiene-induced DNA double-chain fracture maker gamma H2AX proteins are quantitatively analyzed, and the direct and quick detection of the cells is realized, so that the sample treatment is more convenient; through high-resolution imaging, not only can the distribution of the gamma H2AX in cell nucleuses be directly observed, but also image data is convenient to store and re-analyze, and the quantitative analysis on the 1,3-butadiene-induced gamma H2AX in each of the cell nucleuses can be realized, so that detection results are more sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
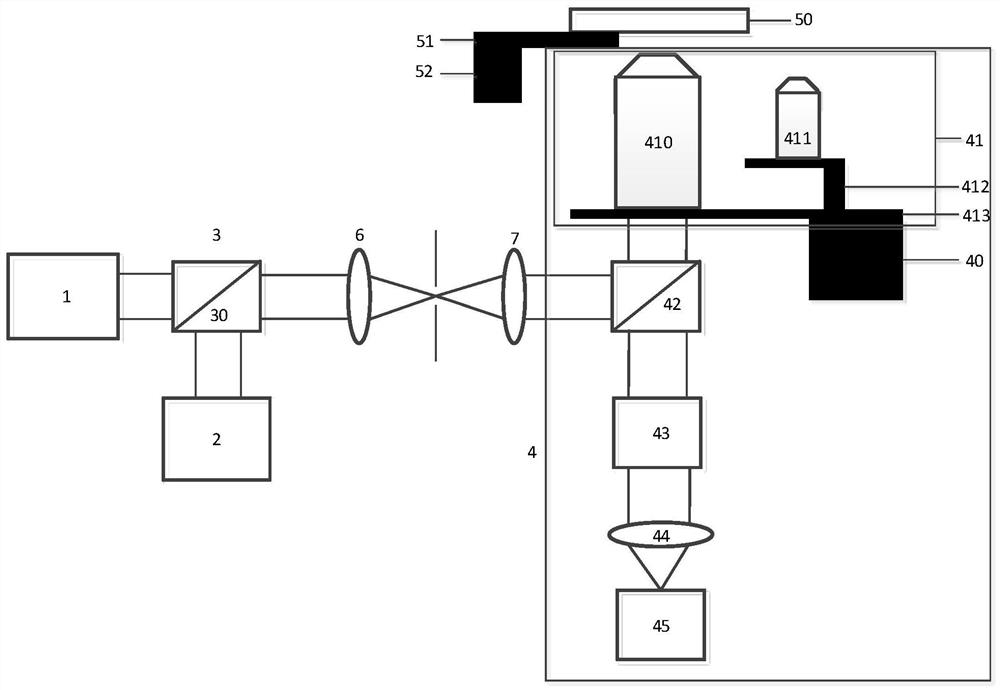
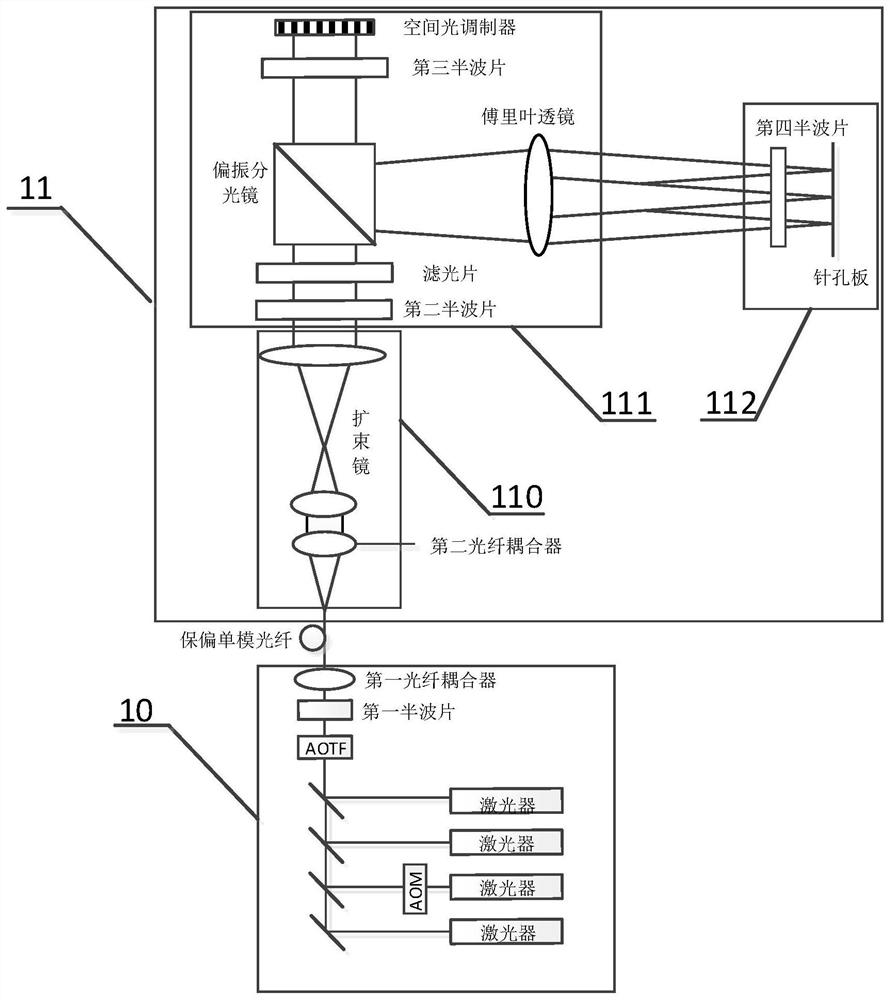
High-content super-resolution integrated microscopic imaging system and method
ActiveCN109856789BImaging method is simple and efficientEasy to operateMicroscopesMicroscopic imageMacroscopic scale
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Application and detection method of dorsal aorta diameter in juvenile zebrafish as an effect marker in detecting PCB126 cardiovascular toxicity
ActiveCN110702658BProtect healthPromote social and economic developmentFluorescence/phosphorescenceJuvenile fishAnimal science
The invention discloses an application of a diameter of aorta dorsalis of a juvenile zebrafish as an effect marker in detection of PCB126 cardiovascular toxicity, and a detection method. The diameterof aorta dorsalis of the juvenile zebrafish is obtained through subjecting a roe of the juvenile zebrafish to PCB126 contamination treatment within 2 hours of fertilization, fixing a posture after culturing the roe, performing image acquisition and carrying out measurement. The juvenile zebrafish is a transgenic juvenile zebrafish of which vascular endothelial cells are labeled with green fluorescence. The juvenile zebrafish is cultured in an illumination constant-temperature incubator with the temperature of 26.5 DEG C in a 14h / 10h light and dark cycle, and is cultured to 72 hpf. The image acquisition is performed by adopting a high-content imaging system for layer scanning to obtain a juvenile zebrafish blood vessel fluorogram. The measurement is carried out by measuring the diameter ofthe aorta dorsalis by using Photoshop software, corresponding original data is recorded by means of EXCEL, and then software GraphPad Prism is used for statistical analysis. The application is beneficial to characterizing cardiovascular toxicity caused by low-dose PCB126 exposure at an ambient level, and provides a technical method and a reference basis for environmental monitoring and evaluationas well as formulation of related technical standards.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
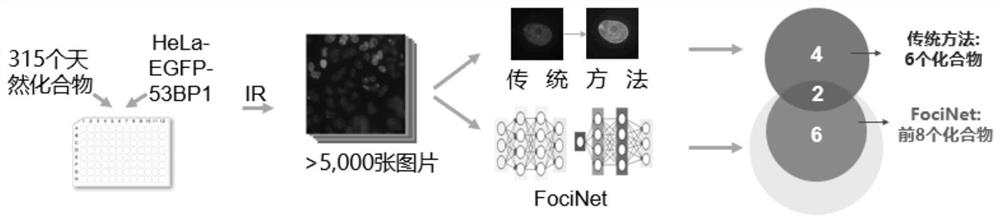
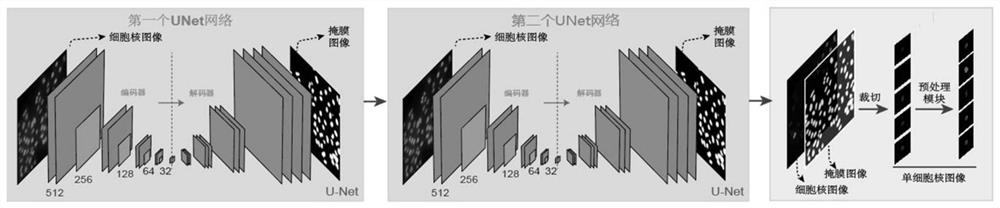
A method for high-throughput screening of DNA damage response inhibitors
The invention discloses a method for high-throughput screening of DNA damage response inhibitors, comprising the following steps: S1, training a cell nucleus segmentation network model based on a U-Net network; S2, constructing and training a cell nucleus category determination network model; S3. Use a high-content imaging device to photograph the cells subjected to the DNA damage response inhibitor to obtain an image to be analyzed; input the to-be-analyzed image into the cell nucleus segmentation network model, and then input the cell nucleus type determination network model, and count each DNA damage response inhibitor The corresponding proportion of damaged nuclei, the smaller the proportion of damaged nuclei, the better the effect of DNA damage response inhibitor. The method of the present invention can automatically and batchly perform segmentation and classification decisions for images obtained by high-content imaging equipment, and compounds with further research value can be preliminarily screened out through statistical analysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Evaluation method of vascular toxicity of aryl phosphate flame retardants based on high-content imaging system
ActiveCN110956625BImprove throughputRapid Vascular Toxicity AssessmentImage enhancementImage analysisJuvenile fishImage segmentation
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the vascular toxicity of aryl phosphate flame retardants based on a high-content imaging system, which comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining vascular fluorescence images of zebrafish embryos / juveniles treated with aryl phosphate flame retardants ; 2) Segmentation, recognition and analysis of blood vessel images; 3) Obtaining evaluation and screening results. By collecting blood vessel images of transgenic zebrafish embryos / juveniles with specific blood vessel fluorescence labeling, and analyzing multiple blood vessel parameters, the evaluation and screening of vascular developmental toxicity of aryl phosphate flame retardants can be realized. The configuration of the method includes: the hardware system is responsible for the acquisition of blood vessel image data, which is composed of a high-content imaging system and a 96-well glass bottom plate coated with agarose; the software system is used for semi-automatic identification of target blood vessels and multi-parameter output analysis, involving Photoshop, Software such as Matlab and GraphPad Prism. The invention has the characteristics of high throughput and stable results, and can quickly and accurately evaluate and screen the vascular developmental toxicity of multi-parameter indexes for aryl phosphate flame retardants.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzene or benzene metabolite based on high connotation technique
InactiveCN107064087AOvercome deficienciesImprove detection efficiencyFluorescence/phosphorescenceMetaboliteHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzene or benzene metabolite based on a high connotation technique. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing cell culture; 2) infecting cells; 3) performing immunofluorescent labeling for gamma H2AX; and 4) performing quantitative analysis by adopting the high connotation technique. The method has the advantages that a high connotation imaging system is utilized for automatically imaging and quantitatively analyzing the gamma H2AX protein of a DNA double-strand breaking mark induced by benzene or benzene metabolite, the direct and quick detection for cells is realized, and the sample treatment is more convenient; and due to high-resolution imaging, the distribution of gamma H2AX in a cell nucleus can be directly observed, the image data can be conveniently stored and analyzed, and the quantitative analysis for gamma H2AX, induced in each cell nucleus, of benzene or benzene metabolite, can be realized, so that the detection result is more sensitive and accurate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
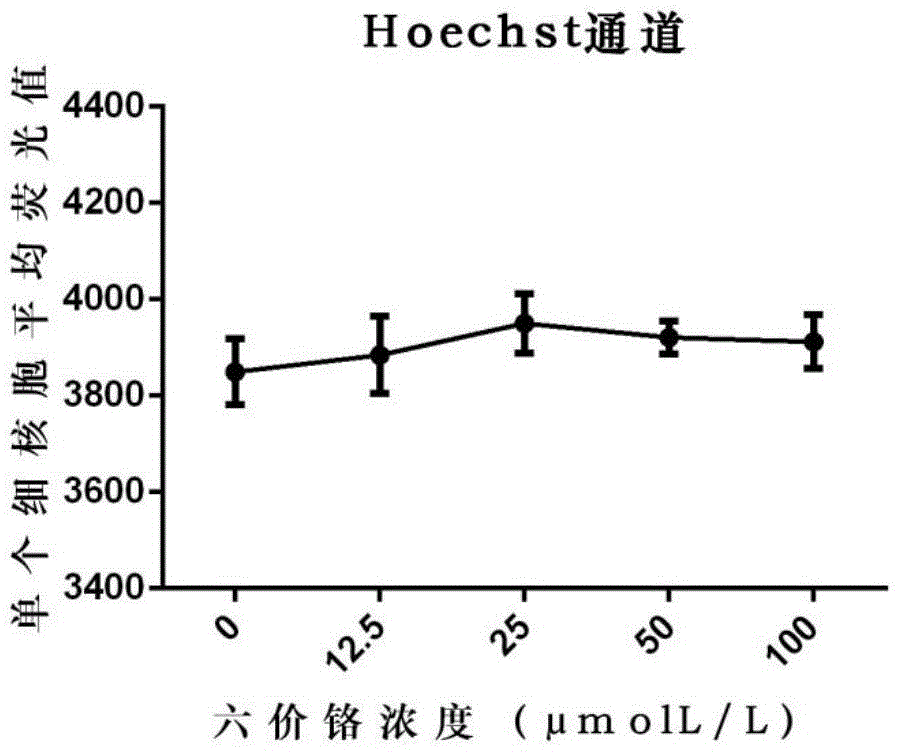
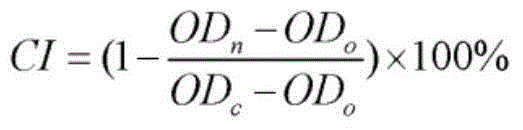
![Method of detecting influence on human oral cell [gamma] H2AX level due to tobacco chewing gum Method of detecting influence on human oral cell [gamma] H2AX level due to tobacco chewing gum](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/c5942c32-8d63-4b10-9544-121449d308f7/BDA0001092847380000071.png)
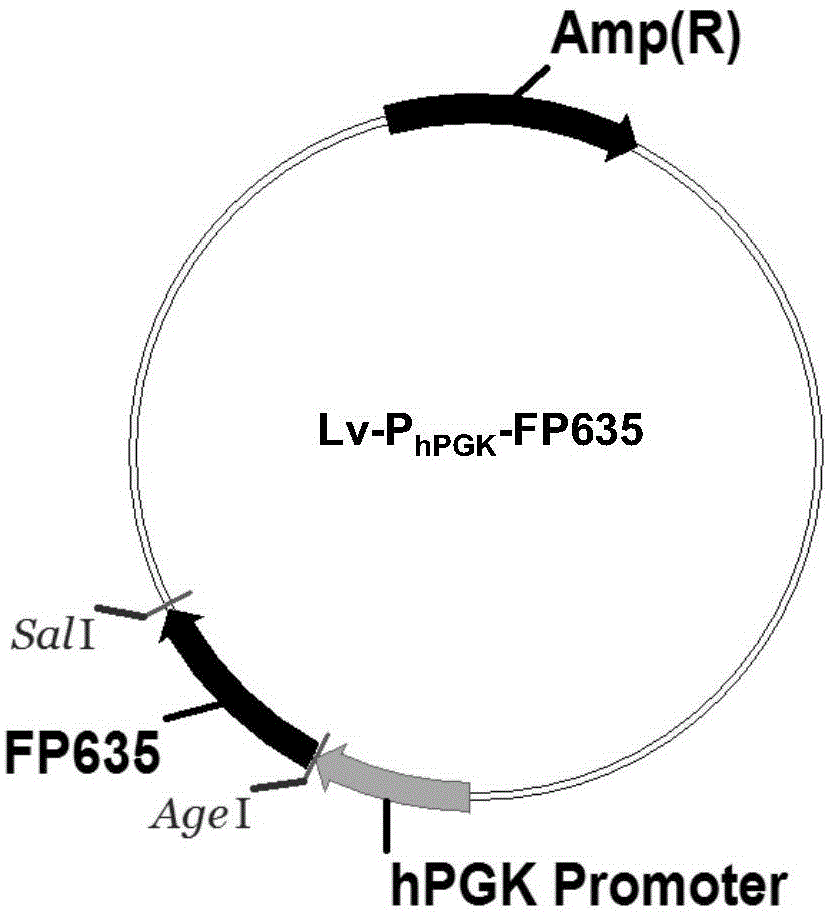
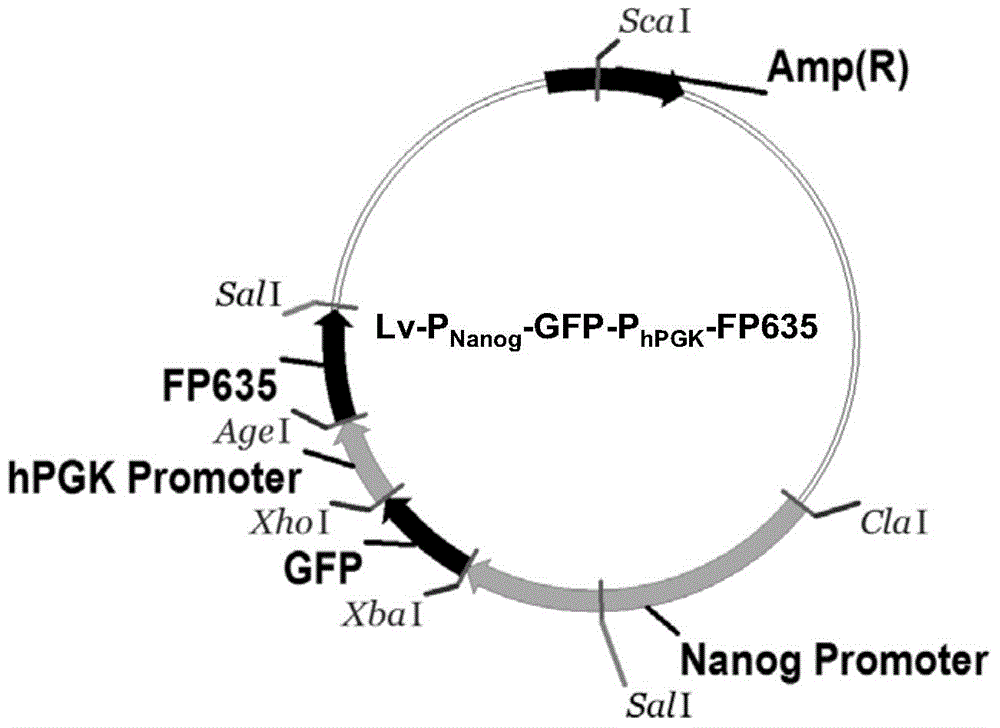





![Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a030fdd0-712b-4383-933c-044a172bd1a0/HDA0001247233460000011.png)
![Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a030fdd0-712b-4383-933c-044a172bd1a0/HDA0001247233460000012.png)
![Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique Method for quantitatively analyzing cell DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene based on high connotation technique](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a030fdd0-712b-4383-933c-044a172bd1a0/HDA0001247233460000021.png)