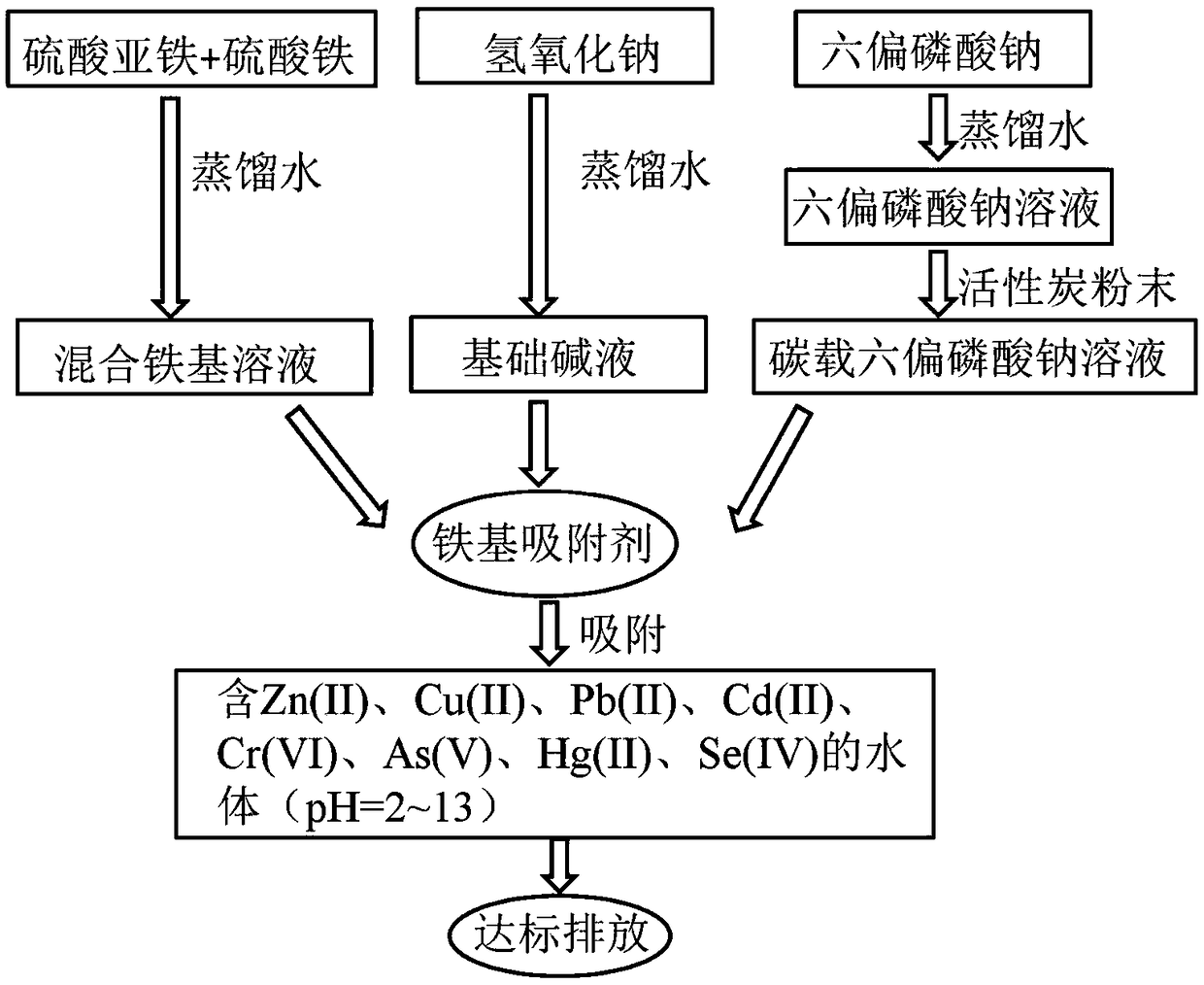
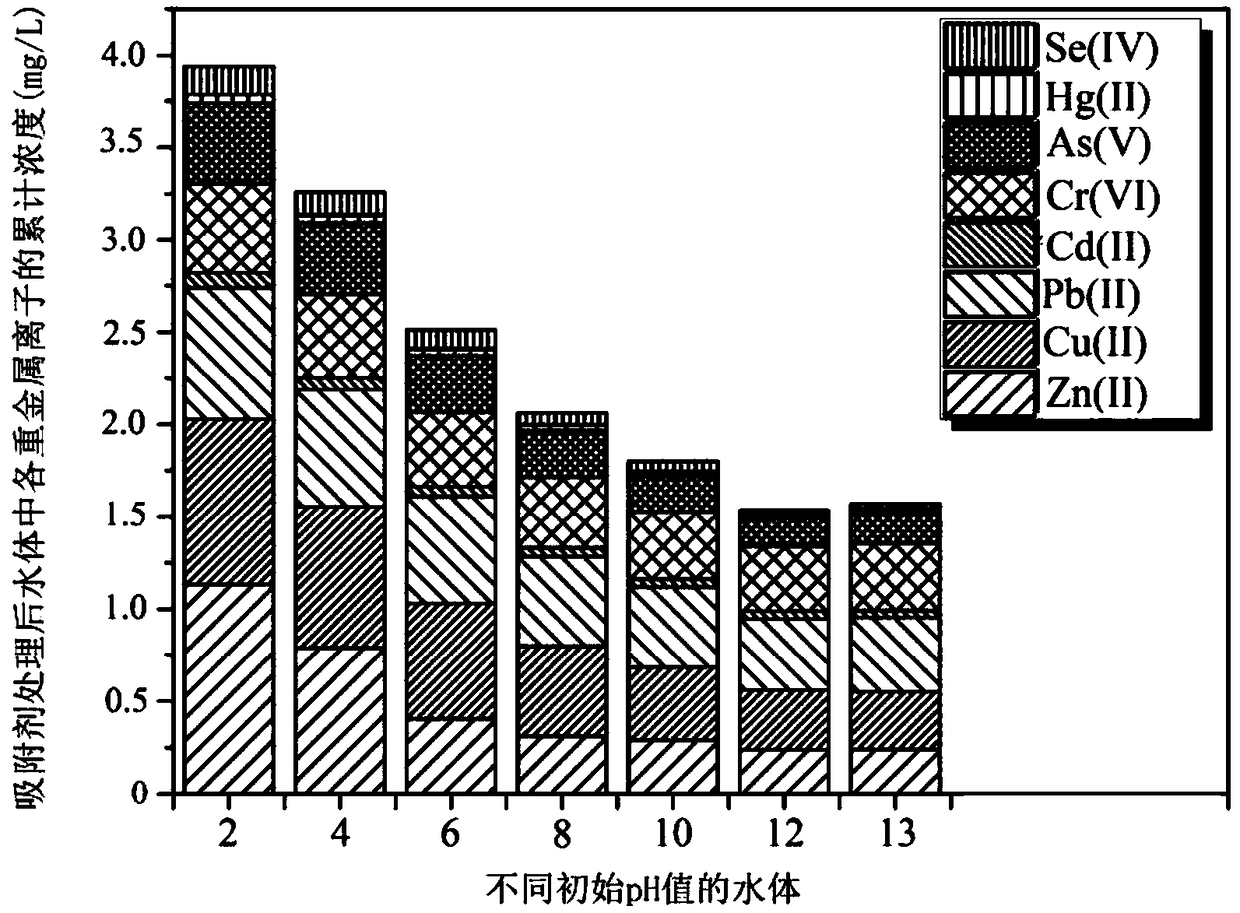
Iron-based adsorbent and preparation method thereof
An adsorbent, iron-based technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the number of active sites on the surface of adsorbent materials, reducing heavy metal cation adsorption, unfavorable solid-liquid separation, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of reducing loss, reducing oxidation rate, and strengthening stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The effect of different molar ratios of Fe(II) and Fe(III) on the removal of various heavy metal ions in water:
[0029] Preparation of mixed iron-based solution: according to the molar ratio of ferrous iron Fe(II) to ferric iron Fe(III) is 2:1, 2.5:1, 3:1, respectively weigh the corresponding mass of ferrous sulfate and ferric sulfate, Mix it into distilled water at the same time, stir until completely dissolved in a sealed state, prepare three mixed iron-based solutions with a concentration of 0.5moL / L respectively, and regard the volume of the mixed iron-based solution as 5 unit volumes.
[0030] Basic lye preparation: according to OH - The molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 2:1, weigh sodium hydroxide, mix it into distilled water, stir until completely dissolved in a sealed state, and prepare a base with a concentration of 2.0moL / L and a volume of 2.5 unit volumes lye.
[0031] Sodium hexametaphosphate solution preparation: according to [P 6 o 18 ] 6- Weigh sodiu...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Different OH - The effect of the molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) on the removal of various heavy metal ions in water:
[0041] Preparation process is with embodiment 1, and embodiment 1 difference is:
[0042] Preparation of mixed iron-based solution: The molar ratio of Fe(II) to Fe(III) was 2.5:1, and three mixed iron-based solutions with a concentration of 0.75moL / L and a volume of 5 unit volumes were prepared.
[0043] Basic lye preparation: OH - The molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, and the three concentrations are 2.5moL / L, 3.75moL / L and 5moL / L respectively, and the volume is 3 units volume of base lye.
[0044] Sodium hexametaphosphate solution preparation: [P 6 o 18 ] 6- The molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 4:6, and a sodium hexametaphosphate solution with a concentration of 1.25moL / L and a volume of 2 unit volumes is prepared.
[0045] Preparation of carbon-supported sodium hexametaphosphate solution: The solid / liquid ratio of activated carbon...
Embodiment 3
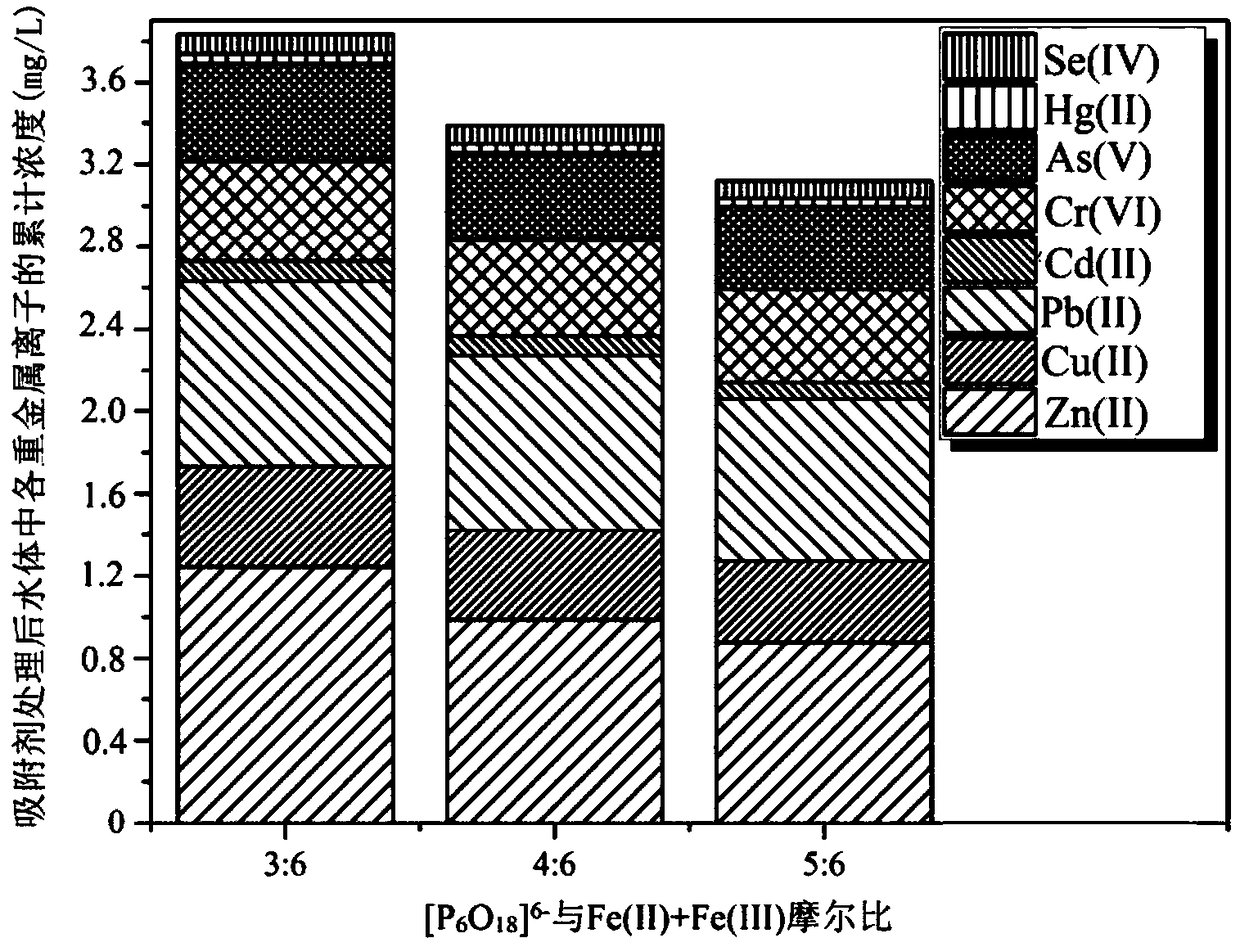
[0052] Different [P 6 o 18 ] 6- The effect of the molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) on the removal of various heavy metal ions in water:
[0053] Preparation process is with embodiment 1, and embodiment 1 difference is:
[0054] Preparation of mixed iron-based solution: The molar ratio of Fe(II) to Fe(III) was 2.5:1, and three mixed iron-based solutions with a concentration of 1moL / L and a volume of 5 unit volumes were prepared.
[0055] Basic lye preparation: OH - The molar ratio to Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 3:1, and the basic lye with a concentration of 4.29moL / L and a volume of 3.5 unit volumes is prepared.
[0056] Sodium hexametaphosphate solution preparation: [P 6 o 18 ] 6- The molar ratio to Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 3:6, 4:6, 5:6, and the prepared concentration is 1.67moL / L, 2.22moL / L, 2.78moL / L, and the volume is 1.5 unit volume of three parts sodium hexametaphosphate solution.
[0057] Preparation of carbon-supported sodium hexametaphosphate solution: The solid / liquid ratio of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com