Vacuum reaction intensity refining method and application of vacuum reaction intensity refining method to prepare nickel-based and iron-based alloys
An iron-based alloy, vacuum induction smelting technology, applied in the vacuum reaction strength refining, the application in the preparation of nickel-based iron-based alloys, the field of vacuum induction refining of nickel or nickel alloys or iron alloys, can solve the problem of not really understanding the melt and iron alloys The importance of contact in the vacuum area, etc., to achieve the effect of smaller size, uniform distribution, and improved stability of magnetic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Taking the nickel-based superalloy Inconel 718 for aero-engine as an example, the implementation details of the vacuum reaction intensity refining method are illustrated.
[0040] Inconel 718 chemical composition percentage: C 0.045 max, Ti 0.80 ~ 1.15, Mn 0.35 max., Fe balance, P 0.010 max., Al 0.40 ~ 0.60, S 0.010 max., Mo 2.80 ~ 3.30, Si 0.35 max., Co 1.00 max., Ni 50. 0~55.0, Cu 0.230 max., Cr 17.0~21.0, B 0.0060max. (60ppm), Pb 0.0010 max. (10 ppm), Bi 0.00005 max. (0.5 ppm), Se0.0005 max. (5 ppm), Mg0.0060 max. (60 ppm), Ca 0.003 max. (30 ppm), Cb (Nb) + Ta 4.87~5.20.
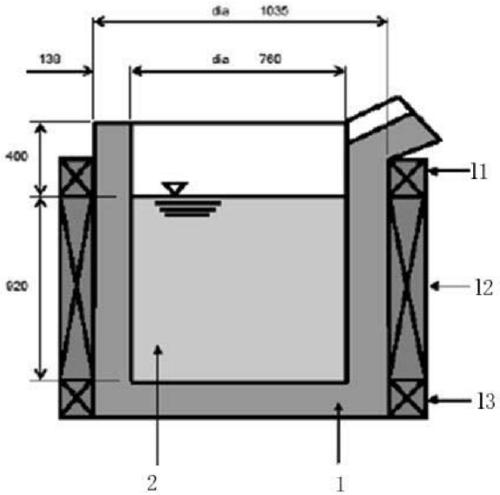
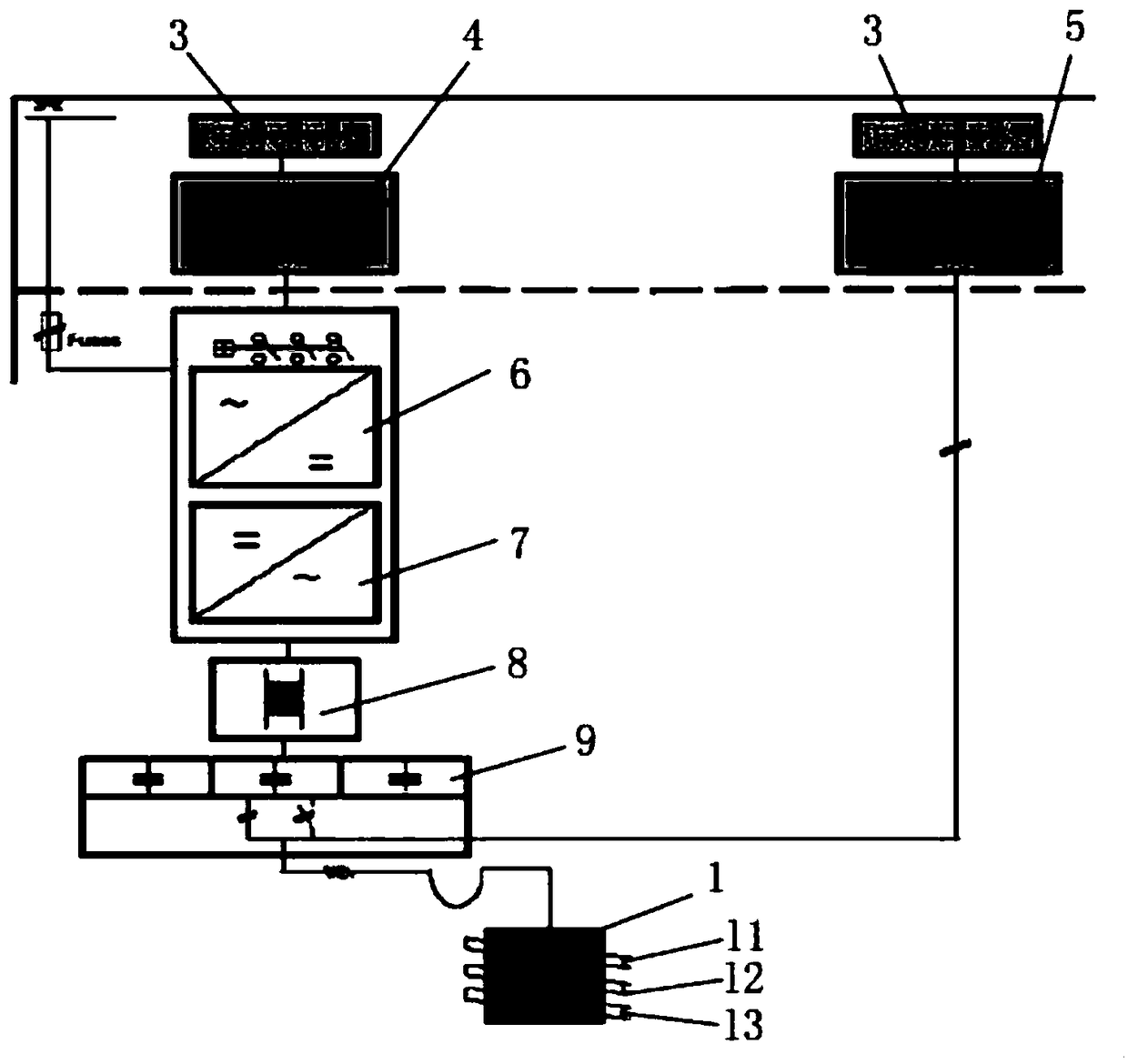
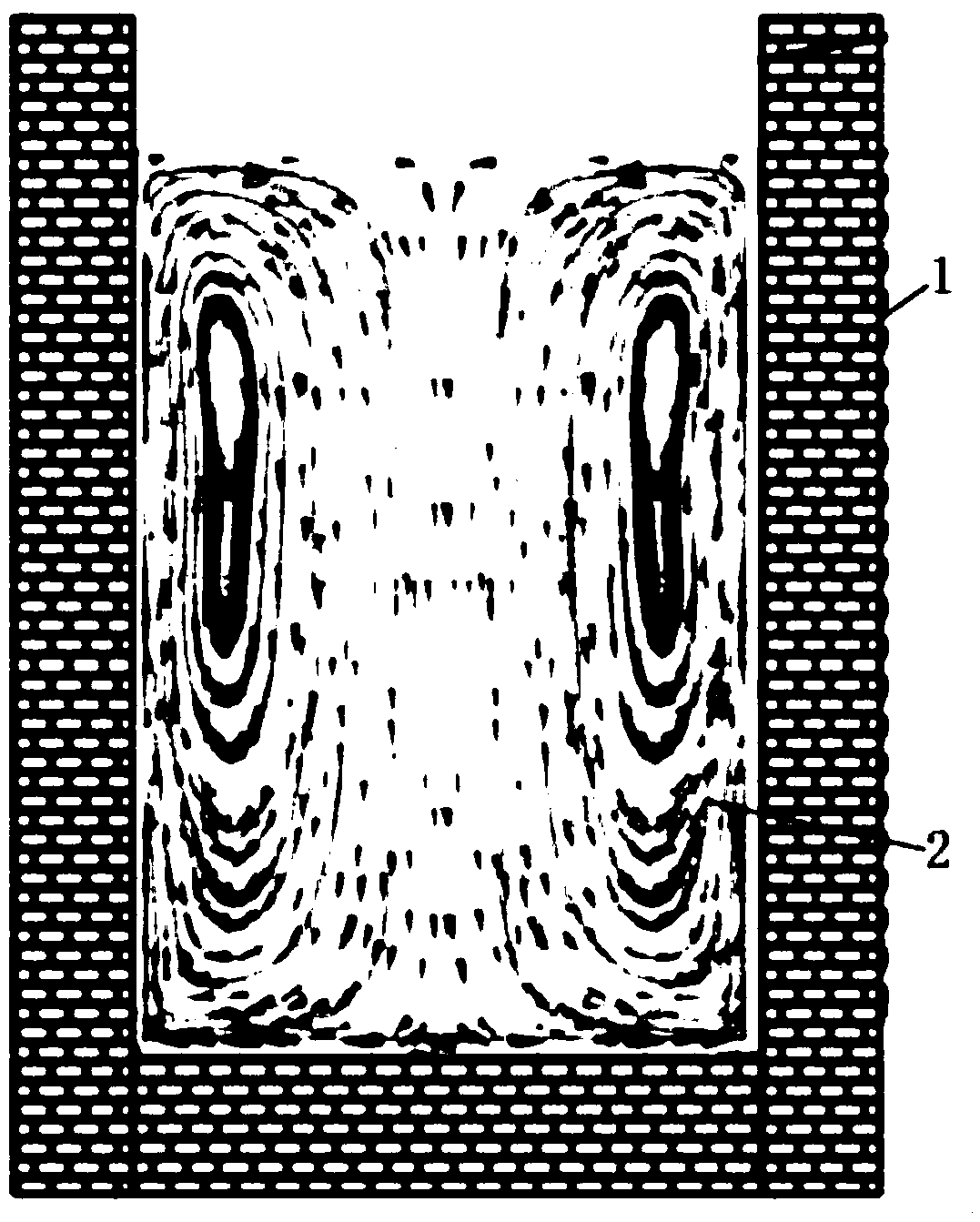
[0041] Vacuum induction melting furnace adopts 3 tons (capacity) German VIDP400 type, with three-phase magnetic stirring function, and the ultimate vacuum degree is 10 -2 Pa. About the vacuum induction melting furnace, please refer to figure 1 , The outer peripheral wall of the furnace body 1 is arranged in sequence from top to bottom with three sets of induction coils, namely l1, l2, l3. see ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Taking the iron-based superalloy A286 for aero-engine fasteners as an example, the implementation details of the vacuum reaction intensity refining method are illustrated.
[0050] A286 chemical composition percentage: C 0.08 max, Ti 1.9 ~ 2.35, Mn 0.35 max. Fe balance, P0.010 max. Al 0.1 ~ 0.35, S 0.002 max. Mo 1 ~ 1.50, Si 0.35 max. V 0.1 ~ 0.50, Ni24. 0~27.0, Cu 0.30 max. Cr 13.5~16.0, B 0.003~0.010, Pb 0.0010 max. , Bi0.00003 max. (0.3 ppm), Se 0.0005 max. (5 ppm), Mg 0.005 max. (50 ppm), Ca 0.004max. (40 ppm), O 20 ppm max, N50ppm.
[0051] A286 is an iron-based alloy, and the vacuum reaction refining temperature is 1550°C to 1650°C.
[0052] Vacuum induction melting furnace adopts 3 tons of German VIDP400 type, with three-phase magnetic stirring function, and the ultimate vacuum degree is 10 - 2 Pa, vacuum stirring cycle density value = 1 cycle / min.
[0053] The melting amount is 3 tons, the vacuum reaction incubation time is 50 minutes in total; the vacuum re...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Taking the American Standard wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron F45009 as an example to illustrate the implementation details of the vacuum reaction intensity refining method.
[0059] F45009 chemical composition percentage: C 2.0-3.3, Mn 2.0max., Fe balance, P 0.10 max., S0.060max., Mo 3 max, Si 1.5 max., Ni 2.5 max, Cu 1.2 max., Cr 23 ~ 30.
[0060] F45009 is an iron-based alloy, and its vacuum reaction refining temperature is 1550°C to 1650°C.
[0061] The vacuum induction melting furnace is a 3-ton German VIDP400 type, with three-phase magnetic stirring function, and the ultimate vacuum degree is 10 - 2 Pa, vacuum stirring cycle density value = 1 cycle / min.
[0062] The melting amount is 3 tons, the vacuum reaction incubation time is 40 minutes in total; the vacuum reaction intensity is 55 weeks, the vacuum cycle reaction time = vacuum reaction intensity value ÷ vacuum stirring cycle density value = 55 weeks ÷ 1 week / min = 55 minutes.
[0063] Determine the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com