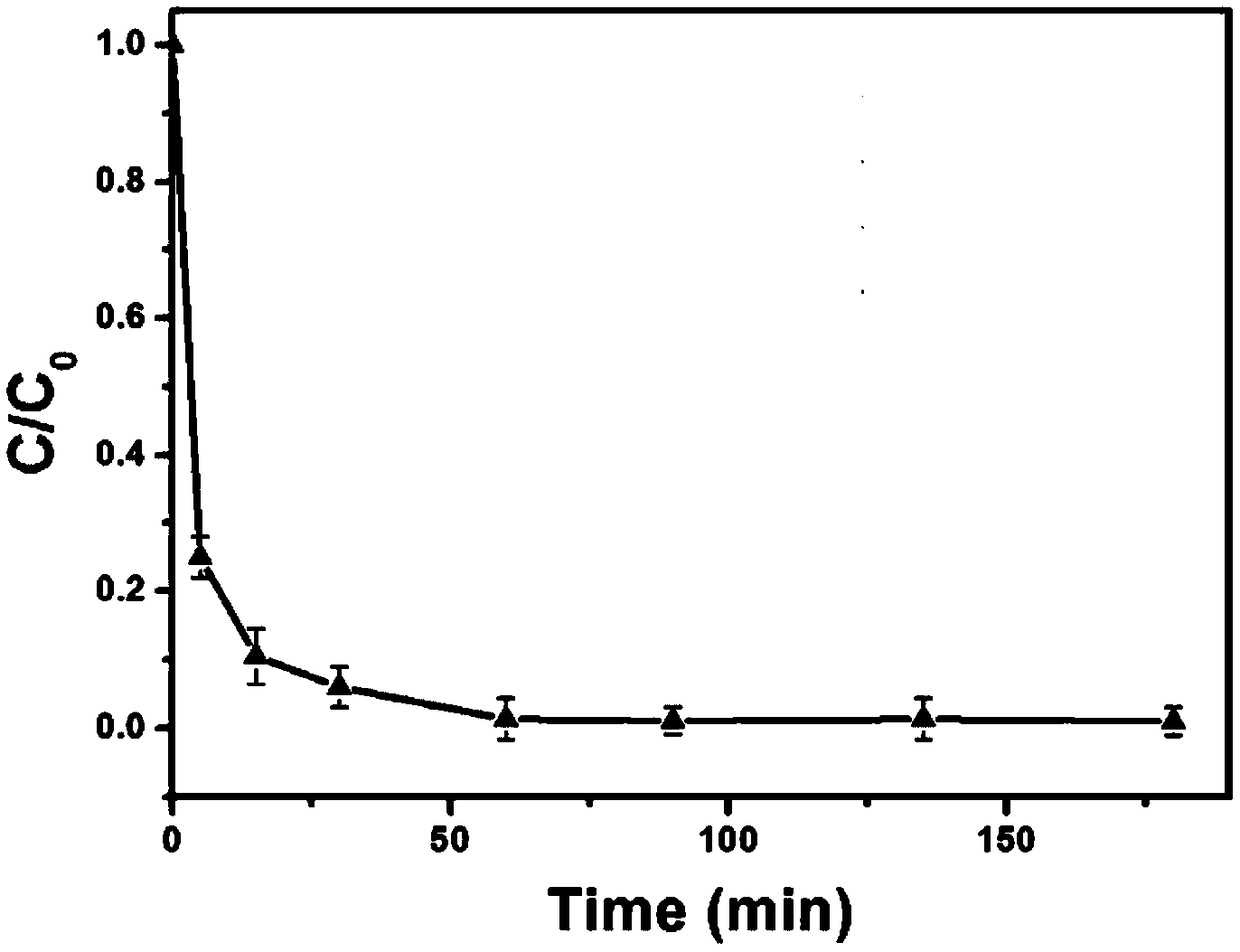
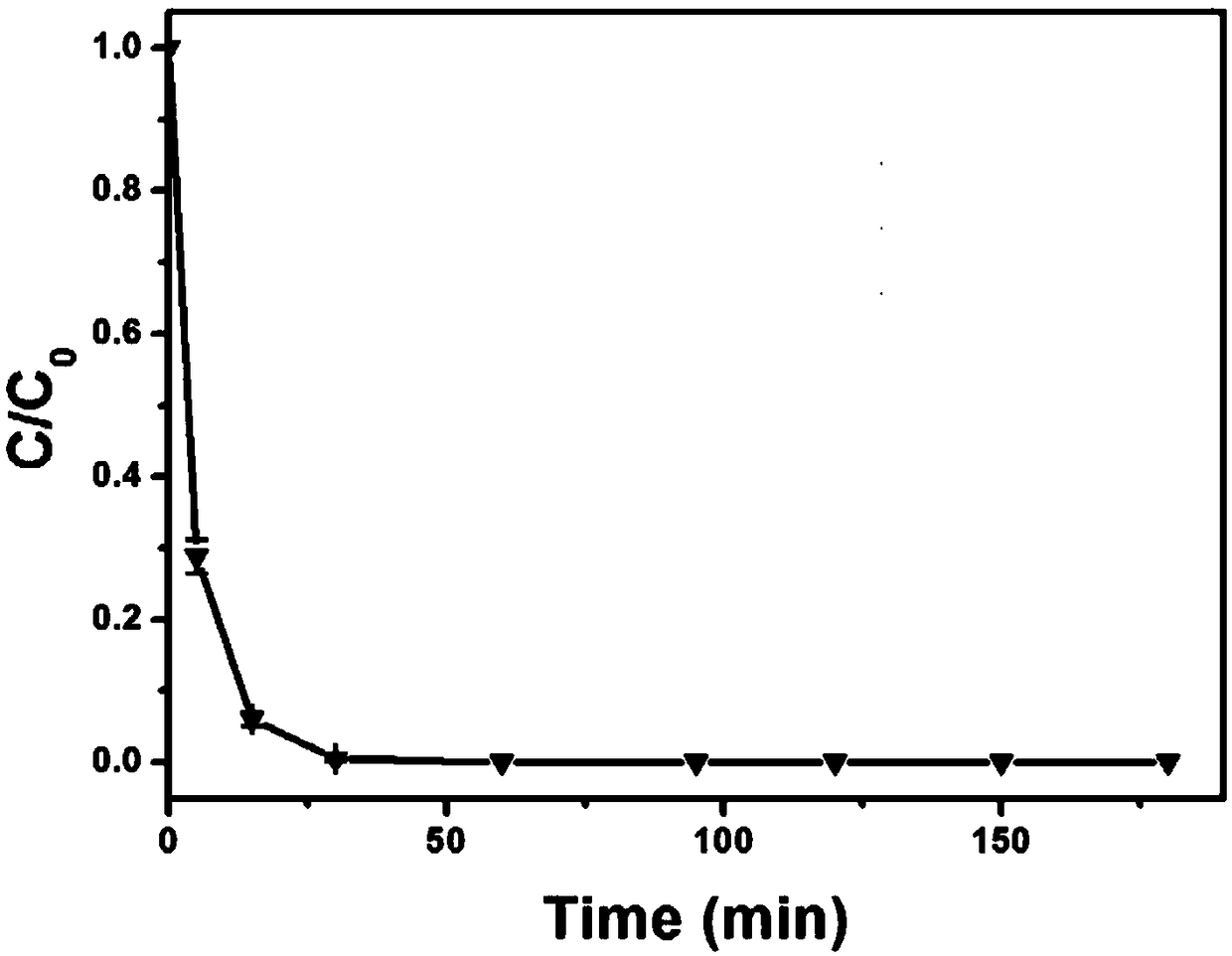
Preparation method of polyglutamic acid modified nanoscale Fe/Pd nanoparticles and application in dechlorination of organic chlorides
A polyglutamic acid and nanoparticle technology, which is applied in the field of water pollution treatment, can solve the problems of inhibiting reaction activity, easily corroded by water, low dechlorination activity, etc., and achieves improved reaction rate constant, good colloidal stability, and good reduction. effect of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for preparing polyglutamic acid-modified nanoscale Fe / Pd nanoparticles, comprising the following steps:
[0025] 1) First weigh 10 mg, 25 mg, and 50 mg of polyglutamic acid (PGA), respectively, and dissolve them in 50 mL of water to prepare four polyglutamic acid solutions. Add 250 mg of ferrous sulfate to the acid solution (the mass ratios of PGA to Fe are 19.9:100, 49.7:100, and 99.5:100), and mix polyglutamic acid and iron salt for 5 minutes to obtain 3 solutions;
[0026] 2) Add 3 mL of freshly prepared potassium borohydride solution (the molar ratio of potassium borohydride to soluble iron salt is 3:1) with a concentration of 50 mg / mL to each solution obtained in step 1) and stir rapidly to react Generate nano-scale zero-valent iron particles modified by polyglutamic acid, and continue to feed argon for 20 minutes to remove the hydrogen generated by the reaction and ensure the sufficient decomposition of excess potassium borohydride;
[0027] 3) 400 micro...
Embodiment 2
[0033] A method for preparing polyglutamic acid-modified nanoscale Fe / Pd nanoparticles, comprising the following steps:
[0034] 1) First weigh 10 mg, 25 mg, and 50 mg of polyglutamic acid (PGA), respectively, and dissolve them in 50 mL of water to prepare four polyglutamic acid solutions. Add 120 mg of ferrous chloride (PGA / Fe mass ratios are 17:100, 48:100, 95:100 respectively) to the acid solution, and mix polyglutamic acid and iron salt for 5 minutes to obtain 3 solutions;
[0035] 2) Add 1 mL of freshly prepared potassium borohydride solution (the molar ratio of potassium borohydride to soluble iron salt is 1:1) with a concentration of 50 mg / mL to the three solutions obtained in step 1) respectively, and stir rapidly to react Generate nano-scale zero-valent iron particles modified by polyglutamic acid, and continue to feed argon for 20 minutes to remove the hydrogen generated by the reaction and ensure the sufficient decomposition of excess potassium borohydride;
[0036...
Embodiment 3
[0041] A method for preparing polyglutamic acid-modified nanoscale Fe / Pd nanoparticles, comprising the following steps:
[0042] 1) First weigh 10 mg, 25 mg, and 50 mg of polyglutamic acid (PGA), respectively, and dissolve them in 50 mL of water to prepare four polyglutamic acid solutions. Add 150 mg of ferric chloride (PGA / Fe mass ratios are 18:100, 47:100, 98:100 respectively) to the acid solution, and mix polyglutamic acid and iron salt for 5 minutes to obtain 3 solutions;
[0043] 2) Rapidly add 5 mL of freshly prepared potassium borohydride solution (the molar ratio of potassium borohydride to soluble iron salt is 5:1) with a concentration of 50 mg / mL to the three solutions obtained in step 1) and stir rapidly to react Generate nano-scale zero-valent iron particles modified by polyglutamic acid, and continue to feed argon for 20 minutes to remove the hydrogen generated by the reaction and ensure the sufficient decomposition of excess potassium borohydride;
[0044] 3) 20...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com