QTLs (quantitative trait loci) of related traits of radish fleshy root and their positioning method
A positioning method, a technique for succulent roots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
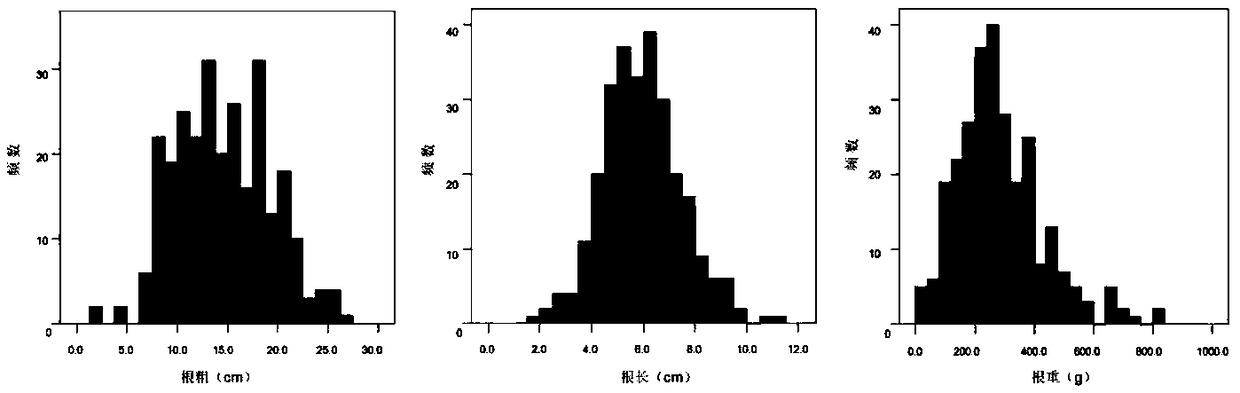
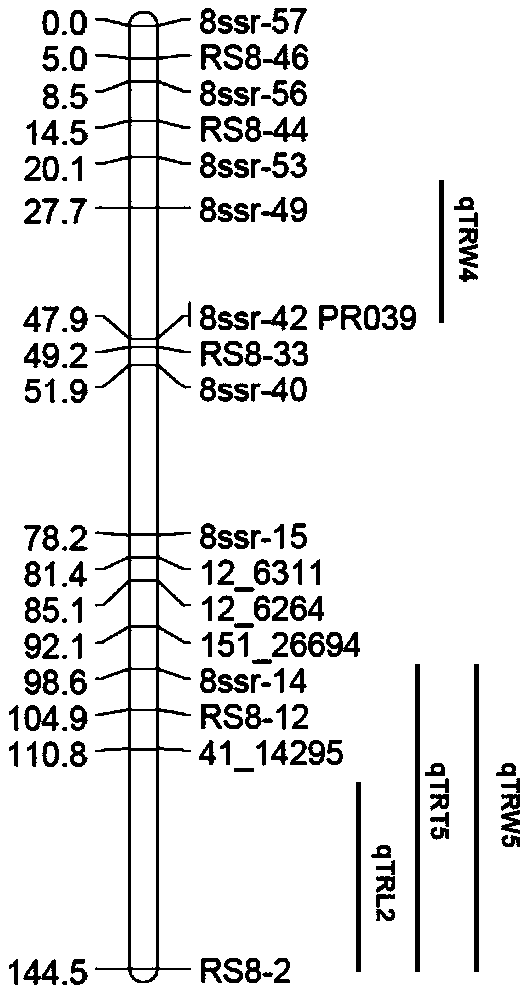
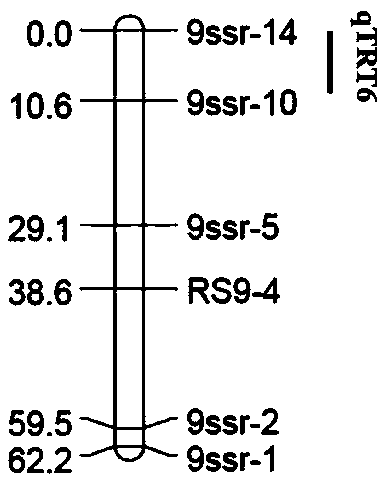
[0039] Example 1: The present invention provides a method for locating QTLs of radish fleshy root-related traits. The method includes the following steps: (1) Using two high-generation radish inbred lines'pp12q-4-2' and '36- 2'as parent material for offspring F 1 , F 2 Separation population construction: the female parent'pp12Q-4-2' is a cultivated long-pod radish with slender roots and does not expand; the male parent '36-2' is a cultivated radish with a long cylindrical fleshy root with white skin and white flesh . The phenotypes of fleshy roots of the two parent materials are significantly different. F 1 Obtained by artificial cross-pollination of two parental materials. 1 Strict artificial bud stage self-pollination to obtain F 2 . Parents (30 plants each), F 1 (30 strains) and F 2 (330 plants) were sown in the greenhouse of the Institute of Vegetables and Flowers of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences in the fall of 2013, and were cultivated and managed by conven...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com