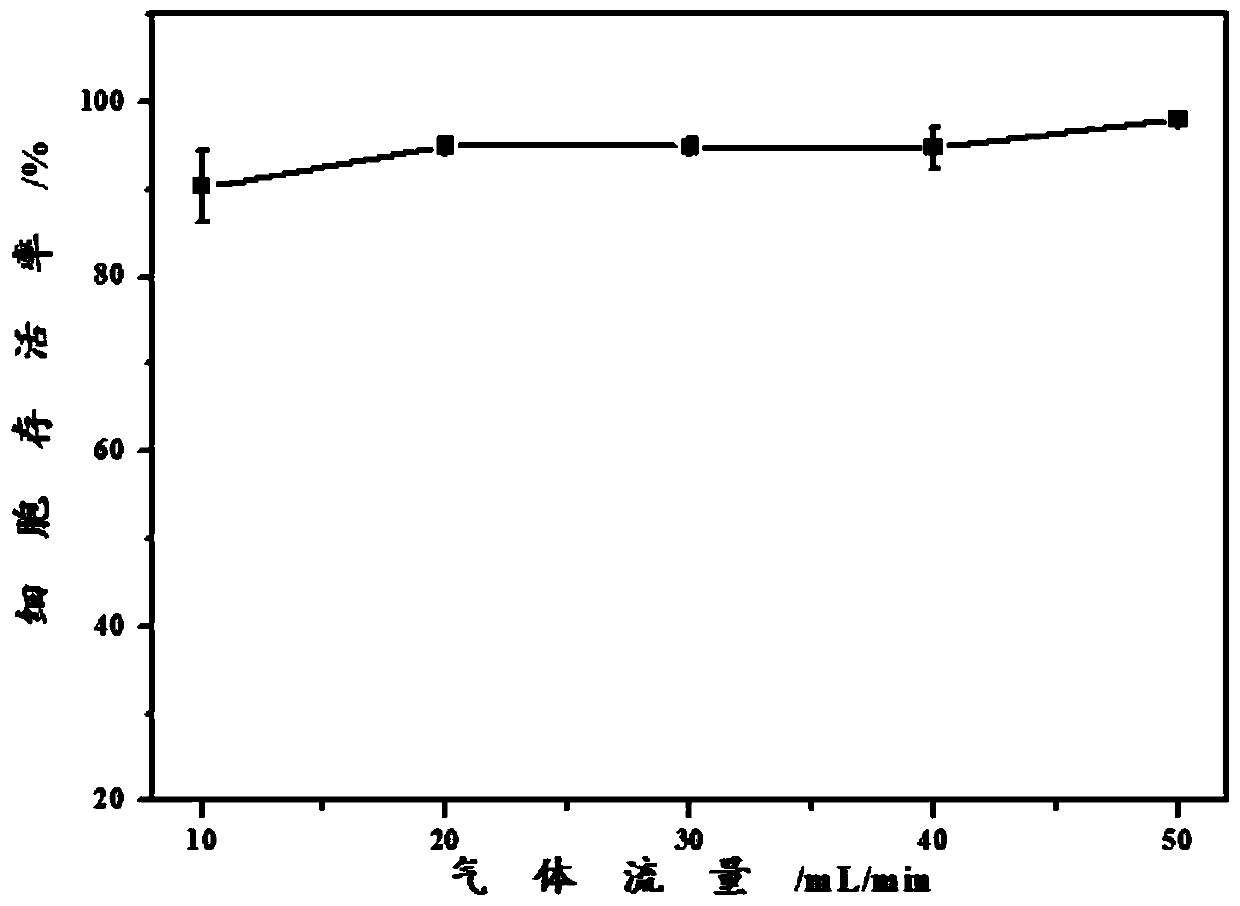
A method for quantitative detection of cellular DNA damage induced by 1,3-butadiene using an air-liquid interface exposure system combined with high-content technology
A quantitative detection, liquid interface technology, applied in the field of in vitro genotoxicity assay, can solve the problems of limited solubility, changing the detection purpose, and it is difficult for cells to achieve sufficient contact.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] The γH2AX induced by 1,3-butadiene after 1 h exposure was measured when the metabolic activation system rat liver S9 was not added to the cell poisoning liquid.
[0079] Add 0.5 and 2 mL of PBS to the top and bottom of the Transwell insert, respectively, and equilibrate at 37°C for 1-2 hours. Aspirate and discard the PBS on the top and bottom of the Transwell insert, add 0.5mL to the top of the insert with a concentration of 4×10 5 The single-cell suspension of A549 cells in the logarithmic growth phase of each cell / mL was added to the bottom of the insert with 2 mL of RPMI-1640 culture medium containing 0.01moL / L HEPES, 2mmoL / LL-glutamine and 10% FBS, and incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO 2 Conditioned for 24h.
[0080] Remove the culture medium on the top of the Transwell insert, take out the top of the Transwell insert and put it into the exposure compartment of the cell exposure system, so that the permeable filter membrane in the Transwell insert and the cell exposure so...
Embodiment 2
[0086] The γH2AX induced by 1,3-butadiene after 1 h exposure was measured when the metabolic activation system rat liver S9 was added to the cell poisoning solution.
[0087] The experimental process was carried out as described in Example 1, the only difference being that the cell poisoning solution in the poisoning chamber was a mixture of cell culture medium and 10% S9 mixture, so that the cell poisoning solution contained 1% S9 mixture.
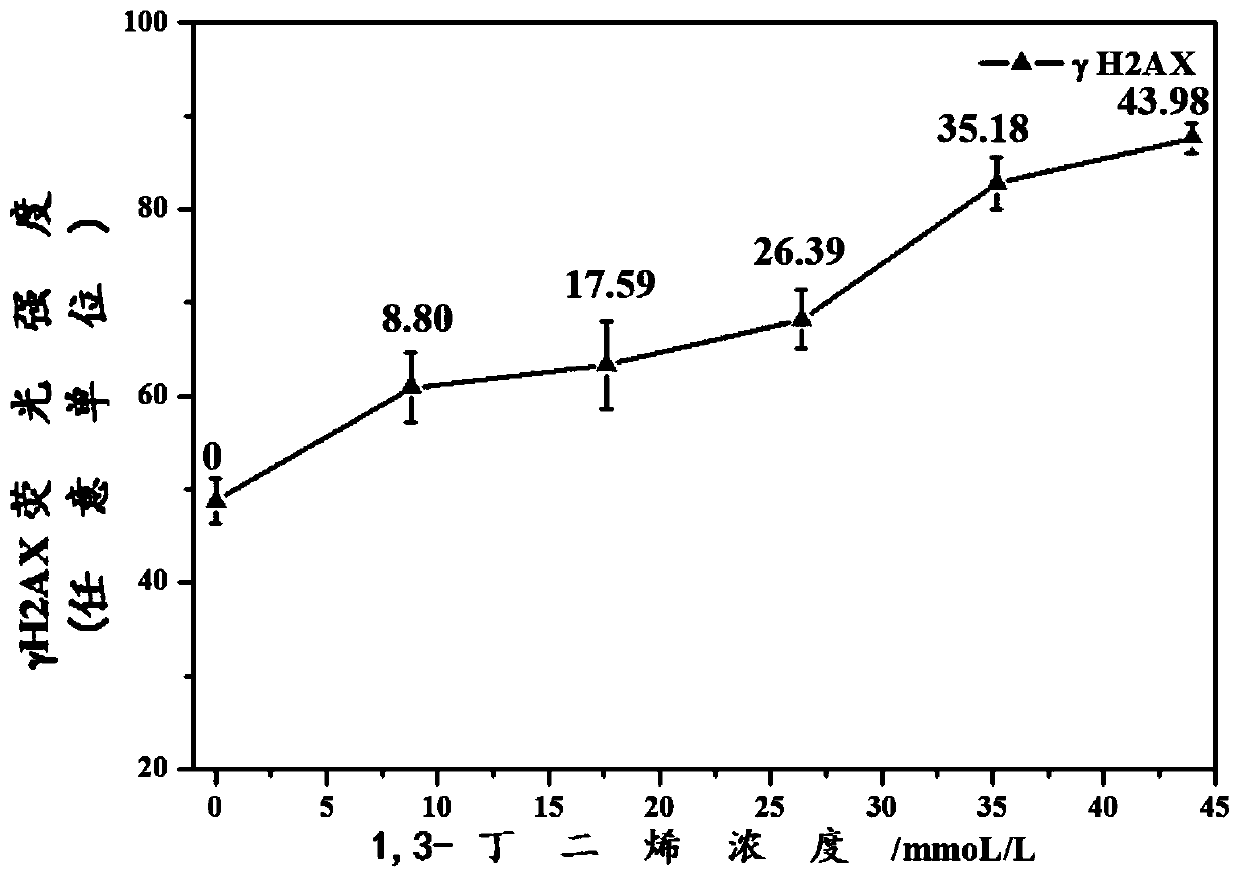
[0088] Figure 4 Shown is the dose-effect relationship curve of γH2AX induced by different concentrations of 1,3-butadiene in A549 cells after adding 1% S9 in the exposure medium, and image 3 The results shown are essentially the same.
[0089] The addition of S9 to the cell poisoning solution can enhance the metabolic transformation of 1,3-butadiene in vitro. Since 1,3-butadiene is a former genotoxic substance, the addition of the in vitro metabolic activation system S9 can avoid the possibility of false negative test results due to i...
Embodiment 3
[0091] When the metabolic activation system rat liver S9 was not added to the cell poisoning liquid, the γH2AX induced by 35.18mmoL / L 1,3-butadiene were measured after 15, 30, 45, 60 and 90min exposure respectively.
[0092] The experimental process was carried out as described in Example 1. The only difference was that the exposure concentration of 1,3-butadiene was fixed at a concentration of 35.18mmoL / L, and the exposure time was 0, 15, 30, 45, 60 and 90 minutes respectively. .
[0093] Figure 5 Shown is the time-effect relationship curve of γH2AX produced by A549 cells induced by 35.18mmoL / L 1,3-butadiene at 0, 15, 30, 45, 60 and 90min after exposure. It can be seen from the figure that as the exposure time increases, the γH2AX produced by A549 cells gradually increases, showing a significant time-effect relationship. When the exposure time was more than 60min, the induced γH2AX was 1.5 times higher than that of the normal group.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com