Method for quantitatively analyzing nicotine-induced cell DNA damage based on high content technology
A DNA damage and quantitative analysis technology, applied in the analysis of materials, material excitation analysis, material analysis by optical means, etc., can solve the problem of unable to provide intracellular fluorescence focus distribution, damage to cell structure and functional integrity, microscopy technology detection problems such as low throughput, to achieve the effect of simple and fast sample processing, improved detection efficiency and sensitivity, and sensitive and accurate detection results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
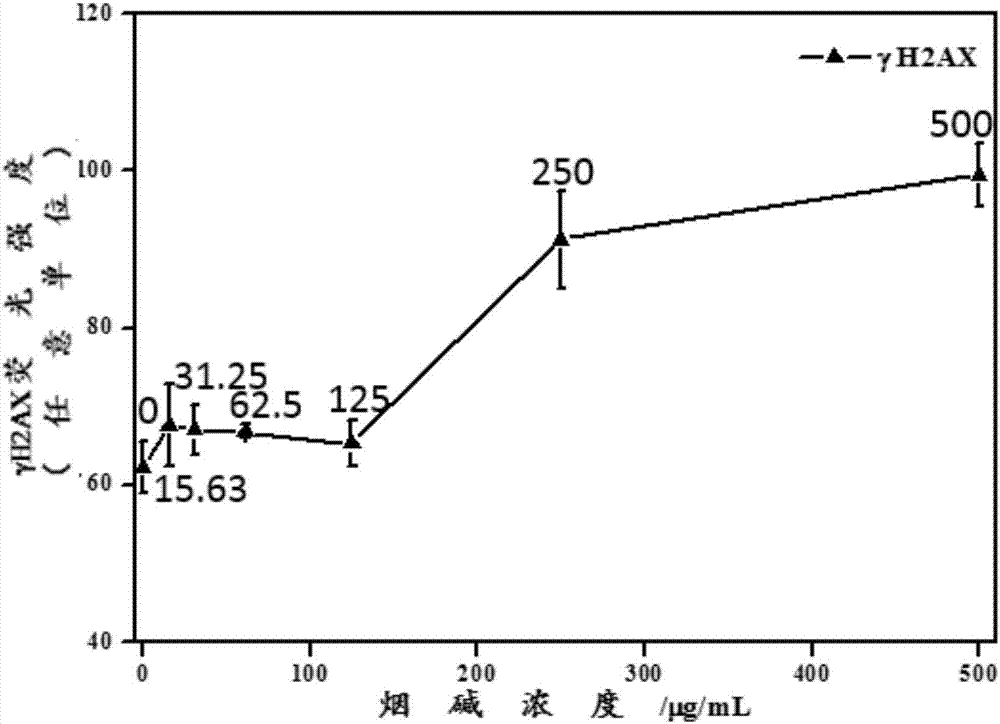
[0064] When the metabolic activation system rat liver S9 was not added to the cell poisoning solution, the γH2AX induced by nicotine after 24h exposure was measured.
[0065] A549 cells in the logarithmic growth phase were collected and planted in 96-well plates at 10,000 cells per well in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% FBS and 2mmoL / LL-glutamine at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Incubate in the incubator for 24h.
[0066] Aspirate and discard the cell culture fluid after culturing for 24 h, and use cell culture fluid containing 0, 15.63, 31.25, 62.5, 125, 250 and 500 μg / mL nicotine respectively (also containing 10% FBS and 2mmoL / LL-glutamine) RPMI-1640 culture medium) was used as the cell poisoning solution, and the cells were continued to be cultured for 24 h.
[0067] Discard the cell poisoning solution after exposure, add 100 μL PBS to each well and wash twice for at least 5 minutes each time; then add 50 μL 4% paraformaldehyde solution to each well and fix at room temperature for 15 min...
Embodiment 2
[0072] When the metabolic activation system rat liver S9 was added to the cell poisoning liquid, the γH2AX induced by nicotine after 24h exposure was measured.
[0073] The experimental process was carried out as described in Example 1, the only difference being that, in addition to the cell culture medium and nicotine, the cell poisoning solution was mixed with 10% S9 mixture, so that the cell poisoning solution contained 1% S9 mixture.
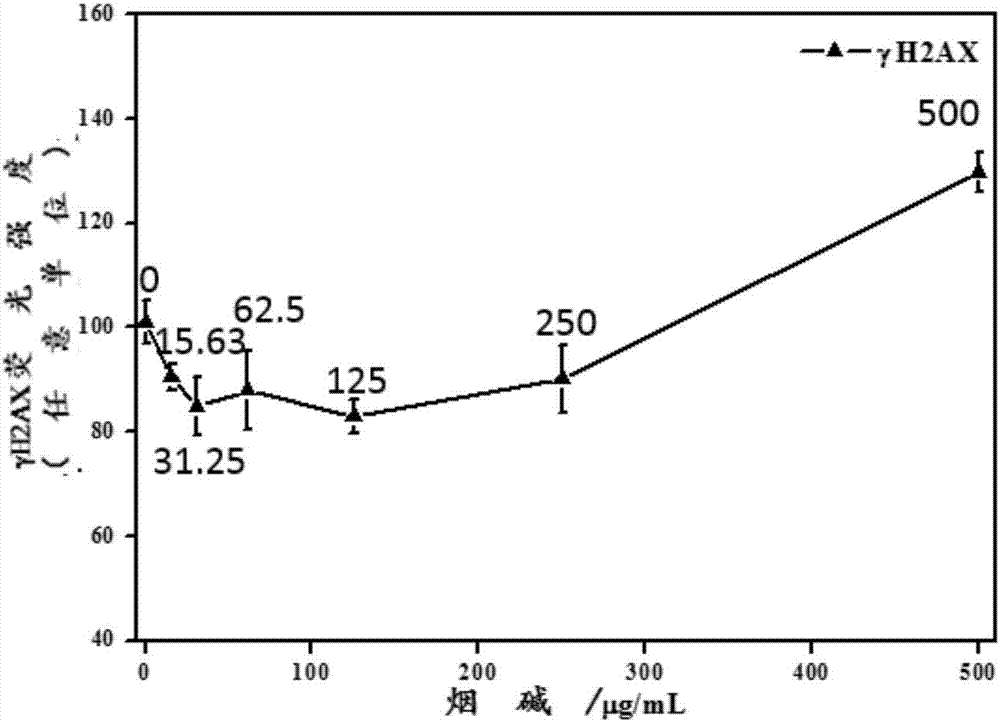
[0074] image 3 Shown is the dose-effect relationship curve of γH2AX produced by A549 cells induced by different concentrations of nicotine after 1% S9 was added to the cell poisoning solution 24 hours after exposure. As can be seen from the figure, with the increase of the exposure concentration, the γH2AX produced in the cells first decreased and then increased.
[0075] The addition of S9 to the cell poisoning solution can enhance the metabolic transformation of nicotine in vitro, so the addition of the in vitro metabolic activation syst...
Embodiment 3
[0077] When the metabolic activation system rat liver S9 was not added to the cell poisoning solution, the γH2AX induced by 500 μg / mL nicotine were measured after 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 hours of exposure, respectively.
[0078] The experimental process was carried out as described in Example 1, with the only difference that the concentration of nicotine in the cell-infected solution was fixed at 500 μg / mL, and the exposure time was 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 hours, respectively.
[0079] Figure 4Shown is the time-effect relationship curve of γH2AX produced by A549 cells induced by 500 μg / mL nicotine at 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 hours after exposure. It can be seen from the figure that as the exposure time increases, the γH2AX produced by A549 cells gradually increases, showing a significant time-effect relationship.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com