Method for polluted groundwater remediation by using in-situ construction of nanometer ferrous sulfide reaction zone
A ferrous sulfide and groundwater technology, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, etc., can solve the problems of limiting pollutant removal capacity and reducing specific surface area, achieving low maintenance cost, good migration effect, and guaranteed removal effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0027] A, the preparation of reducing reagent solution and iron source reagent solution:
[0028] Prepare a reducing agent solution by dissolving 5%-10% reducing agent in 90%-95% deionized water in terms of mass percentage;
[0029] In terms of mass percentage, 5%-10% iron source reagent and 2%-8% dithionite are dissolved in 82%-93% deionized to prepare iron source reagent solution;
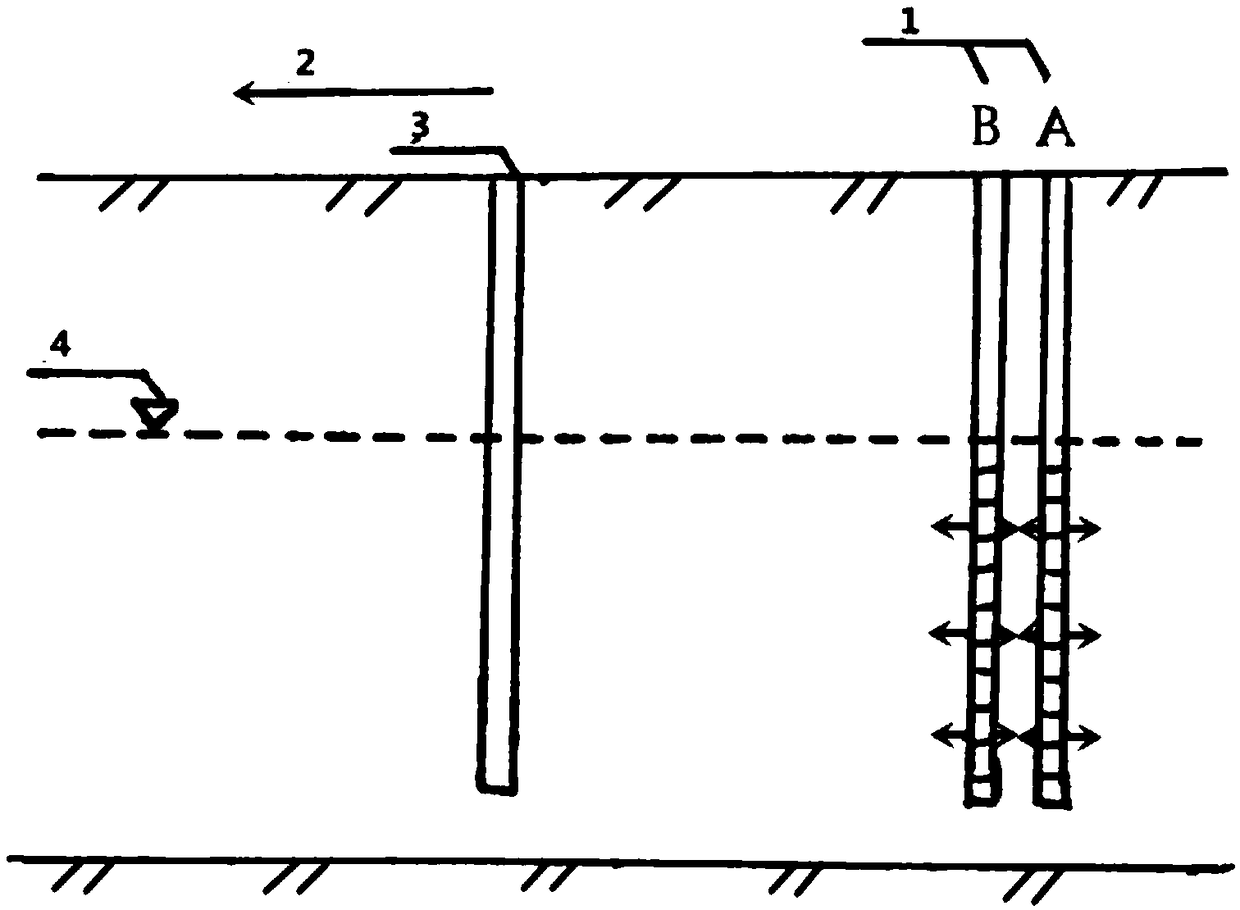
[0030] B. In the polluted groundwater area, the groundwater near the pollution source flows to the upstream position, and at least one pair of reagent injection wells 1 are drilled vertically along the groundwater flow direction. The distance between injection well A and injection well B in each pair of injection wells 1 is 1-2m. At least one observation well 3 is drilled 3-5m downstream of the injection well 1, and the well depths of the injection well 1 and the observation well 3 reach the bottom of the aquifer; mesh;
[0031] C. First inject the reducing reagent solution prepared in step A i...
Embodiment 1
[0037] In the transparent simulation tank filled with fine sand medium, two reagent injection wells (A, B) are drilled vertically along the groundwater flow direction with a distance of 0.3m, and the injection wells are as deep as the aquifer. The size of the simulated tank is 500×330×30 (mm), and the size of the fine sand is 0.09-0.15mm.
[0038] Dissolve 105-210g of sodium sulfide in 2L of deionized water to prepare a sodium sulfide solution; dissolve 100-250g of ferrous sulfate and 40-200g of dithionite in 2L of deionized water to prepare a mixed solution of iron sources.
[0039] Inject the prepared sodium sulfide solution into injection well A first, and inject the prepared iron source mixed solution into injection well B after 1 min; inject sodium sulfide intermittently at equal intervals in the order of injection into well A first and then into well B Solution and iron source mixed solution, and pulse perfusion is used for perfusion. In the mode of intermittent injecti...
Embodiment 2
[0043] In the transparent simulation tank filled with coarse sand medium, two reagent injection wells (A, B) are drilled vertically along the groundwater flow direction with a distance of 0.3m, and the injection wells are as deep as the aquifer. The size of the simulation tank is 500×330×30 (mm), and the size of coarse sand particles is 0.4-0.8mm.
[0044] Dissolve 105-210g of sodium sulfide in 2L of deionized water to prepare a sodium sulfide solution; dissolve 100-250g of ferrous sulfate and 40-200g of dithionite in 2L of deionized water to prepare a mixed solution of iron sources.
[0045] Inject the prepared sodium sulfide solution into injection well A first, and inject the prepared iron source mixed solution into injection well B after 1 min; inject sodium sulfide intermittently at equal intervals in the order of injection into well A first and then into well B Solution and iron source mixed solution, and pulse perfusion is used for perfusion. In the mode of intermitten...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com