Method for extracting RNA from extracellular vesicles
An extraction method and vesicle technology, applied in the field of RNA extraction in extracellular vesicles, can solve the problems of RNA extraction failure, failure to see precipitation, insufficient RNA, etc., achieve short extraction time, facilitate follow-up experiments, and improve yield effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
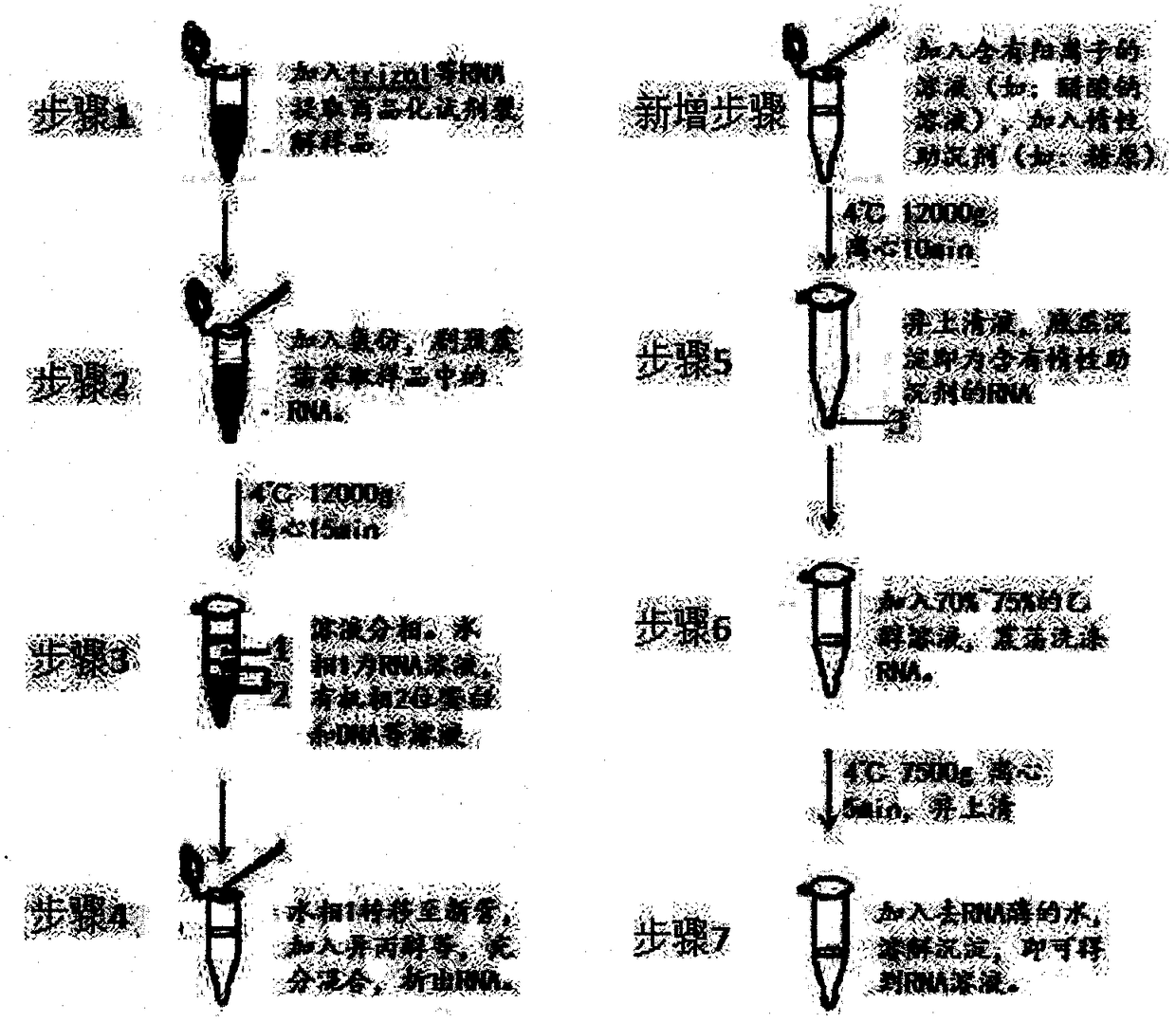
[0036] A method for extracting RNA in extracellular vesicles, the extraction method comprising the following steps:
[0037] S1: Isolate and purify extracellular vesicles in biological samples, add 1 mL of RNA extraction reagent (such as trizol) to 100 μg of extracellular vesicles and repeatedly blow and lyse the isolated and purified extracellular vesicles; the extracellular vesicles Including at least one of exosomes, microvesicles, apoptotic bodies and bacterial outer membrane vesicles (OuterMembrane Vesicles).
[0038] S2: Add 200 μL of chloroform, shake vigorously for 15 seconds, let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes, and centrifuge at 12,000 g for 15 minutes to make the RNA in step S1 enter the water phase; transfer the upper water phase containing RNA to a new centrifuge tube ;
[0039] S3: Add isopropanol having an equal volume to the water in the upper layer of step S2 to the aqueous phase containing RNA obtained in step S2, and gently invert and mix;
[0040]...
Embodiment 2
[0048] A method for extracting RNA in extracellular vesicles, the extraction method comprising the following steps:
[0049] S1: Isolate and purify extracellular vesicles in a biological sample, add 1 mL of RNA extraction reagent (such as trizol) to 200 μg of extracellular vesicles and repeatedly blow and lyse the isolated and purified extracellular vesicles; the extracellular vesicles include extracellular vesicles At least one of exosomes, microvesicles, apoptotic bodies and bacterial outer membrane vesicles;
[0050] S2: Add 200 μL of chloroform, shake vigorously for 15 seconds, let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes, and centrifuge at 12,000 g for 15 minutes to make the RNA in step S1 enter the water phase; transfer the upper water phase containing RNA to a new centrifuge tube ;
[0051] S3: Add isopropanol having an equal volume to the water in the upper layer of step S2 to the aqueous phase containing RNA obtained in step S2, and gently invert and mix;
[0052] S4...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3: Concentration and purity contrast of RNA
[0061] Experimental group: the method in Example 2 was used to extract RNA from extracellular vesicle samples.
[0062] Control group: the RNA in the extracellular vesicles exactly the same as that of the experimental group was extracted by the traditional method (the method mentioned in the background art).
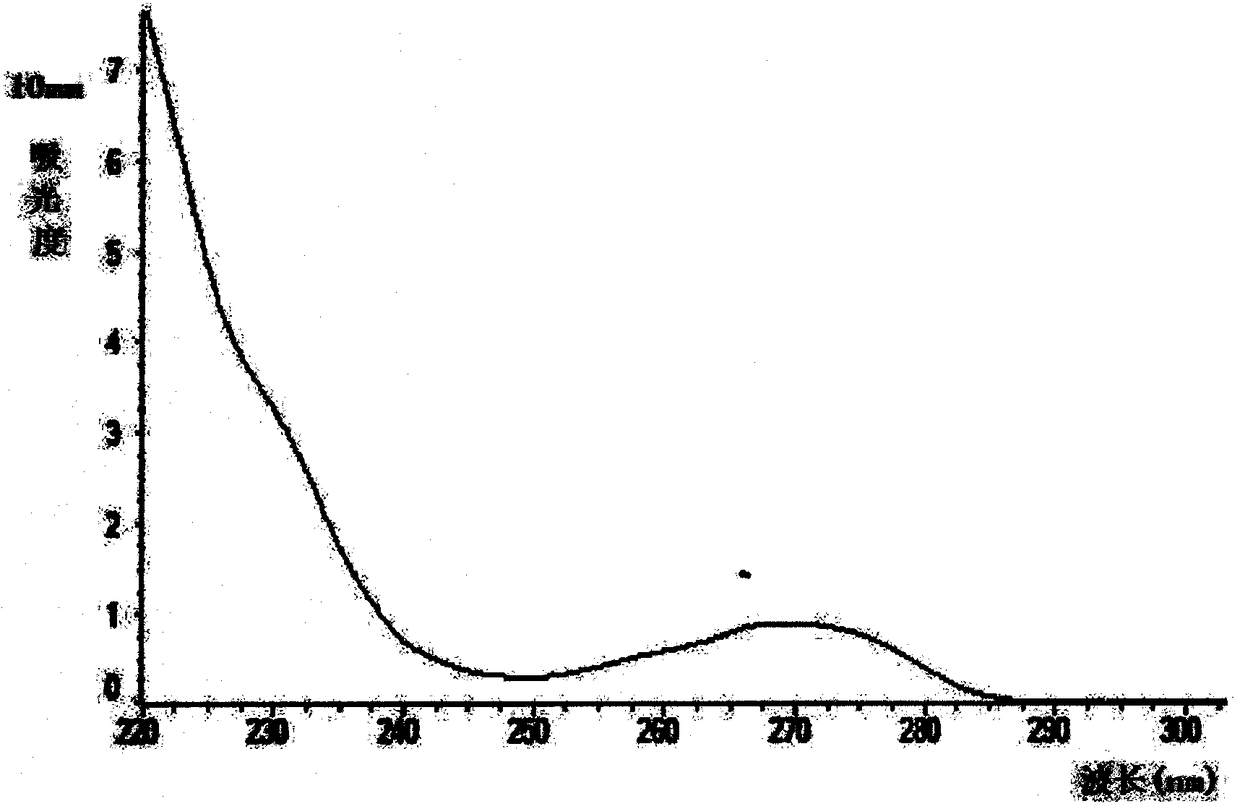
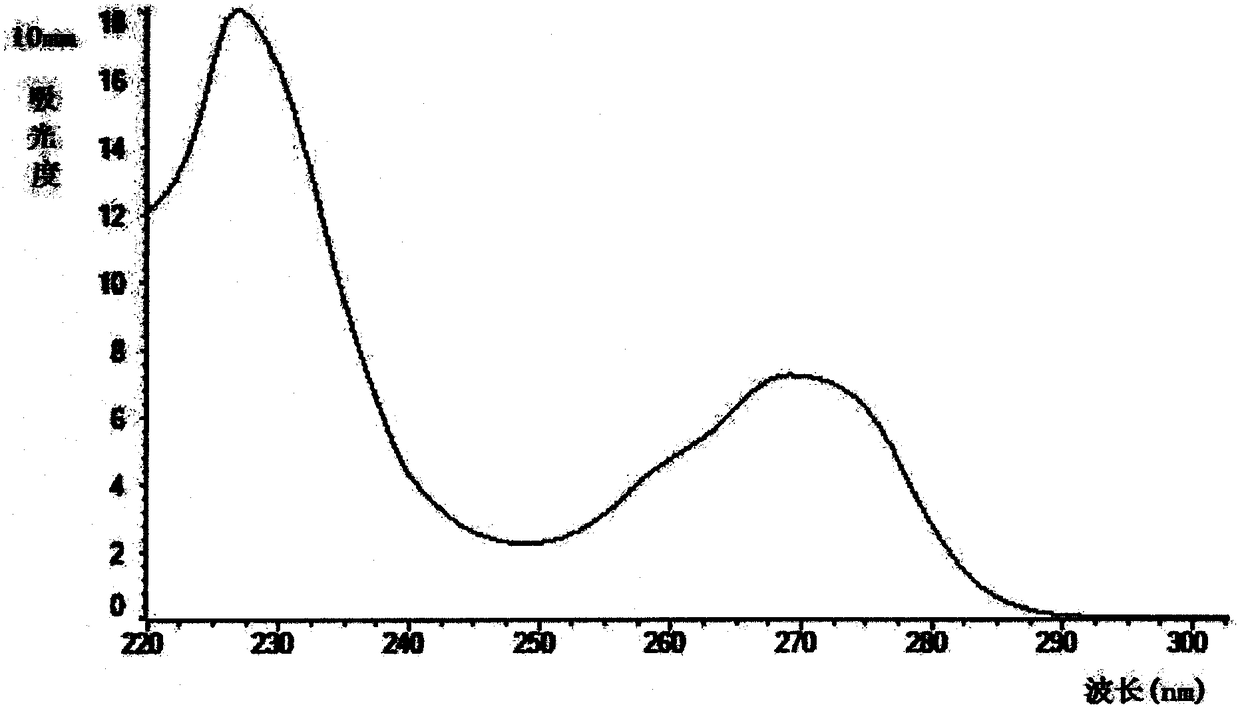
[0063] Nanodrop detects the RNA obtained in the experimental group and the comparison group, as shown in Table 1 and attached Figure 2~3 shown. The RNA concentration detected in the experimental group was 211.7±23.4ng / μL, while that in the control group was only 47.1±22.6ng / μL. For the same type and content of raw extracellular vesicles, the experimental group was more than 160ng / μL higher than the control group , the concentration is more than 5 times higher, the difference is extremely large. The purity (260 / 280) of the obtained RNA is well known in the art, but its purity is better at 1.90 to 2.00, th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com