3D printing material and preparation method and application thereof
A 3D printing and soft technology, applied in the textile field, can solve the problems that have not yet found a solution, affect the feel and wearability, and cannot really realize the application, so as to achieve the effect of improving the performance of rapid curing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
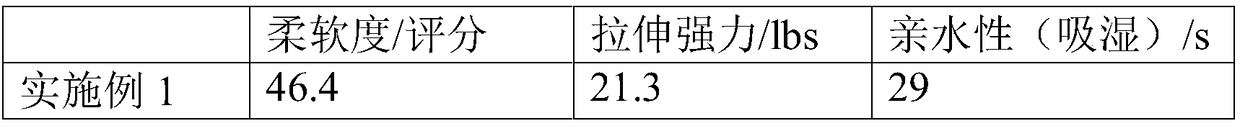
Embodiment 1
[0034] This embodiment provides a 3D printing method, comprising the following steps:
[0035] Step 1. Preparation of cellulose solution: Add 37 parts of cellulose with a polymerization degree of 700-1000 to 63 parts of N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide aqueous solution, fully swell at a temperature of 120°C, stir and shear After cutting, prepare a homogeneous cellulose solution. Wherein, the water content of the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide aqueous solution is 18%.
[0036] Step 2. Melt the soft nylon PA12 at a temperature of 170°C.
[0037] Step 3. Mix 4 parts of cellulose solution with 6 parts of melted soft nylon, and stir evenly. The mixing temperature is 170°C to obtain a 3D printing material.
[0038] Step 4. Feed the above-mentioned printing materials into the silo of the fused deposition 3D printer. The temperature of the hopper is kept at 170°C. The above-mentioned fused deposition 3D printer is equipped with dual nozzles, one of which prints auxiliary support materials, an...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This embodiment provides a 3D printing method for textile garments, comprising the following steps:
[0042] Step 1. Preparation of cellulose solution: Add 26 parts of cellulose with a degree of polymerization of 700-1000 to 74 parts of N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide aqueous solution, fully swell at a temperature of 100°C, stir and shear After cutting, prepare a homogeneous cellulose solution. Wherein, the water content of the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide aqueous solution is 18%.
[0043] Step 2. Mix soft nylon PA12 and PA1010 at a mass ratio of 1:1, and melt at a temperature of 140°C.
[0044] Step 3. Mix 3 parts of cellulose solution with 7 parts of melted soft nylon at a mixing temperature of 140°C to obtain a 3D printing material.
[0045] Step 4. Feed the above-mentioned printing materials into the hopper of the fused deposition 3D printer. The temperature of the hopper is kept at 140°C. The above-mentioned fused deposition 3D printer is equipped with dual nozzles, one...
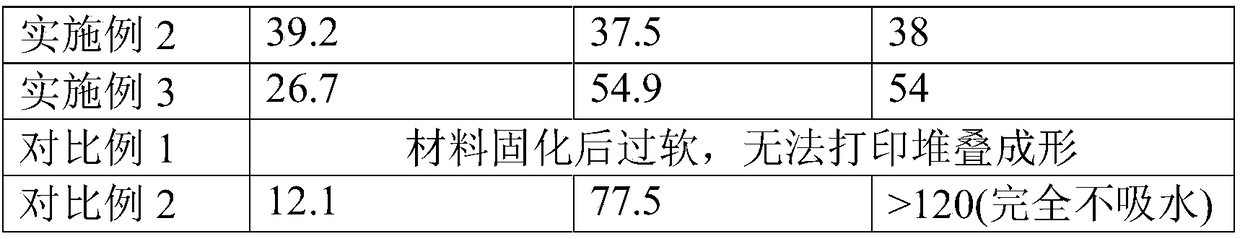
Embodiment 3
[0048] This embodiment provides a 3D printing method for textile garments, comprising the following steps:
[0049] Step 1. Preparation of cellulose solution: Add 17 parts of cellulose with a polymerization degree of 700-1000 to 83 parts of N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide aqueous solution, fully swell at a temperature of 100°C, stir and shear After cutting, prepare a homogeneous cellulose solution. Wherein, the water content of the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide aqueous solution is 18%.
[0050] Step 2. Mix soft nylon PA12 and PA1010 at a mass ratio of 1:2, and melt at a high temperature of 140°C.
[0051] Step 3. Mix 3 parts of cellulose solution with 7 parts of melted soft nylon at a mixing temperature of 140°C to obtain a 3D printing material.
[0052]Step 4. Feed the above-mentioned printing materials into the hopper of the fused deposition 3D printer. The temperature of the hopper is kept at 140°C. The above-mentioned fused deposition 3D printer is equipped with dual nozzles, on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com