Resistive layer self-gating resistive random access memory as well as building method and application thereof
A technology of resistive memory and construction method, applied in the direction of electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of perfect compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
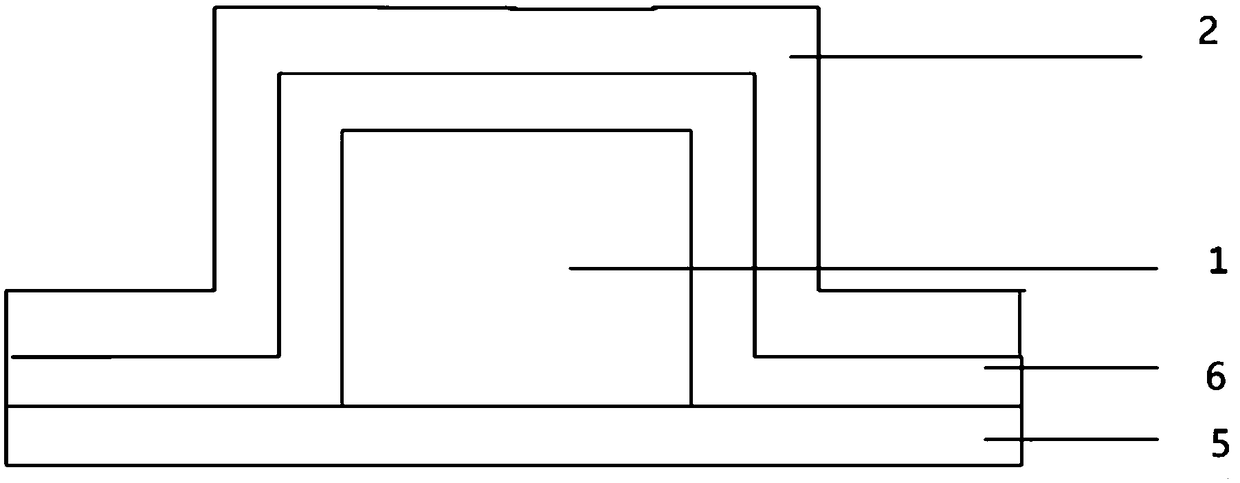
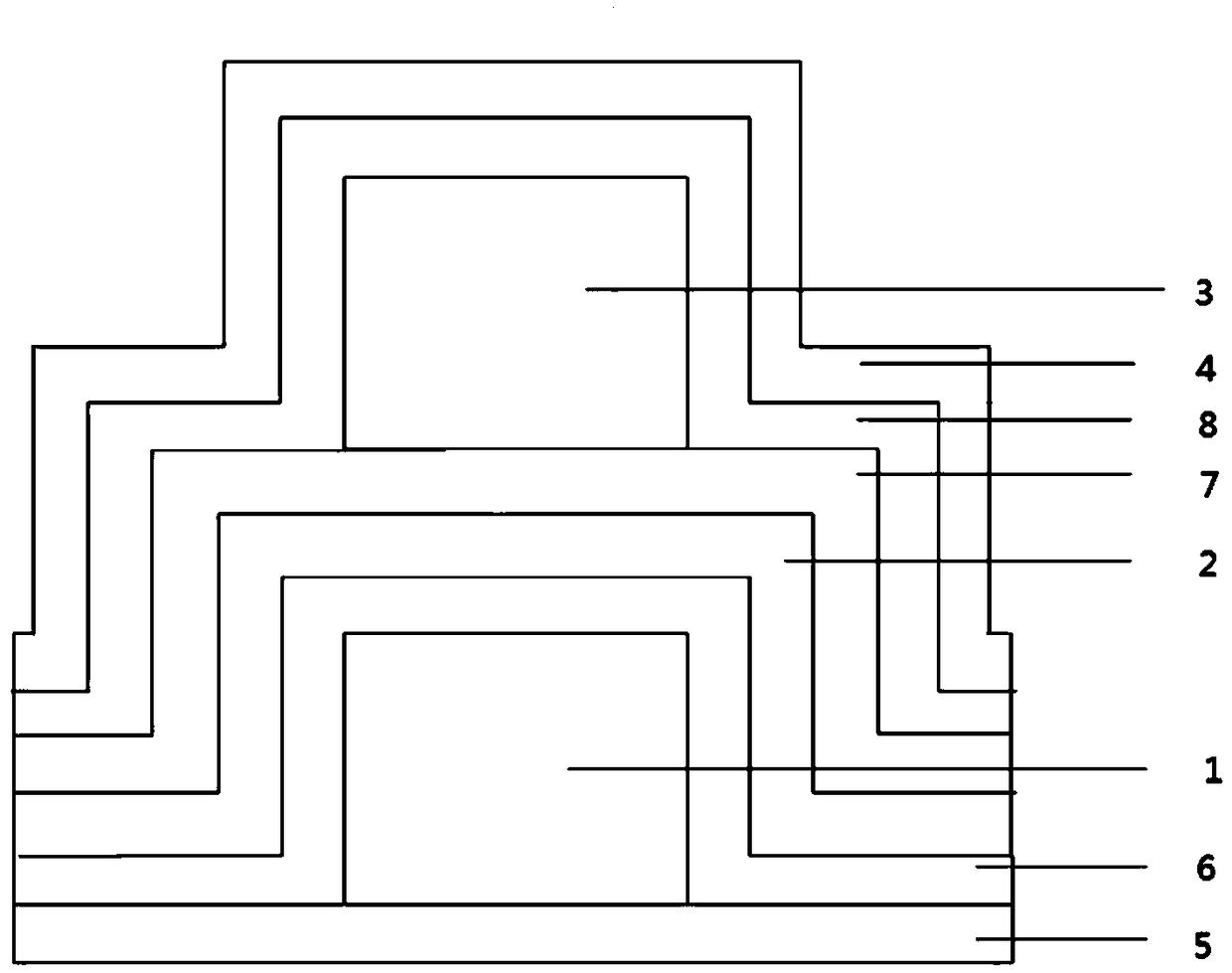
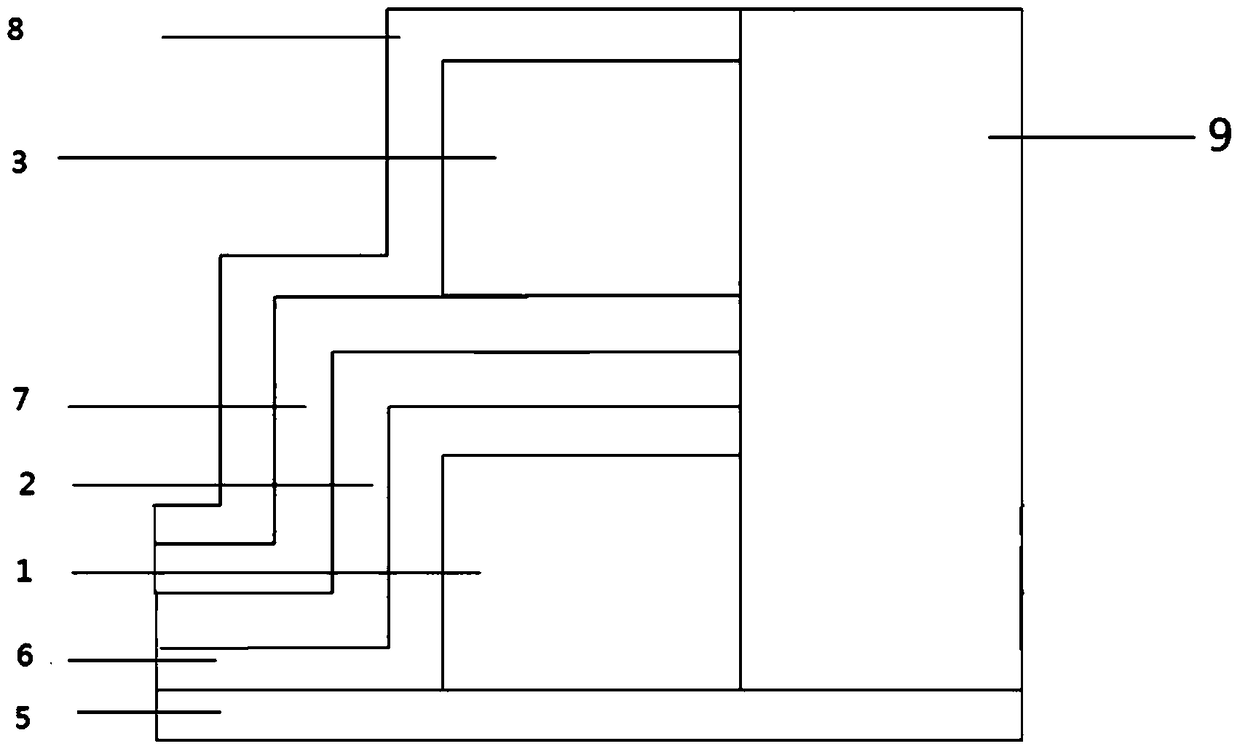
[0063] A resistive variable layer self-selection resistive variable memory, comprising a stacked layer; the stacked layer includes a fourth Hf layer 4, a fourth Si 3 N 4 Layer 8, third Hf layer 3, third Si 3 N 4 Layer 7, second Hf layer 2, second Si 3 N 4 Layer 6, first Hf layer 1 and first Si 3 N 4 Layer 5; the left and right sides of the stacked layer are respectively provided with a bottom electrode and a top electrode; the bottom electrode and the fourth Si 3 N 4 Layer 8, the third Si 3 N 4 Layer 7 communicates with the second Hf layer 2 and is arranged on the upper surface of the second Hf layer 2; the top electrode communicates with the entire stack layer and is arranged on the first Si 3 N 4 top surface of layer 5.
[0064] First Si 3 N 4 The thickness of layer 5 is 25nm; the thickness of the first Hf layer 1 is 110nm; the second Si 3 N 4 The thickness of layer 6 and the second Hf layer 2 is 25nm; the third Si 3 N 4 The thickness of layer 7 is 25nm; the...
Embodiment 2
[0067] The resistive variable layer self-selectable resistive variable memory as described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the resistive variable layer self-selectable resistive variable memory comprises two stacked layers arranged side by side; the top electrode is a bit line; the for the word line.
Embodiment 3
[0069] A method for constructing a resistive variable layer self-selecting resistive variable memory as described in Embodiment 1, comprising the following steps:
[0070] 1) Deposit the first Si on the substrate 3 N 4 Layer 5; depositing the first Si on the substrate 3 N 4 Layer 5 is realized by CVD method; the substrate is a Si substrate;
[0071] 2) In the first Si 3 N 4 Deposit the first Hf layer 1 on the layer 5, then perform photolithography and lift-off treatment; 3 N 4 The deposition of the first Hf layer 1 on the layer 5 is achieved by a DC sputtering method.
[0072] 3) Deposit the second Si sequentially on the first Hf layer 1 3 N 4 Layer 6, the second Hf layer 2; as figure 1 shown. Second Si 3 N 4 Layer 6 is deposited by CVD method and the second Hf layer 2 is deposited by sputtering.
[0073] 4) Deposit the third Si on the second Hf layer 2 3 N4 Layer 7, according to the method of step 2), 3) in the third Si 3 N 4 Deposit the third Hf layer 3, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com