DNA encoded compound screening method for identification tag-free protein or cell lysate with antibody
A technology of cell lysates and identification markers, which is applied in the field of antibody screening of DNA-encoded compounds targeting proteins without identification markers or cell lysates, which can solve the problems of proteins without post-translational modifications and cumbersome process of protein purification, etc., to improve screening efficiency , Avoid cumbersome processes and reduce screening costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Screening of positive compounds on unmarked IDO1 to confirm the feasibility of the method
[0033] 1. Background: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase IDO1 is the rate-limiting enzyme of tryptophan catabolism. In this case, the purchased unlabeled IDO1 was used as the target protein to verify the method.
[0034] 2. Implementation method:
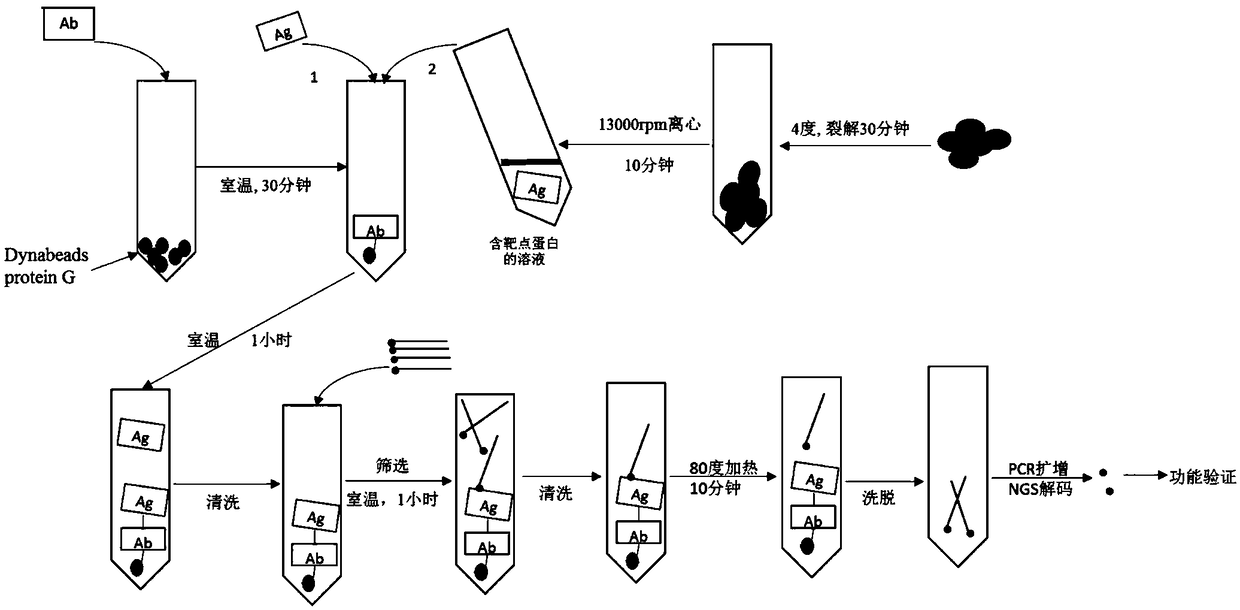
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0036] 1. Preparation of magnetic beads:
[0037] Vortex the Dynabeads magnetic beads for 30 seconds, pipette 20 μL into a 1.5ml Eppendorf tube (microcentrifuge tube, EP tube for short), place the EP tube on a magnetic stand to absorb the magnetic beads, and remove the supernatant. Wash the magnetic beads twice with 100 μL Antibody binding buffer (antibody binding buffer).
[0038] 2. Antibody binding:
[0039] Dilute 4 μg of IDO1 antibody with 100 μL Antibody binding buffer (antibody binding buffer), and incubate at room temperature for 30...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: DNA-encoded compound library screening for LAG3 expressed in cells
[0054] 1. Background: LAG3 is an immune checkpoint inhibitory receptor expressed on the surface of T cells. There are no small molecule compounds known to bind, nor are the binding proteins in the intracellular domain. Human LAG3 is a transmembrane protein, so it is difficult to express and purify it in bacteria or insect cells while retaining its physiological structure and activity. This method can isolate LAG3 and its bound protein from cells, and screen the DNA-encoded compound library for this complex.
[0055] 2. Implementation method:
[0056] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0057] 1. Prepare cell lysate samples:
[0058] The human T cells expressing LAG3 were seeded into suspension cell culture flasks to make their growth saturated. Centrifuge at 800rpm for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, wash the cells twice with 10ml DPB...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com