Degradable bone joining rod implanting apparatus and preparation method thereof
A technology for bone rods and devices, which is applied in the field of degradable bone rod implantation devices and their preparation, can solve the problems of self-degeneration of implant materials, implantation failure, diffusion of metal ions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] The present application also provides a preparation method of the degradable bone rod implantation device, comprising the following steps:
[0035] In-situ growth of Ca-P-Ag coating on the surface of degradable medical bone rod by micro-arc oxidation process;
[0036] The degradable medical bone-setting rod is a pure magnesium material or a magnesium alloy material, and the magnesium alloy material includes: Fe greater than 0 and less than or equal to 0.5wt%, Zn greater than 0 and less than or equal to 1wt%, greater than 0 and less than or equal to 0.6wt% of Mn, greater than 0 and less than or equal to 0.05wt% of Cu, 0.8wt% of Sr and the balance of Mg;
[0037] The coating is a Ca-P-Ag coating.
[0038] In the process of preparing the degradable bone rod implantation device, the present application prepared a Ca-P-Ag coating on the surface of the medical bone rod through a micro-arc oxidation process; the medical bone rod was prepared according to a method well known to ...
Embodiment 1
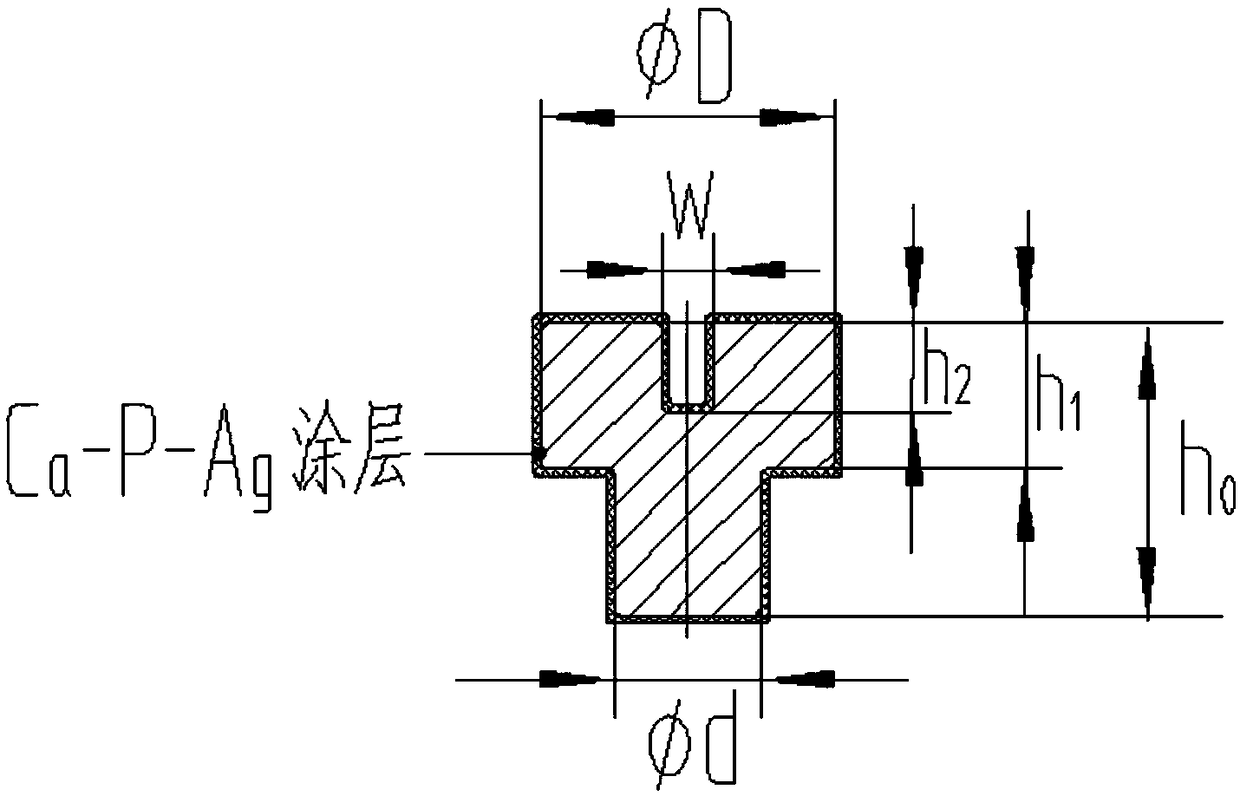
[0042] provide as figure 2 The medical bone-synthesizing rod shown, the diameter D of the bone-synthesized rod connected by the coaxial is 8mm, the height h 0 A base of 10mm with a diameter d of 4mm and a height h 1 The length W of the groove in the center of the bottom of the base is 6mm, and the height h 2 3mm; meanwhile, the bone bonding rod is a magnesium alloy material, which consists of 0.1wt% Fe, 0.6wt% Zn, 0.6wt% Mn, 0.02wt% Cu, 0.8wt% Sr and the rest of Mg;
[0043] The micro-arc oxidation process is used to in-situ grow Ca-P-Ag coating on the surface of the medical bone rod to obtain a degradable magnesium alloy bone rod implant device; the specific composition of the electrolyte in the micro-arc oxidation process is sodium silicate 40wt%+nano Hydroxyapatite powder 50wt% + sodium fluoride 5wt% + glycerin 2wt% + sodium hydroxide 2wt% + 1wt% nano-Ag powder + deionized water 2000mL, the specific process parameters are constant voltage 300V; pulse frequency 350Hz; Ra...
Embodiment 2
[0047] provide as figure 2 As shown in the medical bone rod, the bone rod is coaxially connected with a diameter D of 6 mm and a height h 0 A base of 8mm with a diameter d of 3mm and a height h 1 The length W of the groove in the center of the bottom of the base is 4mm, and the height h 2 2mm; meanwhile, the bone bonding rod is a magnesium alloy material, which consists of 0.4wt% Fe, 0.8wt% Zn, 0.4wt% Mn, 0.03wt% Cu, 0.8wt% Sr and the rest of Mg;
[0048] The Ca-P-Ag coating is grown in situ on the surface of the medical bone rod by using the micro-arc oxidation process to obtain a degradable magnesium alloy bone rod implant device; the specific composition of the electrolyte in the micro-arc oxidation process is sodium silicate 50wt%+nano HA powder 40wt% + sodium fluoride 5wt% + glycerin 2wt% + sodium hydroxide 2wt% + 1wt% nano-Ag powder + deionized water 2000mL, the specific process parameters are constant voltage 400V; pulse frequency 250Hz; duty cycle 10% , oxidation t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com