Chemical stabilization repair method of lead contaminated soil
A lead-contaminated soil and repair method technology, applied in the field of contaminated soil regeneration, can solve the problems of limited molar ratio dosage, limited dosage, high soil moisture content, etc., and achieve the goal of reducing secondary pollution and reducing phosphorus Leaching, reducing the effect of phosphorus leaching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
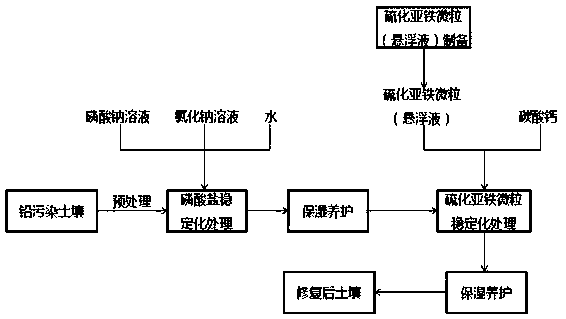
[0030] 1) Preparation of ferrous sulfide particle suspension;
[0031] 2) Soil pretreatment;
[0032]2.1) Use a crusher to crush and screen the contaminated soil to obtain contaminated soil with a particle size of less than 10 cm, and measure the lead content in the soil;
[0033] 2.2) weighing the crushed and sieved contaminated soil obtained in step 2.1);
[0034] 3) Soil chemical stabilization treatment;
[0035] 3.1) Add a certain amount of sodium phosphate solution and sodium chloride solution to the pretreated contaminated soil obtained in step 2.2) to keep the moisture content (water / soil) of the contaminated soil at 30% to 50%. Water can be added, followed by medium-speed mechanical stirring, the stirring rate is controlled at 500-1000rpm, and the stirring time is controlled at 5-10min, so that the contaminated soil and the agent are mixed evenly;
[0036] 3.2) Moisturize and maintain the polluted soil obtained in step 3.1) for 2 to 5 days, then add a certain amount...
Embodiment 1
[0043] Use a crusher to crush the contaminated soil and sieve it to obtain contaminated soil with a particle size of less than 10cm. The concentration of lead in the soil is 200mg / kg, and the weight of the soil is 20kg;
[0044] For the first chemical stabilization treatment, add sodium phosphate solution and sodium chloride solution to the polluted soil, the molar ratio of sodium phosphate addition to lead content in polluted soil is 2:1, the molar ratio of sodium chloride addition to lead content in polluted soil The ratio is 0.5:1; add water to keep the moisture content of the contaminated soil at 30%; mechanically stir at a medium speed at 500rpm for 5 minutes to mix the contaminated soil and the agent evenly, and then moisturize and maintain for 2 days;
[0045] In the second chemical stabilization treatment, ferrous sulfide particulate suspension and calcium carbonate are added to the soil. The molar ratio of the ferrous sulfide particulate addition to the lead content of...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Use a crusher to crush the contaminated soil and sieve it to obtain contaminated soil with a particle size of less than 6cm. The concentration of lead in the soil is 500mg / kg, and the weight of the soil is 30kg;
[0049] For the first chemical stabilization treatment, add sodium phosphate solution and sodium chloride solution to the polluted soil, the molar ratio of sodium phosphate addition to the lead content of the polluted soil is 6:1, the molar ratio of the sodium chloride addition to the lead content of the polluted soil The ratio is 1.3:1; add water to keep the moisture content of the contaminated soil at 40%; mechanically stir at a medium speed at 750rpm for 8 minutes to mix the contaminated soil and the agent evenly, and then moisturize and maintain for 3 days;
[0050] For the second chemical stabilization treatment, ferrous sulfide particulate suspension and calcium carbonate are added to the soil. The molar ratio of the ferrous sulfide particulate addition to...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com